1 of 16
Download to read offline


Recommended
Multiplication -- More Than Repeated Addition and Times Tables



Multiplication -- More Than Repeated Addition and Times TablesChris Hunter
Ã˝
Multiplication is repeated addition... but it also means so much more than that! In this workshop, you will explore several fundamental meanings of this operation (e.g., equal groups, arrays and areas, how a quantity is “stretched,” etc.) through rich tasks that address each of these meanings. Also, you will explore and discuss relationships between the “basic facts.” More importantly, you will learn how to help your students see that these relationships extend to other types of numbers that they come across in BC’s intermediate and middle years mathematics curriculum (e.g., two-digit whole numbers, fractions, decimals, integers, etc.)Making and Justifying Mathematical Decisions.pdf



Making and Justifying Mathematical Decisions.pdfChris Hunter
Ã˝
In BC’s nearly-decade-old “new” curriculum, the curricular competencies describe the processes that students are expected to develop in areas of learning such as mathematics. They reflect the “Do” in the “Know-Do-Understand” model. Under the “Communicating” header falls the curricular competency “Explain and justify mathematical ideas and decisions.” Note that it contains two processes: “Explain mathematical ideas” and “Justify mathematical decisions.” I have broken it down into its separate parts in order to understand--or reveal--its meaning.
The first part is commonplace in classrooms. By now, BC math teachers—and students—understand that “Explain mathematical ideas” means more than “Show your work.” Teachers consistently ask “What did you do?” and “How do you know?” This process is about retelling, not just of steps but of thinking.
The second part happens less frequently. Think back to the last time that you observed a student make—a necessary precursor to justify—a mathematical decision. “Justify” is about defending. Like “explain,” it involves reasoning; unlike “explain,” it also involves opinion and debate.
In order to reinterpret the curricular competency “Explain and justify mathematical ideas and decisions,” I will continue to take apart its constituent part “Justify mathematical decisions” and carefully examine the term “mathematical decisions.” What, exactly, is a “mathematical decision”? Below, I will categorize answers to this question. These categories, and the provided examples, may help to suggest new opportunities for students to justify.Math 8 Proficiency Scales



Math 8 Proficiency ScalesChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document outlines mathematics skills and concepts for grade 8. It covers topics such as squares, square roots, cubes and cube roots; the Pythagorean theorem; operations with fractions; ratios, rates, proportions and percents; linear relations and equations; surface area and volume; and statistics and probability. For each topic, it lists specific skills from emerging to extending levels of understanding.Curricular Competencies -- Proficiency Scales



Curricular Competencies -- Proficiency ScalesChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document outlines curricular competencies in mathematics across several domains: reasoning, problem solving, communicating, representing, and connecting. For each domain, it lists competencies for emerging, developing, proficient, and extending levels of understanding and ability. The competencies describe skills such as recognizing patterns, explaining problem solving processes, using diagrams and symbols, and connecting mathematical concepts to real-world applications.Multiplication -- More Than Repeated Addition and Times Tables.pdf



Multiplication -- More Than Repeated Addition and Times Tables.pdfChris Hunter
Ã˝
Multiplication is repeated addition... but it also means so much more than that! In this workshop, you will explore several fundamental meanings of this operation (e.g., equal groups, arrays and areas, how a quantity is “stretched,” etc.) through rich tasks that address each of these meanings. Also, you will explore and discuss relationships between the “basic facts.” More importantly, you will learn how to help your students see that these relationships extend to other types of numbers that they come across in BC’s intermediate and middle years mathematics curriculum (e.g., two-digit whole numbers, fractions, decimals, integers, etc.).SI 2022.pdf



SI 2022.pdfChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses creating an inclusive community for all learners in mathematics. It emphasizes three key aspects of establishing belonging in math classrooms: interpersonal supports, curriculum, and instructional techniques. Specifically, it states that while interpersonal relationships are important, teachers must also design instructional approaches and choose tasks that provide opportunities for students to experience mathematical belonging. These include using problems that students can relate to their own lives, lowering barriers to entry, allowing multiple solution pathways, and not restricting students' thinking. The goal is for all learners to feel like accepted members of the classroom community and to have opportunities to successfully engage with meaningful mathematics."Yeah But How Do I Translate That to a Percentage?" -- STA Convention 2022.pdf



