Chapter1 9-07
- 1. CCE-EDUSAT SESSION FOR COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS Date : 31.08.2007 Session : Chapter 8 Topic : Memory Units Faculty : Annapurna P Patil Department of CSE M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology Bangalore E mail: [email_address] [email_address]
- 2. CONTENTS Introduction RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs.
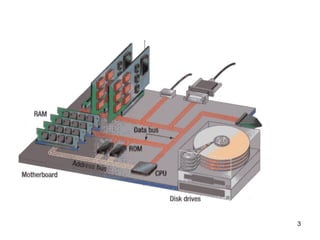
- 3. ╠²
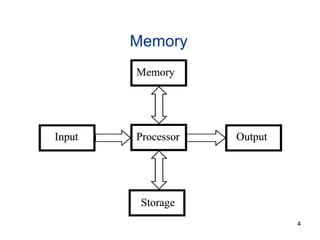
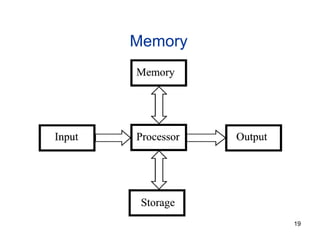
- 4. Memory
- 5. 1. Introduction Memory Devices (RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM) Storage Devices (Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk .Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs)
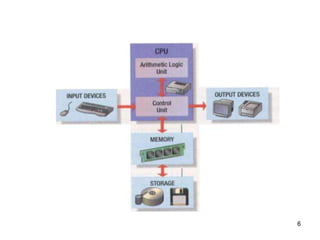
- 6. ╠²
- 7. Characteristics of Storage Devices Speed Volatility Access method Portability Cost and capacity
- 8. Basic Units Of Measurement Bit Bi nary digi t Smallest unit of measurement Two possible values 0 1 on off OR Byte 8 bits
- 9. Small Units Of Measurement (Processor And Memory Speed) Millisecond ( ms ) ŌĆō a thousandth of a second (1/1,000 = 10 -3 ) Microsecond ( ╬╝s ) - a millionth of a second (1/1,000,000 = 10 -6 ) Nanosecond ( ns ) ŌĆō a billionth of a second (1/1,000,000,000 = 10 -9 )
- 10. Large Units Of Measurement (Memory, Storage) Note: powers of two are used because computer memory and storage are based on the basic unit ( bit ). Kilobyte (KB) ŌĆō a thousand bytes (1,024 = 2 10 ) Megabyte (MB) - a million (1,048,576 = 2 20 )
- 11. Large Units Of Measurement (Memory, Storage) Gigabyte (GB) ŌĆō a billion (1,073,741,824 = 2 30 ) ~ A complete set of encyclopedias requires about 700 MB of storage ~ 30 minutes of video (1/4 of the information stored on a typical DVD)
- 12. Large Units Of Measurement (Memory, Storage) Terabyte (TB) ŌĆō a trillion (1,099,511,627,776 = 2 40 ) ~ 20 million four-drawer filing cabinets full of text ~ 200 DVDŌĆÖs of information
- 13. CONTENTS Introduction RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs.
- 14. Memory Devices Memory: Is one or more sets of chips that store data/program instructions, either temporarily or permanently . It is critical processing component in any computer PCs use several different types 2. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM
- 15. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Memory Devices Two most important are RAM (Random Access Memory) ROM (Read-only Memory) They work in different ways and perform distinct functions CPU Registers Cache Memory
- 16. RAM RAM is packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is a cell (one bit per cell). Multiple RAM chips form a memory. R andom A ccess M emory Volatile Used for temporary storage Typical ranges 256 MB - 4 GB Random Access means direct access to any part of memory
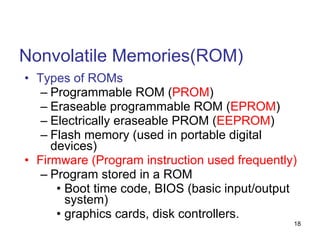
- 17. Nonvolatile Memories(ROM) DRAM and SRAM are volatile memories Lose information if powered off. Nonvolatile memories retain value even if powered off. Generic name is read-only memory ( ROM ). Misleading because some ROMs can be read and modified.
- 18. Nonvolatile Memories(ROM) Types of ROMs Programmable ROM ( PROM ) Eraseable programmable ROM ( EPROM ) Electrically eraseable PROM ( EEPROM ) Flash memory (used in portable digital devices) Firmware (Program instruction used frequently) Program stored in a ROM Boot time code, BIOS (basic input/output system) graphics cards, disk controllers.
- 19. Memory
- 20. 3. Storage Vs. Memory Memory (e.g., RAM) Keep the information for a shorter period of time (usually volatile) Faster More expensive
- 21. 3. Storage Vs. Memory Storage (e.g., Hard disk) The information is retained longer (non-volatile) Slower Cheaper
- 22. CONTENTS Introduction RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs.
