Chapter 10 sharks skates and rays
Download as PPTX, PDF1 like1,209 views
This document summarizes key characteristics of vertebrates like fish, sharks, skates, and rays. It notes that vertebrates have backbones and internal skeletons, compared to invertebrates. Within fish, it distinguishes primitive jawless fish from sharks and rays that have cartilage skeletons and jaws. It provides details on sharks' streamlined bodies, sensing abilities, reproduction, and need to constantly swim due to their density. Skates and rays are described as flattened like stingrays with different swimming and reproductive behaviors.
1 of 16
Downloaded 10 times













Recommended
Chapt 10 bony fishes



Chapt 10 bony fisheskleinkea
Ěý
This document provides information about bony fishes. It begins by introducing the phylum Chordata and class Actinopterygii, which contains over 25,000 species of modern bony fish. It then discusses some key characteristics of bony fishes, including the presence of a swim bladder, bones, and fin rays. The document also describes coelacanths as a "primitive" fish that was thought to be extinct but has been found alive. The majority of the document focuses on ray-finned fishes, including their diversity, body shapes adapted to different habitats, and systems like respiration, circulation, nerves, senses, reproduction, and coloration.C hapter 9 mollusks



C hapter 9 molluskskleinkea
Ěý
The document summarizes the three major classes of mollusks - Gastropoda (snails and slugs), Bivalvia (clams and mussels), and Cephalopoda (octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish). It describes their general body plans, anatomy, locomotion, digestion, respiration, reproduction, ecological roles, and adaptations. Mollusks play important ecological roles as both predators and prey and many species are threatened by human activities like overharvesting, pollution, and habitat loss.Chapter 9 arthropods



Chapter 9 arthropodskleinkea
Ěý
Here are a few methods a scientist could use to determine the population density of barnacle species on a dock post:
1. Count the number of individual barnacles within a defined area on the post (e.g. within a 1 square foot quadrat) and extrapolate the total number per post based on the surface area. This direct count method provides an estimate of density.
2. Weigh a sample of barnacles scraped from a defined area. Compare the wet or dry mass to samples of known densities to estimate individuals per unit area.
3. Take photographic images of sample areas and use image analysis software to automatically count and identify barnacles based on size, shape, color. This provides a repeatable quantitative measureEchinoderms



Echinodermskleinkea
Ěý
Echinoderms are marine invertebrates with spiny skin and five-part radial symmetry. They have a water-vascular system and tube feet used for movement. There are five classes of echinoderms: sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and sea lilies. Sea stars have tube feet and a water vascular system that allows them to move and catch prey as carnivores. Sea urchins also have tube feet and move by grazing on algae and plants as herbivores. Sea cucumbers use their tube feet to move and take nutrients from sand with oral tentacles.Sharks skates and rays



Sharks skates and raysLeeanna Cota
Ěý
Class Chondrichthyes includes sharks, skates, and rays. They are characterized by having cartilage rather than bone for their skeletons. This provides flexibility but less density than bone. They have jaws, paired fins, and placoid scales. Sharks have a streamlined body and most must continuously swim to breathe and pump water over their gills. Skates and rays have flattened bodies adapted for bottom living while rays like manta rays have enlarged pectoral fins and reduced other fins.Meet the arthropoda



Meet the arthropodamswilliams
Ěý
This document provides an overview of arthropods, which are segmented invertebrates with jointed appendages and an external skeleton. It describes their anatomy, including a chitinous exoskeleton, jointed limbs, segmented bodies, and open circulatory and nervous systems. Arthropods reproduce through external fertilization and development of planktonic larvae. The phylum includes two subphyla: chelicerates like sea spiders and horseshoe crabs, and crustaceans such as lobsters, crabs, shrimp, and barnacles. Arthropods are mostly benthic or epifaunal and found worldwide, representing the largest number of species on Earth.Starfish Children's Book Project



Starfish Children's Book ProjectiiDevil
Ěý
Starfish have a complex digestive system with two stomachs that can extend outside the body to engulf prey. They excrete waste through their tube feet and papulae and lack dedicated excretory organs. The nervous system lacks a brain and consists of radial and circular nerves that coordinate movement and sensing. The circulatory system includes the perivisceral coelom, tube feet system, and hemal system to transport nutrients and oxygen. Starfish can reproduce both sexually and asexually, with fertilization occurring externally and larvae developing before settling as adults.Chapt 10 bony fishes



Chapt 10 bony fisheskleinkea
Ěý
This document provides information about bony fishes, including:
- Bony fishes make up about half of all vertebrate species, with over 25,000 species classified. They show great diversity and are classified mainly at the order or family level.
- Characteristics of bony fishes include the presence of a swim bladder or lungs, bones, bony scales, and fin rays.
- Ray-finned fishes are the most numerous and diverse group, with fins attached by fin rays. They are divided into subclasses with cartilaginous or bony skeletons and different tail and scale structures.Chapter 9 arthropods



Chapter 9 arthropodskleinkea
Ěý
Here are a few methods a scientist could use to determine the population density of barnacle species on the dock post:
1. Count the number of individual barnacles within a defined area on the post (e.g. within a 1 square foot quadrat) and extrapolate the total population based on the total surface area of the post.
2. Take photographs of defined areas on the post and count the barnacles visible in the photos back in the lab. Extrapolate totals as above.
3. Carefully scrape off all the barnacles from a defined area and count directly to determine density for that area. Extrapolate as above.
4. Use image analysis software to process high resolution photos of the post surfaceMollusca Notes



Mollusca NotesHeather Fogell
Ěý
The document summarizes the phylum Mollusca. It is divided into four main classes: Gastropoda which includes snails and slugs, Bivalvia which includes clams and mussels, Cephalopoda which includes squid and octopus, and Polyplacophora which includes chitons. Molluscs are soft-bodied animals with bilateral symmetry and most secrete an external shell. They live in aquatic and terrestrial habitats and have well-developed organ systems including digestive, circulatory, respiratory, and nervous systems.Mollusks & annelid worms



Mollusks & annelid wormsjdrinks
Ěý
This document discusses mollusks, including examples such as snails, slugs, clams, and octopuses. It describes the three main classes of mollusks - gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods - and how each eats and has a nervous system. It also provides information on the colossal squid, the largest known invertebrate, and covers mollusk body structures and circulatory systems.Class chondrichthyes zoorepowt(1)