"Yeah But How Do I Translate That to a Percentage?" -- STA Convention 2022.pdfChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses standards-based assessment and answers common questions about the transition from traditional grading to standards-based assessment. Some key points include:
- Standards-based assessment focuses on demonstrating evidence of learning standards rather than accumulating points, and compares student learning to proficiency levels rather than other students.
- The reasons for changing include making assessment more accurate, fair, and relevant to learning, and shifting student focus from grades to learning.
- Assessment should evaluate specific delineated learning standards rather than broad topics. Descriptors define each level of the proficiency scale from emerging to extending.
- Evidence of learning can come from products, observations, and conversations, rather than single events like tests. Tracking data overVisualizing -- Focus Day 2022



Visualizing -- Focus Day 2022Chris Hunter
Ã˝
Visualization is the process of thinking in images to compose, decompose, or transform mathematical concepts."They'll Need It for High School"



"They'll Need It for High School"Chris Hunter
Ã˝
Timed tests cause early onset of math anxiety in students according to research. Studies have shown that students experience stress on timed math tests that they do not experience on untimed tests of the same material. Even young students in 1st and 2nd grade can experience math anxiety, and their levels do not correlate with factors like grade level, reading ability, or family income. Brain imaging has revealed that students who feel panicky about math show increased activity in areas associated with fear and decreased activity in areas involved in problem solving. Timed tests require retrieving math facts from working memory, and higher math anxiety reduces the available working memory. While timed tests are used with good intentions, the evidence suggests they should be reconsidered given the widespread issuesOpening Up Math Class



Opening Up Math ClassChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses opening up math class through asking open-ended questions. It provides strategies for creating open questions, such as turning questions around, asking for similarities and differences, replacing numbers with blanks, and asking for number sentences. Open questions allow for multiple approaches and solutions. Examples show how questions can go from closed to more open, providing more freedom in problem solving.Alike & Different: WODB? and More



Alike & Different: WODB? and MoreChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document contains a series of math problems asking students to identify which two expressions or equations are most alike. It includes problems involving fractions, exponents, order of operations, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, variables, equations, and functions. The document asks students to consider what is the same and what is different between pairs or groups of related mathematical expressions, equations or functions.Indigenous Art Patterns -- Stamps



Indigenous Art Patterns -- StampsChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document lists the names of various artworks along with the artist and their tribal affiliation. There are multiple listings of works featuring eagles, owls, hummingbirds, butterflies, orcas, salmon, bears, and ribbits created by indigenous artists from tribes such as Haida, Tsimshian, Coast Salish, Salish, and Kwagiulth.Cuisenaire Rods



Cuisenaire RodsChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document discusses using Cuisenaire rods to develop conceptual understanding of mathematical concepts. It provides examples of spatial puzzles and activities with the rods to help children decompose and recompose shapes. These activities build the foundation for understanding geometry. Examples also show using the rods to represent numbers in different ways, compare quantities, explore properties like commutative and distributive, build patterns, use measurement conversion and develop fraction concepts. The document emphasizes that experiences with the manipulatives are important for building number sense and geometry understanding in children.Clothesline math



Clothesline mathChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document summarizes a presentation about developing number sense in students. It discusses clothesline math, an instructional tool using an open number line to build understanding of numbers and their relationships. It also defines number sense as a flexibility and automaticity with numbers, and the ability to choose strategies and judge answers. The presentation advocates for instructional routines to focus learning on mathematical practices and make lessons accessible for all. Attendees then planned clothesline math activities considering number choices, strategies, and questioning.Linear relations across the grades