- 23. Categories Of Storage Magnetic Floppy disks Zip disks Hard drives Optical CD-ROM DVD Solid state storage devices USB Key (a very common form of solid state storage)
- 24. Magnetic Storage Exploits duality of magnetism and electricity Converts electrical signals into magnetic charges Captures magnetic charge on a storage medium Later regenerates electrical current from stored magnetic charge Polarity of magnetic charge represents bit values zero and one
- 25. Magnetic Drives
- 26. Magnetic Disk Flat, circular platter with metallic coating that is rotated beneath read/write heads Random access device; read/write head can be moved to any location on the platter Hard disks and floppy disks Cost performance leader for general-purpose on-line secondary storage
- 27. Magnetic Drives: Storage Capacities Floppy disks ~ 1 MB Hard drives ~80 ŌĆō 500 GB (TB is possible but very rare)
- 28. Floppy Disks A floppy disk is a portable, inexpensive storage medium that consists of a thin, circular, flexible plastic disk with a magnetic coating enclosed in a square-shaped plastic shell.
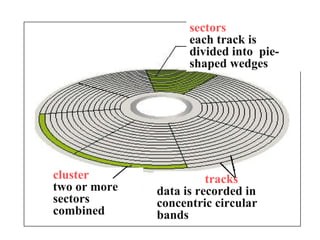
- 29. Structure Of Floppy Disks Initially Floppy disks were 8-inches wide, they then shrank to 5.25 inches, and today the most widely used folly disks are 3.5 inches wide and can typically store 1.44 megabytes of data. A folly disk is a magnetic disk, which means that it used magnetic patterns to store data. Data in floppy disks can be read from and written to. Formatting is the process of preparing a disk for reading and writing. A track is a narrow recording band that forms a full circle on the surface of the disk.
- 30. Hard Disks Another form of auxiliary storage is a hard disk. A hard disk consists of one or more rigid metal plates coated with a metal oxide material that allows data to be magnetically recorded on the surface of the platters. The hard disk platters spin at a high rate of speed, typically 5400 to 7200 revolutions per minute (RPM). Storage capacities of hard disks for personal computers range from 10 GB to 120 GB (one billion bytes are called a gigabyte).
- 31. sectors each track is divided into pie-shaped wedges cluster two or more sectors combined tracks data is recorded in concentric circular bands
- 32. Optical Mass Storage Devices Store bit values as variations in light reflection Higher areal density & longer data life than magnetic storage Standardized and relatively inexpensive Uses: read-only storage with low performance requirements, applications with high capacity requirements & where portability in a standardized format is needed
- 33. Optical Drives CD's (Compact Disk) ~ 700 MB storage CD-ROM (read only) CD-R: ( r ecord) to a CD CD-RW: can write and erase CD to reuse it ( r e- w ritable) DVD(Digital Video Disk)
- 34. Compact Discs (CD) A compact disk (CD), also called an optical disc, is a flat round, portable storage medium that is usually 4.75 inch in diameter. A CD-ROM (read only memory), is a compact disc that used the same laser technology as audio CDs for recording music. In addition it can contain other types of data such as text, graphics, and video. The capacity of a CD-ROM is 650 MB of data.
- 35. DVD-ROM Over 4 GB storage (varies with format) DVD- ROM (read only) Many recordable formats (e.g., DVD-R, DVD-RW; ..) Are more highly compact than a CD. Special laser is needed to read them DVD (Digital Video Disk)
- 36. Blu-ray Technology Name Derived from the blue-violet laser used to read and write data. Developed by the Blu-ray Disc Association with more than 180 members. Dell Sony LG
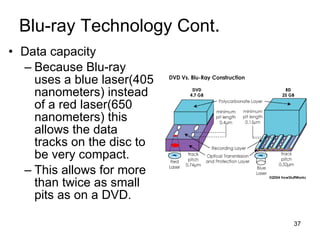
- 37. Blu-ray Technology Cont . Data capacity Because Blu-ray uses a blue laser(405 nanometers) instead of a red laser(650 nanometers) this allows the data tracks on the disc to be very compact. This allows for more than twice as small pits as on a DVD.
- 38. Blu-ray Technology Cont. BD-ROM (read-only) - for pre-recorded content BD-R (recordable) - for PC data storage BD-RW (rewritable) - for PC data storage BD-RE (rewritable) - for HDTV recording Formats
- 39. Summary Introduction RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk Optical Disks: CD-R Drive,CD-RW disks,DVD,Blue ray Discs.
- 40. CCE-EDUSAT SESSION FOR COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS Date : 31.08.2007 Session : Chapter 8 Topic : Memory Units Faculty : Annapurna P Patil Department of CSE M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology Bangalore E mail: [email_address] [email_address]
- 41. Thank You
![CCE-EDUSAT SESSION FOR COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS Date : 31.08.2007 Session : Chapter 8 Topic : Memory Units Faculty : Annapurna P Patil Department of CSE M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology Bangalore E mail: [email_address] [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1-9-07-120112160511-phpapp01/85/Chapter1-9-07-1-320.jpg)






























![CCE-EDUSAT SESSION FOR COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS Date : 31.08.2007 Session : Chapter 8 Topic : Memory Units Faculty : Annapurna P Patil Department of CSE M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology Bangalore E mail: [email_address] [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1-9-07-120112160511-phpapp01/85/Chapter1-9-07-40-320.jpg)
