Decision support systems
Download as PPTX, PDF7 likes2,960 views
Decision support systems (DSS) are computer applications that analyze business data and present it in a way to help users make business decisions more easily. A DSS has three main components - a database or knowledge base, a model representing the decision context and user criteria, and a user interface. It allows managers to perform what-if analysis, sensitivity analysis, goal-seeking analysis, and optimization analysis to evaluate different decisions and scenarios. The goal of a DSS is to improve decision making by providing a better understanding of the business and allowing more alternatives to be considered more quickly and effectively.
1 of 23
Downloaded 86 times






















Recommended
Management information system



Management information systemKalpana B
╠¤
Management Information System (MIS) is a system that provides the right information to managers at the right time to help with decision making. It combines human and computer resources to collect, store, analyze and distribute important data and reports across an organization. The goal of MIS is to enhance communication, support strategic goals, improve efficiency and make management more effective with timely, accurate information.Decision Support System - Management Information System



Decision Support System - Management Information SystemNijaz N
╠¤
Refers to class of system which supports in the process of decision making and does not always give a decision itself.
Decision Support Systems supply computerized support for the decision making process.System Development Life Cycle & Implementation of MIS



System Development Life Cycle & Implementation of MISGeorge V James
╠¤
The document discusses the system development life cycle (SDLC) and implementation of management information systems (MIS). It describes the six main stages of the SDLC as investigation, analysis, design, development, implementation, and maintenance. For MIS implementation, it lists four methods: installing a new system, cutting over from an old system, cutting over in segments, or operating systems in parallel before cutting over. It then provides 14 steps for MIS implementation, including planning, acquiring hardware/software, testing, training users, and providing ongoing system maintenance.Decision support system-MIS



Decision support system-MISYoga Raja
╠¤
The document discusses decision support systems (DSS), including their architecture, characteristics, capabilities, classification, and the steps in designing a DSS. It describes the key components of a DSS architecture as including data management, user interface, model management, and knowledge management. It also classifies DSS as data-driven, model-driven, knowledge-driven, document-driven, communication-driven, and inter/intra-organizational. The design process involves planning, analysis, design, and implementation phases.Management information system



Management information systemPraveenkumar Aivalli
╠¤
This document discusses Management Information Systems (MIS). It defines MIS as a system that converts data from internal and external sources into meaningful information to help managers make timely decisions. The document outlines the importance of MIS in providing the right information to the right people at the right time. It also discusses the components, characteristics, establishment and performance evaluation of effective MIS.Decision Support System



Decision Support SystemAwais Alam
╠¤
A Decision Support System (DSS) is a computer-based information system that supports business or organizational decision-making. It can help managers at different levels of an organization make decisions by providing tools to access and analyze data. A DSS combines data, documents, knowledge, and models to help identify and solve problems. It has evolved over time from focusing on data and models to also include knowledge and documents. A DSS is made up of a database, models, and a user interface. It aims to support semi-structured and unstructured decision-making.Unit 3 Management Information System



Unit 3 Management Information SystemAbhishek Iyer
╠¤
This powerpoint covers all the topics included in 3rd unit of B.com(Hons) Syllabus which is useful for colleges affiliated to GGSIPUForecasting - Principles of Management



Forecasting - Principles of ManagementWe Learn - A Continuous Learning Forum from Welingkar's Distance Learning Program.
╠¤
This document discusses forecasting, which involves analyzing past and present events to estimate future outcomes. It defines forecasting as systematically predicting future events based on analysis. Several forecasting techniques are described, including time series analysis, regression analysis, surveys, and expert opinions. The key benefits of forecasting are facilitating planning and coordination. However, forecasts may be limited by faulty assumptions, lack of reliable data, inability to predict uncertain future events, and high costs. Forecasting provides the basis for planning future actions and decisions, but planning involves setting specific goals, strategies, and timelines to a greater extent.Security and Control Issues in Information System



Security and Control Issues in Information SystemDaryl Conson
╠¤
This document discusses information systems security. It defines an information system as a set of components for collecting, storing, processing, and delivering information and knowledge. Information systems play an important role in modern society and infrastructures. To protect against potential losses, it is crucial for information systems to have security measures from the outset. Information system security aims to establish policies and controls to guarantee the authenticity, confidentiality, availability, and integrity of information assets. It discusses the importance of controls to provide security and quality assurance for information systems.Information system



