Dialects
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
1 like•2,631 views
This document discusses dialects and their development. It defines dialects as mutually intelligible forms of a language that differ systematically. Dialects are not inferior versions of a language, as a language consists of many dialects. Regional dialects develop differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar based on geographic location. Accents reveal information about a speaker's background, while social dialects are influenced by factors like age, gender, and social situation. Standard languages aim to prevent differentiation, but many dialects like Cajun English have been banned despite being legitimate forms of communication.
1 of 20
Download to read offline



















Recommended
Lingua franca



Lingua francaMd. Rana
Ã˝
The document discusses the concept of a lingua franca, which is a language used for communication between groups that do not share a native language. It provides examples such as Arabic serving as a lingua franca in the Islamic world historically and English currently serving as a global lingua franca. When languages are used as lingua francas, they often undergo simplification, reduction, and interference from other languages, which can result in the development of a pidgin language over time if it becomes stabilized and acquires native speakers. Pidgins are then subject to creolization if they are learned as a first language by children and expand in structural complexity and social uses.Dialect 



Dialect BP Arts,SMA Sci,KKC Com.College Chalisgaon Dist.Jalgaon,Maharashtra State, India
Ã˝
The document discusses dialects and provides examples. It defines a dialect as a variety of a language that is associated with a particular region or social group. Dialects are distinguished by differences in pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary. Examples given include British English and American English, which are dialects of English that are mutually intelligible. The document also discusses dialects of Hindi and Marathi that vary regionally within those language areas. It provides lists of dialects for both Hindi and Marathi with descriptions of where each dialect is spoken.Diglossia



DiglossiaYoushaib Alam
Ã˝
I am a lecturer in English at Khawaja Fared Govt. College Rahim Yar Khan. Here is my humble effort to discuss Diglossia. Sapir Whorf hypothesis



Sapir Whorf hypothesisAhmet Ateş
Ã˝
The Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis proposes that the structure of a language affects its speakers' worldview or cognition. It includes two principles: 1) Linguistic determinism, that language determines thought, and 2) Linguistic relativity, that different languages encourage different ways of understanding the world. Debate exists around whether language truly determines thought or just influences it. While some studies support the hypothesis, others have found universal patterns of thought across languages. The hypothesis remains an area of interest in linguistics but is seen as too extreme in its strongest claims.Language death completed presentation



Language death completed presentationzeetariq
Ã˝
Language death occurs when a language is no longer spoken by anyone. Languages do not naturally die out but are instead "killed" when their speakers abandon the language due to pressures to assimilate and adopt dominant languages that have greater social and economic opportunities. There are several types of language death including sudden, radical, gradual, and bottom-to-top death. Major causes of language death include globalization, urbanization, modern education, and the pressure of dominant languages that are given more prestige and power. Efforts can be made to revive languages through programs that promote acquisition by adults, create socially integrated speaker populations, develop literacy in the language, and encourage use of the language in various social domains over time.Language deth, language shift, marker, micro/macro sociolinguistics



Language deth, language shift, marker, micro/macro sociolinguisticsIqramushtaq1142
Ã˝
This document discusses key topics in sociolinguistics including language shift, language death, markers, and micro/macrosociolinguistics. It provides definitions and examples of language shift, where a community gradually abandons its original language for another, often occurring over 3-4 generations through a stage of bilingualism. Language death is the end point of shift when a language has no remaining native speakers. Markers are linguistic variables that correlate with social groups and speech styles. Microsociolinguistics examines language in relation to society at a small scale while macrosociolinguistics looks at larger societal behaviors and impacts on language.Pidgin and creole 



Pidgin and creole ayeshahussain47
Ã˝
This document discusses pidgins and creoles. It defines pidgins as mixtures of languages formed for communication between communities, while creoles develop when a pidgin becomes the native language of a community. Pidgins have simple structures without native speakers, whereas creoles have more complex structures and are the first language of a group. Theories on the origins of pidgins and creoles include baby talk theory, polygenesis, relexification, and monogenesis. Creoles are influenced by but distinct from their lexifier languages in terms of vocabulary, grammar, and social functions.Code switching &; code mixing



Code switching &; code mixingYoushaib Alam
Ã˝
The document defines various linguistic terms related to code switching including code, monolingual, bilingual, and multilingual. It then discusses types of code switching such as inter-sentential, intra-sentential, and tag code switching. Finally, it outlines some common reasons for code switching such as to fulfill a need, show solidarity, reflect social status, based on topic, to express affection, and to persuade an audience.Chapter 4 Languages in Contact: Multilingual Societies and Multilingual Disco...



