Common problems in paediatric surgery.pptx
- 1. Common paediatric surgical problems Speaker : Dr.Md.Mokarabin(Robin) Asst. Professor & Head Dept of Paediatric Surgery , SHMCJ
- 2. Introduction ŌĆó All encountered surgical conditions in paediatric age group, mostly surgically correctable congenital anomalies. ŌĆó Requires specialized knowledge & expertise, concentration of facilities including the sophisticated support services of anesthesia, laboratories facilities , imaging & nursing care.
- 3. contd ŌĆó Antenatal & postnatal checkups are helpful. ŌĆó Outcome depends on time on attention , evaluation , resuscitations including pre , peri & postoperative care.
- 4. Antenatal Diagnosis Possibilities : - Extremes of maternal age. - Primi gravida. - High multiparous mothers. - Low socioeconomics - Smoker mother - Diabetic & hypertensive mother.
- 5. Indicator: Polyhydramnios - GIT anomaly. Oligohydramnios ŌĆō Renal anomaly
- 6. Pregnancy profile ŌĆó USG ŌĆō Capable of detects a wide range of fetal anomalies during pregnancy. ŌĆó Fetal ECHO. ŌĆó Maternal serum level of AFP. ŌĆó Amniocentesis ŌĆó Endoscopy
- 7. Post-natal ŌĆó Revealed anomalies - detected by routine physical examinations. ŌĆó Concealed anomalies - by recognition of clinical presentation like vomiting , failure to or delayed passes of meconium, respiratory distress with or without cyanotic spell, failure to or difficult micturation , rectal bleeding & abdominal masses .
- 8. Diagnostic tools ŌĆó Clinical presentation ŌĆó Laboratory investigations ŌĆó USG ŌĆó Plain & contrast imaging including CT & MRI. ŌĆó Endoscopy
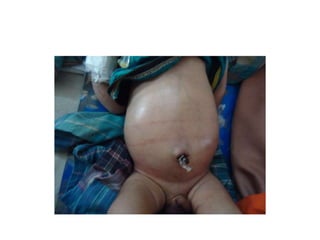
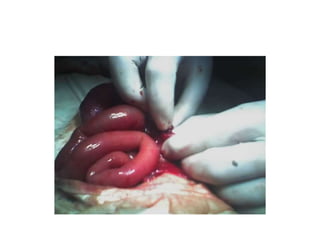
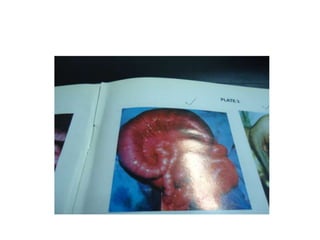
- 9. NEONATAL INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ŌĆó Neonatal intestinal obstruction presents with a triad of bilious vomiting, abdominal distension and failure to pass meconium. It is an urgent condition that requires the immediate involvement of a team of Paediatric Surgeons and Neonatologist for perioperative management.
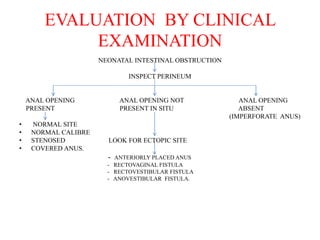
- 10. EVALUATION BY CLINICAL EXAMINATION NEONATAL INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION INSPECT PERINEUM ANAL OPENING ANAL OPENING NOT ANAL OPENING PRESENT PRESENT IN SITU ABSENT (IMPERFORATE ANUS) ŌĆó NORMAL SITE ŌĆó NORMAL CALIBRE ŌĆó STENOSED LOOK FOR ECTOPIC SITE ŌĆó COVERED ANUS. - ANTERIORLY PLACED ANUS - RECTOVAGINAL FISTULA - RECTOVESTIBULAR FISTULA - ANOVESTIBULAR FISTULA.
