Dssociation vs ionization.ppt
Download as pptx, pdf4 likes5,495 views
This document discusses dissociation and ionization when substances dissolve in water. It explains that ionic compounds dissociate into their constituent ions, while molecular compounds either disperse as neutral particles (non-electrolytes) or ionize to form hydrogen ions (acids). Specifically, it states that dissociation involves the separation of pre-existing ions in ionic compounds or bases, while ionization produces new ions through the reaction of acids in water. Examples of dissociation and ionization equations are also provided.
1 of 8
Downloaded 37 times







Ad
Recommended
arrhenius concept of acids and bases
arrhenius concept of acids and basesAhmadminhas2
╠²
According to Arrhenius' concept of acids and bases presented in 1887, acids are substances that dissociate in water to produce hydrogen ions, while bases are substances that dissociate in water to produce hydroxide ions. Examples given are that HCl produces H+ ions in water to act as an acid and KOH produces OH- ions to act as a base. However, this concept has limitations in that it only applies to substances in water and cannot explain the behavior of acids and bases in non-aqueous solutions or compounds without H+ or OH- ions like CO2 and NH3.Equilibrium constant-presentation
Equilibrium constant-presentationstarlanter
╠²
The document discusses equilibrium constants (Kc) and how to calculate them using concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium. It provides examples of calculating Kc values for reactions, including determining initial and change in concentrations. It also discusses using Kc to predict the direction a reaction will proceed based on comparing the reaction quotient (Q) to Kc.Acids & Bases
Acids & Basessondang29
╠²
This document discusses acids and bases. It defines acids as substances that produce H+ ions in aqueous solution and bases as substances that produce OH- ions. The document describes the pH scale for measuring acidity and alkalinity. It provides examples of the characteristic reactions of acids with metals, bases, and carbonates. It also discusses the importance of controlling acidity in the environment and describes how acids and bases are encountered in everyday life such as in soil, water, and air.Metallic bonds and the properties of metals
Metallic bonds and the properties of metalsKamal Metwalli
╠²
This document describes metallic bonding and the properties of metals and alloys. It explains that metallic bonding results from the delocalization of valence electrons among metal atoms, forming a "sea" of electrons. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity due to the mobility of these electrons. The properties of a metal, such as its hardness and melting point, depend on the number of delocalized electrons. Alloys are mixtures of elements that are substitutional, with one metal replacing atoms of another, or interstitial, with smaller atoms filling holes in the metallic crystal structure.3.3 Acids and Bases
3.3 Acids and BasesMelinda MacDonald
╠²
The pink colour in test tubes #2 and #4 was caused by the basic solution (NaOH) reacting with the phenolphthalein indicator, which turns pink in basic solutions with a pH between 8.2-12.
The colour disappeared in test tube #5 because the acidic solution (HCl) was added, and phenolphthalein is colourless in acidic solutions below pH 8.2.
We could use an acidic solution like HCl to take away the pink colour in test tube #6, as it would neutralize the basic solution and lower the pH below 8.2, making the phenolphthalein colourless again.6.1 electrolyte& non electrolyte
6.1 electrolyte& non electrolyteramly5597
╠²
This document defines electrolytes and non-electrolytes. An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity when molten or dissolved in water, allowing ions to move freely. A liquid is an electrolyte if it contains ions that can move through it. Examples include molten salts, saltwater solutions, and acidic or alkaline aqueous solutions. A non-electrolyte does not conduct electricity in any state because it lacks freely moving ions, such as sulfur, wood, or sugar. The movement of ions in an electrolyte allows electricity to flow, as seen by the movement of an ammeter needle in a circuit with batteries and an electrolyte.Electrochemical cell
Electrochemical cellRenuDhetarwal
╠²
This document discusses electrochemical cells. It defines an electrochemical cell as a device that can generate electrical energy from chemical reactions or use electrical energy to drive chemical reactions. There are two main types of electrochemical cells: galvanic/voltaic cells which convert chemical energy to electrical energy, and electrolytic cells which convert electrical energy to chemical energy.