Class chondrichthyes zoorepowt(1)Our Lady Of Fatima University
Ěý
The document discusses the class Chondrichthyes, which includes cartilaginous fishes such as sharks, rays, and skates. Key characteristics include a cartilaginous skeleton, placoid scales, ventral mouth and nostrils, jaws, paired appendages, and male claspers. The class contains two subclasses: Elasmobranchii containing sharks and rays/skates, and Holocephali containing chimaeras. Elasmobranchii have a four-chambered heart and seasonal reproduction cycles, while Holocephali have smaller mouths bounded by three lips and tooth plates instead of scales.Arthropods & echinoderms



Arthropods & echinodermsjdrinks
Ěý
Arthropods and echinoderms are invertebrate animals that share some key characteristics. Arthropods have segmented bodies, jointed limbs, an external skeleton, and a well-developed nervous system. They include insects, spiders, crustaceans, and others. Echinoderms have a spiny endoskeleton and radial symmetry as adults, though their larvae have bilateral symmetry. They use a water vascular system and include sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and others. Both groups display diverse adaptations for movement, feeding, and survival.Chordata uro and ceph



Chordata uro and cephMahesh Thakur
Ěý
- Urochordata and Cephalochordata are two phylums that make up the subphylum Chordata. They share four defining characteristics with all chordates: a notochord, dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and an early tail.
- As larvae, both urochordates and cephalochordates display these chordate traits but urochordates lose many during metamorphosis while cephalochordates retain them as adults. Cephalochordates are also known as lancelets.
- The notochord is a flexible rod that runs between the digestive and nervous systems and allows these primitive chordates to swim and move.Chondrichthyes.



Chondrichthyes.guest41ca4c
Ěý
This document provides information about sharks, skates, and rays (Chondrichthyes). It discusses their habitats in temperate and cold, deep waters. It describes how they hunt and feed near coastal areas. The document also outlines the evolution of Chondrichthyes, noting their appearance in the Devonian period and placoderm ancestors. Key adaptations like cartilage skeletons, spiral valves, and specialized jaws are also summarized.Phylum Chordata- Sub Phylum Vertebrata- Class Chondrichthyes By: Al-John Ahmad



Phylum Chordata- Sub Phylum Vertebrata- Class Chondrichthyes By: Al-John AhmadWestern Mindanao State University
Ěý
The document discusses the evolution and characteristics of cartilaginous fishes (class Chondrichthyes). It notes that this class includes sharks, rays, and chimeras, and that they have persisted largely unchanged for hundreds of millions of years, thriving as marine predators. An example of an extinct genus discussed is Cladoselache, a shark-like predator from the Devonian period. The largest predatory shark known, the now-extinct Megalodon, reached approximately 16 meters long.Echinoderms



Echinodermskleinkea
Ěý
Echinoderms are marine invertebrates with spiny skin and five-part radial symmetry. They include sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and sea lilies. Sea stars have tube feet and a water vascular system to move. They are predators that eat mollusks and crustaceans. Sea urchins are herbivores that graze on algae and plants using their tube feet. Sea cucumbers extract nutrients from sand and release toxic organs as a defense.Meet the mollusks & arthropods



Meet the mollusks & arthropodsmswilliams
Ěý
The document summarizes two kingdoms - Mollusca and Arthropoda. Mollusca includes three classes: Gastropods (snails and nudibranchs), Cephalopods (squid and octopus), and Bivalves (clams, mussels and scallops). Arthropoda includes two subphyla: Chelicerata (sea spiders and horseshoe crabs) and Crustacea (lobsters, crabs, shrimp, etc.). It provides examples of different organisms in each class or subphylum and notes some of their key characteristics like shells, tentacles, blood composition, and mating behaviors. Videos and references are also included for further information.Phyla Echinodermata



Phyla Echinodermatamcdevittapbio
Ěý
Echinoderms are marine invertebrates with radial symmetry and a water vascular system. There are 6 classes: sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea lilies, sea cucumbers, and sea daisies. They have tube feet for movement and respiration, and most are sessile or slow-moving. Reproduction involves releasing gametes into water. Characteristics include radial symmetry in adults and bilateral symmetry in larvae.16. Class Osteichthyes Notes



16. Class Osteichthyes Notesmgitterm
Ěý
The document summarizes the key characteristics of the bony fish class Osteichthyes. Bony fish have a skeleton made of bone, scales, and an operculum covering their gills. They possess fins, swim bladders, and their mouths and jaws allow for better movement than sharks to aid feeding. Their internal anatomy includes two-chambered hearts, gills for gas exchange, lateral lines for sensing vibrations, and various sensory organs like eyes and ears. Bony fish exhibit diverse behaviors such as forming territories, schools, and undertaking migrations.Phylum mollusca



Phylum molluscaJessi Dildy
Ěý
The phylum Mollusca includes soft-bodied animals with shells, including gastropods, bivalves, polyplacophora, and cephalopods. They have bilateral symmetry, triploblastic bodies with three germ layers, and a coelom body cavity. Their basic body plan includes a foot, mantle, visceral mass, and sometimes a shell. They have complete digestive and open or closed circulatory systems. Most reproduce sexually but some can reproduce asexually. They have nerves, ganglia, and eyespots or advanced eyes. They respire and excrete through gills, nephridia, and an anus. Molluscs fill diverse ecological rolesMullusk 



Mullusk ninzrose
Ěý
Mollusks are a diverse phylum of soft-bodied animals that usually have an external or internal shell. They include snails, slugs, clams, squids, and octopuses. The basic body plan of mollusks consists of a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. The three main classes of mollusks are gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods. Gastropods are shelled or shell-less mollusks that move using a foot, while bivalves have two shells held together by muscles. Cephalopods like squid and octopus have a head attached to a muscular foot that is modified into tentacles.Classification of fishes



Classification of fishesTuharMukherjee
Ěý
Classification of Fishes can be summarized as follows:
1. Fishes are classified based on their anatomical features and placed in a systematic hierarchy ranging from superclass to species. Some key groups include chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes like sharks), osteichthyes (bony fishes), actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) and sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fishes).
2. Important historical schemes for classifying fishes were proposed by scientists such as Berg in 1940, who grouped fishes based on characteristics like jaw structure, fin morphology, scale type and vertebral structure.
3. Major fish groups discussed inFish anatomy and physilogy 



