Chennie
- 1. Ěý
- 2. Ěý
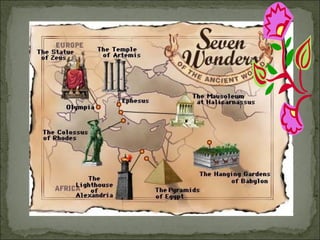
- 3. The Seven Wonders of the World (or the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World ) is a well known list of remarkable constructions of classical antiquity. It was based on guidebooks popular among the ancient Hellenic tourists. The historian Herodotus (484 – ca. 425 BCE), and the scholar Callimachus of Cyrene (ca. 305 – 240 BCE) at the Museum of Alexandria, made early lists of seven wonders but their writings have not survived, except as references. The seven wonders included: Great Pyramid of Giza Ěý 2500 BC Approximate - Egyptians Hanging Gardens of Babylon 600 BC - Babylonians Statue of Zeus at Olympia 435 BC - Greeks Temple of Artemis at Ephesus 550 BC - Anatolians Mausoleum of Maussollos at Halicarnassus 315 BC Colossus of Rhodes 292-280 BC - Hellenistic Civilization Lighthouse of Alexandria 3rd Century BC - Ěý
- 4. Today, archaeological evidence reveals some of the mysteries that surrounded the history of the Wonders for centuries. For their builders, the Seven Wonders were a celebration of religion, mythology, art, power, and science. For us, they reflect the ability of humans to change the surrounding landscape by building massive yet beautiful structures, one of which stood the test of time to this very day. The seven wonders of the ancient world implied that even the ancient civilization created wonderful things based on there customs, traditions and beliefs.
- 5. Date of Construction - 2584-2561 BC Builders - Egyptians Notable Features - Believed to have been built as the tomb of fourth dynasty Egyptian Pharaoh Khufu. Location - Giza Necropolis, Egypt The Giza Necropolis stands on the Giza Plateau, on the outskirts of Cairo, Egypt. This complex of ancient monuments is located some 8 km (5 mi) inland into the desert from the old town of Giza on the Nile, some 25 km (15 mi) southwest of Cairo city centre. One of the monuments, the Great Pyramid of Giza, is the only remaining monument of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The Giza Valley Plateau consists of 11 Pyramids, 4 Valley Temples, 3 Mortuary Temples, 3 Procession ways, and the Great Sphinx.
- 6. Ěý
- 7. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon (also known as the Hanging Gardens of Semiramis) and the walls of Babylon (present-day Iraq) were considered one of the Seven Wonders of the World. They were both supposedly built by Nebuchadnezzar II around 600 BC . According to accounts, the gardens were built to cheer up Nebuchadnezzar's homesick wife, Amyitis. Amyitis, daughter of the king of the Medes, was married to Nebuchadnezzar to create an alliance between the nations. The land she came from, though, was green, rugged and mountainous, and she found the flat, sun-baked terrain of the Mesopotamia (a region of southwest Asia) depressing. The king decided to recreate her homeland by building an artificial mountain with rooftop gardens. The Hanging Gardens probably did not really "hang" in the sense of being suspended from cables or ropes. The name comes from an inexact translation of the Greek word kremastos or the Latin word pensilis, which means not just "hanging² but "overhanging," as in the case of a terrace or balcony.
- 8. Ěý
- 9. The Temple of Artemis (Greek: Artemision; Latin: Artemisium ), also known as the Temple of Diana, was a Greek temple dedicated to Artemis completed around 550 BC at Ephesus (in present-day Turkey) under the Achaemenid dynasty of the Persian Empire. The temple was a 120-year project started by Croesus of Lydia. The Temple of Artemis was located in the ancient city of Ephesus, about 50 km south from the modern port city of Izmir, in Turkey. It was located at an economically robust region, seeing merchants and travelers from all over Asia Minor. The temple was influenced by many beliefs, and can be seen as a symbol of faith for many different peoples. The Ephesians worshipped Cybele, and incorporated many of their beliefs into the worship of Artemis.
