Comp App Lect 2 System Unit.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes17 views
The CPU is the central processing unit of the computer that acts as its brain. It contains two main components - the control unit and the arithmetic logic unit. The control unit fetches instructions from memory and directs the overall flow of data by orchestrating the operation of all other parts of the CPU. It decodes and executes instructions by determining the sequence of operations. The arithmetic logic unit performs arithmetic and logical operations and contains registers for temporary data storage. It executes the instructions by performing calculations on data stored in registers. The CPU follows an instruction cycle of fetching, decoding, executing and storing instructions to process data according to programs.
1 of 31
Download to read offline

























Recommended
COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION.ppt



COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION.pptAtul Kumar Rana
?
The document discusses computer organization and architecture. It describes the four main functional blocks of a computer as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, input unit, and output unit. The CPU consists of a control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers. The control unit fetches instructions from memory and directs the other units. The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations. Memory temporarily stores data and instructions and can be accessed randomly. The input and output units allow data to enter and exit the computer. All units communicate via buses that connect the processor, memory, and input/output devices.Computer Organization (1).pdf



Computer Organization (1).pdfmysthicrious
?
The document discusses the basic components and architecture of a computer system. It describes the four main functional blocks - the central processing unit (CPU), memory, input unit, and output unit. The CPU consists of three main subsystems: the control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers. The control unit fetches and decodes instructions from memory and directs the other units. The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations. These functional blocks are interconnected via a system bus consisting of address, data, and control lines to allow communication and processing of data within the computer.Comp App Lect 2.pptx



Comp App Lect 2.pptxMehwishKanwal14
?
The document discusses the basic organization and functioning of a computer system. It describes the five basic operations of a computer as inputting, storing, processing, outputting, and controlling. It then provides details about each operation, the components involved, and how they work together in a coordinated manner to process information. The control unit ensures proper coordination and synchronization of the four main operations to efficiently carry out tasks.co1_aiml_new.pptx



co1_aiml_new.pptxKUNTALADAS5
?
The document discusses the Von Neumann computer architecture. It describes the basic structure of a Von Neumann computer which includes a central processing unit (CPU), main memory, and input/output devices. The CPU contains a control unit, arithmetic logic unit, and registers. The main memory stores both programs and data. The architecture specifies that all components are connected via buses that transfer data, addresses, and control signals. It also notes that the Von Neumann design processes instructions sequentially, which can create a performance bottleneck.Introduction to Processor



Introduction to ProcessorAshish KC
?
The document summarizes key components of a computer processor. It discusses how the CPU, which contains the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit (CU), acts as the "brain" of the computer by manipulating data. The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations on data under the direction of the CU. The CU fetches and decodes instructions, manages the execution of operations, and stores results. Registers temporarily hold data during processing. Buses transmit data, addresses, and control signals between the CPU and other components like memory and I/O devices.COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION.ppttwhehteeeteehte



COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION.ppttwhehteeeteehteNishaTariq1
?
TjyekdydydyyydddyddydydyddydnydsssyddtsnddydydydydyddydydysysysysysyysnysysysysysysgsgsnysngsgsysysysysmsydydydyddydydydyddhysmdyysysysysysnysysssysysysmysnysysntsysysnysysnysysysysysysysysysysnysysysysgsysgsysgsgsngshshsgsgsgsysdhmgshshshshshsgsgsngsysgsgsnysgssygsgssyysysgsgsgsnysgsgsgssggsgsnsggsgsgsngsgsgsCOMPUTER_ORGANIZATION (1).pptx



COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION (1).pptxnodov66591
?
The document discusses the basic components and architecture of a computer system. It describes the four main functional blocks as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, input unit, and output unit. The CPU consists of three main subsystems: the control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers. The CPU fetches and executes instructions from memory through an instruction cycle. The functional blocks are interconnected via a system bus that includes data, address, and control lines to allow communication and transfer of data and instructions throughout the computer system.Bindura university of science education



Bindura university of science educationInnocent Tauzeni
?
The document discusses computer architecture and the Von Neumann architecture. It describes:
- The main components of a CPU including registers for temporary storage, buses for transmitting data/instructions, and functional units like the ALU.
- The fetch-execute cycle where the control unit fetches instructions and data from memory, decodes and executes the instructions using functional units, and writes results back to memory.
- The differences between RISC and CISC architectures, where RISC uses simpler instructions that can execute in one clock cycle while CISC incorporates complex operations into single instructions.
- Key components like the program counter, memory address register, and accumulator.
- The Von Neumann architecture where the CPUFp203 chp1.1



Fp203 chp1.1Norhayati Ismail
?
The document discusses the major operations performed by a computer system: input, storage, processing, output, and control. It describes how each operation works, such as entering data through input devices, storing data and instructions in storage, the central processing unit performing arithmetic and logical operations, output producing results, and the control unit coordinating all operations. It then explains the three basic functional units that control a computer's operations: the arithmetic logic unit performs calculations, the control unit determines instruction sequence and coordinates activities, and the central processing unit acts as the brain that directs functions.Architecture



ArchitectureMark Muhama
?
This document contains the solutions to multiple choice questions about converting binary numbers to octal numbers. It also discusses computer organization and architecture topics like CPU modules, types of transfers between modules, functional units of a computer with a diagram, data transfer and arithmetic operations, external devices and classification of external devices, and DMA function and configurations.Control unit