Fish anatomy and physilogy Vijay Hemmadi
Ěý
if your doing fish dissection and need some anatomical information then go through my slides.
in this i have written fish anatomy with its physiological implications 17. Class Chondrichthyes Notes



17. Class Chondrichthyes Notesmgitterm
Ěý
Class Chondrichthyes includes cartilaginous fish such as sharks, rays, and skates. They have skeletons made of cartilage and possess movable jaws and teeth. Their skin is rough and sandpaper-like, made of scales with the same composition as teeth. Sharks have been largely unchanged for over 100 million years. The largest predatory fish ever was the ancient megalodon shark, which was twice the size of a great white shark.13.1 john and spencer



13.1 john and spencerbabcocke
Ěý
Vertebrates are animals with backbones and internal skeletons. They include fish, frogs, snakes, birds, and mammals. The defining characteristic of vertebrates is the endoskeleton, which allows for flexibility and protection of organs. While vertebrates make up only 5% of animal species, the majority are fish, of which there are over 20,000 species that live in water and have specialized organs like gills and a lateral line. Most fish reproduce sexually, where the female lays eggs that are fertilized by the male.Mollusks



MollusksReychel Faith Siyang
Ěý
Mollusks are soft-bodied invertebrates that mostly have shells covering their bodies. They have complex organ systems and three main body parts: a muscular foot, mantle, and visceral mass containing internal organs. There are three main classes of mollusks: gastropods with one shell, bivalves with two attached shells, and cephalopods with an internal skeleton. Many mollusk species are used as food sources for humans while others like golden kuhol have become agricultural pests. Certain species can also transmit diseases.Chordate classes



Chordate classesJessi Dildy
Ěý
The document summarizes the key characteristics of the major vertebrate classes: Agnatha, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, and Mammalia. It describes their distinguishing features such as respiration, circulation, fertilization, eggs/young, metabolism, skin/covering, and other defining traits. The classes generally increase in complexity from jawless fish to mammals, with mammals exhibiting the most advanced adaptations including fur/hair, mammary glands, and internal gestation/live birth.7 - Molluscs.pptx



7 - Molluscs.pptxDr. Manoj Garg
Ěý
The document discusses the phylum Mollusca. It describes key characteristics of molluscs including their soft unsegmented bodies protected by a calcium carbonate shell secreted by the mantle. There are over 200,000 mollusc species found mainly in oceans. The three main classes are gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods. Gastropods include snails and slugs. Bivalves include clams, mussels and oysters which have two shells. Cephalopods like octopuses, squid and cuttlefish are advanced predators. The document also discusses mollusc anatomy, physiology, behavior and life cycles.The vertebrates



The vertebratesRhenzoDocman10
Ěý
Vertebrates are chordates that have a backbone or spine replacing their notochord as they develop. They are divided into several classes: Agnatha (jawless fish), Chondrichthyes (cartilage fish like sharks), Osteichthyes (bony fish), Amphibia (amphibians), Reptilia (reptiles), Aves (birds), and Mammalia (mammals). Vertebrates are characterized by features like an internal skeleton, vertebral column, cranium, and organ systems like respiratory, circulatory, and digestive. The major groups of vertebrates first appeared between 550-150 million years ago.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Chapter 9 arthropods



Chapter 9 arthropodskleinkea
Ěý
Here are a few methods a scientist could use to determine the population density of barnacle species on the dock post:
1. Count the number of individual barnacles within a defined area on the post (e.g. within a 1 square foot quadrat) and extrapolate the total population based on the total surface area of the post.
2. Take photographs of defined areas on the post and count the barnacles visible in the photos back in the lab. Extrapolate totals as above.
3. Carefully scrape off all the barnacles from a defined area and count directly to determine density for that area. Extrapolate as above.
4. Use image analysis software to process high resolution photos of the post surfaceMollusca Notes



Mollusca NotesHeather Fogell
Ěý
The document summarizes the phylum Mollusca. It is divided into four main classes: Gastropoda which includes snails and slugs, Bivalvia which includes clams and mussels, Cephalopoda which includes squid and octopus, and Polyplacophora which includes chitons. Molluscs are soft-bodied animals with bilateral symmetry and most secrete an external shell. They live in aquatic and terrestrial habitats and have well-developed organ systems including digestive, circulatory, respiratory, and nervous systems.Mollusks & annelid worms



Mollusks & annelid wormsjdrinks
Ěý
This document discusses mollusks, including examples such as snails, slugs, clams, and octopuses. It describes the three main classes of mollusks - gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods - and how each eats and has a nervous system. It also provides information on the colossal squid, the largest known invertebrate, and covers mollusk body structures and circulatory systems.Class chondrichthyes zoorepowt(1)



Class chondrichthyes zoorepowt(1)Our Lady Of Fatima University
Ěý
The document discusses the class Chondrichthyes, which includes cartilaginous fishes such as sharks, rays, and skates. Key characteristics include a cartilaginous skeleton, placoid scales, ventral mouth and nostrils, jaws, paired appendages, and male claspers. The class contains two subclasses: Elasmobranchii containing sharks and rays/skates, and Holocephali containing chimaeras. Elasmobranchii have a four-chambered heart and seasonal reproduction cycles, while Holocephali have smaller mouths bounded by three lips and tooth plates instead of scales.Arthropods & echinoderms



Arthropods & echinodermsjdrinks
Ěý
Arthropods and echinoderms are invertebrate animals that share some key characteristics. Arthropods have segmented bodies, jointed limbs, an external skeleton, and a well-developed nervous system. They include insects, spiders, crustaceans, and others. Echinoderms have a spiny endoskeleton and radial symmetry as adults, though their larvae have bilateral symmetry. They use a water vascular system and include sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and others. Both groups display diverse adaptations for movement, feeding, and survival.Chordata uro and ceph



Chordata uro and cephMahesh Thakur
Ěý
- Urochordata and Cephalochordata are two phylums that make up the subphylum Chordata. They share four defining characteristics with all chordates: a notochord, dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and an early tail.
- As larvae, both urochordates and cephalochordates display these chordate traits but urochordates lose many during metamorphosis while cephalochordates retain them as adults. Cephalochordates are also known as lancelets.
- The notochord is a flexible rod that runs between the digestive and nervous systems and allows these primitive chordates to swim and move.Chondrichthyes.