A galvanic cell consists of two half-cells with different metal electrodes immersed in electrolyte solutions, connected by a salt bridge or porous membrane. Chemical reactions at the electrodes produce a spontaneous flow of electrons through an external circuit. For example, in a Daniell cell zinc undergoes oxidation and copper undergoes reduction. The overall cell reaction is Zn + CuIonic bonds and Ionic compounds
Ionic bonds and Ionic compoundsKamal Metwalli
╠²
This document describes the formation and properties of ionic compounds. Ionic bonds form when oppositely charged ions attract each other to form electrically neutral compounds. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because the ionic bonds between ions require a large amount of energy to overcome. The ions are tightly packed in a crystal lattice structure. Physical properties like conductivity depend on whether the ions are free to move or locked in place. Smaller or more highly charged ions result in stronger ionic bonds and higher lattice energies.Acids and Bases
Acids and BasesKevin Cram
╠²
This document discusses the chemistry of acids and bases. It outlines three definitions of acids and bases: Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis. The Arrhenius definition states that acids produce hydrogen ions in water and bases produce hydroxide ions. The Br├Ėnsted-Lowry definition broadened this to include acids as hydrogen ion donors and bases as acceptors. The Lewis definition focuses on electron pair donation and acceptance. Acids react with bases to form salts and water in a neutralization reaction. Common acids include sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid.Hydrogen
Hydrogen tanushseshadri
╠²
Hydrogen is the simplest and most abundant element. It exists as three isotopes and can be prepared through the electrolysis of water or through reactions between acids and reactive metals like zinc. Hydrogen burns readily with oxygen to form water and is highly flammable, making its handling and storage require safety precautions. It has various industrial uses including energy production, oil refining, and ammonia synthesis.Acid Base Equilibrium
Acid Base EquilibriumDavid Richardson
╠²
The document discusses acid-base equilibrium, defining Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis acids and bases, along with the relationships between their strengths and corresponding equilibrium constants (K). It includes examples of calculating pH and the dissociation constants (Ka and Kb) for various acids and bases, alongside applications for calculating equilibrium concentrations and pH in different solutions. The content also covers specific cases, such as weak acids and bases, auto ionization of water, and the common ion effect.TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTION
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONjuliemae123
╠²
The document summarizes the six main types of chemical reactions:
1) Combustion reactions involve oxygen combining with another compound to produce heat, water, and carbon dioxide.
2) Synthesis reactions involve simple compounds combining to form more complex compounds.
3) Decomposition reactions involve complex molecules breaking down into simpler ones.
4) Single displacement reactions involve one element replacing another in a compound.
5) Double displacement reactions involve the switching of anions and cations between compounds to form new compounds.
6) Acid-base reactions specifically involve acids and bases reacting to form water and an ionic salt.IGCSE Electricity
IGCSE ElectricityCarole Paquette
╠²
The document provides information about electrolysis, including:
1) Electrolysis is the chemical effect of electricity on ionic compounds, causing them to break up into simpler substances like elements.
2) During electrolysis, ions move to electrodes of opposite charge where chemical reactions occur - non-metals form at the anode and metals or hydrogen form at the cathode.
3) Examples of electrolysis include molten lead(II) bromide producing lead at the cathode and bromine at the anode, and aqueous copper(II) chloride producing copper at the cathode and chlorine at the anode.Theories
Theoriesrafamunoa
╠²
The document discusses several theories of acids and bases:
1. According to Arrhenius, acids are compounds that produce H+ ions in water and bases produce OH- ions. Strong acids fully dissociate while weak acids only partially dissociate.
2. Bronsted and Lowry defined acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. An acid and base always work together in a proton transfer reaction. Some substances can act as both an acid and a base depending on the reaction.
