Data Modelling..pptx
- 2. Introduction ’üĄ Process of creating a data model for an information system by applying formal data modeling techniques. ’üĄ Process used to define and analyze data requirements needed to support the business processes. ’üĄ Therefore, the process of data modeling involves professional data modelers working closely with business stakeholders, as well as potential users of the information system.
- 3. What is Data Model ’üĄ Data Model is a collection of conceptual tools for describing data, data relationships, data semantics and consistency constraint. ’üĄ A data model is a conceptual representation of data structures required for data base and is very powerful in expressing and communicating the business requirements ’üĄ A data model visually represents the nature of data, business rules governing the data, and how it will be organized in the database
- 4. ’üĄ A data model provides a way to describe the design of a database at the physical, logical and view levels. ’üĄ There are three different types of data models produced while progressing from requirements to the actual database to be used for the information system
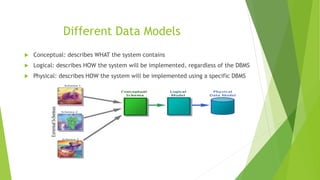
- 5. ’üĄ Conceptual: describes WHAT the system contains ’üĄ Logical: describes HOW the system will be implemented, regardless of the DBMS ’üĄ Physical: describes HOW the system will be implemented using a specific DBMS Different Data Models
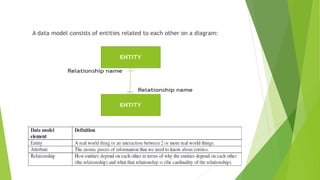
- 6. A data model consists of entities related to each other on a diagram:
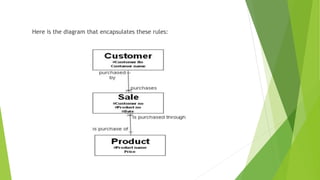
- 7. Example: Given that ŌĆ” ’üĄ ŌĆ£CustomerŌĆØ is an entity. ’üĄ ŌĆ£ProductŌĆØ is an entity. ’üĄ For a ŌĆ£CustomerŌĆØ we need to know their ŌĆ£customer numberŌĆØ attribute and ŌĆ£nameŌĆØ attribute. ’üĄ For a ŌĆ£ProductŌĆØ we need to know the ŌĆ£product nameŌĆØ attribute and ŌĆ£priceŌĆØ attribute. ’üĄ ŌĆ£SaleŌĆØ is an entity that is used to record the interaction of ŌĆ£CustomerŌĆØ and ŌĆ£ProductŌĆØ.
- 8. Here is the diagram that encapsulates these rules:
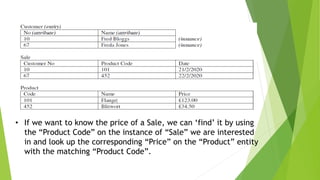
- 9. Notes ’üĄ By convention, entities are named in the singular. ’üĄ The attributes of ŌĆ£CustomerŌĆØ are ŌĆ£Customer NoŌĆØ (which is the unique identifier or primary key of the ŌĆ£CustomerŌĆØ entity and is shown by the # symbol) and ŌĆ£Customer NameŌĆØ. ’üĄ ŌĆ£SaleŌĆØ has a composite primary key made up of the primary key of ŌĆ£CustomerŌĆØ, the primary key of ŌĆ£ProductŌĆØ and the date of the sale. ’üĄ Think of entities as tables, think of attributes as columns on the table and think of instances as rows on that table:
- 10. ŌĆó If we want to know the price of a Sale, we can ŌĆśfindŌĆÖ it by using the ŌĆ£Product CodeŌĆØ on the instance of ŌĆ£SaleŌĆØ we are interested in and look up the corresponding ŌĆ£PriceŌĆØ on the ŌĆ£ProductŌĆØ entity with the matching ŌĆ£Product CodeŌĆØ.
- 11. Types of Data Models ’üĄ Entity-Relationship (E-R) Models ’üĄ UML (unified modeling language)
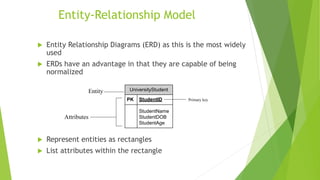
- 12. Entity-Relationship Model ’üĄ Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERD) as this is the most widely used ’üĄ ERDs have an advantage in that they are capable of being normalized ’üĄ Represent entities as rectangles ’üĄ List attributes within the rectangle UniversityStudent PK StudentID StudentName StudentDOB StudentAge Entity Attributes Primary key
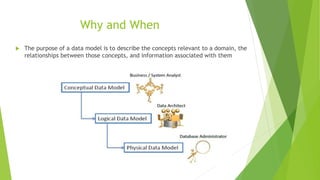
- 13. Why and When ’üĄ The purpose of a data model is to describe the concepts relevant to a domain, the relationships between those concepts, and information associated with them
- 14. Significance of Model data ’üĄ Used to model data in a standard, consistent, predictable manner in order to manage it as a resource. ’üĄ To have a clear picture of the base data that your business needs ’üĄ To identify missing and redundant base data
- 15. Concluding ’üĄ To Establish a baseline for communication across functional boundaries within your organization ’üĄ Provides a basis for defining business rules ’üĄ Makes it cheaper, easier, and faster to upgrade your IT solutions