Chondrichthyes.guest41ca4c
Ěý
This document provides information about sharks, skates, and rays (Chondrichthyes). It discusses their habitats in temperate and cold, deep waters. It describes how they hunt and feed near coastal areas. The document also outlines the evolution of Chondrichthyes, noting their appearance in the Devonian period and placoderm ancestors. Key adaptations like cartilage skeletons, spiral valves, and specialized jaws are also summarized.Phylum Chordata- Sub Phylum Vertebrata- Class Chondrichthyes By: Al-John Ahmad



Phylum Chordata- Sub Phylum Vertebrata- Class Chondrichthyes By: Al-John AhmadWestern Mindanao State University
Ěý
The document discusses the evolution and characteristics of cartilaginous fishes (class Chondrichthyes). It notes that this class includes sharks, rays, and chimeras, and that they have persisted largely unchanged for hundreds of millions of years, thriving as marine predators. An example of an extinct genus discussed is Cladoselache, a shark-like predator from the Devonian period. The largest predatory shark known, the now-extinct Megalodon, reached approximately 16 meters long.Echinoderms



Echinodermskleinkea
Ěý
Echinoderms are marine invertebrates with spiny skin and five-part radial symmetry. They include sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and sea lilies. Sea stars have tube feet and a water vascular system to move. They are predators that eat mollusks and crustaceans. Sea urchins are herbivores that graze on algae and plants using their tube feet. Sea cucumbers extract nutrients from sand and release toxic organs as a defense.Meet the mollusks & arthropods



Meet the mollusks & arthropodsmswilliams
Ěý
The document summarizes two kingdoms - Mollusca and Arthropoda. Mollusca includes three classes: Gastropods (snails and nudibranchs), Cephalopods (squid and octopus), and Bivalves (clams, mussels and scallops). Arthropoda includes two subphyla: Chelicerata (sea spiders and horseshoe crabs) and Crustacea (lobsters, crabs, shrimp, etc.). It provides examples of different organisms in each class or subphylum and notes some of their key characteristics like shells, tentacles, blood composition, and mating behaviors. Videos and references are also included for further information.Phyla Echinodermata



Phyla Echinodermatamcdevittapbio
Ěý
Echinoderms are marine invertebrates with radial symmetry and a water vascular system. There are 6 classes: sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea lilies, sea cucumbers, and sea daisies. They have tube feet for movement and respiration, and most are sessile or slow-moving. Reproduction involves releasing gametes into water. Characteristics include radial symmetry in adults and bilateral symmetry in larvae.16. Class Osteichthyes Notes



16. Class Osteichthyes Notesmgitterm
Ěý
The document summarizes the key characteristics of the bony fish class Osteichthyes. Bony fish have a skeleton made of bone, scales, and an operculum covering their gills. They possess fins, swim bladders, and their mouths and jaws allow for better movement than sharks to aid feeding. Their internal anatomy includes two-chambered hearts, gills for gas exchange, lateral lines for sensing vibrations, and various sensory organs like eyes and ears. Bony fish exhibit diverse behaviors such as forming territories, schools, and undertaking migrations.Phylum mollusca



Phylum molluscaJessi Dildy
Ěý
The phylum Mollusca includes soft-bodied animals with shells, including gastropods, bivalves, polyplacophora, and cephalopods. They have bilateral symmetry, triploblastic bodies with three germ layers, and a coelom body cavity. Their basic body plan includes a foot, mantle, visceral mass, and sometimes a shell. They have complete digestive and open or closed circulatory systems. Most reproduce sexually but some can reproduce asexually. They have nerves, ganglia, and eyespots or advanced eyes. They respire and excrete through gills, nephridia, and an anus. Molluscs fill diverse ecological rolesMullusk 



Mullusk ninzrose
Ěý
Mollusks are a diverse phylum of soft-bodied animals that usually have an external or internal shell. They include snails, slugs, clams, squids, and octopuses. The basic body plan of mollusks consists of a foot, mantle, shell, and visceral mass. The three main classes of mollusks are gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods. Gastropods are shelled or shell-less mollusks that move using a foot, while bivalves have two shells held together by muscles. Cephalopods like squid and octopus have a head attached to a muscular foot that is modified into tentacles.Classification of fishes



Classification of fishesTuharMukherjee
Ěý
Classification of Fishes can be summarized as follows:
1. Fishes are classified based on their anatomical features and placed in a systematic hierarchy ranging from superclass to species. Some key groups include chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes like sharks), osteichthyes (bony fishes), actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) and sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fishes).
2. Important historical schemes for classifying fishes were proposed by scientists such as Berg in 1940, who grouped fishes based on characteristics like jaw structure, fin morphology, scale type and vertebral structure.
3. Major fish groups discussed inFish anatomy and physilogy 



Fish anatomy and physilogy Vijay Hemmadi
Ěý
if your doing fish dissection and need some anatomical information then go through my slides.
in this i have written fish anatomy with its physiological implications 17. Class Chondrichthyes Notes



17. Class Chondrichthyes Notesmgitterm
Ěý
Class Chondrichthyes includes cartilaginous fish such as sharks, rays, and skates. They have skeletons made of cartilage and possess movable jaws and teeth. Their skin is rough and sandpaper-like, made of scales with the same composition as teeth. Sharks have been largely unchanged for over 100 million years. The largest predatory fish ever was the ancient megalodon shark, which was twice the size of a great white shark.13.1 john and spencer



13.1 john and spencerbabcocke
Ěý
Vertebrates are animals with backbones and internal skeletons. They include fish, frogs, snakes, birds, and mammals. The defining characteristic of vertebrates is the endoskeleton, which allows for flexibility and protection of organs. While vertebrates make up only 5% of animal species, the majority are fish, of which there are over 20,000 species that live in water and have specialized organs like gills and a lateral line. Most fish reproduce sexually, where the female lays eggs that are fertilized by the male.Mollusks



MollusksReychel Faith Siyang
Ěý
Mollusks are soft-bodied invertebrates that mostly have shells covering their bodies. They have complex organ systems and three main body parts: a muscular foot, mantle, and visceral mass containing internal organs. There are three main classes of mollusks: gastropods with one shell, bivalves with two attached shells, and cephalopods with an internal skeleton. Many mollusk species are used as food sources for humans while others like golden kuhol have become agricultural pests. Certain species can also transmit diseases.Chordate classes