3. Lewis defined acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors.Acids & Bases
Acids & BasesOhMiss
╠²
Acids and bases can be identified by their names or chemical formulas. Acids contain hydrogen (H) or a carboxyl group (COOH) and have a pH below 7. Bases contain a metallic or ammonium ion and hydroxide (OH) and have a pH above 7. Acid-base indicators change color at specific pH levels and can be used to determine if a solution is acidic or basic. A neutralization reaction occurs between an acid and base, producing water and a salt.Lewis Structures
Lewis Structuresalchemist
╠²
The document discusses Lewis structures and the rules for drawing them. It explains that Lewis structures show how atoms bond via shared electron pairs to achieve stable noble gas configurations. It provides a 4-step process for drawing Lewis structures, covering counting electrons, identifying the central atom, adding lone pairs to complete octets, and checking that all electrons are accounted for. Exceptions to the octet rule and drawing structures for ions are also covered. modern periodic table
modern periodic tableNinth Grade
╠²
This document provides an overview of the modern periodic table. It discusses how the elements are organized by atomic number and chemical properties into periods and groups. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity, can be hammered into sheets, and drawn into wires, while nonmetals do not share these properties. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons and influence chemical properties. Group 1 elements have 1 valence electron and form 1+ ions, with reactivity increasing down the group. Group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons and form 2+ ions, with reactivity also increasing down the group.Soluion and colligative propertries 2017
Soluion and colligative propertries 2017nysa tutorial
╠²
This document discusses the factors affecting solvation, including the nature of the solute and solvent, the amount of solvent, temperature, and pressure, particularly in relation to gases. It elaborates on Henry's law and Raoult's law, emphasizing their applications and the impact on solubility, boiling points, and colligative properties of solutions. Additionally, it covers concepts such as osmotic pressure, the experiment by Abbe Nollet, and the calculation of molarity and abnormal molar mass.Electronegativity
Electronegativitysumathiasir
╠²
Linus Pauling introduced the concept of electronegativity in 1932 to help explain the nature of chemical bonds. Electronegativity is a property that reflects an atom's ability to attract electrons in a bond. Atoms with high electronegativity strongly attract electrons, while atoms with low electronegativity attract electrons weakly. Whether a bond is ionic or covalent depends on the difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms - a large difference leads to ionic bonds where one atom takes the electrons, while a small difference leads to covalent bonds where electrons are shared. Electronegativity values help predict bond type based on this principle.Redox Reactions
Redox ReactionsArrehome
╠²
The document defines oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions in terms of oxygen/hydrogen gain or loss, electron transfer, and changes in oxidation state. It provides examples of redox reactions like combustion and corrosion. Redox involves both oxidation, defined as gaining oxygen, losing hydrogen, losing electrons, or increasing oxidation state, and reduction, defined as the opposite of these processes. Common oxidizing and reducing agents can be identified through color changes using potassium iodide and dichromate solutions.Lesson 1 Intro to Chemical Bonding
Lesson 1 Intro to Chemical Bondingtvacco
╠²
This document discusses covalent bonding and molecular compounds. It defines a chemical bond as a force that holds atoms together, and describes covalent bonding as atoms sharing electrons. As two atoms approach each other to form a bond, their potential energy decreases to a minimum at the bond length. Bond length and bond energy vary between different bonded atoms. The octet rule states atoms want 8 electrons in their valence shell. Practice problems classify bonds and identify valence electrons.Chapter 7 and 8 notes
Chapter 7 and 8 notesTia Hohler
╠²
This document provides an overview of ionic and covalent bonding. It discusses the formation of ions through the loss or gain of valence electrons to achieve stable electron configurations. Ionic compounds are formed between metallic and nonmetallic elements and are held together by ionic bonds between cations and anions. Molecular compounds are formed by the sharing of valence electrons between nonmetallic elements to form covalent bonds. Polar and nonpolar covalent bonds are discussed based on differences in electronegativity between bonded atoms. Hydrogen bonds that occur between polar molecules like water are also summarized. Key terms related to ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and molecular structure are defined.Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical Equilibriumwalt sautter
╠²
The document explains the concept of chemical equilibrium, detailing the conditions under which equilibrium occurs, the distinction between forward and reverse reactions, and how equilibrium constants (ke) are calculated. It covers how changes in the coefficients of a balanced equation affect ke values and introduces the concept of heterogeneous and homogeneous equilibrium systems. Additionally, the document outlines how to compute the equilibrium constant from concentration or pressure measurements and provides examples of equilibrium calculations.Chapter 6.1 : Introduction to Chemical Bonding
Chapter 6.1 : Introduction to Chemical BondingChris Foltz
╠²