Control unitSameer Patil
?
The control unit is responsible for controlling the operations of all parts of the CPU. It decodes instructions, manages data flow between components, and issues control signals to coordinate execution. The main elements of the control unit are the decoder, timer/clock, and control logic circuits. The decoder determines the required actions for each instruction. The timer ensures operations are performed at the right time. And the control logic circuits create and send control signals to components like the ALU and registers.Fundamental units of computer



Fundamental units of computerSandeep Menon
?
The document discusses the functional components of a computer. It explains that a computer accepts input, stores data, processes data, provides output, and controls operations. It then describes each of these functions in more detail. Specifically, it notes that input involves entering data, storage saves data permanently, processing performs calculations on stored data, and output produces results. Control coordinates all internal operations. The document further breaks down the processing function among the arithmetic logical unit, control unit, and central processing unit. The arithmetic logical unit performs calculations, the control unit coordinates operations, and the central processing unit directs different parts of the computer.Basic organisation of computer system



Basic organisation of computer systemParvathy Ashok
?
A computer performs five basic functions: input, storage, processing, output, and control. It accepts data through input, stores the data and instructions, processes the data using the central processing unit (CPU), produces output, and has a control unit that coordinates operations. A computer system is divided into three main units - the arithmetic logical unit that performs calculations, the control unit that directs the sequence of operations, and the central processing unit that consists of the arithmetic logical and control units and acts as the computer's brain to make decisions and control functions.Components of computer hardware



Components of computer hardwareA. S. M. Shafi
?
The document summarizes the main components of computer hardware. It describes the three main components as the input/output unit, the central processing unit (CPU), and the memory unit. The CPU controls and coordinates the other components. It has an arithmetic logic unit to perform calculations and a control unit to manage the sequence of operations. The memory unit temporarily stores data, instructions, and results during processing.Components Of Computer unit-2



Components Of Computer unit-2Amit Chandra
?
The document discusses the key components of a computer system. It describes hardware as the physical components like the CPU, monitor, keyboard, disks, and printer. Software refers to programs that allow the hardware to function. The main components of a computer are the input and output devices, central processing unit (CPU), and memory. The CPU acts as the brain and performs all processing. It consists of an arithmetic logic unit, control unit, registers, buses, and clock. The control unit manages data and instruction transfer between components. Memory is used to store data, instructions, and information before, during, and after processing. Storage devices like hard disks allow for permanent data storage.Computer Architecture Design (CAD)



Computer Architecture Design (CAD)Saira Kanwal
?
This document summarizes a presentation on computer architecture design. It discusses the components of a processor, including the data path and control. The data path contains registers and execution units, as well as buses like the system bus, expansion bus, data bus, address bus, and control bus. The control unit commands the data path and memory according to instructions from memory. It selects and interprets program instructions and coordinates their execution.3. IICT_Lecture 03_Computer Org Personal



3. IICT_Lecture 03_Computer Org PersonalNational College of Business Administration and Economics
?
3. IICT_Lecture 03_Computer Org.pdfLesson 1 anatomy of a digital computer (230 kb)



Lesson 1 anatomy of a digital computer (230 kb)IMRAN KHAN
?
The document discusses the anatomy and components of a digital computer. It describes the five main hardware components as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, input devices, output devices, and storage devices. The CPU contains the control unit and arithmetic logic unit (ALU). Memory temporarily stores data and instructions. Common input devices include keyboards, mice, and scanners. Output devices like monitors and printers allow users to see results. Mass storage devices like hard disks permanently store large amounts of data. The document provides details on how these components work together to receive input, process information, produce output, and store information.Chap2 comp architecture



Chap2 comp architectureraksharao
?
This document provides an overview of the central processing unit (CPU). It discusses that the CPU is referred to as the brain of the computer and contains an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit (CU). The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations, while the CU directs other parts of the system. The CPU also includes registers for temporary storage. Communication between the CPU and other components like memory and I/O devices occurs via buses that transfer data, addresses, and control signals. Caches provide faster access to frequently used data and instructions.Functional Units of Digital System & Their Interconnection.pptx



Functional Units of Digital System & Their Interconnection.pptxJyotiSingh885672
?
Functional Units of Digital System & Their Interconnection
A digital system is composed of various functional units that work together to process, store, and communicate information. These units can be categorized into several key components, each serving distinct roles:
Input Units: These devices, such as keyboards, mice, and sensors, convert external data into a format that the system can process. They facilitate user interaction and data acquisition.
Processing Units: The central processing unit (CPU) is the core of a digital system, executing instructions and performing calculations. It often includes arithmetic logic units (ALUs) and control units (CUs) that manage data flow and operations.
Memory Units: These units store data temporarily or permanently. Random Access Memory (RAM) provides fast, volatile storage for active processes, while read-only memory (ROM) and storage devices like hard drives and SSDs offer non-volatile data retention.
Output Units: Devices such as monitors, printers, and speakers display or convey processed information to users. They translate digital signals back into a human-readable or usable format.
Communication Units: These facilitate data exchange between different systems or components. Examples include network interfaces, modems, and buses that allow various parts of the system to communicate efficiently.
Interconnection: The functional units are interconnected through buses and communication protocols, which define the pathways and rules for data transfer. This interconnectivity ensures seamless operation and coordination among units, allowing for the integration of complex functions and multi-tasking capabilities.
In summary, the functional units of a digital system and their interconnection form the backbone of modern computing, enabling a wide range of applications and services that drive our digital world.Processing Devices



Processing Devicesitsvineeth209
?
The document discusses processing devices and central processing units (CPUs). It describes a CPU as having three main parts: registers that hold information for processing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that performs calculations and comparisons, and a control unit that directs the system. The document outlines the evolution of CPUs from early chips like the Intel 4004 to modern multi-core processors. Buses connect the CPU and memory to transfer data and instructions for processing.CS410 Visual Programming Master of Information Technology VU University Past ...