Chapter 4 Languages in Contact: Multilingual Societies and Multilingual Disco...أحمد يوسف
Ã˝
- Multilingualism is common across the world, with speakers often using multiple languages in daily life depending on the context. This document discusses concepts like diglossia, where distinct "high" and "low" varieties of the same language are used under different conditions.
- Code-switching refers to switching between languages or language varieties within conversations. It can be obligatory, as in diglossia, or optional. Accommodation through convergence and divergence also influences code-switching.
- Multilingual identities are fluid and culturally constructed, as seen in examples of Dominican Americans in the US asserting their own identity through language use.Brief Introduction to Psycholinguistics



Brief Introduction to PsycholinguisticsIqra Abadullah
Ã˝
This document discusses psycholinguistics and language acquisition. It defines psycholinguistics as the study of the relationship between the human mind and language. Key aspects covered include language production, which involves conceptualization, formulation, articulation and self-monitoring. Language acquisition examines first language acquisition in children and theories like nature vs nurture. Second language acquisition looks at factors like age and motivation and compares it to first language acquisition.Style Register and Dialect



Style Register and DialectSidra Shahid
Ã˝
Language varieties refer to different forms of a language influenced by social factors such as situation, occupation, age, geography, education, gender, social status, and ethnicity. There are several types of language varieties including dialects, registers, pidgins, and creoles. A dialect is a variety of a language used in a specific region or social class. Registers are varieties used in different situations based on formality. A pidgin is a simplified mixed language with reduced vocabulary and grammar used for communication between speakers of different languages, while a creole develops when a pidgin becomes the primary language of a group and acquires more complex grammar.Accent & dialect



Accent & dialectAdit Ishraque Rezwan
Ã˝
An accent describes aspects of pronunciation that identify where a speaker is from regionally or socially, while a dialect describes features of grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. Specifically, an accent is how a word is pronounced, whereas a dialect can include different words altogether or variations in grammar. For example, the Noakhali language dialect of Bangladesh includes distinctive words and grammar compared to other dialects.Language maintenance and Shift.



Language maintenance and Shift.Awan Kamal
Ã˝
This document discusses language maintenance and shift. It defines language maintenance as the continuing use of a minority language in the face of a dominant language, while language shift refers to one language displacing another in a community's linguistic repertoire. The document then examines factors that can contribute to language shift, including the prestige of the dominant language, economic pressures, and institutional domains like schools. It analyzes language shift patterns among migrant minorities, non-migrant minorities, and migrant majorities. Finally, it discusses factors that accelerate language shift and ways that minority languages can be maintained, such as through community ties, contact with homelands, institutional support, and positive language attitudes.Pidgins and creoles



Pidgins and creolesHassa Alfafa
Ã˝
This document provides definitions and information about pidgins and creoles. It discusses how pidgins are contact languages with no native speakers, while creoles develop from pidgins and become the first language of a new generation. It describes the typical characteristics of pidgin and creole languages, including reduced phonology, morphology, and syntax compared to related standard languages. The document also discusses theories about the origins and development of pidgin and creole languages.Social factors governing language variation



Social factors governing language variationZaraAnsari6
Ã˝
Social factors like class, ethnicity, gender, age, and education influence language variation. Labov's study found class affected pronunciation patterns, with upper classes using standard variants and lower classes using non-standard variants. Ethnic groups develop language varieties through substrates and adstrates. Gender influences language choice, with men using more direct and non-standard forms while women use more standard forms. Younger generations adopt new slang that differs from older generations. Education level also impacts language, with more educated speakers using standard dialects. These social dimensions are core to understanding sociolinguistic variation.Language Planning



Language PlanningAyesha Mir
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of language planning. It defines language planning as efforts to influence and modify a language's structure and function. It discusses key aspects of language planning including its goals, processes, types (status and corpus planning), ideologies, and issues. The summary focuses on language planning's aim to alter a language's role and how it is implemented through selection, codification, elaboration, and acceptance of a standardized variety.Culture and language



Culture and languageSairish khokhar
Ã˝
Culture is defined as the set of learned behaviors, beliefs, attitudes, values and ideas that characterize a society. Language is the primary means of preserving and transmitting culture between generations. There is a close relationship between language and culture - they influence each other. Language reflects the physical and social environment of its culture through vocabulary related to areas like climate, occupations, and kinship terms. Different cultures categorize family relationships differently, and this is reflected in their language.Mutual intelligibility



Mutual intelligibilityMuslimah Alg
Ã˝
Mutual intelligibility refers to the extent that speakers of related languages or dialects can understand each other without special training. It is sometimes used as a criterion to distinguish languages from dialects, with dialects being mutually intelligible and languages not. However, this characterization is problematic, as some languages like Scandinavian tongues are mutually intelligible while some dialects of languages like German are not. Degree of mutual intelligibility and non-linguistic political/historical factors can also influence whether related varieties are considered languages or dialects. Mutual intelligibility is not an absolute criterion.language death



language deathTahirRafique10
Ã˝
Group 04 presented on the topic of endangered languages. The document defined language death as occurring when a language loses its last native speaker. It noted that over 7,000 languages are currently spoken but many are endangered and being replaced by more dominant languages. The types of language death were described as gradual, bottom-to-top, top-to-bottom, radical, and linguicide. Factors that can help preserve endangered languages were also discussed, such as strong ethnic identity, school programs in the language, and community involvement.Allophone and phoneme. persentation