Information systemрж░рзЗржжржУрзЯрж╛ржи рж╣рзГржжрзЯ
╠¤
This document provides an overview of information systems concepts. It discusses the basic components of an information system, including hardware, software, data, personnel and procedures. It also outlines different types of information systems like personal, workgroup, organizational, interorganizational and global systems. Transaction processing systems, management information systems, decision support systems and executive support systems are described as the major types of systems used in organizations. The document also covers information systems users and how users connect to technology through networks, the internet and electronic commerce. Finally, it discusses benefits of information systems like better information, improved service and competitive advantage.Executive Support System (ESS)



Executive Support System (ESS)Arun Savera
╠¤
Executive support systems (ESS) are software tools that allow executive managers to access summarized reports from across an organization to help with strategic decision making. An ESS aggregates both internal and external data, enables online analysis like trend and scenario analysis, and has a user interface to quickly retrieve relevant information. The system's hardware, software, communication networks, and user interface work together to provide executives with timely summarized data and the ability to drill down into more detail if needed. ESS tools are intended to support strategic decision making by streamlining access to organizational data.MIS concepts



MIS conceptssajappy
╠¤
This presentation is detailed PPT on Management Information System. Infact it is a combination of various presentations that are downloaded from the internet.
The presentation is self explanatory and is very helpful for Management and Commerce studentsSecurity & ethical challenges



Security & ethical challengesLouie Medinaceli
╠¤
The document discusses various security and ethical challenges related to management information systems. It covers topics such as hacking, cyber theft, unauthorized computer use at work, software piracy, computer viruses, privacy issues, health issues related to computer use, and theories of corporate social responsibility. It also provides details on security measures like encryption, firewalls, denial of service defenses, email monitoring, virus defenses, security codes, backup files, biometric security, fault tolerant systems, and disaster recovery.Mis & Decision Making



Mis & Decision MakingArun Mishra
╠¤
Decision making involves selecting a course of action from various options. Business decision making models include SWOT analysis, buyer decision processes, and cost-benefit analysis. The decision making process involves phases like intelligence gathering, problem definition, alternative identification, choice, and implementation. Management information systems, decision support systems, executive support systems, and group decision support systems can provide information and tools to support decision making. Intelligent techniques like artificial intelligence and expert systems are also used for decision support.Management Information System



Management Information SystemZeinul Haleem
╠¤
The document discusses management information systems (MIS) and related concepts. It defines MIS as a computerized business processing system that generates information for decision-making throughout an organization. The MIS collects data from various sources, processes it, and communicates relevant information to managers. This enables timely and effective decision-making for planning, directing, and controlling organizational activities. The document also discusses the roles and types of information used at different levels of an organization, including strategic, tactical, operational, and knowledge-based information. Executive information systems and decision support systems are described as tools that analyze data to support executive and managerial decision-making.Multiple approaches to structure of MIS



Multiple approaches to structure of MISMohammed Jasir PV
╠¤
Multiple approaches to the structure of MIS
Operational elements (physical components, process, and outputs for users),
Activity subsystems
Functional subsystems
Decision supportInformation Management unit 1 introduction



Information Management unit 1 introductionGanesha Pandian
╠¤
This document provides an overview of information management concepts including data, information, intelligence, and knowledge. It discusses how data is collected and transformed into information and intelligence. Information technology and its impact on organizations is also examined. Different types of information systems are introduced, including transaction processing systems, management information systems, decision support systems, and executive information systems. The document outlines the evolution of information systems from early data processing to modern enterprise resource planning systems. Key characteristics, components, advantages, and applications of information technology are also summarized.Mis introduction



Mis introductionhimanshu5star
╠¤
Management information systems (MIS) provide information to support decision making and operations in organizations. An MIS combines human and computer resources to collect, store, retrieve, communicate, and use data. It serves various functions like strategic planning, management control, operational control, and transaction processing. An MIS benefits organizations by facilitating planning, minimizing information overload, encouraging decentralization, bringing coordination, and making control easier.DSS and decision support system and its types



DSS and decision support system and its typesHammalAkhtar
╠¤
The document discusses a group project on decision support systems (DSS). It defines DSS as a computer-based system that supports business or organizational decision-making. It describes the key components and characteristics of DSS, including that they facilitate decision-making, allow interaction, and are intended for repeated use to improve decision accuracy and quality. The document also outlines several applications of DSS and lists advantages like time savings and competitive benefits, as well as potential disadvantages like information overload.Quantitative Techniques: Introduction