CS410 Visual Programming Master of Information Technology VU University Past ...MehwishKanwal14
?
document14420-Article Text-17938-1-2-20201228.pdf



14420-Article Text-17938-1-2-20201228.pdfMehwishKanwal14
?
This document summarizes an algorithm for efficiently clustering short messages like tweets into general domains or topics. The algorithm breaks the clustering task into two stages: (1) batch clustering of user-annotated data using hashtags to create dense virtual documents, and (2) online clustering of new tweets using the centroids from stage 1. Experimental results show the algorithm outperforms other clustering methods and can accurately cluster large streams of sparse, short messages efficiently.More Related Content
Similar to Comp App Lect 2 System Unit.pptx (20)
Comp App Lect 2.pptx



Comp App Lect 2.pptxMehwishKanwal14
?
The document discusses the basic organization and functioning of a computer system. It describes the five basic operations of a computer as inputting, storing, processing, outputting, and controlling. It then provides details about each operation, the components involved, and how they work together in a coordinated manner to process information. The control unit ensures proper coordination and synchronization of the four main operations to efficiently carry out tasks.co1_aiml_new.pptx



co1_aiml_new.pptxKUNTALADAS5
?
The document discusses the Von Neumann computer architecture. It describes the basic structure of a Von Neumann computer which includes a central processing unit (CPU), main memory, and input/output devices. The CPU contains a control unit, arithmetic logic unit, and registers. The main memory stores both programs and data. The architecture specifies that all components are connected via buses that transfer data, addresses, and control signals. It also notes that the Von Neumann design processes instructions sequentially, which can create a performance bottleneck.Introduction to Processor



Introduction to ProcessorAshish KC
?
The document summarizes key components of a computer processor. It discusses how the CPU, which contains the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit (CU), acts as the "brain" of the computer by manipulating data. The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations on data under the direction of the CU. The CU fetches and decodes instructions, manages the execution of operations, and stores results. Registers temporarily hold data during processing. Buses transmit data, addresses, and control signals between the CPU and other components like memory and I/O devices.COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION.ppttwhehteeeteehte



COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION.ppttwhehteeeteehteNishaTariq1
?
TjyekdydydyyydddyddydydyddydnydsssyddtsnddydydydydyddydydysysysysysyysnysysysysysysgsgsnysngsgsysysysysmsydydydyddydydydyddhysmdyysysysysysnysysssysysysmysnysysntsysysnysysnysysysysysysysysysysnysysysysgsysgsysgsgsngshshsgsgsgsysdhmgshshshshshsgsgsngsysgsgsnysgssygsgssyysysgsgsgsnysgsgsgssggsgsnsggsgsgsngsgsgsCOMPUTER_ORGANIZATION (1).pptx



COMPUTER_ORGANIZATION (1).pptxnodov66591
?
The document discusses the basic components and architecture of a computer system. It describes the four main functional blocks as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, input unit, and output unit. The CPU consists of three main subsystems: the control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers. The CPU fetches and executes instructions from memory through an instruction cycle. The functional blocks are interconnected via a system bus that includes data, address, and control lines to allow communication and transfer of data and instructions throughout the computer system.Bindura university of science education



Bindura university of science educationInnocent Tauzeni
?
The document discusses computer architecture and the Von Neumann architecture. It describes:
- The main components of a CPU including registers for temporary storage, buses for transmitting data/instructions, and functional units like the ALU.
- The fetch-execute cycle where the control unit fetches instructions and data from memory, decodes and executes the instructions using functional units, and writes results back to memory.
- The differences between RISC and CISC architectures, where RISC uses simpler instructions that can execute in one clock cycle while CISC incorporates complex operations into single instructions.
- Key components like the program counter, memory address register, and accumulator.
- The Von Neumann architecture where the CPUFp203 chp1.1



Fp203 chp1.1Norhayati Ismail
?
The document discusses the major operations performed by a computer system: input, storage, processing, output, and control. It describes how each operation works, such as entering data through input devices, storing data and instructions in storage, the central processing unit performing arithmetic and logical operations, output producing results, and the control unit coordinating all operations. It then explains the three basic functional units that control a computer's operations: the arithmetic logic unit performs calculations, the control unit determines instruction sequence and coordinates activities, and the central processing unit acts as the brain that directs functions.Architecture



ArchitectureMark Muhama
?
This document contains the solutions to multiple choice questions about converting binary numbers to octal numbers. It also discusses computer organization and architecture topics like CPU modules, types of transfers between modules, functional units of a computer with a diagram, data transfer and arithmetic operations, external devices and classification of external devices, and DMA function and configurations.Control unit



Control unitSameer Patil
?
The control unit is responsible for controlling the operations of all parts of the CPU. It decodes instructions, manages data flow between components, and issues control signals to coordinate execution. The main elements of the control unit are the decoder, timer/clock, and control logic circuits. The decoder determines the required actions for each instruction. The timer ensures operations are performed at the right time. And the control logic circuits create and send control signals to components like the ALU and registers.Fundamental units of computer



Fundamental units of computerSandeep Menon
?
The document discusses the functional components of a computer. It explains that a computer accepts input, stores data, processes data, provides output, and controls operations. It then describes each of these functions in more detail. Specifically, it notes that input involves entering data, storage saves data permanently, processing performs calculations on stored data, and output produces results. Control coordinates all internal operations. The document further breaks down the processing function among the arithmetic logical unit, control unit, and central processing unit. The arithmetic logical unit performs calculations, the control unit coordinates operations, and the central processing unit directs different parts of the computer.Basic organisation of computer system