Allophone and phoneme. persentationDessy Restu Restu
Ã˝
Phonemes are the basic sound units of a language. Each phoneme comprises a set of allophones, which are the phonetic variants of that phoneme. Allophones are predictable realizations of a phoneme that depend on the linguistic environment, whereas phonemes are non-predictable and significant for meaning. Different languages can organize the same sounds differently - for example, English has aspirated and unaspirated /p/ phonemes, while Mandarin treats these as different phonemes. The distribution and organization of phonemes versus their allophonic variants distinguishes languages.Pidgins creoles - sociolinguistics 



Pidgins creoles - sociolinguistics Amal Mustafa
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of pidgins and creoles. It defines pidgins as contact languages that arise between distinct linguistic groups for communication, featuring reduced grammar and vocabulary. Creoles develop from pidgins when a new generation acquires the contact language as its native tongue, expanding its structure. The document outlines the processes of pidginization and creolization, and notes that creoles may decreolize over time to resemble the standard language. It provides examples of pidgins and creoles, and a model of their life cycle from jargon to creole and possible convergence with the standard form.Language maintenance 



Language maintenance Mah Noor
Ã˝
The document discusses factors that influence language maintenance or loss. It summarizes Giles, Bourhis and Taylor's model which identifies three main factors: 1) Status - including economic, social, and language status, 2) Demographic factors like population size and distribution, and 3) Institutional support through representation of the minority language in various institutions. Additional linguistic factors like standardization and cultural factors like emphasis on ethnic identity and community also influence whether a language is maintained or lost.Regional variation



Regional variationDemoriza
Ã˝
This document discusses various linguistic concepts related to regional variation and dialects, including:
1) Regional dialects arise from variations in language associated with different places, and are an easy way to observe language variety.
2) Over time and distance, dialects can diverge and become unintelligible to one another, as seen with the evolution of Latin into the distinct languages of French, Spanish, and Italian.
3) Dialect atlases aim to map the geographical boundaries of linguistic features using lines called isoglosses, showing where different pronunciations, words, or syntactic features are used on either side.
4) Bundles of intersecting isoglosses often delineate clear dialect boundaries between regions.Dialects and Accents



Dialects and AccentsA Faiz
Ã˝
Dialect refers to a variety of a language spoken by a group of people that is characterized by systematic differences in phonological, lexical, and grammatical features from other varieties of the same language. An accent is a variation in pronunciation and is a subset of dialect. The document discusses factors like geographical location, social class, and education that can influence dialect variation. It provides examples of prominent dialects in American English like New England and Southern accents, as well as British English dialects like Received Pronunciation and Cockney. Dialects and accents vary in terms of phonology, morphology, syntax, and semantics.Language change



Language changeDr. Mohsin Khan
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of language change from both a historical and sociological perspective. It discusses the different types and levels of language change, including sound changes, lexical changes, semantic changes, and syntactic changes. Several theories of language change are presented, such as functional theory, random fluctuation theory, substratum theory, and the S-curve theory. The document also examines the routes language change can take, such as through language learning, contact, social differentiation, and natural usage processes. Finally, it outlines the major levels of language change - phonological, syntactic, semantic, and lexical - providing examples of sound changes like assimilation, dissimilation, and the Great Vowel Shift.Language shift



Language shiftBas Bas
Ã˝
This document discusses language maintenance and shift. It explains that language shift occurs when a minority language is displaced by the language of the dominant group over time, especially in contexts of migration or military occupation. Factors that can lead to language shift include economic and social pressures associated with the dominant language, as well as demographic factors like urbanization and intermarriage. Language shift happens more slowly when minority languages are highly valued as symbols of ethnic identity. The document also discusses language death, which occurs when no one speaks a language anymore, and language loss or erosion over time. It provides strategies for maintaining minority languages, such as institutional support through education.Language, culture and thought



Language, culture and thoughtzhian fadhil
Ã˝
This document discusses the relationship between language, culture, and thought. It makes three key points:
1. Culture can be defined as the knowledge that is learned from other people, either through direct instruction or observation. Since language is learned from others, it is closely connected to culture.
2. Concepts and meanings that underlie language are based on a person's general knowledge and concepts. Understanding language relies on shared knowledge between speakers and listeners.
3. Some concepts and categories may be organized differently in different languages due to cultural differences. While core meanings of words are often shared across languages and cultures, there can be variation, especially in more peripheral concepts. Prototypes provide a framework for analyzing these differencesIntroduction to Soicolinguistics



Introduction to SoicolinguisticsFarjana Ela
Ã˝
The document discusses sociolinguistics and language variation. It defines sociolinguistics as the systematic study of language in society, focusing on how individuals and groups use language in social contexts. There are three main perspectives in sociolinguistics: geographic, examining regional dialects; anthropological, studying the relationship between language, culture and thought; and sociological, analyzing the link between social relations and language varieties. Speech communities are groups that share the same or similar language varieties. Varieties include dialects, sociolects, and idiolects, which differ by region, social class, gender, age, and ethnicity at the lexical, phonological and syntactic levels. Pidgins are simplified mixed languages for basic communication betweenLANGUAGE.ppt dialect vs language reporting