- 11. Anal opening present in normal site ŌĆó Gentle introduction of lubricated plain rubber catheter no 5 FR. ŌĆó Not pass beyond the limit 2-3cm-Rectal atresia. ŌĆó Pass more than 5-6cm & then withdraw catheter. ŌĆó Look for tip of catheter. ŌĆó If tip of catheter contain meconium- HirschsprungŌĆÖs disease, meconium ileus disease. ŌĆó If tip of catheter not contain meconium only mucus & blood ŌĆō Intestinal atresia.
- 12. DIAGNOSIS Antenatal: - Maternal polyhydramnios - Maternal USG - Family history of HPD or Cystic fibrosis Postnatal : - Plain X Ray abdomen - Abdominal / Transperineal USG - Invertogram - Contrast imaging study of upper & lower GIT - Laboratory Investigations
- 13. Management ŌĆó Resuscitation by NPO , N/G suction, I/V fluid, I/V antibiotic. ŌĆó Definitive treatment : According cause either in a single or staged procedure
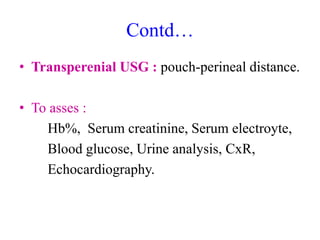
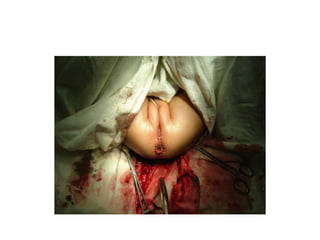
- 17. Anorectal malformation. ŌĆó A perineum without an anal opening described as imperforate, embraces a number of anomalies. ŌĆó Mostly communicate by a fistulaŌĆōurinary/genital, skin. ŌĆó Incidence :1 in 5000 live birth ,more in male. ŌĆó Outcome depends on associated anomalies which is more common in high varieties.
- 18. EVALUATION BY CLINICAL EXAMINATION ANORECTAL MALFORMATION INSPECT PERINEUM ANAL OPENING ANAL OPENING NOT ANAL OPENING PRESENT PRESENT IN SITU ABSENT (IMPERFORATE ANUS) ŌĆó NORMAL SITE ŌĆó NORMAL CALIBRE ŌĆó STENOSED LOOK FOR ECTOPIC SITE ŌĆó COVERED ANUS. - ANTERIORLY PLACED ANUS - RECTOVAGINAL FISTULA - RECTOVESTIBULAR FISTULA - ANOVESTIBULAR FISTULA.
- 19. Diagnosis. ŌĆó History ŌĆó Clinical examination ŌĆó Investigation : a) Invertogram : - pouch-perenial distence - sacral anomaly/agenesis - vertebral anomaly b) Cross table lat. prone invertogram : safer more informative. ŌĆó
- 20. ContdŌĆ” ŌĆó Transperenial USG : pouch-perineal distance. ŌĆó To asses : Hb%, Serum creatinine, Serum electroyte, Blood glucose, Urine analysis, CxR, Echocardiography.
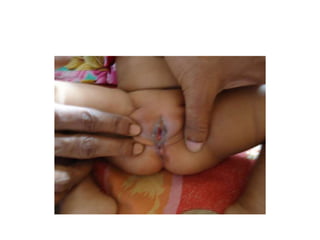
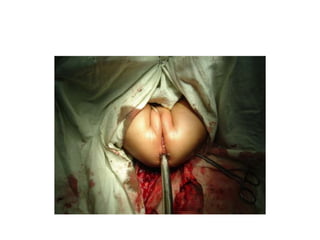
- 21. Management. ŌĆó Resuscitation : ŌĆó Low ---Anorectoplasty ŌĆó High--- Staged procedure: single procedure, PSARP/ ASARP/ Abdominoperenial pull through.
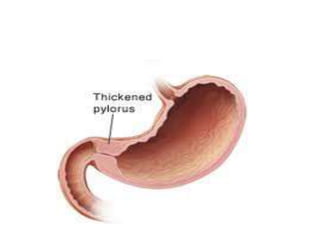
- 27. INFANTILE HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOSIS(IHPS) ŌĆó Commonest cause of vomiting in infant, severe in nature, usually commences between 3 to 6 weeks of age in an other wise well baby. ŌĆó Vomiting is non bilious and projectile ŌĆó Olive shaped mass in the epigastrium ŌĆó Severe dehydration & electrolyte imbalance leads to metabolic alkalosis
- 28. ŌĆó Diagnosis mostly obvious. ŌĆó Imaging studies of upper GIT are helpful. ŌĆó Needs urgent evaluation & surgical intervention which is very simple & permanent relief, other wise fatal outcome will be the result.