Quantitative Techniques: IntroductionDayanand Huded
╠¤
Quantitative management╠¤is not a modern business idea but a management theory that came into existence after World War II. Business owners initially used it in Japan to pick up the pieces of the devastation caused by the war and started taking baby steps toward reconstruction. It focuses on the following elements of business operations:
Customer satisfaction
Business value enhancement
Empowerment of employees
Creating synergy among teams
Creating quality products
Preventing defects
Being responsible for quality
Focusing on continuous improvement
Leveraging statistical measurement
Remaining focused on the processes
Commitment to refinement and learning
Quantitative techniques in management╠¤as a collection of mathematical and statistical tools. TheyтАЩre known by different names, such as management science or operation research. In modern business methods, statistical techniques are also viewed as a part of╠¤quantitative management╠¤techniques.
When appropriately used,╠¤quantitative approaches to management╠¤can become a powerful means of analysis, leading to effective decision-making. These techniques help resolve complex business problems by leveraging systematic and scientific methods.2 approaches to system development



2 approaches to system developmentcymark09
╠¤
The document discusses several system development approaches and methodologies including the waterfall model, prototype model, spiral model, extreme programming, unified process, agile modeling, rapid application development, and joint application development. It provides an overview of each approach/methodology including typical phases, activities, advantages, and disadvantages.MIS Support to Management



MIS Support to ManagementMaria Stella Solon
╠¤
MIS uses computer technology to process and analyze large amounts of data, quickly search and retrieve information, and communicate information to users in a timely manner. It supports management functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating, and controlling. MIS helps ensure the appropriate data is collected, processed, and distributed to where it is needed. It provides information to support strategic planning, management control, operational control, and transaction processing.Decision support system



Decision support systemreddragn619
╠¤
A decision support system (DSS) is an interactive, flexible computer system that helps managers access and manipulate data to make decisions. A DSS provides information to decision makers at different levels - strategic, tactical, and operational. Decisions can be structured, unstructured, or semi-structured. Key characteristics of a DSS include interactivity, flexibility, supporting discovery, and accessibility. Components include a database, models, and a user interface. DSS can be model-driven, communication-driven, data-driven, document-driven, or knowledge-driven. Benefits include improved efficiency, faster problem solving, better communication, and a competitive advantage.Management information system ( MIS )



Management information system ( MIS )QualitativeIn
╠¤
Management Information System (MIS) is a planned system of collecting, storing, and disseminating data in the form of information needed to carry out the functions of management. A Management Information System is an information system that evaluates, analyzes, and processes an organization's data to produce meaningful and useful information based on which the management can take right decisions to ensure future growth of the organization.Security & control in management information system



Security & control in management information systemOnline
╠¤
The document discusses security concepts in information systems including prevention of unauthorized access, modification, and deletion of information. It outlines unintentional threats like human error and intentional threats like criminal attacks. The goals of information security are prevention, detection, and response. Risks to applications and data include computer crime, hacking, cyber-theft, unauthorized work use, software piracy, and viruses/worms. Risks to hardware include natural disasters, blackouts, and vandalism. Major defense strategies are encryption, authentication, firewalls, email monitoring, antivirus software, backup files, security monitors, and biometric controls. The document also discusses disaster recovery, business recovery plans, and general controls to minimize errors and disasters.System concept in MIS



System concept in MISMohammed Jasir PV
╠¤
This document discusses systems concepts in management information systems. It defines a system as an orderly grouping of interdependent components working together according to a plan to achieve a specific objective. A system has inputs, processes, outputs, and feedback/control mechanisms. It also has boundaries and interacts with its environment. The document describes different types of systems including closed/open, deterministic/probabilistic, human/machine, adaptive/non-adaptive, simple/complex, and abstract/concrete systems. It provides examples of systems like an educational institution and a manufacturing plant.Mis chapter 2 infomation, management and decision making



Mis chapter 2 infomation, management and decision makingAjay Khot
╠¤
The document discusses three models of decision making: the classical model, administrative model, and Herbert Simon's model. It also covers attributes of information and their relevance to decision making. The chapter focuses on models of decision making, including individual and organizational models. It discusses the intelligence, design, and choice phases of Herbert Simon's model of decision making.MA- UNIT -1.pptx for ipu bba sem 5, complete pdf



MA- UNIT -1.pptx for ipu bba sem 5, complete pdfzm2pfgpcdt
╠¤
Marketing analytics is the practice of using data to evaluate the effectiveness and success of marketing activities. It allows marketers to gather deeper consumer insights, optimize marketing objectives, and get a better return on investment. Popular analytics models include media mix models, multi-touch attribution, and unified marketing measurement. Organizations use marketing analytics data to make decisions regarding ad spend, product updates, branding, and more. Common predictive analytics techniques used in marketing include decision trees, regression, and neural networks.Dss