Basic organisation of computer systemParvathy Ashok
?
A computer performs five basic functions: input, storage, processing, output, and control. It accepts data through input, stores the data and instructions, processes the data using the central processing unit (CPU), produces output, and has a control unit that coordinates operations. A computer system is divided into three main units - the arithmetic logical unit that performs calculations, the control unit that directs the sequence of operations, and the central processing unit that consists of the arithmetic logical and control units and acts as the computer's brain to make decisions and control functions.Components of computer hardware



Components of computer hardwareA. S. M. Shafi
?
The document summarizes the main components of computer hardware. It describes the three main components as the input/output unit, the central processing unit (CPU), and the memory unit. The CPU controls and coordinates the other components. It has an arithmetic logic unit to perform calculations and a control unit to manage the sequence of operations. The memory unit temporarily stores data, instructions, and results during processing.Components Of Computer unit-2



Components Of Computer unit-2Amit Chandra
?
The document discusses the key components of a computer system. It describes hardware as the physical components like the CPU, monitor, keyboard, disks, and printer. Software refers to programs that allow the hardware to function. The main components of a computer are the input and output devices, central processing unit (CPU), and memory. The CPU acts as the brain and performs all processing. It consists of an arithmetic logic unit, control unit, registers, buses, and clock. The control unit manages data and instruction transfer between components. Memory is used to store data, instructions, and information before, during, and after processing. Storage devices like hard disks allow for permanent data storage.Computer Architecture Design (CAD)



Computer Architecture Design (CAD)Saira Kanwal
?
This document summarizes a presentation on computer architecture design. It discusses the components of a processor, including the data path and control. The data path contains registers and execution units, as well as buses like the system bus, expansion bus, data bus, address bus, and control bus. The control unit commands the data path and memory according to instructions from memory. It selects and interprets program instructions and coordinates their execution.3. IICT_Lecture 03_Computer Org Personal



3. IICT_Lecture 03_Computer Org PersonalNational College of Business Administration and Economics
?
3. IICT_Lecture 03_Computer Org.pdfLesson 1 anatomy of a digital computer (230 kb)



Lesson 1 anatomy of a digital computer (230 kb)IMRAN KHAN
?
The document discusses the anatomy and components of a digital computer. It describes the five main hardware components as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, input devices, output devices, and storage devices. The CPU contains the control unit and arithmetic logic unit (ALU). Memory temporarily stores data and instructions. Common input devices include keyboards, mice, and scanners. Output devices like monitors and printers allow users to see results. Mass storage devices like hard disks permanently store large amounts of data. The document provides details on how these components work together to receive input, process information, produce output, and store information.Chap2 comp architecture



Chap2 comp architectureraksharao
?
This document provides an overview of the central processing unit (CPU). It discusses that the CPU is referred to as the brain of the computer and contains an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit (CU). The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations, while the CU directs other parts of the system. The CPU also includes registers for temporary storage. Communication between the CPU and other components like memory and I/O devices occurs via buses that transfer data, addresses, and control signals. Caches provide faster access to frequently used data and instructions.Functional Units of Digital System & Their Interconnection.pptx



Functional Units of Digital System & Their Interconnection.pptxJyotiSingh885672
?
Functional Units of Digital System & Their Interconnection
A digital system is composed of various functional units that work together to process, store, and communicate information. These units can be categorized into several key components, each serving distinct roles:
Input Units: These devices, such as keyboards, mice, and sensors, convert external data into a format that the system can process. They facilitate user interaction and data acquisition.
Processing Units: The central processing unit (CPU) is the core of a digital system, executing instructions and performing calculations. It often includes arithmetic logic units (ALUs) and control units (CUs) that manage data flow and operations.
Memory Units: These units store data temporarily or permanently. Random Access Memory (RAM) provides fast, volatile storage for active processes, while read-only memory (ROM) and storage devices like hard drives and SSDs offer non-volatile data retention.
Output Units: Devices such as monitors, printers, and speakers display or convey processed information to users. They translate digital signals back into a human-readable or usable format.
Communication Units: These facilitate data exchange between different systems or components. Examples include network interfaces, modems, and buses that allow various parts of the system to communicate efficiently.
Interconnection: The functional units are interconnected through buses and communication protocols, which define the pathways and rules for data transfer. This interconnectivity ensures seamless operation and coordination among units, allowing for the integration of complex functions and multi-tasking capabilities.
In summary, the functional units of a digital system and their interconnection form the backbone of modern computing, enabling a wide range of applications and services that drive our digital world.Processing Devices



Processing Devicesitsvineeth209
?
The document discusses processing devices and central processing units (CPUs). It describes a CPU as having three main parts: registers that hold information for processing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that performs calculations and comparisons, and a control unit that directs the system. The document outlines the evolution of CPUs from early chips like the Intel 4004 to modern multi-core processors. Buses connect the CPU and memory to transfer data and instructions for processing.More from MehwishKanwal14 (10)
CS410 Visual Programming Master of Information Technology VU University Past ...