- 29. CLINICAL PRESENTATION ŌĆó Usual presentation is with severe non bilious, projectile vomiting which starts 3 - 6 weeks of age in an other wise well baby, rarely 10 days to 11 weeks. ŌĆó Vomitus contains only milk the child is active & hungry. ŌĆó Readiness & ability to feed immediately after vomiting. ŌĆó Constipation, jaundice & failure to thrive.
- 30. DIAGNOSIS ŌĆó Mostly by clinical presentation ŌĆó USG of upper GIT shows ŌĆō ’ā╝ Olive shaped mass in epigastrium. ’ā╝ Increase pyloric length mean 22 mm (range is 16-28 mm);normal length is 14mm ’ā╝ Diameter of pyloric canal mean 16mm(range is 12-22 mm);normal is less than12 mm.
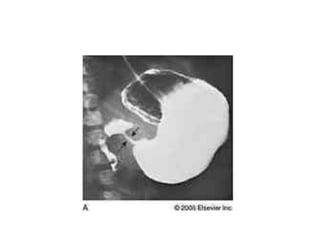
- 31. ŌĆó Upper GIT contrast study shows ŌĆō large gastric residue, delayed gastric empting, "string signŌĆØ & pyloric canal is elongated. ŌĆó CBC, S creatinin , S electrolytes .
- 34. TREATMENT ŌĆó Correction of nutrition, fluid & electrolytes are the utmost part of treatment. ŌĆó Pyloromyotomy ŌĆō Fredet-RamstedtŌĆÖs pyloromyotomy. ŌĆó Complications: Perforation of duodenum. Incomplete pyloromyotomy
- 36. POST-OPERATIVE CARE ŌĆó Trial feeds are given after 12 hours & when these are retained, milk feed are started & the baby is usually discharged on 3rd or 4th post- operative day.
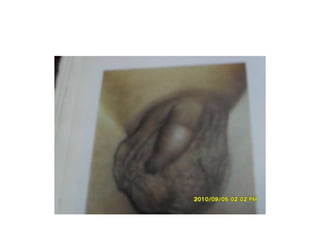
- 37. Inguinoscrotal swelling in children ŌĆó Commonest surgical condition encountered in children ŌĆó The duration & extent of the swelling can vary. ŌĆó The swelling can be either acute or insidious in onset ŌĆó Either congenital or acquired ŌĆó Accurate anatomical knowledge helps making correct diagnosis
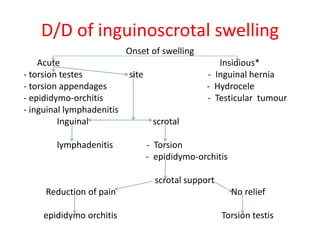
- 38. D/D of inguinoscrotal swelling Onset of swelling Acute Insidious* - torsion testes site - Inguinal hernia - torsion appendages - Hydrocele - epididymo-orchitis - Testicular tumour - inguinal lymphadenitis Inguinal scrotal lymphadenitis - Torsion - epididymo-orchitis scrotal support Reduction of pain No relief epididymo orchitis Torsion testis
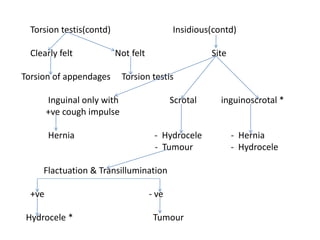
- 39. Torsion testis(contd) Insidious(contd) Clearly felt Not felt Site Torsion of appendages Torsion testis Inguinal only with Scrotal inguinoscrotal * +ve cough impulse Hernia - Hydrocele - Hernia - Tumour - Hydrocele Flactuation & Transillumination +ve - ve Hydrocele * Tumour