Linear relations across the gradesChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses linear relations across grades and includes the following key points:
- It describes how the concept of linear relations is developed from discrete points in one quadrant in grade 6 to continuous relations with rational coordinates in grade 9.
- Constant rate of change is an essential attribute of linear relations and has meaning when represented in tables, graphs, and equations.
- It lists big ideas, competencies, and content topics related to teaching slopes and equations of lines.Alike & Different



Alike & DifferentChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document contains a series of math problems asking which two expressions are most alike or what is the same and different between expressions. It focuses on comparing fractions, division, subtraction, and algebraic expressions. The high level theme is evaluating similarity and differences between mathematical terms and expressions.Paint Splatter Arrays



Paint Splatter ArraysChris Hunter
Ã˝
Paint splatter arrays are inspired by Steve Wyborney's Splat! project. Chris Hunter shares the idea of creating abstract art by splattering paint onto a canvas in an organized array of dots or lines. The end result is colorful non-representational art that captures the randomness of splattered paint in an orderly composition.The "MathTwitterBlogoSphere": Creating Your Own Professional Learning Community



The "MathTwitterBlogoSphere": Creating Your Own Professional Learning CommunityChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses the "MathTwitterBlogoSphere" (MTBoS), an online professional learning community of mathematics educators who use Twitter and blogs. It defines the MTBoS as an informal organization without official membership where educators from all levels share resources and have professional conversations. The MTBoS values both redundancy through shared practices and diversity through different approaches and representations. The document encourages educators to join the MTBoS to access instructional routines, rich tasks, and testimonials about the benefits of participation. It provides hashtags to explore and discusses norms for respectful participation.Operations Across the Grades



Operations Across the GradesChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) across different grade levels and domains. It provides examples of how the same operations can be applied conceptually and procedurally in different contexts, such as algebra, measurement, and word problems. The key point is that while the operations may look different depending on the context, the fundamental meanings remain the same.Proportional Reasoning: Focus on Sense-Making



Proportional Reasoning: Focus on Sense-MakingChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses proportional reasoning and focuses on sense-making. It emphasizes using multiple strategies to solve problems and communicating explanations in various ways. Proportional reasoning involves understanding multiplicative relationships, such as ratios, rates, proportions, unit prices, and percents. Representing problems with bar models and ratio tables can help make sense of these relationships. The document also provides examples of proportional reasoning problems and tasks involving missing values and comparisons.ASN Math 8 June 2014



ASN Math 8 June 2014Chris Hunter
Ã˝
The document contains a list of mathematical statements about numbers, patterns and relations, shape and space, and statistics and probability. Some key statements include: when you add three consecutive numbers, your answer is a multiple of three; when you divide a whole number by a fraction, the quotient is greater than the whole number; a whole number has an odd number of factors if it is a perfect square; if the sides of a right triangle are given, the third side can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem; when you multiply two integers, the product is greater than either integer; if the price of an item is decreased by 25% and later increased by 25%, the final price will be the same as the original; the ratioThe Selfiest Cities in the World



The Selfiest Cities in the WorldChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document examines data on the number of selfies and selfie-takers in various cities to determine the "selfiest" city. Makati City, Philippines had the most selfies (4,155) and selfie-takers (2,915), followed by Manhattan, New York and then Milan, Italy. While selfies/selfie-takers is an imperfect metric, the author argues it is the most comprehensive means available to compare selfie-taking across world cities. Some question whether the ranking can truly be considered definitive given limitations of the data and metric used.Exploring the Pythagorean Relationship



Exploring the Pythagorean RelationshipChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document explores the Pythagorean relationship through an activity with cut-out squares that form three triangles. Students are asked to measure the sides and angles of the triangles, record the data in a table, and identify which triangles are right triangles based on having a 90 degree angle. For right triangles, students state the relationship between the areas of the squares and describe the relationship between the side lengths as being the Pythagorean relationship, where the area of the hypotenuse square equals the sum of the areas of the other two squares.Math scavenger hunt (secondary)