CS410 Visual Programming Master of Information Technology VU University Past ...MehwishKanwal14
?
document14420-Article Text-17938-1-2-20201228.pdf



14420-Article Text-17938-1-2-20201228.pdfMehwishKanwal14
?
This document summarizes an algorithm for efficiently clustering short messages like tweets into general domains or topics. The algorithm breaks the clustering task into two stages: (1) batch clustering of user-annotated data using hashtags to create dense virtual documents, and (2) online clustering of new tweets using the centroids from stage 1. Experimental results show the algorithm outperforms other clustering methods and can accurately cluster large streams of sparse, short messages efficiently.projects2021C3.pdf



projects2021C3.pdfMehwishKanwal14
?
This document describes a project that aims to predict heart disease using machine learning algorithms. It analyzes a heart disease dataset using various algorithms like decision trees, naive bayes, logistic regression, SVM, random forest, AdaBoost and XGBoost. The project aims to find the best performing algorithm for heart disease prediction by comparing their accuracies. It collects a heart disease dataset, preprocesses it, balances the data, runs various algorithms on it and evaluates their performance using metrics like confusion matrix.Wajid Shah-MCS143027.pdf



Wajid Shah-MCS143027.pdfMehwishKanwal14
?
- Wajid Shah submitted a thesis titled "Cardiovascular and Chronic Respiratory Diseases Prediction System" in partial fulfillment of a Master of Science degree in computer science at Capital University of Science and Technology, Islamabad.
- The thesis proposed a system to predict symptoms of cardiovascular diseases and chronic respiratory diseases using patient vital sign data, which could help diagnose diseases earlier and start treatment.
- Vital sign data from the University of Queensland dataset was used, containing monitoring data from 32 surgical situations. Regression and classification models were developed and evaluated to predict medical situations based on vital signs.Comp App Lect 5 part 2.pptx



Comp App Lect 5 part 2.pptxMehwishKanwal14
?
Input devices capture information from the external environment and translate it into a form that can be processed by computers. Common input devices include keyboards, pointing devices like mice and trackballs, game controllers, scanners, styluses, microphones, digital cameras, and webcams. Trackballs are upside-down mice that rotate in place to move the cursor, requiring less workspace but more cleaning than mice. Touchpads and pointing sticks are found on laptops to control the cursor. Light pens, touch screens, styluses, graphic tablets, and pen-based devices allow entering information via touch. Voice recognition and handwriting recognition translate spoken words and handwriting into text.Comp App Lect 4.pptx



Comp App Lect 4.pptxMehwishKanwal14
?
A secondary storage device refers to any non-volatile storage device, either internal or external to the computer, that allows for permanent data storage beyond the computer's primary storage. Common types of secondary storage devices include magnetic disks like hard disks, which provide high storage capacities and fast access, and optical discs like CDs and DVDs, which can store large volumes of data safely but provide slower access. Proper care and handling of storage media is important to prevent damage or loss of stored data.Comp App Lect 1.ppt



Comp App Lect 1.pptMehwishKanwal14
?
Computer technology has progressed through five generations. First generation computers used vacuum tubes, punched cards, and were bulky, unreliable, and costly. The second generation saw the introduction of transistors, magnetic storage, and programming languages. Third generation computers integrated circuits, larger memory, and operating systems. The fourth generation began in 1971 with microprocessors on a single chip, GUIs, networks, and personal computers. Current and future fifth generation computers are based on artificial intelligence and natural language capabilities.Comp App Lect 3.pptx



Comp App Lect 3.pptxMehwishKanwal14
?
The document discusses different types of computer memory. It defines memory as the component that stores instructions and data. There are two main types of memory: primary memory (RAM) that is directly accessed by the CPU, and secondary memory like hard disks. RAM is volatile and temporarily stores data during use, while ROM is non-volatile and stores permanent instructions. The document outlines different RAM technologies like DRAM, SRAM, and MRAM and compares their characteristics. It also discusses cache memory, ROM, flash memory, and CMOS memory.Comp App lect 3 (Software).ppt



Comp App lect 3 (Software).pptMehwishKanwal14
?
The document discusses different types of computer hardware, software, and the relationship between them. It defines hardware as the physical computing equipment, and software as the set of instructions that tell the computer what to do. It then summarizes different categories of software including system software, application software, open source software, closed source software, free software, and shareware.C# console applications.docx



C# console applications.docxMehwishKanwal14
?
This document provides 50 examples of C# programs that demonstrate basic coding concepts like printing text, taking user input, performing calculations, and using conditional logic. The examples progress from simple concepts like "Hello World" to more complex topics such as calculating factorials, Fibonacci sequences, and determining if a number is prime. Each example includes the full source code and output for that program.Recently uploaded (20)
L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardness



L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardnessRostislavDaniel
?
Introduction to NanoindentationDAO UTokyo 2025 DLT mass adoption case studies IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)



DAO UTokyo 2025 DLT mass adoption case studies IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)Tsuyoshi Hirayama
?
DAO UTokyo 2025
–|¾©´óѧÇéˆóѧh ¥Ö¥í¥Ã¥¯¥Á¥§©`¥óÑо¿¥¤¥Ë¥·¥¢¥Æ¥£¥Ö
https://utbciii.com/2024/12/12/announcing-dao-utokyo-2025-conference/
Session 1 :DLT mass adoption
IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)Field Device Management Market Report 2030 - TechSci Research