Chordate classesJessi Dildy
Ěý
The document summarizes the key characteristics of the major vertebrate classes: Agnatha, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, and Mammalia. It describes their distinguishing features such as respiration, circulation, fertilization, eggs/young, metabolism, skin/covering, and other defining traits. The classes generally increase in complexity from jawless fish to mammals, with mammals exhibiting the most advanced adaptations including fur/hair, mammary glands, and internal gestation/live birth.Phylum Chordata- Sub Phylum Vertebrata- Class Chondrichthyes By: Al-John Ahmad



Phylum Chordata- Sub Phylum Vertebrata- Class Chondrichthyes By: Al-John AhmadWestern Mindanao State University
Ěý
Similar to Chapter 10 sharks skates and rays (20)
7 - Molluscs.pptx



7 - Molluscs.pptxDr. Manoj Garg
Ěý
The document discusses the phylum Mollusca. It describes key characteristics of molluscs including their soft unsegmented bodies protected by a calcium carbonate shell secreted by the mantle. There are over 200,000 mollusc species found mainly in oceans. The three main classes are gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods. Gastropods include snails and slugs. Bivalves include clams, mussels and oysters which have two shells. Cephalopods like octopuses, squid and cuttlefish are advanced predators. The document also discusses mollusc anatomy, physiology, behavior and life cycles.The vertebrates



The vertebratesRhenzoDocman10
Ěý
Vertebrates are chordates that have a backbone or spine replacing their notochord as they develop. They are divided into several classes: Agnatha (jawless fish), Chondrichthyes (cartilage fish like sharks), Osteichthyes (bony fish), Amphibia (amphibians), Reptilia (reptiles), Aves (birds), and Mammalia (mammals). Vertebrates are characterized by features like an internal skeleton, vertebral column, cranium, and organ systems like respiratory, circulatory, and digestive. The major groups of vertebrates first appeared between 550-150 million years ago.Fish Unit



Fish UnitKlamath Union High School
Ěý
The document discusses key anatomical terms used to describe directionality in the body. It then summarizes the evolution of chordates, highlighting four defining characteristics and advantages conferred by these traits. Various hypotheses on vertebrate evolution are presented, along with an overview of major chordate subgroups and their defining features.Naturalists at Large: Marine vertebrates



Naturalists at Large: Marine vertebratesPhat Nattie
Ěý
Vertebrates share the characteristic of having a notochord or backbone at some point in their development. The backbone provides support, protection, and structure to the body. It allows vertebrates like fish, birds, and mammals to move effectively through their environments. Fish specifically use gills and fins to breathe and move through water, and can be categorized into three main groups: jawless fish, cartilaginous fish, and bony fish.Mollusks bivalves:gastro:cepha marine



Mollusks bivalves:gastro:cepha marineLeeanna Cota
Ěý
The document describes three classes of mollusks: Gastropoda (snails and slugs), Bivalvia (clams, mussels, oysters), and Cephalopods (octopuses, squid, cuttlefish). All mollusks have a visceral mass containing organs and a mantle cavity with gills. Gastropods have a muscular foot and radula for scraping food. Bivalves have two shells called valves held together by adductor muscles. Cephalopods are predators with advanced brains, eyes, and tentacles used to capture prey.Sharks powerpoint



Sharks powerpointSmithtown High School West
Ěý
Class Chondrichthyes includes sharks, skates, and rays that have inhabited Earth for 280 million years. They are characterized by cartilage instead of bone and range in size from whale sharks over 60 feet long to smaller species. Sharks have streamlined bodies, denticles, and various adaptations for sensing prey and maintaining buoyancy. While some species prey on fish and marine mammals, others feed on plankton or scavenge. Shark attacks are rare with few species posing a danger to humans.Fishes Zoology Report



Fishes Zoology ReportAzenith Matutina
Ěý
The first vertebrates were jawless fishlike animals that appeared over 500 million years ago. They had cartilaginous internal skeletons. Ostracoderms had bony armor. Early vertebrates evolved in both marine and freshwater environments. Modern fish classes include cartilaginous Chondrichthyes like sharks and bony Osteichthyes including Sarcopterygii with lungs and Actinopterygii with ray fins, including most common fish species.Mollusks%20bivalves%3agastro[1]![Mollusks%20bivalves%3agastro[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/mollusks20bivalves3agastro1-120203103120-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Mollusks%20bivalves%3agastro[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/mollusks20bivalves3agastro1-120203103120-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Mollusks%20bivalves%3agastro[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/mollusks20bivalves3agastro1-120203103120-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Mollusks%20bivalves%3agastro[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/mollusks20bivalves3agastro1-120203103120-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Mollusks%20bivalves%3agastro[1]kleinkea
Ěý
The document summarizes two classes of mollusks - Gastropoda and Bivalvia. Gastropoda includes snails, limpets and slugs. Their body plan includes a head foot, visceral mass and mantle. They undergo a process called torsion which twists their organs and benefits protection and sensitivity. Bivalvia includes clams, oysters and mussels. Their defining feature is having two halves to their shell called valves. They filter feed using cilia and rely on water currents for food and oxygen exchange. Many mollusks are threatened by human impacts like overharvesting, pollution and habitat loss.evolution of mammals by davendran



evolution of mammals by davendranDavendran Narayan
Ěý
Mammals evolved from synapsid ancestors during the Mesozoic era. The earliest mammals had specialized teeth, small bodies, and various skeletal adaptations including differentiated dentition. The three main modern mammal groups are monotremes, marsupials, and placentals. Key mammalian adaptations include hair, three middle ear bones derived from jaw bones, and a four-chambered heart and diaphragm. Mammals exhibit diverse diets, habitats, and locomotion across nearly 4000 living species.The Origin of Vertebrates



The Origin of VertebratesJessabeth Aluba
Ěý
This document summarizes the evolution of vertebrates from their earliest ancestors to modern forms. It describes the key traits that unite each major group, from non-vertebrate chordates like tunicates and lancelets, to the earliest jawless fish like hagfish and lampreys, to jawed fish groups like sharks and bony fish. It outlines the major transitions from marine to freshwater habitats and the evolutionary innovations in skeletal and sensory systems that occurred in the main vertebrate lineages over 500 million years.Fishes