DssDr. Vardhan choubey
╠¤
Herbert Simon proposed a 4-phase model of problem solving: intelligence, design, choice, and review. Decision making involves either programmed or non-programmed decisions. Decision support systems (DSS) provide interactive support for semi-structured and unstructured decisions through queries, models, and reports without making the final decision. A DSS collects data, allows for group work, and can incorporate artificial intelligence. Common DSS models include behavioral, management science, and operations research models. Group decision support systems (GDSS) facilitate group problem solving through individual workstations, facilitation software, and aggregation of ideas, comments, and votes.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Security and Control Issues in Information System



Security and Control Issues in Information SystemDaryl Conson
╠¤
This document discusses information systems security. It defines an information system as a set of components for collecting, storing, processing, and delivering information and knowledge. Information systems play an important role in modern society and infrastructures. To protect against potential losses, it is crucial for information systems to have security measures from the outset. Information system security aims to establish policies and controls to guarantee the authenticity, confidentiality, availability, and integrity of information assets. It discusses the importance of controls to provide security and quality assurance for information systems.Information system



Information systemрж░рзЗржжржУрзЯрж╛ржи рж╣рзГржжрзЯ
╠¤
This document provides an overview of information systems concepts. It discusses the basic components of an information system, including hardware, software, data, personnel and procedures. It also outlines different types of information systems like personal, workgroup, organizational, interorganizational and global systems. Transaction processing systems, management information systems, decision support systems and executive support systems are described as the major types of systems used in organizations. The document also covers information systems users and how users connect to technology through networks, the internet and electronic commerce. Finally, it discusses benefits of information systems like better information, improved service and competitive advantage.Executive Support System (ESS)



Executive Support System (ESS)Arun Savera
╠¤
Executive support systems (ESS) are software tools that allow executive managers to access summarized reports from across an organization to help with strategic decision making. An ESS aggregates both internal and external data, enables online analysis like trend and scenario analysis, and has a user interface to quickly retrieve relevant information. The system's hardware, software, communication networks, and user interface work together to provide executives with timely summarized data and the ability to drill down into more detail if needed. ESS tools are intended to support strategic decision making by streamlining access to organizational data.MIS concepts



MIS conceptssajappy
╠¤
This presentation is detailed PPT on Management Information System. Infact it is a combination of various presentations that are downloaded from the internet.
The presentation is self explanatory and is very helpful for Management and Commerce studentsSecurity & ethical challenges



Security & ethical challengesLouie Medinaceli
╠¤
The document discusses various security and ethical challenges related to management information systems. It covers topics such as hacking, cyber theft, unauthorized computer use at work, software piracy, computer viruses, privacy issues, health issues related to computer use, and theories of corporate social responsibility. It also provides details on security measures like encryption, firewalls, denial of service defenses, email monitoring, virus defenses, security codes, backup files, biometric security, fault tolerant systems, and disaster recovery.Mis & Decision Making



Mis & Decision MakingArun Mishra
╠¤
Decision making involves selecting a course of action from various options. Business decision making models include SWOT analysis, buyer decision processes, and cost-benefit analysis. The decision making process involves phases like intelligence gathering, problem definition, alternative identification, choice, and implementation. Management information systems, decision support systems, executive support systems, and group decision support systems can provide information and tools to support decision making. Intelligent techniques like artificial intelligence and expert systems are also used for decision support.Management Information System



Management Information SystemZeinul Haleem
╠¤
The document discusses management information systems (MIS) and related concepts. It defines MIS as a computerized business processing system that generates information for decision-making throughout an organization. The MIS collects data from various sources, processes it, and communicates relevant information to managers. This enables timely and effective decision-making for planning, directing, and controlling organizational activities. The document also discusses the roles and types of information used at different levels of an organization, including strategic, tactical, operational, and knowledge-based information. Executive information systems and decision support systems are described as tools that analyze data to support executive and managerial decision-making.Multiple approaches to structure of MIS



Multiple approaches to structure of MISMohammed Jasir PV
╠¤
Multiple approaches to the structure of MIS
Operational elements (physical components, process, and outputs for users),
Activity subsystems
Functional subsystems
Decision supportInformation Management unit 1 introduction



Information Management unit 1 introductionGanesha Pandian
╠¤
This document provides an overview of information management concepts including data, information, intelligence, and knowledge. It discusses how data is collected and transformed into information and intelligence. Information technology and its impact on organizations is also examined. Different types of information systems are introduced, including transaction processing systems, management information systems, decision support systems, and executive information systems. The document outlines the evolution of information systems from early data processing to modern enterprise resource planning systems. Key characteristics, components, advantages, and applications of information technology are also summarized.Mis introduction



Mis introductionhimanshu5star
╠¤
Management information systems (MIS) provide information to support decision making and operations in organizations. An MIS combines human and computer resources to collect, store, retrieve, communicate, and use data. It serves various functions like strategic planning, management control, operational control, and transaction processing. An MIS benefits organizations by facilitating planning, minimizing information overload, encouraging decentralization, bringing coordination, and making control easier.DSS and decision support system and its types