This document discusses chemical bonding. It defines chemical bonds as how most atoms are joined together in nature. It describes the two main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonding which results from the transfer of electrons between ions, and covalent bonding which results from the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Atoms form chemical bonds to decrease their potential energy and become more stable. Bonds are rarely purely ionic or covalent, but instead exist on a spectrum depending on the electronegativity difference between the atoms.AQUEOUS REACTIONS
AQUEOUS REACTIONSINSTITUTO TECNOL├ōGICO DE SONORA
╠²
This document discusses properties of aqueous solutions and acid-base reactions. It describes how ionic compounds and electrolytes dissolve in water, forming ions that are solvated. Precipitation reactions that form insoluble products are explained. Strong and weak acids and bases are defined, and neutralization reactions that produce salts and water are covered. Some acid-base reactions evolve gas as one of the products.Equilibrium constant
Equilibrium constantNawaz Shah
╠²
The document defines the equilibrium constant and how it is calculated from the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium. Specifically:
- The equilibrium constant (Kc) is calculated by multiplying the equilibrium concentrations of products, each raised to their coefficient, and dividing by the equilibrium concentrations of reactants each raised to their coefficient.
- This is demonstrated using the example reaction N2 + 3H2 Ōćŗ 2NH3, where Kc = [NH3]2 / [N2][H2]3.
- The value of the equilibrium constant is temperature dependent and has the same value for a given reaction at a set temperature.9. Coordination compounds class 12-1.pptx
9. Coordination compounds class 12-1.pptxHarishParthasarathy4
╠²
This document provides an overview of coordination compounds and key concepts in coordination chemistry. It discusses the discovery of coordination compounds, Werner's theory of coordination compounds, types of ligands and isomerism in coordination compounds. Specifically, it introduces coordination numbers, colors and shapes of complexes, IUPAC nomenclature, bonding theories like VBT and CFT. It also discusses applications of coordination compounds in daily life and metallurgy. Common coordination polyhedra and their geometries are described.Electrode kinetics
Electrode kineticslakshmi.ec
╠²
1. The document discusses electrode kinetics and the Butler-Volmer equation, which describes the relationship between current and overpotential during a redox reaction.
2. It explains how applying a potential above the equilibrium potential Eo lowers the activation barrier for oxidation and raises it for reduction.
3. The Butler-Volmer equation contains terms for the forward and backward rate constants that are dependent on the applied potential relative to Eo, as well as the exchange current density io which is proportional to the surface concentrations.Water
Water Nidhi D
╠²
The document discusses the molecular structure of water. It explains that a water molecule is formed by two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom bonded together at an angle of 104.5 degrees. The polarity of the water molecule arises from oxygen's higher electronegativity which gives it a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atoms a partial positive charge. This polar nature is an important feature of water and causes it to have unique properties.Electrolytic Dissociation
Electrolytic DissociationLaurikitikis Velazquez
╠²
The electrolytic dissociation is a mechanical process that allows ionic compounds to dissolve in water. When ionic compounds dissolve in water, the polarity of the water molecule causes the ions to separate. Positively charged ions are attracted to the negatively charged part of the water molecule, and negatively charged ions are attracted to the positively charged part. This produces homogeneous mixtures of separated ions called electrolyte solutions.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Acids and Bases
Acids and BasesKevin Cram
╠²
This document discusses the chemistry of acids and bases. It outlines three definitions of acids and bases: Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis. The Arrhenius definition states that acids produce hydrogen ions in water and bases produce hydroxide ions. The Br├Ėnsted-Lowry definition broadened this to include acids as hydrogen ion donors and bases as acceptors. The Lewis definition focuses on electron pair donation and acceptance. Acids react with bases to form salts and water in a neutralization reaction. Common acids include sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid.Hydrogen
Hydrogen tanushseshadri
╠²
Hydrogen is the simplest and most abundant element. It exists as three isotopes and can be prepared through the electrolysis of water or through reactions between acids and reactive metals like zinc. Hydrogen burns readily with oxygen to form water and is highly flammable, making its handling and storage require safety precautions. It has various industrial uses including energy production, oil refining, and ammonia synthesis.Acid Base Equilibrium
Acid Base EquilibriumDavid Richardson
╠²
The document discusses acid-base equilibrium, defining Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis acids and bases, along with the relationships between their strengths and corresponding equilibrium constants (K). It includes examples of calculating pH and the dissociation constants (Ka and Kb) for various acids and bases, alongside applications for calculating equilibrium concentrations and pH in different solutions. The content also covers specific cases, such as weak acids and bases, auto ionization of water, and the common ion effect.TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTION
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONjuliemae123
╠²
The document summarizes the six main types of chemical reactions:
1) Combustion reactions involve oxygen combining with another compound to produce heat, water, and carbon dioxide.