LANGUAGE.ppt dialect vs language reportingtrishamaeilaganlomio
Ã˝
This document discusses language, dialects, and registers. It begins by defining the difference between a language and dialect, noting that a dialect is a regional variety of a larger language. It then discusses two types of dialects: geographical/regional dialects, which vary based on geographic location; and social dialects, also called sociolects, which vary based to social factors like occupation, age, or class. Finally, it defines language registers as levels of formality, outlining five main registers from frozen to intimate and factors like audience and purpose that influence register choice.Phonetics: Varieties of English Language



Phonetics: Varieties of English LanguageYamileth Urriola
Ã˝
Language can be defined as a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used by a social group to communicate and express ideas, identities, and emotions. There are many variations within and across languages, including dialects, registers, sociolects, and ethnolects that vary by region, social group, ethnicity, gender, and even individual. Some key types of linguistic variations include dialects, which can differ in vocabulary, grammar and pronunciation depending on geography; sociolects, which vary based on social factors like education and class; and idiolects, an individual's unique way of speaking. Languages exist on spectrums and can be classified based on various social and historical contexts.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Chapter 4 Languages in Contact: Multilingual Societies and Multilingual Disco...



Chapter 4 Languages in Contact: Multilingual Societies and Multilingual Disco...أحمد يوسف
Ã˝
- Multilingualism is common across the world, with speakers often using multiple languages in daily life depending on the context. This document discusses concepts like diglossia, where distinct "high" and "low" varieties of the same language are used under different conditions.
- Code-switching refers to switching between languages or language varieties within conversations. It can be obligatory, as in diglossia, or optional. Accommodation through convergence and divergence also influences code-switching.
- Multilingual identities are fluid and culturally constructed, as seen in examples of Dominican Americans in the US asserting their own identity through language use.Brief Introduction to Psycholinguistics



Brief Introduction to PsycholinguisticsIqra Abadullah
Ã˝
This document discusses psycholinguistics and language acquisition. It defines psycholinguistics as the study of the relationship between the human mind and language. Key aspects covered include language production, which involves conceptualization, formulation, articulation and self-monitoring. Language acquisition examines first language acquisition in children and theories like nature vs nurture. Second language acquisition looks at factors like age and motivation and compares it to first language acquisition.Style Register and Dialect



Style Register and DialectSidra Shahid
Ã˝
Language varieties refer to different forms of a language influenced by social factors such as situation, occupation, age, geography, education, gender, social status, and ethnicity. There are several types of language varieties including dialects, registers, pidgins, and creoles. A dialect is a variety of a language used in a specific region or social class. Registers are varieties used in different situations based on formality. A pidgin is a simplified mixed language with reduced vocabulary and grammar used for communication between speakers of different languages, while a creole develops when a pidgin becomes the primary language of a group and acquires more complex grammar.Accent & dialect



Accent & dialectAdit Ishraque Rezwan
Ã˝
An accent describes aspects of pronunciation that identify where a speaker is from regionally or socially, while a dialect describes features of grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. Specifically, an accent is how a word is pronounced, whereas a dialect can include different words altogether or variations in grammar. For example, the Noakhali language dialect of Bangladesh includes distinctive words and grammar compared to other dialects.Language maintenance and Shift.



Language maintenance and Shift.Awan Kamal
Ã˝
This document discusses language maintenance and shift. It defines language maintenance as the continuing use of a minority language in the face of a dominant language, while language shift refers to one language displacing another in a community's linguistic repertoire. The document then examines factors that can contribute to language shift, including the prestige of the dominant language, economic pressures, and institutional domains like schools. It analyzes language shift patterns among migrant minorities, non-migrant minorities, and migrant majorities. Finally, it discusses factors that accelerate language shift and ways that minority languages can be maintained, such as through community ties, contact with homelands, institutional support, and positive language attitudes.Pidgins and creoles



Pidgins and creolesHassa Alfafa
Ã˝
This document provides definitions and information about pidgins and creoles. It discusses how pidgins are contact languages with no native speakers, while creoles develop from pidgins and become the first language of a new generation. It describes the typical characteristics of pidgin and creole languages, including reduced phonology, morphology, and syntax compared to related standard languages. The document also discusses theories about the origins and development of pidgin and creole languages.Social factors governing language variation



Social factors governing language variationZaraAnsari6
Ã˝
Social factors like class, ethnicity, gender, age, and education influence language variation. Labov's study found class affected pronunciation patterns, with upper classes using standard variants and lower classes using non-standard variants. Ethnic groups develop language varieties through substrates and adstrates. Gender influences language choice, with men using more direct and non-standard forms while women use more standard forms. Younger generations adopt new slang that differs from older generations. Education level also impacts language, with more educated speakers using standard dialects. These social dimensions are core to understanding sociolinguistic variation.Language Planning



Language PlanningAyesha Mir
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of language planning. It defines language planning as efforts to influence and modify a language's structure and function. It discusses key aspects of language planning including its goals, processes, types (status and corpus planning), ideologies, and issues. The summary focuses on language planning's aim to alter a language's role and how it is implemented through selection, codification, elaboration, and acceptance of a standardized variety.Culture and language