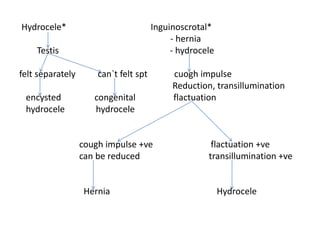
- 40. Hydrocele* Inguinoscrotal* - hernia Testis - hydrocele felt separately can`t felt spt cuogh impulse Reduction, transillumination encysted congenital flactuation hydrocele hydrocele cough impulse +ve flactuation +ve can be reduced transillumination +ve Hernia Hydrocele
- 41. INVESTIGATION ŌĆó Hb , TC, DC, BT, CT ŌĆó S Creatinin ŌĆó Chest - x - ray ŌĆó USG of inguinoscrotal region
- 42. Treatment ŌĆó Hernia: - Herniotomy as soon as diagnosed ŌĆó Hydrocele : - Neonates & Infants - wait & observe - Older children - Herniotomy + open the sac distally
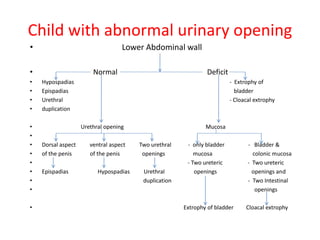
- 49. Child with abnormal urinary opening ŌĆó Lower Abdominal wall ŌĆó Normal Deficit ŌĆó Hypospadias - Extrophy of ŌĆó Epispadias bladder ŌĆó Urethral - Cloacal extrophy ŌĆó duplication ŌĆó Urethral opening Mucosa ŌĆó ŌĆó Dorsal aspect ventral aspect Two urethral - only bladder - Bladder & ŌĆó of the penis of the penis openings mucosa colonic mucosa ŌĆó - Two ureteric - Two ureteric ŌĆó Epispadias Hypospadias Urethral openings openings and ŌĆó duplication - Two Intestinal ŌĆó openings ŌĆó Extrophy of bladder Cloacal extrophy
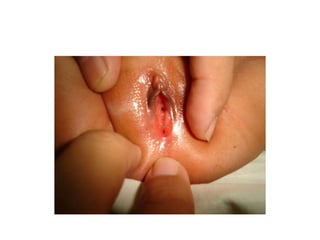
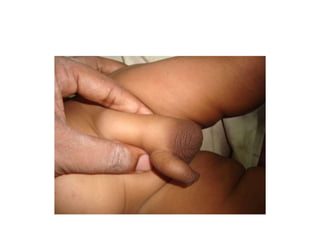
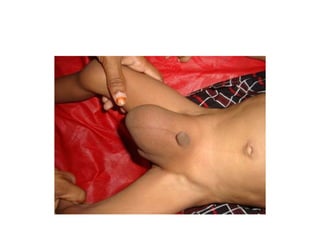
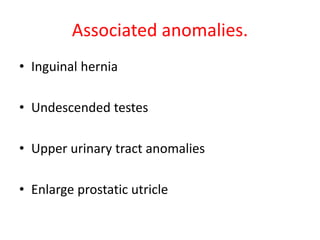
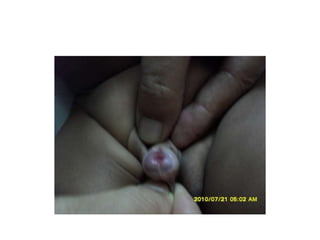
- 50. Hypospadias ŌĆó Hypospadias is a developmental anomaly characterized by a urethral meatus that opens on the ventral aspect of the penis, proximal to the end of the glans. ŌĆó Commonest congenital anomalies of the male genitalia occuring in 1 in 300 male birth.
- 51. ŌĆó Causes ventral curvature of the shaft of the penis more marked during erection. ŌĆó Deficiency in ventral aspect of the prepuce producing an unsightly dorsal hood of redundant skin. ŌĆó Meatus usually narrow may causes back pressure effect in the upper urinary system. ŌĆó Early treatment reduce morbidity, relief parent`s worries & anxiety
- 52. ŌĆó Imaging studies of urinary system, renal function tests & urinalysis are helpful to detect associated anomalies or co-existing morbidities.