2) Synthesis reactions involve simple compounds combining to form more complex compounds.
3) Decomposition reactions involve complex molecules breaking down into simpler ones.
4) Single displacement reactions involve one element replacing another in a compound.
5) Double displacement reactions involve the switching of anions and cations between compounds to form new compounds.
6) Acid-base reactions specifically involve acids and bases reacting to form water and an ionic salt.IGCSE Electricity
IGCSE ElectricityCarole Paquette
╠²
The document provides information about electrolysis, including:
1) Electrolysis is the chemical effect of electricity on ionic compounds, causing them to break up into simpler substances like elements.
2) During electrolysis, ions move to electrodes of opposite charge where chemical reactions occur - non-metals form at the anode and metals or hydrogen form at the cathode.
3) Examples of electrolysis include molten lead(II) bromide producing lead at the cathode and bromine at the anode, and aqueous copper(II) chloride producing copper at the cathode and chlorine at the anode.Theories
Theoriesrafamunoa
╠²
The document discusses several theories of acids and bases:
1. According to Arrhenius, acids are compounds that produce H+ ions in water and bases produce OH- ions. Strong acids fully dissociate while weak acids only partially dissociate.
2. Bronsted and Lowry defined acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. An acid and base always work together in a proton transfer reaction. Some substances can act as both an acid and a base depending on the reaction.
3. Lewis defined acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors.Acids & Bases
Acids & BasesOhMiss
╠²
Acids and bases can be identified by their names or chemical formulas. Acids contain hydrogen (H) or a carboxyl group (COOH) and have a pH below 7. Bases contain a metallic or ammonium ion and hydroxide (OH) and have a pH above 7. Acid-base indicators change color at specific pH levels and can be used to determine if a solution is acidic or basic. A neutralization reaction occurs between an acid and base, producing water and a salt.Lewis Structures
Lewis Structuresalchemist
╠²
The document discusses Lewis structures and the rules for drawing them. It explains that Lewis structures show how atoms bond via shared electron pairs to achieve stable noble gas configurations. It provides a 4-step process for drawing Lewis structures, covering counting electrons, identifying the central atom, adding lone pairs to complete octets, and checking that all electrons are accounted for. Exceptions to the octet rule and drawing structures for ions are also covered. modern periodic table
modern periodic tableNinth Grade
╠²
This document provides an overview of the modern periodic table. It discusses how the elements are organized by atomic number and chemical properties into periods and groups. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity, can be hammered into sheets, and drawn into wires, while nonmetals do not share these properties. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons and influence chemical properties. Group 1 elements have 1 valence electron and form 1+ ions, with reactivity increasing down the group. Group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons and form 2+ ions, with reactivity also increasing down the group.Soluion and colligative propertries 2017
Soluion and colligative propertries 2017nysa tutorial
╠²
This document discusses the factors affecting solvation, including the nature of the solute and solvent, the amount of solvent, temperature, and pressure, particularly in relation to gases. It elaborates on Henry's law and Raoult's law, emphasizing their applications and the impact on solubility, boiling points, and colligative properties of solutions. Additionally, it covers concepts such as osmotic pressure, the experiment by Abbe Nollet, and the calculation of molarity and abnormal molar mass.Electronegativity
Electronegativitysumathiasir
╠²
Linus Pauling introduced the concept of electronegativity in 1932 to help explain the nature of chemical bonds. Electronegativity is a property that reflects an atom's ability to attract electrons in a bond. Atoms with high electronegativity strongly attract electrons, while atoms with low electronegativity attract electrons weakly. Whether a bond is ionic or covalent depends on the difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms - a large difference leads to ionic bonds where one atom takes the electrons, while a small difference leads to covalent bonds where electrons are shared. Electronegativity values help predict bond type based on this principle.Redox Reactions