DSS and decision support system and its typesHammalAkhtar
╠¤
The document discusses a group project on decision support systems (DSS). It defines DSS as a computer-based system that supports business or organizational decision-making. It describes the key components and characteristics of DSS, including that they facilitate decision-making, allow interaction, and are intended for repeated use to improve decision accuracy and quality. The document also outlines several applications of DSS and lists advantages like time savings and competitive benefits, as well as potential disadvantages like information overload.Quantitative Techniques: Introduction



Quantitative Techniques: IntroductionDayanand Huded
╠¤
Quantitative management╠¤is not a modern business idea but a management theory that came into existence after World War II. Business owners initially used it in Japan to pick up the pieces of the devastation caused by the war and started taking baby steps toward reconstruction. It focuses on the following elements of business operations:
Customer satisfaction
Business value enhancement
Empowerment of employees
Creating synergy among teams
Creating quality products
Preventing defects
Being responsible for quality
Focusing on continuous improvement
Leveraging statistical measurement
Remaining focused on the processes
Commitment to refinement and learning
Quantitative techniques in management╠¤as a collection of mathematical and statistical tools. TheyтАЩre known by different names, such as management science or operation research. In modern business methods, statistical techniques are also viewed as a part of╠¤quantitative management╠¤techniques.
When appropriately used,╠¤quantitative approaches to management╠¤can become a powerful means of analysis, leading to effective decision-making. These techniques help resolve complex business problems by leveraging systematic and scientific methods.2 approaches to system development



2 approaches to system developmentcymark09
╠¤
The document discusses several system development approaches and methodologies including the waterfall model, prototype model, spiral model, extreme programming, unified process, agile modeling, rapid application development, and joint application development. It provides an overview of each approach/methodology including typical phases, activities, advantages, and disadvantages.MIS Support to Management



MIS Support to ManagementMaria Stella Solon
╠¤
MIS uses computer technology to process and analyze large amounts of data, quickly search and retrieve information, and communicate information to users in a timely manner. It supports management functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating, and controlling. MIS helps ensure the appropriate data is collected, processed, and distributed to where it is needed. It provides information to support strategic planning, management control, operational control, and transaction processing.Decision support system



Decision support systemreddragn619
╠¤
A decision support system (DSS) is an interactive, flexible computer system that helps managers access and manipulate data to make decisions. A DSS provides information to decision makers at different levels - strategic, tactical, and operational. Decisions can be structured, unstructured, or semi-structured. Key characteristics of a DSS include interactivity, flexibility, supporting discovery, and accessibility. Components include a database, models, and a user interface. DSS can be model-driven, communication-driven, data-driven, document-driven, or knowledge-driven. Benefits include improved efficiency, faster problem solving, better communication, and a competitive advantage.Management information system ( MIS )



Management information system ( MIS )QualitativeIn
╠¤
Management Information System (MIS) is a planned system of collecting, storing, and disseminating data in the form of information needed to carry out the functions of management. A Management Information System is an information system that evaluates, analyzes, and processes an organization's data to produce meaningful and useful information based on which the management can take right decisions to ensure future growth of the organization.Security & control in management information system



Security & control in management information systemOnline
╠¤
The document discusses security concepts in information systems including prevention of unauthorized access, modification, and deletion of information. It outlines unintentional threats like human error and intentional threats like criminal attacks. The goals of information security are prevention, detection, and response. Risks to applications and data include computer crime, hacking, cyber-theft, unauthorized work use, software piracy, and viruses/worms. Risks to hardware include natural disasters, blackouts, and vandalism. Major defense strategies are encryption, authentication, firewalls, email monitoring, antivirus software, backup files, security monitors, and biometric controls. The document also discusses disaster recovery, business recovery plans, and general controls to minimize errors and disasters.System concept in MIS



System concept in MISMohammed Jasir PV
╠¤
This document discusses systems concepts in management information systems. It defines a system as an orderly grouping of interdependent components working together according to a plan to achieve a specific objective. A system has inputs, processes, outputs, and feedback/control mechanisms. It also has boundaries and interacts with its environment. The document describes different types of systems including closed/open, deterministic/probabilistic, human/machine, adaptive/non-adaptive, simple/complex, and abstract/concrete systems. It provides examples of systems like an educational institution and a manufacturing plant.Mis chapter 2 infomation, management and decision making