Fishesjdrinks
Ěý
This document discusses chordates and vertebrates. It notes that vertebrates have backbones and belong to the phylum chordata. It also describes two other chordate groups, lancelets and tunicates. Key characteristics of chordates include having a tail, nerve cord, pharyngeal pouches and notochord. The document then focuses on characteristics of vertebrates like their backbone and skull. It classifies vertebrates as either warm-blooded or cold-blooded. Finally, it outlines the three classes of fish and characteristics like breathing with gills and reproduction through external fertilization.U nit 6 vertebrates (1)



U nit 6 vertebrates (1)Irene Santos Fraile
Ěý
This document provides an overview of vertebrates, including their key characteristics and how they are classified. It discusses the main groups of vertebrates - fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. For each group, it describes physical features, temperature regulation, reproduction methods, and examples of common types. The largest sections are devoted to fish, amphibians, and reptiles, explaining their distinguishing attributes and subgroups in detail.Marine artopoda 2 -



Marine artopoda 2 -siddheshwar laddha
Ěý
This document summarizes the key marine arthropod classes. It describes their general characteristics including bilateral symmetry, exoskeleton, molting, digestion, and circulatory and nervous systems. The major classes included are Malacostraca, Branchiopoda, Ostracoda, Copepoda, Pentastomida, and Cirripedia. These classes are distinguished by features like body plan, habitat, appendages, life cycle, and ecology.Joko re modified



Joko re modifiedAsikawili George
Ěý
The document discusses the comparative anatomy of the skeletal system across vertebrates. It provides details on the skeletal system of fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. The skeletal system evolved for support and movement on land. Key adaptations include the diapsid skull in reptiles and birds, fused bones and reduction of weight in birds, and the presence of both axial and appendicular skeleton in most vertebrate groups.CLASSIFICATION OF VERTEBRATES ANIMALS.pptx



CLASSIFICATION OF VERTEBRATES ANIMALS.pptxssuserd64ef8
Ěý
Vertebrates are animals that possess a vertebral column or notochord at some point in their life. They evolved from a common ancestor around 600 million years ago and include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, bony fishes, cartilaginous fishes, and jawless fishes. Vertebrates are classified into these 7 classes based on their anatomical and physiological features such as their skeleton, body temperature regulation, reproductive strategies, and more.Introduction to Animals



Introduction to AnimalsJohana Matta
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to invertebrates and vertebrates. It discusses the main groups of invertebrates including sponges, cnidarians, worms, mollusks, arthropods, and echinoderms. It then covers the key characteristics of chordates and vertebrates, including having a notochord, nerve cord, and throat pouches. It differentiates between ectotherms and endotherms based on temperature regulation. The document also discusses fast felines like cheetahs and how their body structure and muscles enable incredible speed. Finally, it covers how skeletons and muscles work together to support, protect, and enable animal movement.Bony fish



Bony fishLhen Katipunan
Ěý
Bony fish have a backbone, skull, brain and kidneys. They are classified into two main types - ray-finned fish and lobe-finned fish. Ray-finned fish make up the majority of fish and have fins supported by bony rays, while lobe-finned fish have fleshy lobes supporting their fins. Bony fish display a variety of adaptations for respiration, circulation, buoyancy and sensory functions.A survery of kingdom animalia



A survery of kingdom animaliaPeter Egorov
Ěý
Chordates are classified into 3 subphyla: Cephalochordata, Urochordata, and Vertebrata. Cephalochordata and Urochordata are invertebrates while Vertebrata includes fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. All chordates share structures like a notochord, dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and postanal tail. The subphylum Urochordata includes tunicates that are marine filter feeders while Cephalochordata includes lancelets that have elongated segmented bodies and retain their notochord. Vertebrates are distinguished by having a head, brain, vertebrae,Vertebrates



Vertebrateslegoscience
Ěý
This document describes the key characteristics of the major groups of vertebrates including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. It outlines traits such as having backbones, lungs, amniotic eggs, feathers, fur and mammary glands. The document also provides examples of types of fish (jawless, cartilaginous, bony), amphibians (frogs, salamanders), reptiles (snakes, lizards, crocodiles), birds (chickens, ducks) and mammals (rodents, primates, ungulates).634199322-LAS-34-Vertebrates-Invertebrates-ppt.ppt



634199322-LAS-34-Vertebrates-Invertebrates-ppt.pptShefaCapuras1
Ěý
Vertebrates are animals with backbones and include fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. They can be ectothermic (cold-blooded) or endothermic (warm-blooded). Invertebrates lack backbones and make up 97% of animal species, with bodies that have radial, bilateral, or asymmetric symmetry. They are divided into phyla including sponges, cnidarians, worms, arthropods like crustaceans and insects, mollusks, and echinoderms.More from kleinkea (20)
Session 4 calender



Session 4 calenderkleinkea
Ěý
This schedule outlines the week-by-week plan for a biology class focusing on arthropods, echinoderms, and fish. In the first week, students will take notes on arthropods and echinoderms, and participate in labs examining preserved specimens of these phyla. The second week involves dissecting starfish, analyzing lab results, and taking article-based and identification tests on echinoderms and arthropods. Later weeks shift to topics on fish, including their adaptations, building a model fish, quizzes, and a field trip to SeaWorld to observe aquatic life.C hapter 9 mollusks



C hapter 9 molluskskleinkea
Ěý
The document summarizes the three major classes of mollusks - Gastropoda (snails and slugs), Bivalvia (clams and oysters), and Cephalopoda (octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish). It describes their general body plans, anatomy, locomotion, digestion, respiration, reproduction, ecological roles, and adaptations for predation. Mollusks exhibit a diversity of forms and play important roles in both marine and terrestrial ecosystems.Marine science national invasive species week!!!!