Redox ReactionsArrehome
╠²
The document defines oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions in terms of oxygen/hydrogen gain or loss, electron transfer, and changes in oxidation state. It provides examples of redox reactions like combustion and corrosion. Redox involves both oxidation, defined as gaining oxygen, losing hydrogen, losing electrons, or increasing oxidation state, and reduction, defined as the opposite of these processes. Common oxidizing and reducing agents can be identified through color changes using potassium iodide and dichromate solutions.Lesson 1 Intro to Chemical Bonding
Lesson 1 Intro to Chemical Bondingtvacco
╠²
This document discusses covalent bonding and molecular compounds. It defines a chemical bond as a force that holds atoms together, and describes covalent bonding as atoms sharing electrons. As two atoms approach each other to form a bond, their potential energy decreases to a minimum at the bond length. Bond length and bond energy vary between different bonded atoms. The octet rule states atoms want 8 electrons in their valence shell. Practice problems classify bonds and identify valence electrons.Chapter 7 and 8 notes
Chapter 7 and 8 notesTia Hohler
╠²
This document provides an overview of ionic and covalent bonding. It discusses the formation of ions through the loss or gain of valence electrons to achieve stable electron configurations. Ionic compounds are formed between metallic and nonmetallic elements and are held together by ionic bonds between cations and anions. Molecular compounds are formed by the sharing of valence electrons between nonmetallic elements to form covalent bonds. Polar and nonpolar covalent bonds are discussed based on differences in electronegativity between bonded atoms. Hydrogen bonds that occur between polar molecules like water are also summarized. Key terms related to ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and molecular structure are defined.Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical Equilibriumwalt sautter
╠²
The document explains the concept of chemical equilibrium, detailing the conditions under which equilibrium occurs, the distinction between forward and reverse reactions, and how equilibrium constants (ke) are calculated. It covers how changes in the coefficients of a balanced equation affect ke values and introduces the concept of heterogeneous and homogeneous equilibrium systems. Additionally, the document outlines how to compute the equilibrium constant from concentration or pressure measurements and provides examples of equilibrium calculations.Chapter 6.1 : Introduction to Chemical Bonding
Chapter 6.1 : Introduction to Chemical BondingChris Foltz
╠²
This document discusses chemical bonding. It defines chemical bonds as how most atoms are joined together in nature. It describes the two main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonding which results from the transfer of electrons between ions, and covalent bonding which results from the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Atoms form chemical bonds to decrease their potential energy and become more stable. Bonds are rarely purely ionic or covalent, but instead exist on a spectrum depending on the electronegativity difference between the atoms.AQUEOUS REACTIONS
AQUEOUS REACTIONSINSTITUTO TECNOL├ōGICO DE SONORA
╠²
This document discusses properties of aqueous solutions and acid-base reactions. It describes how ionic compounds and electrolytes dissolve in water, forming ions that are solvated. Precipitation reactions that form insoluble products are explained. Strong and weak acids and bases are defined, and neutralization reactions that produce salts and water are covered. Some acid-base reactions evolve gas as one of the products.Equilibrium constant
Equilibrium constantNawaz Shah
╠²
The document defines the equilibrium constant and how it is calculated from the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium. Specifically:
- The equilibrium constant (Kc) is calculated by multiplying the equilibrium concentrations of products, each raised to their coefficient, and dividing by the equilibrium concentrations of reactants each raised to their coefficient.