Mis chapter 2 infomation, management and decision makingAjay Khot
╠¤
The document discusses three models of decision making: the classical model, administrative model, and Herbert Simon's model. It also covers attributes of information and their relevance to decision making. The chapter focuses on models of decision making, including individual and organizational models. It discusses the intelligence, design, and choice phases of Herbert Simon's model of decision making.Similar to Decision support systems (20)
MA- UNIT -1.pptx for ipu bba sem 5, complete pdf



MA- UNIT -1.pptx for ipu bba sem 5, complete pdfzm2pfgpcdt
╠¤
Marketing analytics is the practice of using data to evaluate the effectiveness and success of marketing activities. It allows marketers to gather deeper consumer insights, optimize marketing objectives, and get a better return on investment. Popular analytics models include media mix models, multi-touch attribution, and unified marketing measurement. Organizations use marketing analytics data to make decisions regarding ad spend, product updates, branding, and more. Common predictive analytics techniques used in marketing include decision trees, regression, and neural networks.Dss



DssDr. Vardhan choubey
╠¤
Herbert Simon proposed a 4-phase model of problem solving: intelligence, design, choice, and review. Decision making involves either programmed or non-programmed decisions. Decision support systems (DSS) provide interactive support for semi-structured and unstructured decisions through queries, models, and reports without making the final decision. A DSS collects data, allows for group work, and can incorporate artificial intelligence. Common DSS models include behavioral, management science, and operations research models. Group decision support systems (GDSS) facilitate group problem solving through individual workstations, facilitation software, and aggregation of ideas, comments, and votes.Decision making systems



Decision making systemsShwetabh Jaiswal
╠¤
The document discusses decision making systems and decision support systems. It defines decision making as a process of choosing between alternatives to achieve goals. Decision making involves individuals, alternatives, data analysis, risk, and conflicting objectives. The document then describes models of decision making, phases of decision making including intelligence, design, choice, and implementation. It defines decision support systems as interactive computer systems that support decision making for semi-structured problems. The document outlines components of decision support systems including data management, model management, user interface, and knowledge management subsystems.Decision Making Process and algorithms to take decisions



Decision Making Process and algorithms to take decisionsSnehalBhatt7
╠¤
Operational research techniques are to analyze the problem of decision making such as good site for plant , whether to open a new storehouse, etc. It also helps in assortment of cost-effective means of transportation, jobs sequencing, production scheduling, replacement of old machinery, etc. Decision making is the process of making choices by identifying a decision, gathering information, and assessing alternative resolutions. Using a step-by-step decision-making process can help you make more deliberate, thoughtful decisions by organizing relevant information and defining alternatives.Data mining



Data miningGILM Project
╠¤
What is data mining? The process of analyzing data to discover hidden patterns and relationships that can help you manage and improve your business.
Check out: www.eleaderstochange.com
Follow #eleaders2change
Decision making systems



Decision making systemsShwetabh Jaiswal
╠¤
1. The document discusses decision making systems and decision support systems. It defines decision making as choosing between alternatives to achieve goals and discusses the characteristics and phases of decision making.
2. It describes the components and configurations of decision support systems, including data management, model management, user interface, and knowledge-based subsystems.
3. Decision support systems are intended to support managers in semi-structured and unstructured decision making situations by providing data, models, and expertise without replacing human judgment. They can be classified based on their communication, data, document, knowledge, model or hybrid focus.Information and decision support system



Information and decision support systemNaveed Zahoor
╠¤
Good decision making and problem solving skills are key to developing effective information and decision support systems. These systems include management information systems (MIS), decision support systems (DSS), group support systems (GSS), and executive support systems (ESS). MIS provides the right information to managers at the right time to support decision making. DSS are used for unstructured problems and can optimize, satisfice, or use heuristics to find solutions. GSS and ESS apply the DSS approach specifically to group and executive decision making.Mis notes unit 5 -BBA/BCA



Mis notes unit 5 -BBA/BCANikita Sharma
╠¤
This document provides an overview of decision support systems (DSS), including what they are, how they differ from management information systems, their components and characteristics, types of decisions they support, and examples of DSS tools and models. A DSS is an interactive IT system that helps managers make semi-structured or unstructured decisions. It uses databases, models, and software to analyze large amounts of internal and external data and support decision-making at all management levels. DSS can incorporate various tools like spreadsheets, solvers, rules, and more to help evaluate alternatives, identify problems, and recommend or identify optimal solutions.PEGA Decision strategy manager (DSM)



PEGA Decision strategy manager (DSM)bhaskarvittal
╠¤
Introduction to Decision Strategy Manager, the tool used to create Decision Strategies.
Introduction to the Decisioning Components, the building blocks of Decision Strategies
Data Analytics .pptx