Field Device Management Market Report 2030 - TechSci ResearchVipin Mishra
?
The Global Field Device Management (FDM) Market is expected to experience significant growth in the forecast period from 2026 to 2030, driven by the integration of advanced technologies aimed at improving industrial operations.
? According to TechSci Research, the Global Field Device Management Market was valued at USD 1,506.34 million in 2023 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.72% through 2030. FDM plays a vital role in the centralized oversight and optimization of industrial field devices, including sensors, actuators, and controllers.
Key tasks managed under FDM include:
Configuration
Monitoring
Diagnostics
Maintenance
Performance optimization
FDM solutions offer a comprehensive platform for real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making, enabling:
Proactive maintenance
Predictive analytics
Remote monitoring
By streamlining operations and ensuring compliance, FDM enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves asset reliability, ultimately leading to greater performance in industrial processes. FDM¡¯s emphasis on predictive maintenance is particularly important in ensuring the long-term sustainability and success of industrial operations.
For more information, explore the full report: https://shorturl.at/EJnzR
Major companies operating in Global?Field Device Management Market are:
General Electric Co
Siemens AG
ABB Ltd
Emerson Electric Co
Aveva Group Ltd
Schneider Electric SE
STMicroelectronics Inc
Techno Systems Inc
Semiconductor Components Industries LLC
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM)
#FieldDeviceManagement #IndustrialAutomation #PredictiveMaintenance #TechInnovation #IndustrialEfficiency #RemoteMonitoring #TechAdvancements #MarketGrowth #OperationalExcellence #SensorsAndActuatorsFuture-Proof Your Career with AI Options



Future-Proof Your Career with AI OptionsDianaGray10
?
Learn about the difference between automation, AI and agentic and ways you can harness these to further your career. In this session you will learn:
Introduction to automation, AI, agentic
Trends in the marketplace
Take advantage of UiPath training and certification
In demand skills needed to strategically position yourself to stay ahead
? If you have any questions or feedback, please refer to the "Women in Automation 2025" dedicated Forum thread. You can find there extra details and updates.The Future of Repair: Transparent and Incremental by Botond De?nes



The Future of Repair: Transparent and Incremental by Botond De?nesScyllaDB
?
Regularly run repairs are essential to keep clusters healthy, yet having a good repair schedule is more challenging than it should be. Repairs often take a long time, preventing running them often. This has an impact on data consistency and also limits the usefulness of the new repair based tombstone garbage collection. We want to address these challenges by making repairs incremental and allowing for automatic repair scheduling, without relying on external tools.THE BIG TEN BIOPHARMACEUTICAL MNCs: GLOBAL CAPABILITY CENTERS IN INDIA



THE BIG TEN BIOPHARMACEUTICAL MNCs: GLOBAL CAPABILITY CENTERS IN INDIASrivaanchi Nathan
?
This business intelligence report, "The Big Ten Biopharmaceutical MNCs: Global Capability Centers in India", provides an in-depth analysis of the operations and contributions of the Global Capability Centers (GCCs) of ten leading biopharmaceutical multinational corporations in India. The report covers AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Novartis, Sanofi, Roche, Pfizer, Novo Nordisk, and Eli Lilly. In this report each company's GCC is profiled with details on location, workforce size, investment, and the strategic roles these centers play in global business operations, research and development, and information technology and digital innovation.EaseUS Partition Master Crack 2025 + Serial Key



EaseUS Partition Master Crack 2025 + Serial Keykherorpacca127
?
https://ncracked.com/7961-2/
Note: >> Please copy the link and paste it into Google New Tab now Download link
EASEUS Partition Master Crack is a professional hard disk partition management tool and system partition optimization software. It is an all-in-one PC and server disk management toolkit for IT professionals, system administrators, technicians, and consultants to provide technical services to customers with unlimited use.
EASEUS Partition Master 18.0 Technician Edition Crack interface is clean and tidy, so all options are at your fingertips. Whether you want to resize, move, copy, merge, browse, check, convert partitions, or change their labels, you can do everything with a few clicks. The defragmentation tool is also designed to merge fragmented files and folders and store them in contiguous locations on the hard drive.
DevNexus - Building 10x Development Organizations.pdf



DevNexus - Building 10x Development Organizations.pdfJustin Reock
?
Developer Experience is Dead! Long Live Developer Experience!
In this keynote-style session, we¡¯ll take a detailed, granular look at the barriers to productivity developers face today and modern approaches for removing them. 10x developers may be a myth, but 10x organizations are very real, as proven by the influential study performed in the 1980s, ¡®The Coding War Games.¡¯
Right now, here in early 2025, we seem to be experiencing YAPP (Yet Another Productivity Philosophy), and that philosophy is converging on developer experience. It seems that with every new method, we invent to deliver products, whether physical or virtual, we reinvent productivity philosophies to go alongside them.
But which of these approaches works? DORA? SPACE? DevEx? What should we invest in and create urgency behind today so we don¡¯t have the same discussion again in a decade?UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 2



UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 2DianaGray10
?
In session 2, we will introduce you to Data manipulation in UiPath Studio.
Topics covered:
Data Manipulation
What is Data Manipulation
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
RegEx Builder
Date and Time
Required Self-Paced Learning for this session:
Data Manipulation with Strings in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h 30m - https://academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-strings-in-studio
Data Manipulation with Lists and Dictionaries in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h - https:/academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-lists-and-dictionaries-in-studio
Data Manipulation with Data Tables in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h 30m - https:/academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-data-tables-in-studio
?? For any questions you may have, please use the dedicated Forum thread. You can tag the hosts and mentors directly and they will reply as soon as possible. Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptx



Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptxkaylagaze
?
In this presentation, I will discuss how technology has changed consumer behaviour and its impact on consumers and businesses. I will focus on internet access, digital devices, how customers search for information and what they buy online, video consumption, and lastly consumer trends.
FinTech - US Annual Funding Report - 2024.pptx



FinTech - US Annual Funding Report - 2024.pptxTracxn
?
US FinTech 2024, offering a comprehensive analysis of key trends, funding activities, and top-performing sectors that shaped the FinTech ecosystem in the US 2024. The report delivers detailed data and insights into the region's funding landscape and other developments. We believe this report will provide you with valuable insights to understand the evolving market dynamics.Understanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptx



Understanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptxshyamraj55
?
Understanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptx | ### ºİºİߣ Deck Description:
This presentation features Atul, a Senior Solution Architect at NTT DATA, sharing his journey into traditional AI using Azure's Custom Vision tool. He discusses how AI mimics human thinking and reasoning, differentiates between predictive and generative AI, and demonstrates a real-world use case. The session covers the step-by-step process of creating and training an AI model for image classification and object detection¡ªspecifically, an ad display that adapts based on the viewer's gender. Atulavan highlights the ease of implementation without deep software or programming expertise. The presentation concludes with a Q&A session addressing technical and privacy concerns.Revolutionizing-Government-Communication-The-OSWAN-Success-Story



Revolutionizing-Government-Communication-The-OSWAN-Success-Storyssuser52ad5e
?
? ????? ??????? ????? ?
???????? ??????????? is proud to be a part of the ?????? ????? ???? ???? ??????? (?????) success story! By delivering seamless, secure, and high-speed connectivity, OSWAN has revolutionized e-?????????? ?? ??????, enabling efficient communication between government departments and enhancing citizen services.
Through our innovative solutions, ???????? ?????????? has contributed to making governance smarter, faster, and more transparent. This milestone reflects our commitment to driving digital transformation and empowering communities.
? ?????????? ??????, ?????????? ??????????!
Unlock AI Creativity: Image Generation with DALL¡¤E



Unlock AI Creativity: Image Generation with DALL¡¤EExpeed Software
?
Discover the power of AI image generation with DALL¡¤E, an advanced AI model that transforms text prompts into stunning, high-quality visuals. This presentation explores how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing digital creativity, from graphic design to content creation and marketing. Learn about the technology behind DALL¡¤E, its real-world applications, and how businesses can leverage AI-generated art for innovation. Whether you're a designer, developer, or marketer, this guide will help you unlock new creative possibilities with AI-driven image synthesis.Fl studio crack version 12.9 Free Download



Fl studio crack version 12.9 Free Downloadkherorpacca127
?
Google the copied link ???? https://activationskey.com/download-latest-setup/
????
The ultimate guide to FL Studio 12.9 Crack, the revolutionary digital audio workstation that empowers musicians and producers of all levels. This software has become a cornerstone in the music industry, offering unparalleled creative capabilities, cutting-edge features, and an intuitive workflow.
With FL Studio 12.9 Crack, you gain access to a vast arsenal of instruments, effects, and plugins, seamlessly integrated into a user-friendly interface. Its signature Piano Roll Editor provides an exceptional level of musical expression, while the advanced automation features empower you to create complex and dynamic compositions.Gojek Clone Multi-Service Super App.pptx



Gojek Clone Multi-Service Super App.pptxV3cube
?
Gojek Clone is a versatile multi-service super app that offers ride-hailing, food delivery, payment services, and more, providing a seamless experience for users and businesses alike on a single platform.Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)



Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)nick896721
?
Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation preview by User Interviews.UiPath Agentic Automation Capabilities and Opportunities