Math scavenger hunt (secondary)Chris Hunter
Ã˝
The document provides instructions for a group photo assignment involving mathematical concepts. It asks students to take or make a photo depicting: a perfect square, using a referent to measure an object's length, a positive and negative slope, a non-linear relation, an irrational number, similar 2D or 3D shapes, angles formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal, a word problem using sine or cosine law, a z-score of ±2, set operations like complement and union, or someone not in the group doing math. It encourages finding the most relevant or interesting photo for the assignment.Math Scavenger Hunt (Secondary)



Math Scavenger Hunt (Secondary)Chris Hunter
Ã˝
The document provides a list of 11 math-related concepts for a group to photograph, including a perfect square, using a referent to measure an object's length, positive and negative slopes, a non-linear relation, an irrational number, similar 2D and 3D shapes, angles formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal, a contextual problem using sine or cosine law, a z-score of ±2, elements in the union, intersection, or complement of two sets, and a stranger engaged in math.Master 6 19



Master 6 19Chris Hunter
Ã˝
This document is about triangles and contains 3 sentences or less of essential information. It discusses properties of triangles, different types of triangles such as right, acute, obtuse and isosceles triangles, as well as triangle inequality theorem.Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ã˝
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ã˝
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxMore Related Content
More from Chris Hunter (20)
"They'll Need It for High School"



"They'll Need It for High School"Chris Hunter
Ã˝
Timed tests cause early onset of math anxiety in students according to research. Studies have shown that students experience stress on timed math tests that they do not experience on untimed tests of the same material. Even young students in 1st and 2nd grade can experience math anxiety, and their levels do not correlate with factors like grade level, reading ability, or family income. Brain imaging has revealed that students who feel panicky about math show increased activity in areas associated with fear and decreased activity in areas involved in problem solving. Timed tests require retrieving math facts from working memory, and higher math anxiety reduces the available working memory. While timed tests are used with good intentions, the evidence suggests they should be reconsidered given the widespread issuesOpening Up Math Class



Opening Up Math ClassChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses opening up math class through asking open-ended questions. It provides strategies for creating open questions, such as turning questions around, asking for similarities and differences, replacing numbers with blanks, and asking for number sentences. Open questions allow for multiple approaches and solutions. Examples show how questions can go from closed to more open, providing more freedom in problem solving.Alike & Different: WODB? and More



Alike & Different: WODB? and MoreChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document contains a series of math problems asking students to identify which two expressions or equations are most alike. It includes problems involving fractions, exponents, order of operations, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, variables, equations, and functions. The document asks students to consider what is the same and what is different between pairs or groups of related mathematical expressions, equations or functions.Indigenous Art Patterns -- Stamps



Indigenous Art Patterns -- StampsChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document lists the names of various artworks along with the artist and their tribal affiliation. There are multiple listings of works featuring eagles, owls, hummingbirds, butterflies, orcas, salmon, bears, and ribbits created by indigenous artists from tribes such as Haida, Tsimshian, Coast Salish, Salish, and Kwagiulth.Cuisenaire Rods



Cuisenaire RodsChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document discusses using Cuisenaire rods to develop conceptual understanding of mathematical concepts. It provides examples of spatial puzzles and activities with the rods to help children decompose and recompose shapes. These activities build the foundation for understanding geometry. Examples also show using the rods to represent numbers in different ways, compare quantities, explore properties like commutative and distributive, build patterns, use measurement conversion and develop fraction concepts. The document emphasizes that experiences with the manipulatives are important for building number sense and geometry understanding in children.Clothesline math



Clothesline mathChris Hunter
Ã˝
This document summarizes a presentation about developing number sense in students. It discusses clothesline math, an instructional tool using an open number line to build understanding of numbers and their relationships. It also defines number sense as a flexibility and automaticity with numbers, and the ability to choose strategies and judge answers. The presentation advocates for instructional routines to focus learning on mathematical practices and make lessons accessible for all. Attendees then planned clothesline math activities considering number choices, strategies, and questioning.Linear relations across the grades