Data Analytics .pptxnagarajan740445
╠¤
The document discusses how various types of analytics, including descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics can be applied across different business functions and industries. Descriptive analytics are used to understand past performance, predictive analytics analyze past data to predict future outcomes, and prescriptive analytics use optimization techniques to recommend decisions. Examples are provided of how different industries like retail use different analytic techniques to improve operations and decision making.Decision Support System /Chapter one.pptx



Decision Support System /Chapter one.pptxKelemAlebachew
╠¤
Introduction To decision support system and BIForecasting.pptx



Forecasting.pptxSairaali51
╠¤
The document discusses various aspects of forecasting, including:
- Forecasting involves making predictions about future values of variables like demand. Accurate forecasts are important for planning operations, supply chains, staffing needs etc.
- Forecasts can be short-term (hours to months) or long-term (years). Both the expected level and accuracy of forecasts are important.
- Qualitative and quantitative methods can be used. Qualitative methods rely more on subjective judgment while quantitative methods analyze objective historical data.
- Specific qualitative methods discussed include Delphi, surveys, consensus among executives. Quantitative time series models examine trends, seasonality and irregular patterns in past data.Decision Support System.pptx



Decision Support System.pptxKondwaniKumwenda3
╠¤
The basic components of a Decision Support System (DSS) include hardware, software, data, and users. DSS are designed to support decision-making by providing access to relevant information and analytical tools. There are several types of DSS, including model-driven systems that use mathematical models, data-driven systems that provide tools for users to perform their own analysis, and knowledge-driven systems that provide access to stored knowledge bases. DSS can improve organizational performance by enhancing decision-making and leading to more efficient operations.BI Knowledge Sharing Session 1



BI Knowledge Sharing Session 1Kelvin Chan
╠¤
Here are the 3 types of slowly changing dimensions:
Type 1 SCD - Overwrite current attribute value with new value. Only current value is stored.
Type 2 SCD - Add a new row with a new surrogate key and mark old row as inactive and new row as active. Both old and new values are stored.
Type 3 SCD - Add new columns to capture attribute changes rather than new rows. New columns capture attribute history.Foundations of analytics.ppt



Foundations of analytics.pptSurekha98
╠¤
To introduce students to key concepts in business analytics and familiarize the students with major areas of application of business analytics .segmentda



segmentdaSteven Cosgrove, Ph.D.
╠¤
This document discusses DataActiva's approach to customer segmentation. It describes different levels and types of segmentation including mass, segmented, individual, and targeted segmentation. It also covers segmentation description techniques like a priori, cluster-based, and hybrid models. The document provides an overview of cluster analysis techniques including hierarchical, non-hierarchical, k-means, and Ward's methods. It discusses best practices for variable selection, standardization, response style effects, number of clusters, and validity checks in segmentation analysis. Finally, it notes how segmentation can be activated through customer relationship management processes and linked to other data sources.Decisionmaking 



Decisionmaking Jugal Gudlani
╠¤
The document discusses decision making and various decision making processes. It defines decision as a choice between two or more alternatives. Decision making involves setting objectives, perceiving problems, analyzing problems, developing alternative solutions, screening alternatives, selecting the best alternative, implementing decisions, and providing feedback and control. It then describes the steps in the rational decision making process and various decision making techniques used, including operational research, the Delphi method, expert panels, decision trees, and responsibility for decision making within organizations.Recently uploaded (20)
One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀гs



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀гsCeline George
╠¤
In this slide, weтАЩll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠¤
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatAzure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠¤
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatBISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
╠¤
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHHow to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠¤
In this slide, weтАЩll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
╠¤
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
тЬЕ Soft Tissue Therapy тАУ The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
тЬЕ Sports Taping Techniques тАУ Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
тЬЕ Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia тАУ A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠¤
Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatRRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)



RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)SONU HEETSON
╠¤
RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ PDF Free Download. Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Mechanic Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Important Questions.ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat
╠¤
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatHelping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar ║▌║▌▀гs



Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar ║▌║▌▀гsPooky Knightsmith
╠¤
For more information about my speaking and training work, visit: https://www.pookyknightsmith.com/speaking/Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
╠¤
NAPD Annual Symposium
тАЬEquity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?тАЭEffective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
╠¤
In this slide weтАЩll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠¤
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatYear 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠¤
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxDecision support systems
- 2. WHAT IS DECISION MAKING? тАв A selection process, concerned with selecting the best type of alternative тАв The thought process of selecting a logical choice from the available options тАв The process by which managers respond to opportunities and threats тАв It leads to commitment. The commitment depends upon the nature of the decision whether short term or long term.
- 3. MANAGERS AND DECISION MAKING тАв It is very difficult for managers to make good decisions without valid, timely and relevant information: яВз Number of alternatives to be considered is increasing яВз Many decisions are made under time pressure
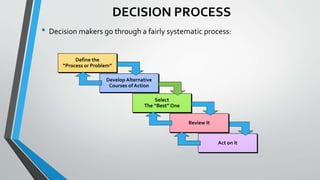
- 4. DECISION PROCESS тАв Decision makers go through a fairly systematic process: Act on it Review It Define the тАЬProcess or ProblemтАЭ Develop Alternative Courses of Action Select The тАЬBestтАЭ One
- 5. THE NATURE OF DECISIONS тАв Information systems can support decision-making levels. тАв These include the three levels of management activity. яВз Strategic management яВз Tactical management яВз Operational management
- 6. INFORMATION REQUIREMENTS BY MANAGEMENT LEVEL Strategic Management Tactical Management Operational Management
- 7. TYPES OF DECISIONS тАв The decision fall into one of the following categories: яВз Structured Decisions яВз Unstructured яВз Semi-Structured
- 8. STRUCTURED DECISIONS тАв Structured decisions are repetitive and routine problems for which standard solutions exist тАв Ex: finding an appropriate inventory level, finding an optimal investment strategy
- 9. UNSTRUCTURED DECISIONS тАв Unstructured decisions are non-routine and complex. тАв We cannot specify some procedures to make a decision тАв Ex: expanding the business, moving operations to foreign countries. тАв IS must provide a wide range of information products to support these types of decisions at all levels of the organization
- 10. SEMI-STRUCTURED DECISIONS тАв Semi-structured decisions fall between structured and unstructured decisions тАв It requires a combination of standard procedures and individual judgment. тАв Ex: annual evaluation of employees, trading bonds, setting marketing budgets for consumer products.
- 11. WHAT IS DSS? тАв A decision support system is a computer application that analyzes business data and presents it so that users can make business decisions more easily. тАв It is an informational application. тАв Typical information that a decision support application might gather and present would be: яВз Comparative sales figures between one week and the next яВз Projected revenue figures based on new product sales assumptions яВз The consequences of different decision alternatives, given past experience in a context that is described
- 12. DSS ARCHITECTURE тАв Three fundamental components of a DSS architecture are: тАв the database (or knowledge base), тАв the model (i.e., the decision context and user criteria), and тАв the user interface The users themselves are also important components of the architecture.
- 13. TYPES OF MODELS тАв DSS software is a collection of software tools that are used for data analysis or a collection of mathematical and analytical models. тАв There can be 3 different types of modeling software for DSSs: яВз Statistical models яВз Optimization models яВз Forecasting models
- 14. STATISTICAL MODELING тАв Statistical modeling software can be used to help establish relationships such as relating product sales to differences in age, income or other factors between communities. тАв Ex: SPSS.
- 15. OPTIMIZATION MODELS тАв Optimization models often using Linear Programming (LP) determine the proper mix of products within a given market to maximize profit.
- 16. FORECASTING MODELS тАв The user of this type of model might supply a range of historical data to project future conditions and sales that might result from those conditions. тАв Companies often use this software to predict the action of competitors.
- 17. CAPABILITIES OF DSS тАв Using a DSS involves 4 basic types of analytical modeling activities: яВз What-if analysis яВз Sensitivity analysis яВз Goal-seeking analysis яВз Optimization analysis
- 18. WHAT-IF ANALYSIS тАв What-If analysis is used to determine what some of the possible changes could be on a theoretical solution. тАв Observing how changes to selected variables affect the other variables. тАв E.g. What if we cut advertising by 10%?What would happen to sales?
- 19. SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS тАв Sensitivity analysis is the study of how different variables effect one and other, when change occurs. тАв Observing how repeated changes to a single variables affect other variables. тАв E.g: Let's cut advertising by $1000 repeatedly so we can see its relationship to sales.
- 20. GOAL-SEEKING ANALYSIS тАв Compiles all of the given data and determines what inputs are required to reach specific goals. тАв Making repeated changes to selected variables until a chosen variable reaches to a target value. тАв E.g. Let's try increase in advertising until sales reach to target
- 21. OPTIMIZATION ANALYSIS тАв To find the optimum value for one or more target variables, given certain constraints. тАв Finding an optimum value for selected variables, given certain constraints. тАв E.g. What's the best amount of advertising to have, our budget and choice of media?
- 22. CHARACTERISTICS OF DSS тАв Improved decision making through better understanding of the businesses тАв An increased number of decision alternatives examined тАв The ability to implement ad hoc analysis тАв Faster response тАв Improved communication тАв More effective teamwork тАв Better control тАв Time and costs savings
- 23. THANKYOU