- 53. Anatomy of the defect. ŌĆó Abnormal location of the meatus on the ventral surface of the penis ŌĆó Meatal stenosis ŌĆó Chordee.
- 54. Problems. ŌĆó Due to chordee stream of urine is deflected and splayed ŌĆó Difficulties in voiding in posterior variant of hypospadias ŌĆó Painful erection and interfere in sexual act leading to infertility
- 55. Associated anomalies. ŌĆó Inguinal hernia ŌĆó Undescended testes ŌĆó Upper urinary tract anomalies ŌĆó Enlarge prostatic utricle
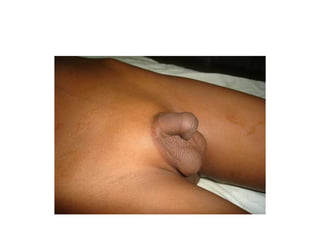
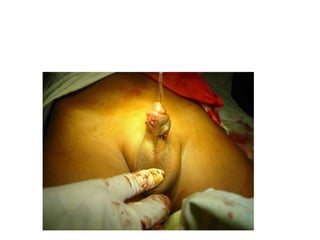
- 56. Treatment. ŌĆó Aim : - straitening of the penis - placing the meatus at tip of the glans symmetric conical shaped - satisfactory cosmetic skin coverage ŌĆó Time: - preschool going age - meatotomy at any age after birth if needed ŌĆó Treatment modalities : - Orthoplasty & urethroplasty either in a single or stage procedure depends on types of hypospadias in various procedures.
- 60. Epispadias ŌĆó Relatively uncommon in which the urethra opens on the dorsal aspect of the penis ŌĆó Usually associated with exstrophy of the bladder, dorsal chordee is a coexisting problem ŌĆó Surgical reconstruction in a single or stage procedures at pre school going age
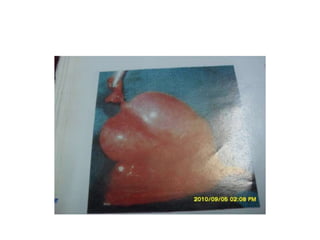
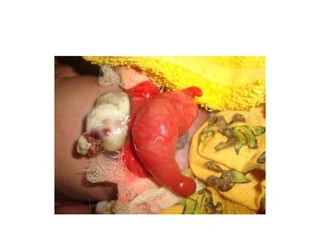
- 62. Exstrophy bladder ŌĆó Anterior abdominal wall & anterior wall of urinary bladder deficit, posterior wall of the urinary bladder with two ureteric orifices exposed ŌĆó Symphysis pubis apart from each other ŌĆó Anteriorly placed anus ŌĆó Epispadias with dorsal chordee and small/ micro penis in male , bifid clitoris and missing of roof of the urethra in female
- 63. ŌĆó Bilateral Undescended testis in male and bilateral direct Inguinal hernia in both sexes are associated ŌĆó Surgery is challenging and stage procedures
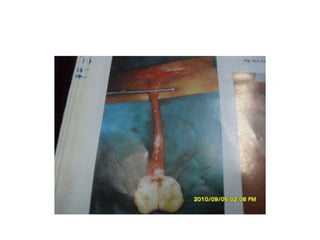
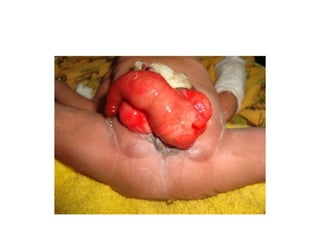
- 64. Cloacal exstrophy ŌĆó Most severe form of abdominal wall defect in which omphalocele superiorly, posterior walls of the hemi bladder on either side with central inter position of bowel, ŌĆó Symphysis pubis apart from each other ŌĆó Epispadias with dorsal chordee and small/ micro penis in male , bifid clitoris and missing of roof of the urethra in female ŌĆó Imperforate anus
- 65. ŌĆó Successful treatment requires an aggressive multispecialty effort