Linear relations across the gradesChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses linear relations across grades and includes the following key points:
- It describes how the concept of linear relations is developed from discrete points in one quadrant in grade 6 to continuous relations with rational coordinates in grade 9.
- Constant rate of change is an essential attribute of linear relations and has meaning when represented in tables, graphs, and equations.
- It lists big ideas, competencies, and content topics related to teaching slopes and equations of lines.Alike & Different



Alike & DifferentChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document contains a series of math problems asking which two expressions are most alike or what is the same and different between expressions. It focuses on comparing fractions, division, subtraction, and algebraic expressions. The high level theme is evaluating similarity and differences between mathematical terms and expressions.Paint Splatter Arrays



Paint Splatter ArraysChris Hunter
Ã˝
Paint splatter arrays are inspired by Steve Wyborney's Splat! project. Chris Hunter shares the idea of creating abstract art by splattering paint onto a canvas in an organized array of dots or lines. The end result is colorful non-representational art that captures the randomness of splattered paint in an orderly composition.The "MathTwitterBlogoSphere": Creating Your Own Professional Learning Community



The "MathTwitterBlogoSphere": Creating Your Own Professional Learning CommunityChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses the "MathTwitterBlogoSphere" (MTBoS), an online professional learning community of mathematics educators who use Twitter and blogs. It defines the MTBoS as an informal organization without official membership where educators from all levels share resources and have professional conversations. The MTBoS values both redundancy through shared practices and diversity through different approaches and representations. The document encourages educators to join the MTBoS to access instructional routines, rich tasks, and testimonials about the benefits of participation. It provides hashtags to explore and discusses norms for respectful participation.Operations Across the Grades



Operations Across the GradesChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) across different grade levels and domains. It provides examples of how the same operations can be applied conceptually and procedurally in different contexts, such as algebra, measurement, and word problems. The key point is that while the operations may look different depending on the context, the fundamental meanings remain the same.Proportional Reasoning: Focus on Sense-Making



Proportional Reasoning: Focus on Sense-MakingChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document discusses proportional reasoning and focuses on sense-making. It emphasizes using multiple strategies to solve problems and communicating explanations in various ways. Proportional reasoning involves understanding multiplicative relationships, such as ratios, rates, proportions, unit prices, and percents. Representing problems with bar models and ratio tables can help make sense of these relationships. The document also provides examples of proportional reasoning problems and tasks involving missing values and comparisons.ASN Math 8 June 2014



ASN Math 8 June 2014Chris Hunter
Ã˝
The document contains a list of mathematical statements about numbers, patterns and relations, shape and space, and statistics and probability. Some key statements include: when you add three consecutive numbers, your answer is a multiple of three; when you divide a whole number by a fraction, the quotient is greater than the whole number; a whole number has an odd number of factors if it is a perfect square; if the sides of a right triangle are given, the third side can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem; when you multiply two integers, the product is greater than either integer; if the price of an item is decreased by 25% and later increased by 25%, the final price will be the same as the original; the ratioThe Selfiest Cities in the World



The Selfiest Cities in the WorldChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document examines data on the number of selfies and selfie-takers in various cities to determine the "selfiest" city. Makati City, Philippines had the most selfies (4,155) and selfie-takers (2,915), followed by Manhattan, New York and then Milan, Italy. While selfies/selfie-takers is an imperfect metric, the author argues it is the most comprehensive means available to compare selfie-taking across world cities. Some question whether the ranking can truly be considered definitive given limitations of the data and metric used.Exploring the Pythagorean Relationship



Exploring the Pythagorean RelationshipChris Hunter
Ã˝
The document explores the Pythagorean relationship through an activity with cut-out squares that form three triangles. Students are asked to measure the sides and angles of the triangles, record the data in a table, and identify which triangles are right triangles based on having a 90 degree angle. For right triangles, students state the relationship between the areas of the squares and describe the relationship between the side lengths as being the Pythagorean relationship, where the area of the hypotenuse square equals the sum of the areas of the other two squares.Math scavenger hunt (secondary)