Culture and languageSairish khokhar
Ã˝
Culture is defined as the set of learned behaviors, beliefs, attitudes, values and ideas that characterize a society. Language is the primary means of preserving and transmitting culture between generations. There is a close relationship between language and culture - they influence each other. Language reflects the physical and social environment of its culture through vocabulary related to areas like climate, occupations, and kinship terms. Different cultures categorize family relationships differently, and this is reflected in their language.Mutual intelligibility



Mutual intelligibilityMuslimah Alg
Ã˝
Mutual intelligibility refers to the extent that speakers of related languages or dialects can understand each other without special training. It is sometimes used as a criterion to distinguish languages from dialects, with dialects being mutually intelligible and languages not. However, this characterization is problematic, as some languages like Scandinavian tongues are mutually intelligible while some dialects of languages like German are not. Degree of mutual intelligibility and non-linguistic political/historical factors can also influence whether related varieties are considered languages or dialects. Mutual intelligibility is not an absolute criterion.language death



language deathTahirRafique10
Ã˝
Group 04 presented on the topic of endangered languages. The document defined language death as occurring when a language loses its last native speaker. It noted that over 7,000 languages are currently spoken but many are endangered and being replaced by more dominant languages. The types of language death were described as gradual, bottom-to-top, top-to-bottom, radical, and linguicide. Factors that can help preserve endangered languages were also discussed, such as strong ethnic identity, school programs in the language, and community involvement.Allophone and phoneme. persentation



Allophone and phoneme. persentationDessy Restu Restu
Ã˝
Phonemes are the basic sound units of a language. Each phoneme comprises a set of allophones, which are the phonetic variants of that phoneme. Allophones are predictable realizations of a phoneme that depend on the linguistic environment, whereas phonemes are non-predictable and significant for meaning. Different languages can organize the same sounds differently - for example, English has aspirated and unaspirated /p/ phonemes, while Mandarin treats these as different phonemes. The distribution and organization of phonemes versus their allophonic variants distinguishes languages.Pidgins creoles - sociolinguistics 



Pidgins creoles - sociolinguistics Amal Mustafa
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of pidgins and creoles. It defines pidgins as contact languages that arise between distinct linguistic groups for communication, featuring reduced grammar and vocabulary. Creoles develop from pidgins when a new generation acquires the contact language as its native tongue, expanding its structure. The document outlines the processes of pidginization and creolization, and notes that creoles may decreolize over time to resemble the standard language. It provides examples of pidgins and creoles, and a model of their life cycle from jargon to creole and possible convergence with the standard form.Language maintenance 



Language maintenance Mah Noor
Ã˝
The document discusses factors that influence language maintenance or loss. It summarizes Giles, Bourhis and Taylor's model which identifies three main factors: 1) Status - including economic, social, and language status, 2) Demographic factors like population size and distribution, and 3) Institutional support through representation of the minority language in various institutions. Additional linguistic factors like standardization and cultural factors like emphasis on ethnic identity and community also influence whether a language is maintained or lost.Regional variation



Regional variationDemoriza
Ã˝
This document discusses various linguistic concepts related to regional variation and dialects, including:
1) Regional dialects arise from variations in language associated with different places, and are an easy way to observe language variety.
2) Over time and distance, dialects can diverge and become unintelligible to one another, as seen with the evolution of Latin into the distinct languages of French, Spanish, and Italian.
3) Dialect atlases aim to map the geographical boundaries of linguistic features using lines called isoglosses, showing where different pronunciations, words, or syntactic features are used on either side.
4) Bundles of intersecting isoglosses often delineate clear dialect boundaries between regions.Dialects and Accents



Dialects and AccentsA Faiz
Ã˝
Dialect refers to a variety of a language spoken by a group of people that is characterized by systematic differences in phonological, lexical, and grammatical features from other varieties of the same language. An accent is a variation in pronunciation and is a subset of dialect. The document discusses factors like geographical location, social class, and education that can influence dialect variation. It provides examples of prominent dialects in American English like New England and Southern accents, as well as British English dialects like Received Pronunciation and Cockney. Dialects and accents vary in terms of phonology, morphology, syntax, and semantics.Language change



Language changeDr. Mohsin Khan
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of language change from both a historical and sociological perspective. It discusses the different types and levels of language change, including sound changes, lexical changes, semantic changes, and syntactic changes. Several theories of language change are presented, such as functional theory, random fluctuation theory, substratum theory, and the S-curve theory. The document also examines the routes language change can take, such as through language learning, contact, social differentiation, and natural usage processes. Finally, it outlines the major levels of language change - phonological, syntactic, semantic, and lexical - providing examples of sound changes like assimilation, dissimilation, and the Great Vowel Shift.Language shift