- 10. Ěý
- 11. It was carved by the famed Classical sculptor Phidias (5th century BC) circa 435 BC in Olympia, Greece. It was 40 feet (12 meters) tall.
- 12. The Mausoleum of Maussollos, or Mausoleum of Halicarnassus was a tomb built between 353-350 BC at Halicarnassus (present Bodrum, Turkey), for Mausolus a provincial king in the Persian Empire, and Artemisia, his wife and sister. It was designed by the Greek architects Satyrus and Pythius. The structure was approximately 45-metres (135 feet) in height, and each of the four sides was adorned by a freize created by one of four famous Greek sculptors.
- 13. Ěý
- 14. The Colossus of Rhodes was a giant statue of the god Helios, erected on the Greek island of Rhodes by Chares of Lindos between 292 BC and 280 BC. It was roughly the same size as the Statue of Liberty in New York, although it stood on a lower platform. standing on a 15-metre-high (50 feet) white marble pedestal near the Mandraki harbor entrance . The statue itself was over 34 meters (110 feet) tall. After 12 years, in 280 BC, the great statue was completed.
- 15. The Pharos of Alexandria was a lighthouse built in the 3rd century BC on the island of Pharos in Alexandria, Egypt to serve as that port's landmark, and later, a lighthouse. With a height variously estimated at between 115 and 135 meters (383 - 440 ft) it was among the tallest man-made structures on Earth for many centuries. The tower was made up of three stages: a lower square section with a central core, a middle octagonal section, and, at the top, a circular section.
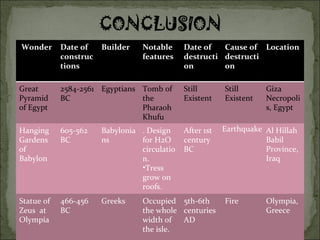
- 16. Wonder Date of constructions Builder Notable features Date of destruction Cause of destruction Location Great Pyramid of Egypt 2584-2561 BC Egyptians Tomb of the Pharaoh Khufu Still Existent Still Existent Giza Necropolis, Egypt Hanging Gardens of Babylon 605-562 BC Babylonians . Design for H2O circulation. Tress grow on roofs. After 1st century BC Earthquake Al Hillah Babil Province, Iraq Statue of Zeus at Olympia 466-456 BC Greeks Occupied the whole width of the isle. 5th-6th centuries AD Fire Olympia, Greece
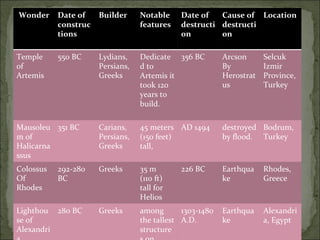
- 17. Wonder Date of constructions Builder Notable features Date of destruction Cause of destruction Location Temple of Artemis 550 BC Lydians, Persians, Greeks Dedicated to Artemis it took 120 years to build. 356 BC Arcson By Herostratus Selcuk Izmir Province, Turkey Mausoleum of Halicarnassus 351 BC Carians, Persians, Greeks 45 meters (150Ěýfeet) tall, AD 1494 destroyed by flood. Bodrum, Turkey Colossus Of Rhodes 292-280 BC Greeks 35Ěým (110Ěýft) tall for Helios 226 BC Earthquake Rhodes, Greece Lighthouse of Alexandria 280 BC Greeks among the tallest structures on Earth. 1303-1480 A.D. Earthquake Alexandria, Egypt
- 18. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seven_Wonders_of_the_Ancient_World http://www.unmuseum.org/wonders.htm http://www.livius.org/se-sg/7wonders/seven_wonders.html http://www.authenticwonders.com/Wonders/
- 19. Ěý
- 20. Presented by: CHENNIE L. SOLANIA