Math scavenger hunt (secondary)Chris Hunter
Ã˝
The document provides instructions for a group photo assignment involving mathematical concepts. It asks students to take or make a photo depicting: a perfect square, using a referent to measure an object's length, a positive and negative slope, a non-linear relation, an irrational number, similar 2D or 3D shapes, angles formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal, a word problem using sine or cosine law, a z-score of ±2, set operations like complement and union, or someone not in the group doing math. It encourages finding the most relevant or interesting photo for the assignment.Math Scavenger Hunt (Secondary)



Math Scavenger Hunt (Secondary)Chris Hunter
Ã˝
The document provides a list of 11 math-related concepts for a group to photograph, including a perfect square, using a referent to measure an object's length, positive and negative slopes, a non-linear relation, an irrational number, similar 2D and 3D shapes, angles formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal, a contextual problem using sine or cosine law, a z-score of ±2, elements in the union, intersection, or complement of two sets, and a stranger engaged in math.Master 6 19



Master 6 19Chris Hunter
Ã˝
This document is about triangles and contains 3 sentences or less of essential information. It discusses properties of triangles, different types of triangles such as right, acute, obtuse and isosceles triangles, as well as triangle inequality theorem.Recently uploaded (20)
Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ã˝
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ã˝
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxResearch & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ã˝
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
Ã˝
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfEssentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
Ã˝
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APM’s Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APM’s PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMO’s within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£s



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£sCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide we’ll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
Ã˝
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirMate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
Ã˝
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£s



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£sCeline George
Ã˝
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
Ã˝
In this slide, we‚Äôll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£s



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£sCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
Ã˝
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
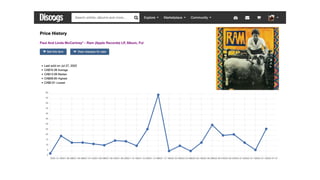
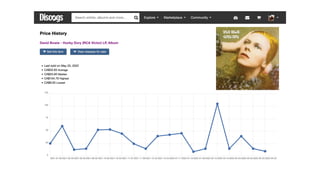
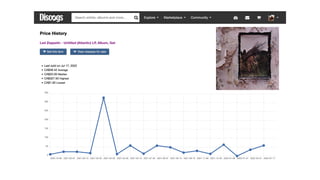
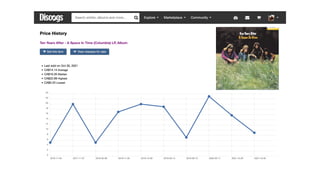
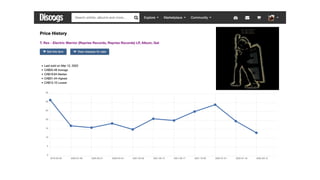
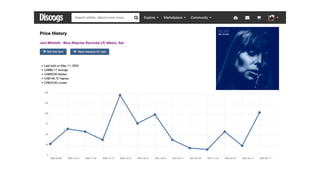
Discogs.pdf
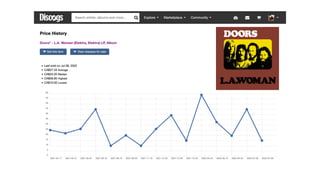
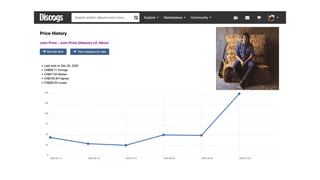
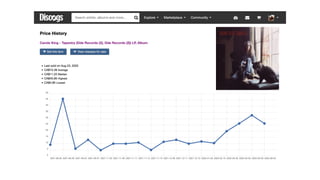
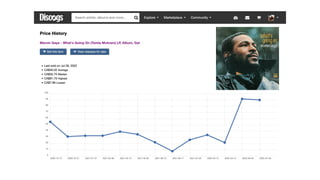
- 16. 1971