Language shiftBas Bas
Ã˝
This document discusses language maintenance and shift. It explains that language shift occurs when a minority language is displaced by the language of the dominant group over time, especially in contexts of migration or military occupation. Factors that can lead to language shift include economic and social pressures associated with the dominant language, as well as demographic factors like urbanization and intermarriage. Language shift happens more slowly when minority languages are highly valued as symbols of ethnic identity. The document also discusses language death, which occurs when no one speaks a language anymore, and language loss or erosion over time. It provides strategies for maintaining minority languages, such as institutional support through education.Language, culture and thought



Language, culture and thoughtzhian fadhil
Ã˝
This document discusses the relationship between language, culture, and thought. It makes three key points:
1. Culture can be defined as the knowledge that is learned from other people, either through direct instruction or observation. Since language is learned from others, it is closely connected to culture.
2. Concepts and meanings that underlie language are based on a person's general knowledge and concepts. Understanding language relies on shared knowledge between speakers and listeners.
3. Some concepts and categories may be organized differently in different languages due to cultural differences. While core meanings of words are often shared across languages and cultures, there can be variation, especially in more peripheral concepts. Prototypes provide a framework for analyzing these differencesIntroduction to Soicolinguistics



Introduction to SoicolinguisticsFarjana Ela
Ã˝
The document discusses sociolinguistics and language variation. It defines sociolinguistics as the systematic study of language in society, focusing on how individuals and groups use language in social contexts. There are three main perspectives in sociolinguistics: geographic, examining regional dialects; anthropological, studying the relationship between language, culture and thought; and sociological, analyzing the link between social relations and language varieties. Speech communities are groups that share the same or similar language varieties. Varieties include dialects, sociolects, and idiolects, which differ by region, social class, gender, age, and ethnicity at the lexical, phonological and syntactic levels. Pidgins are simplified mixed languages for basic communication betweenSimilar to Dialects (20)
LANGUAGE.ppt dialect vs language reporting



LANGUAGE.ppt dialect vs language reportingtrishamaeilaganlomio
Ã˝
This document discusses language, dialects, and registers. It begins by defining the difference between a language and dialect, noting that a dialect is a regional variety of a larger language. It then discusses two types of dialects: geographical/regional dialects, which vary based on geographic location; and social dialects, also called sociolects, which vary based to social factors like occupation, age, or class. Finally, it defines language registers as levels of formality, outlining five main registers from frozen to intimate and factors like audience and purpose that influence register choice.Phonetics: Varieties of English Language



Phonetics: Varieties of English LanguageYamileth Urriola
Ã˝
Language can be defined as a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used by a social group to communicate and express ideas, identities, and emotions. There are many variations within and across languages, including dialects, registers, sociolects, and ethnolects that vary by region, social group, ethnicity, gender, and even individual. Some key types of linguistic variations include dialects, which can differ in vocabulary, grammar and pronunciation depending on geography; sociolects, which vary based on social factors like education and class; and idiolects, an individual's unique way of speaking. Languages exist on spectrums and can be classified based on various social and historical contexts.Language Variation



Language VariationDr. Cupid Lucid
Ã˝
This document discusses various types of language variation including dialects, sociolects, idiolects, registers, pidgins, and creoles. It notes that dialects are varieties of a language used by a particular group that share non-linguistic characteristics. Pidgins develop for communication between groups that don't share a common language, while creoles emerge when a pidgin becomes a community's native language.Language Variation



Language VariationDr. Cupid Lucid
Ã˝
This document discusses various types of language variation including dialects, sociolects, idiolects, registers, pidgins, and creoles. It notes that dialects are varieties of a language used by a specific group that share non-linguistic characteristics. Pidgins develop for communication between groups that don't share a common language, while creoles emerge when a pidgin becomes a community's native language.Language Varieties and Registers (MIDTERM).pptx



Language Varieties and Registers (MIDTERM).pptxeliopascual
Ã˝
Here are the answers to the drill questions:
1. a
2. d
3. a
4. c
5. a
6. a
7. a
8. a
9. b
10. bAndrews Ch. 8 - Dialect



Andrews Ch. 8 - DialectNC State University
Ã˝
PPT used to facilitate discussion about dialect and teaching literature for ECI 430, Class 12, Fall 2012.6. Aftermath of language variation.pptx



6. Aftermath of language variation.pptxMemonMemon4
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of language varieties that emerge from natural variation in language, including dialects, registers, pidgins, creoles, jargon, and more. It provides definitions and examples of each. Key varieties discussed are:
- Dialects emerge from regional, social, or ethnic differences in vocabulary, grammar and pronunciation. Examples include Southern American English.
- Registers vary based on social context or formality, like casual conversation versus formal writing.
- Pidgins develop for communication between speakers of different languages but become more standardized over time.
- Creoles emerge when a pidgin becomes a community's native language over generations with its own grammar.
- JargonLEE 4 - GROUP - UNIT 19



LEE 4 - GROUP - UNIT 19AgostinaSanguinetti
Ã˝
This document summarizes key aspects of sociolinguistics and language variation discussed in George Yule's book "The Study of Language". It covers topics like social dialects, speech styles, prestige varieties, and features of vernacular languages. The document is presented as a slideshow with headings, bullet points, and images to define important terminology related to how social factors influence language use and the grammar of non-standard dialects.Lee 4 - Group 8 - Unit 19