Marine science national invasive species week!!!!kleinkea
Ěý
National Invasive Species Week is being celebrated, with students assigned to research and create a warning flyer about an invasive species in Florida. The Burmese python is highlighted as an example, with details provided that it is native to Southeast Asia but has been released in Florida, where it has no natural predators and is attacking wildlife in the Everglades. Students are warned to keep Burmese pythons in Asia and not buy exotic pets. The assignment is due by March 8th.Chapter 8 porfera cnardarians



Chapter 8 porfera cnardarianskleinkea
Ěý
This document summarizes key characteristics of sponges, cnidarians, and comb jellies. Sponges are sessile, multicellular organisms that filter feed and lack tissues. Cnidarians are radially symmetric and have stinging cells, with forms including polyps, jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones. Comb jellies differ in having eight rows of comb plates with cilia for locomotion and lack stinging cells.Chapter 7 multicellular plants



Chapter 7 multicellular plantskleinkea
Ěý
This document discusses the four main phyla of multicellular primary producers: seaweeds (Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta, Chlorophyta), seagrasses, salt marsh plants, and mangroves. It describes their key structures, reproduction methods, ecological roles, and representative species found in Florida. The main environmental factors that influence seaweeds are light, temperature, tidal exposure, salinity, and nutrient availability.Chapter 6 study guide marine microbes



Chapter 6 study guide marine microbeskleinkea
Ěý
This study guide covers the key structures, reproductive systems, digestive systems, levels of organization, and ecological roles of diatoms, dinoflagellates, foraminiferans, Euglena, and Volvox. It includes diagrams of representative organisms and definitions of important terms. Short answer questions ask the student to compare and contrast diatoms, dinoflagellates, and forams, and describe the food capture methods of foraminiferans.Chapter 6 study guide marine microbes



Chapter 6 study guide marine microbeskleinkea
Ěý
This study guide covers the key structures, reproductive systems, digestive systems, levels of organization, and ecological roles of diatoms, dinoflagellates, foraminiferans, Euglena, and Volvox. It includes diagrams of representative organisms and definitions of important terms. Short answer questions ask the student to compare and contrast diatoms, dinoflagellates, and forams, and describe the food capture methods of foraminiferans.Chapter 6 marine microbes



Chapter 6 marine microbeskleinkea
Ěý
This document summarizes key marine microbes found in plankton. It discusses diatoms, dinoflagellates, and forams in detail, including their structure, reproduction, digestion/energy processes, and ecological roles. Diatoms are the most common and distinctive plankton, contributing greatly to primary productivity. Dinoflagellates can cause harmful algae blooms and red tides. Forams consume other microbes and turn over nutrients. The document also briefly outlines euglena and volvox characteristics.Chapter 6 marine microbes



Chapter 6 marine microbeskleinkea
Ěý
This document summarizes key marine microbes found in plankton. It discusses diatoms, dinoflagellates, forams, euglena, and volvox. Diatoms are the most common phytoplankton and have a glassy cell wall and symmetrical shape. Dinoflagellates can cause red tides and some are in a mutualism with corals. Forams have a shell and pseudopod and are an important part of the marine food web. Euglena can photosynthesize or absorb nutrients and reproduce by binary fission. Volvox forms multicellular colonies through asexual reproduction and provides a model for cell regeneration studies.Questions for plankton article



Questions for plankton articlekleinkea
Ěý
This document provides questions to guide the reader in understanding key concepts about plankton from a scientific text. It includes questions about why plankton are called "drifters", how they are able to live near the surface of oceans, and adaptations like buoyancy. Questions also address the thermocline, how water density affects mixing, and how this benefits plankton. Further questions explore plankton's role in food chains, characteristics of "jello-plankton", and the process of vertical diurnal migration. The final question looks at what time of year is optimal for plankton growth and why.Ecology



Ecologykleinkea
Ěý
Ecology is the study of interactions between organisms and their environment. It examines these relationships across different levels of biological organization, from cells to the biosphere. An organism's environment, or abiotic factors like temperature and salinity, as well as biotic interactions with predators, prey and parasites, define its habitat and ecological niche. Competition occurs when organisms require the same limited resources, preventing two groups from occupying the same niche. Predator-prey relationships and keystone species also shape ecosystem structure. Symbiosis describes close biological interactions, which can be mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic. Scientists sample populations using methods like transect lines and quadrats to make inferences about ecosystem health.Session 2 research paper



Session 2 research paperkleinkea
Ěý
This document provides directions for a research paper assignment. Students must choose one of seven topics covered in class and write a 6-page paper in 12pt font and double spaced with a cover page and works cited page. The paper must include at least 10 sources, with 5 being primary sources. The final draft is due on December 14th by 2:15pm as a Word 2007 attachment via email. Plagiarized papers will receive a grade of 0.Marine science syllabus



Marine science syllabuskleinkea
Ěý
This document is a syllabus for a marine science course taught by Ms. Kleinke. The syllabus outlines the course objectives, description, materials required, grading breakdown, behavior expectations, homework policy, tests/quizzes, and learning recovery options. The objective is for students to gain a deeper understanding of the unique and interconnected properties and organisms of the ocean. Labs and hands-on activities are emphasized. Students are expected to be prepared, respectful, engaged, and work hard. Consequences are outlined for violations and late work policies are described.Osmosis article marine



Osmosis article marinekleinkea
Ěý
The study explored the effects of low salinity water on ion transporter expression and distribution in the gill of the longhorn sculpin (Myoxocephalus octodecimspinosus). Sculpins were exposed to 10% or 20% seawater for 24 or 72 hours. Exposure to 10% seawater resulted in 20-25% lower plasma ion levels but did not affect transporter localization or expression. Sculpins maintained ion levels in 20% seawater and showed no physiological effects. The results suggest sculpins can tolerate brackish water for days but not long term due to an inability to regulate transporters at low salinities.Fish osmoregulation



Fish osmoregulationkleinkea
Ěý
The document discusses the central role played by the Mt. Desert Island Biological Laboratory (MDIBL) in advancing the study of fish osmoregulation over the past 80 years. Some of the key discoveries made by scientists at MDIBL include demonstrating that marine fish ingest seawater and absorb water and ions from their intestines, determining that aglomerular fish kidneys can function excretory like glomerular kidneys, and elucidating the role of gills in salt secretion. The MDIBL has hosted many influential researchers in fish physiology and helped establish the basic mechanisms of osmoregulation in fish.Lesson 2 osmosis and diffusion in the marine environment



