Cystic fibrosis[1]
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive genetic disease that causes a dysfunctional epithelial cell membrane protein called CFTR. A mutation in the CFTR gene, most commonly a deletion of phenylalanine at position 508, results in a misfolded CFTR protein that cannot function properly. This leads to dehydrated mucus in the lungs and pancreas due to impaired chloride and sodium transport. In the lungs, the thick mucus promotes chronic infections and inflammation, eventually causing damage through scarring and fibrosis if not properly treated. Cystic fibrosis diagnosis involves genetic testing, sweat tests, and evaluation of symptoms affecting the lungs, pancreas, and other organs. Treatment focuses on airway clearance and lifelong antibiotics, enzymes,






![Cystic fibrosis[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cysticfibrosis1-101115143757-phpapp01/85/Cystic-fibrosis-1-8-320.jpg)











Recommended


























































More Related Content
Viewers also liked (6)












Similar to Cystic fibrosis[1] (20)




































Recently uploaded (20)


































Cystic fibrosis[1]
- 3. What is Cystic Fibrosis? CF also known as mucovisidosis is an autosomal recessive genetic disease that primarily causes dysfunction of the epithelial cells of the respiratory and digestive systems.
- 4. How does mutated DNA cause disease? A protein's function is determined by its SHAPE!
- 6. HOMOZYGOUS DELTA F 508 = Misfolded Protein
- 9. Where is CFTR found? http://www.epgonline.org/cystic-fibrosis/understanding/understanding-cystic-fibrosis-definition.cfm
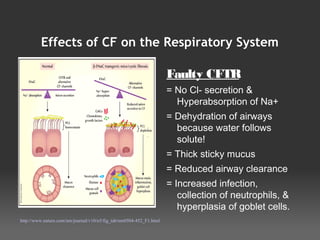
- 10. Effects of CF on the Respiratory System Faulty CFTR = No Cl- secretion & Hyperabsorption of Na+ = Dehydration of airways because water follows solute! = Thick sticky mucus = Reduced airway clearance = Increased infection, collection of neutrophils, & hyperplasia of goblet cells. http://www.nature.com/nm/journal/v10/n5/fig_tab/nm0504-452_F1.html
- 11. Inflammation! Excessive Neutrophils – Neutrophil Elastase = Damage http://www.stanford.edu/group/cfcenter/BasicsOfCF.html
- 12. Complications of CF Lung Disease Bronchietasis – dilation of bronchial tree = reduced airflow and airway clearance Chronic Pneumonia Remodling, scarring / fibrosis of lung tissue Hemoptysis – coughing blood Pulmonary Hypertension Cor Pulmonale
- 14. Effects of CF on other systems Digestive – impaired absorption of fat and fat soluble vitamins due to lack of enzymes from the pancreas – failure to thrive Sinuses – nasal polyps, frequent sinus infections Pancreas – Blocked ducts lead to fibrosis of tissue destroying beta cells – development of CFRD – diabetes mellitus Reproductive – decreased fertility in females and infertility in males.
- 15. Diagnosis • Sweat Test* “Gold Standard” • Prenatal – genetic screening and testing • Newborn Screening – IRT • Genetic Testing • Nasal Potential Difference
- 16. Typical Treatment Regimen * Physical airway clearance *Pulmozyme *Hypertonic Saline *Antiinflammatory / Steroids *Oral Antibiotics *Enzyme Replacements *Nutritional Supplements
- 17. 2 week course IV Antibiotics / Hospitalization - “Tune up”
- 18. Feeding Tube
- 20. Clinical Research -Trying to correct the basic defect - CFTR - Gene Therapy - Potentiators / Activators -Using alternate chloride channels
Editor's Notes
- #2: - Background: my daughter Cassidy has CF. - She was diagnosed prenatally - She has been hospitalized 2 times in 2 years and is scheduled to go in after Thanksgiving - I hope to teach you enough about CF today that if you ever encounter someone with CF, either personally or in your career, that you realize the incredible amount of work it takes for them to stay alive.
- #3: -Cassidy has CF -Kaylee is a carrier – she could have a child with CF if she has a partner that is also a carrier.
- #4: - Recessive genetic disease - Carrier mother / father unaffected by mutation – Darien and I – 1 in 20 white people - Possible heterozygote advantage – cholera -1 in 4 chance of having child with CF - Cassidy - 2 in 4 chance of having unaffected carrier child - Kaylee - 1 in 4 chance of having child with no genetic mutations
- #5: -How exactly does a mutation in the DNA cause a disease in the lungs? - The answer is in what is called the Central Dogma of Biology - DNA is transcribed into mRNA - RNA is translated into protein - A protein's function is determined by it's SHAPE!
- #7: - There are over 1000 mutations of genotype that result in CF. There are some differences in phenotype associated with different mutations, but I will talk mostly about the most common mutation that causes “classic CF”. - The most common mutation is DeltaF508 – accounts for more than half of all people with CF including Cassidy. She has this present on both alleles. Most people with CF have at least one allele with this mutation, but is sometimes combined with a different mutation on the other allele. In either case – CF results, just some genotypes cause more severe disease. -When deltaf508 is present on both alleles, there is a 3 base pair deletion that results in a missing amino acid in the CFTR protein. -The missing amino acid causes the CFTR protein to misfold – resulting in a defective protein because, as I said, a protein's function is determined by its SHAPE!
- #8: -Different Defective CFTR genotypes result in different Classes of mutations. -Some get to the cell surface, but are in reduced numbers. -Some get to the cell surface but do not open properly -Some get to the cell surface but open and close to fast -Some do not get made at all -Detla F 508 results in CFTR protein that becomes arrested in the golgi apparatus – never making it to the cell surface
- #9: The CFTR protein is an epithelial cell chloride channel and an important regulator of other epithelial chloride and sodium channels. The defective protein leads to abnormal salt transport onto epithelial surfaces, leading to dehydration of secretions.
- #10: -CFTR is found in the sinuses, lungs, sweat glands, liver, pancreas, intestines and reproductive tracts. - CF was originally called CF of the pancreas because infants with CF did not survive their first year due to the lack of pancreatic enzymes which resulted in starvation. Upon autopsy, the docs noted that the pancreas was full of scarring and cysts, hence the name cystic fibrosis. At this point they did not even have a chance to develop the lung disease that we all associate with CF. -Though it really is a multiorgan complex disease, we focus primarily on pulmonary health since respiratory failure is the primary cause of death for people with CF.
- #12: - Cilia are impaired by viscous fluid - This allows mucus and bacteria to adhere to airway epithelium - A proliferation of neutrophils trying to clear the the bacteria / mucus – damage lungs with Neutrophil Elastase - NE causes direct damage to lung proteins especially elastin. - Also stimulates lung cells to produce IL8 – calling in more neutrophils and increasing mucus production– leading to more inflammation and damage - see the cycle? -NE cleaves IgG antibodies and complement proteins that normally clear pathogens Resulting in colonization of the airways with pathogens – bacterial particularly Pa and Bc– also exacerbates the situation by causing more inflammation. =Decline in pulmonary function
- #13: Pulmonary hypertension begins when tiny arteries and capillaries in the lungs become narrowed, blocked or destroyed. This makes it harder for blood to flow through the lungs, which raises pressure within the arteries in the lungs. The heart's lower right chamber must work harder to pump blood through the lungs, eventually causing your heart muscle to weaken and eventually fail completely (cor pulmonale).