Lee 4 - Group 8 - Unit 19FlorrFranco1
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of sociolinguistics and language variation. It discusses how social factors like education, occupation, age and ethnicity can influence language use. Key points include:
1) Social dialects exist between groups with different education levels and occupations, seen through differences in pronunciation and vocabulary.
2) Style shifting refers to adjusting one's speech style between formal and informal registers depending on social context.
3) Prestige dialects reflect higher social status, while covert prestige makes some working class varieties desirable.
4) African American English is a prominent vernacular variety in the US with distinctive phonological and grammatical features.WEEK 6-PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION Varieties and Registers of Language.pdf



WEEK 6-PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION Varieties and Registers of Language.pdfbalbalosaherbert
Ã˝
It is very important to engage communication.Language variartion and varities of language



Language variartion and varities of languageUmm-e-Rooman Yaqoob
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation and the different types of language varieties. It defines varieties as forms of language that differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, or grammar between regions, social classes, or functions. The key varieties discussed are standard language, dialects, registers, pidgins, creoles, classical languages, and lingua francas. Standard language is used widely for official purposes, while dialects vary regionally or among social groups. Registers differ based on social or occupational context. Pidgins emerge for communication between groups with no shared language, and creoles develop when pidgins are passed to children as a native language.Social variation in language 



Social variation in language AhedAlhariri
Ã˝
This document discusses social variation in language and key concepts in sociolinguistics. It covers social dialects defined by education and occupation. It also discusses speech styles that vary based on formality, as well as speech accommodation theories of convergence and divergence. Registers are varieties used for different purposes, and examples of jargon, slang, and taboo terms are provided. The document also summarizes African American English as a vernacular continuum and describes some typical sound changes observed.Standard Language



Standard LanguageShathaRashedAlMutair
Ã˝
Standard language is an official form of a language used for formal situations like newspapers and speeches. It is established through social, economic and political influences and codified to be accessible to all speakers of the language. Characteristics of a standard language include being a prestigious variety recognized by a community and used for high functions. In contrast, a dialect is a form of a language spoken by a particular group in a region, shown through accent and vocabulary. While dialects have benefits like developing characters, they also have risks like being confusing, offensive or distracting. Standard languages differ from dialects in having more speakers, being used in all fields, and representing all dialects under it, whereas dialects have limitations.Language variation assgnmnt



Language variation assgnmntAyesha Mir
Ã˝
The document is a 9-page assignment on the topic of language variation submitted for a sociolinguistics course. It defines key concepts in sociolinguistics such as standard language, dialects, registers, and style. It discusses how factors like region, social class, gender, and formality influence language variation. Specific language varieties covered include regional dialects, social dialects, individual dialects, accent, jargon, slang, and styles. Speech accommodation processes like convergence and divergence are also summarized.social variation ( dialects and accents)



social variation ( dialects and accents)Mohammed Mallah
Ã˝
social variation according to sociolinguistcs, and the variation between accents and dialects in addition to RP Language, dialect, and varieties



Language, dialect, and varietiesSari Kusumaningrum
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation and the different varieties of language. It defines key terms like dialect, idiolect, and varieties. A dialect is a language variety spoken by a speech community that is distinguished by systematic features. An idiolect refers to the speech variety of an individual speaker. Varieties refer to forms of language associated with social factors like region, social class, situation, and individual. Dialects and varieties differ based on factors like geography, occupation, age, education, gender, and ethnicity. While some dialects have more prestige than others due to historical and social factors, all languages consist of dialects and everyone speaks at least one dialect.Language and Regional Variations by Yule



Language and Regional Variations by YuleRonald Suplido Jr
Ã˝
There are three main points made in the document:
1. Variation in language reflects social identity, as ways of speaking are associated with social groups and attitudes. People's language use can indicate their socioeconomic class, ethnicity, gender, age, and other social factors.
2. Every person has their own idiolect made up of the languages and dialects they command, and they code-switch between styles depending on the social situation or context.
3. Dialects are not inferior versions of a language but natural linguistic variations, and studying dialects can provide insights into how languages diverge regionally without any variety being inherently better than others.Principal types of english pronunciation



Principal types of english pronunciationSanobarAbdullaeva
Ã˝
The document discusses the principal types and variations of English pronunciation. It notes that there are four components of phonetic structure - phonemic, syllabic, accentual, and intonational - that constitute a language's pronunciation. Accents refer solely to pronunciation differences, whereas dialects involve differences in vocabulary, grammar, and word order as well. There are many accents within England, Britain, and across the other regions of the UK, with Northern and Southern accents being a broad distinction in England. The study of variations in accents was traditionally part of dialectology, which aimed to identify all geographical differences in a language.Varieties of English



Varieties of Englishgabrielucsc
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of variation in English, including regional dialects, social variations, and national standards. It notes that regional dialects depend on where people live, social variations depend on social groups and education levels, and national standards of English include British, American, and other country-specific variations with some differences in grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. Standard English aims for uniformity but still varies based on factors like medium, attitude, and situation.Language, dialect, and varieties