Lesson 2 osmosis and diffusion in the marine environmentkleinkea
Ěý
The document summarizes how different fish species regulate water concentration in their cells when in environments with different salt concentrations. Some fish, like those in marine environments, actively transport ions to maintain higher internal salt concentrations than the surrounding water to prevent their cells from bursting. Other fish, called osmoconformers, allow their internal salt concentrations to rise and fall passively with the environment. Maintaining precise internal regulation requires energy, so some species like cod produce high concentrations of urea to control balances. The document emphasizes the importance of these mechanisms for fish to adapt to varying salinity conditions in their habitats.Lesson 2 properties of water ppt



Lesson 2 properties of water pptkleinkea
Ěý
Water has unusual properties due to its polar molecular structure and ability to form hydrogen bonds between molecules. Hydrogen bonds give water high surface tension, heat capacity, and adhesion/cohesion properties responsible for capillary action and plant water transport. These hydrogen bonds also cause water to be an anomalous substance with a density higher in liquid form than solid, allowing aquatic life to survive under frozen surfaces.Waters unique properties lesson 2



Waters unique properties lesson 2kleinkea
Ěý
The document provides information about a lab activity on the properties of water. It includes 7 objectives that students should understand after completing the lab, such as describing the dipolar structure of water and how it relates to hydrogen bonding. It also lists materials needed and safety issues. The introduction discusses water's unique properties that result from its polar nature and ability to form hydrogen bonds. The activity section then has students complete 7 stations exploring topics like cohesion, surface tension, adhesion, and how these properties are affected by changes in temperature and salinity.Lesson 1 marine ecosystems



Lesson 1 marine ecosystemskleinkea
Ěý
This document provides an overview of several key marine ecosystems:
- Coral reefs are the most biodiverse marine ecosystem due to symbiotic relationships between corals and zooxanthellae algae. However, they are threatened by factors like coral bleaching, disease, and human impacts.
- Salt marshes are important estuarine ecosystems located between land and salt/brackish water. They support food webs and provide habitat for many species.
- Mangroves are found in subtropical regions and have distinctive root systems that provide shelter and habitat. They play an important ecological role by exporting nutrients.
- Deep sea ecosystems rely on chemosynthesis rather than photosynthesis. Organisms in these ecosystems mustChapter 10 sharks skates and rays
- 1. Chapter 10
- 2. Vertebrates • Everything up till now has been Invertebrates – What does this mean? • From now on all Fishes, reptiles, birds and mammals are all Vertebrates – What does this mean? • Can you think of some functions of Vertebrae that are advantageous? – Support – Attachment of muscles= increased movement
- 3. Primitive Fish • Class Myxini (hagfish) and Cephalospidomorphi (lampreys) – Lack jaws and paired appendages (fins in fish) – Lack scales and muscles (all cartilage) Only living representatives of primitive fish
- 4. Class Chondrichthyes • Sharks, Skates, and Rays – Defining characteristics • Skeletons composed of cartilage • Jaws • Paired fins • Placoid scales
- 5. Sharks!!!!! • Streamlined body shape • Heterocercal tail • Two dorsal fins • Paired pectoral fins • Paired pelvic fins – Modified in males (claspers) to transfer sperm
- 6. Why do sharks have to “just keep swimming”? • Has to do with Density!!!! – The are denser than the water so what will happen if they stop swimming?
- 7. Osmoregulation • Maintain homeostasis – By holding large amounts of urea in body – If they did not have this adaptation they would lose body water. • Then what would happen to the shark – Dehydrate and cells would……… » Shrink -> remember osmosis chapter????? – http://dsc.discovery.com/videos/the-ultimate- guide-to-sharks-how-sharks-swim.html
- 8. Sensory in Sharks • Sight – Lack eyelids – Scientists predict that they can see color, but what sense is most dominant in shark? • Smell!!!! – 2/3 of cells in brain are used to process sense of smell – Can detect 1 drop of blood in 1 million parts of water – http://dsc.discovery.com/videos/ultimate-guide-the- sharks-shark-smell.html
- 9. • Lateral Line System – Canals that run length of body and open up to surrounding H2O – Used to detect movements in water • Locate prey and predators – Ampullae of Lorezini • Organs around head (what is the term for sense organs near the head?) – Sense electrical – http://dsc.discovery.com/vide os/ultimate-guide-the-sharks- vibrations-and-shark- vision.html
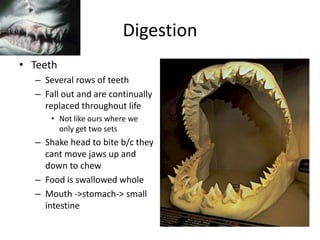
- 10. Digestion • Teeth – Several rows of teeth – Fall out and are continually replaced throughout life • Not like ours where we only get two sets – Shake head to bite b/c they cant move jaws up and down to chew – Food is swallowed whole – Mouth ->stomach-> small intestine
- 11. Great White Jumping!!! • http://dsc.discovery.com/videos/planet-earth- pole-to-pole-great-white-hunt.html
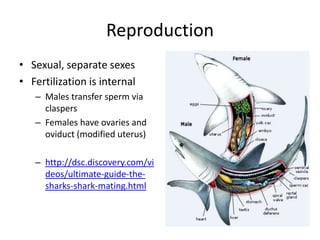
- 12. Reproduction • Sexual, separate sexes • Fertilization is internal – Males transfer sperm via claspers – Females have ovaries and oviduct (modified uterus) – http://dsc.discovery.com/vi deos/ultimate-guide-the- sharks-shark-mating.html
- 13. 3 types of Reproductive types – Oviparity (most primitive) • Eggs are laid outside body • Develop in protective case that attaches to seafloor • smaller b/c limited nutrients • Whale sharks, bullhead sharks – Ovoviviparity (most common) • Eggs hatch in mothers uterus • No placenta, nourishment is yolk stored in egg • Single pup – Viviparity (most recent, advanced) • Babies get milk directly from mother • Hammerhead shark
- 14. Skates and Rays characteristics What animal from previous chapter do they resemble? • Flattened bodies shape – Suited for bottom living • Always exception = manta ray – Enlarged pectoral fins attached to head – Reduced dorsal and caudal fins – Eyes and spiracles on top of head – Lack of anal fin – Specialized teeth for crushing prey
- 15. Differences between skates and rays • Skates – Small fins on tail – Swim by creating a wave and starts at head then ripples down rest of body – Oviparous - “mermaids purse” • Rays – Venomous barb or spines – Swim by moving fins up and down (like a bird) – Ovoviviparous