UiPath Agentic Automation Capabilities and OpportunitiesDianaGray10
?
Learn what UiPath Agentic Automation capabilities are and how you can empower your agents with dynamic decision making. In this session we will cover these topics:
What do we mean by Agents
Components of Agents
Agentic Automation capabilities
What Agentic automation delivers and AI Tools
Identifying Agent opportunities
? If you have any questions or feedback, please refer to the "Women in Automation 2025" dedicated Forum thread. You can find there extra details and updates.Comp App Lect 2 System Unit.pptx
- 2. The CPU
- 3. CPU
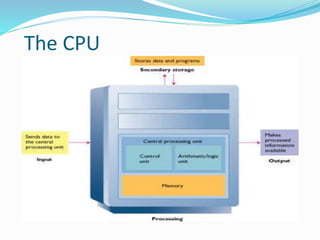
- 4. The CPU ? CPU stands for central processing unit. it is brain of computer ? It is most important component of the computer. it is also called processor. ? Converts data into information ? It continually receives instructions to execute. Each instruction tells CPU to process data. ? CPU performs all operations on data according to the given instructions.
- 5. It executes instructions and tells other parts of computers what to do. Most of the work consists of calculations and data transfer. Two parts Control Unit (CU) Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
- 6. Control Unit CU ? Control Unit is an important component of CPU. It acts Like a supervisor of the computer. ? It controls all activities of the computer system ? All the computers resources are managed from the control unit. ? Think of the control unit as a traffic signal directing the flow of data through the CPU.
- 7. ? The CPU?s instruction for carrying out commands are built into the control unit. ? The instruction or instruction set, list all the operations that the CPU can perform. ? Each instruction in the instruction set is expressed in microcode¨C a series of basic directions that tell the CPU how to execute more complex operations.
- 8. Control Unit CU ? It performs the following operations: 1. It fetches(makes) or retrieve instruction from main memory. 2. It interprets9understands) the instruction to find what operation is to be performed. 3. It controls the execution of instruction. The control unit determines the sequence in which computer programs and instructions are executed
- 9. Arithmetic / Logic Unit ALU ALU is a part of CPU. Actual Execution of instructions takes place in this part. All Arithmetic and Logical operations are performed in ALU. It consists of two units ? Arithmetic Unit Performs arithmetic operations ? Logic Unit Performs logical operations
- 11. Logical Operations ? Evaluates conditions ? Makes comparisons ? Can compare ? Numbers ? Letters ? Special characters
- 12. ALU ? Many instructions carried out by the control unit involve simply moving data from one place to another. ? From memory to storage, from memory to the printer, and so on. ? When the control unit encounters an instruction that involves arithmetic or logic , however, it passes that instruction to the second component of the CPU, the ALU.
- 13. ALU ? The ALU performs these operations. ? ALU includes a group of registers--- high speed memory locations built directly into the CPU that are used to hold the data currently being processed. ? ALU will use the register to hold the data currently being used for calculation.
- 14. For example ? CU might load two numbers from memory into the registers in the ALU. ? Then it might tell the ALU divide the two numbers (an arithmetic operation) or to see whether the numbers are equal (a logical operation). ? The answer to this calculation will be stored in another register before being sent out of the CPU.
- 16. What is the Information Processing Cycle? ? These are the steps that are taken to convert raw facts, which is data, into information. It starts with data collection. ? The 4 basic operations of the information processing cycle are input, processing, output, storage and/or distribution. ? A computer is the machine that performs the cycle. 16
- 17. IP Cycle: 17
- 18. Machine cycles ? Each time the CPU executes an instruction, it takes a series of steps. ? The completed series of steps is called machine cycles. ? A machine cycle itself can be broken down into two smaller cycles- 1. Instruction cycle 2. Execution cycle Machine cycle - fetch? decode? execute? store
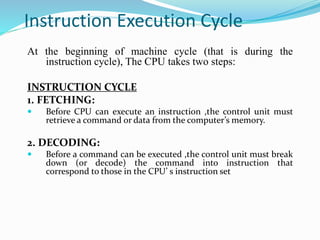
- 19. Instruction Execution Cycle ? The CPU continuously transfer data to and from memory ? Data transfer is done in units called instruction or words ? When computer is switched on, the CPU continuously goes through a process called Fetch-Decode-Execute-Store.
- 20. Example ? What happens when you load up a game from disk into your computer? The program is stored as data, for example on a disc. You have to read that data, and store it in the memory of your computer. When you have done that, you can treat it as a program, (i.e. as a set of instructions) and run (execute) it.
- 21. Instruction Execution Cycle At the beginning of machine cycle (that is during the instruction cycle), The CPU takes two steps: INSTRUCTION CYCLE 1. FETCHING: ? Before CPU can execute an instruction ,the control unit must retrieve a command or data from the computer¡¯s memory. 2. DECODING: ? Before a command can be executed ,the control unit must break down (or decode) the command into instruction that correspond to those in the CPU¡¯ s instruction set
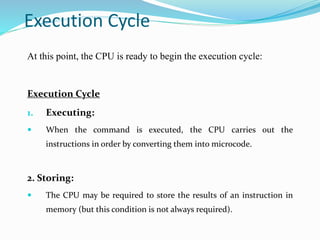
- 22. Execution Cycle At this point, the CPU is ready to begin the execution cycle: Execution Cycle 1. Executing: ? When the command is executed, the CPU carries out the instructions in order by converting them into microcode. 2. Storing: ? The CPU may be required to store the results of an instruction in memory (but this condition is not always required).
- 23. Multiplication of two numbers: Steps of Machine Cycle
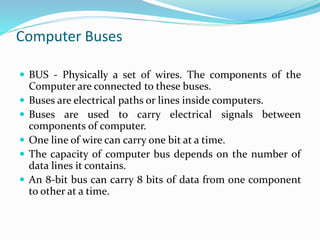
- 24. Computer Buses ? BUS - Physically a set of wires. The components of the Computer are connected to these buses. ? Buses are electrical paths or lines inside computers. ? Buses are used to carry electrical signals between components of computer. ? One line of wire can carry one bit at a time. ? The capacity of computer bus depends on the number of data lines it contains. ? An 8-bit bus can carry 8 bits of data from one component to other at a time.
- 25. Types of buses There are two types of buses ? System Buses ? Expansion Buses
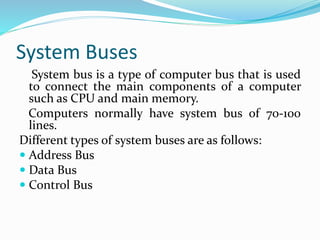
- 26. System Buses System bus is a type of computer bus that is used to connect the main components of a computer such as CPU and main memory. Computers normally have system bus of 70-100 lines. Different types of system buses are as follows: ? Address Bus ? Data Bus ? Control Bus
- 27. Data Bus ? The electrical path through which data is transferred between components of a computer. ? The data bus consists of 8,16,32 or 64 separate lines. ? The data bus lines are bi-directional 1. Read data from memory using these lines 2. Write data to memory locations using these lines
- 28. Basic block diagram of a typical computer system including common peripherals. The computer itself is shown within the gray block.
- 29. Address Bus ? Many components are connected to one another through buses. ? Each component is assigned a unique ID.This Id is called address of that component. ? Each I/O devices has a unique address. (monitor, mouse, CD-ROM) ? If a component wants to communicate with another component, it uses address of that component. ? The address bus is uni-directional. ? It can carry information only in one direction. ? It carries address of memory location from microprocessor to the main memory
- 30. Control Bus ? Collection of individual control signals. ? Whether the CPU will read or write data. ? CPU is accessing memory or an I/O device. ? Memory or I/O is ready to transfer data. ? For example, If CPU wants to read data from main memory ,it uses control bus to send the memory read command to the main memory of the computer.
- 31. Expansion Buses Expansion bus is a type of computer that is used to connect CPU with peripheral devices such as mouse, Keyboard , Scanners, Printers etc