Language, dialect, and varietiesSari Kusumaningrum
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation and varieties. It defines key terms such as language, dialect, and varieties. Some main points:
- No two speakers speak exactly the same way and an individual's speech varies across situations.
- Language varieties refer to different forms of language influenced by social factors like region, social class, individual, and situation.
- A dialect is a language variety spoken by a community that has distinguishing phonological, lexical, and grammatical features.
- Varieties refer to sets of linguistic items associated with external social factors like a geographical area and social group.
- Dialects are influenced by various social factors and everyone speaks at least one dialect. Standard dialects have more prestige than others dueRecently uploaded (20)
One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£s



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£sCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ã˝
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatAI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Ã˝
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, vinodpr111@gmail.comChapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
Ã˝
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ã˝
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatMeeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
Ã˝
NAPD Annual Symposium
“Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?”Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ã˝
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxBỘ TEST KIỂM TRA GIỮA KÌ 2 - TIẾNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUẨN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



BỘ TEST KIỂM TRA GIỮA KÌ 2 - TIẾNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUẨN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Ã˝
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgHannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
Ã˝
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
Ã˝
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spots—systemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AI—that could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
Ã˝
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHAI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Ã˝
BỘ TEST KIỂM TRA GIỮA KÌ 2 - TIẾNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUẨN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



BỘ TEST KIỂM TRA GIỮA KÌ 2 - TIẾNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUẨN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Ã˝
Dialects
- 1. Introduction This presentation consists in some of the most relevant aspects related with dialects. It contains all the elements that contribute in the development process of a dialect. DIALECTS
- 2. Dialects are mutually intelligible forms of a language that differ in systematic ways. DEFINITION
- 3. A dialect is not an inferior or degraded form of a language, and logically could not be so because a language is a collection of dialects. DIALECTS
- 4. All English speakers can talk to each other and be understood. However not two of them speak exactly alike. Word choice, pronunciation of the words, and grammatical rules are affected by some factors like age, sex, social situation, when and how the language was learned. DIALECTS
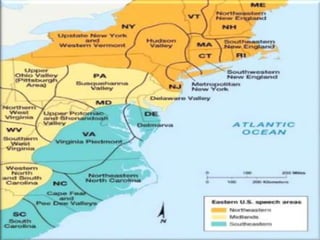
- 5. Each version of a language is referred to as a regional dialect when various linguistic differences are accumulate in a particular geographic region. REGIONAL DIALECTS
- 6. Regional dialects may differ not only in their pronunciation but also in their lexical choices and grammatical rules. REGIONAL DIALECTS
- 7. ÔÉòSpeech of non-native speakers, who have learned a language as a second language. ÔÉòRegional phonological o phonetic distinctions. ACCENTS
- 8. Accent refers to the characteristic of speech that convey information about the speaker’s dialect, which may reveal in what country or in what part of the country the speaker grew up, or to which sociolinguistic group the speaker belong. ACCENTS
- 9. Regional dialects may differ in the words people use for the same object, as well as in phonology. LEXICAL DIFFERENCES
- 10. ÔÉòDialect Areas: the concentrations defined by different word usages and varying pronunciation, among other linguistic differences. ÔÉòIsogloss: a line draw on a map to separate the dialects areas. DIALECT ATLASES
- 12. Dialect differences that seem to come about because of social factor. There are regional aspects to social dialects, clearly, social aspects to regional dialects, so the distinction is not entirely cut and dried. SOCIAL DIALECTS
- 13. Many people talk and think about a language as if it were a well-defined system with various dialects diverging from this norm. This is false, although it is a falsehood that is widespread. THE “STANDARD”
- 14. Prescriptive grammarians, or language purists, usually consider the dialect used by political leaders and national newscasters as the correct form of the language. LANGUAGE PURISTS
- 15. SAE refers to the standard or prestige dialect of English, that many Americans nearly speaks. STANDARD AMERICAN ENGLISH (SAE)
- 16. The aim of the languages purists is to prevent languages differentiation because of their false belief that some languages are better that others. BANNED LANGUAGES
- 17. Many dialects like; Cajun English and French in Louisiana, Korean in Japan, Sing language in many countries including USA, have been banned based on the wishes of languages purists. BANNED LANGUAGES
- 18. The AAE is spoken by a large population of Americans of African descent. The distinghishing features of this English dialect persist for social, educational, and economic reasons. AFRICAN AMERICAN ENGLISH
- 19. A major group of American English dialects is spoken by native Spanish speakers or their descendants. There are also those born in Spanish- speaking homes whose native language is English, some of whom are monolingual, and others who speak Spanish as a second language. LATINO (HISPANIC) ENGLISH
- 20. It is acquired as a first language by many children, making it the native language of hundreds of thousands, if not millions of Americans. It is not English with a Spanish accent but, like AAE, a mutually intelligible dialect that differs systematically from SAE. CHICANO ENGLISH