- This is demonstrated using the example reaction N2 + 3H2 Ōćŗ 2NH3, where Kc = [NH3]2 / [N2][H2]3.
- The value of the equilibrium constant is temperature dependent and has the same value for a given reaction at a set temperature.9. Coordination compounds class 12-1.pptx
9. Coordination compounds class 12-1.pptxHarishParthasarathy4
╠²
This document provides an overview of coordination compounds and key concepts in coordination chemistry. It discusses the discovery of coordination compounds, Werner's theory of coordination compounds, types of ligands and isomerism in coordination compounds. Specifically, it introduces coordination numbers, colors and shapes of complexes, IUPAC nomenclature, bonding theories like VBT and CFT. It also discusses applications of coordination compounds in daily life and metallurgy. Common coordination polyhedra and their geometries are described.Electrode kinetics
Electrode kineticslakshmi.ec
╠²
1. The document discusses electrode kinetics and the Butler-Volmer equation, which describes the relationship between current and overpotential during a redox reaction.
2. It explains how applying a potential above the equilibrium potential Eo lowers the activation barrier for oxidation and raises it for reduction.
3. The Butler-Volmer equation contains terms for the forward and backward rate constants that are dependent on the applied potential relative to Eo, as well as the exchange current density io which is proportional to the surface concentrations.Viewers also liked (13)
Water
Water Nidhi D
╠²
The document discusses the molecular structure of water. It explains that a water molecule is formed by two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom bonded together at an angle of 104.5 degrees. The polarity of the water molecule arises from oxygen's higher electronegativity which gives it a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atoms a partial positive charge. This polar nature is an important feature of water and causes it to have unique properties.Electrolytic Dissociation
Electrolytic DissociationLaurikitikis Velazquez
╠²
The electrolytic dissociation is a mechanical process that allows ionic compounds to dissolve in water. When ionic compounds dissolve in water, the polarity of the water molecule causes the ions to separate. Positively charged ions are attracted to the negatively charged part of the water molecule, and negatively charged ions are attracted to the positively charged part. This produces homogeneous mixtures of separated ions called electrolyte solutions.Electrolytes
Electrolytesethelremitio
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts about solutions and electrolytes from a chemistry post-lab report. It defines solute, solvent, and solution. It explains that electrolytes are substances that produce solutions able to conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Strong acids and bases are strong electrolytes as they completely ionize in water, while weak acids and bases only partially ionize, making them weak electrolytes. The document compares strong and weak electrolytes and provides examples of each.Hemoglobin Electrophoresis (Biochemistry)
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis (Biochemistry)Charmaine Ignatius
╠²
Hemoglobin is a tetramer composed of two alpha and two beta subunits that carries oxygen in red blood cells. Each subunit contains an iron molecule that binds oxygen. Hemoglobin picks up oxygen in the lungs and delivers it to tissues while maintaining a high oxygen affinity in the lungs and low affinity in tissues. Variations in hemoglobin structure can result in hemoglobinopathies like sickle cell anemia, where the abnormal hemoglobin polymerizes and causes red blood cells to sickle.Solutions
SolutionsMichelle Jeffcoat
╠²
- The document discusses solutions and mixtures, explaining that a solution is a type of mixture where a solid dissolves evenly into a liquid. It provides examples like sugar dissolving in water to form a solution.
- Key properties of solutions are discussed, such as solids breaking apart into particles when dissolved and how solutions can be separated through evaporation.
- An activity is described where students use a diagram to identify items that do or do not dissolve in water to form solutions.Mixtures powerpoint
Mixtures powerpointJose Mart├Łnez Alcolea
╠²
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are physically mixed together without undergoing a chemical reaction. Mixtures can be heterogeneous, with each component clearly visible, or homogeneous, where the components are evenly distributed and not visible individually. Mixtures differ from compounds in that their components can be separated by physical means and do not have a fixed composition.Chemistry of solutions
Chemistry of solutionsHoney Jean Duvidoo
╠²
This document discusses chemistry of solutions. It defines key terms like solute, solvent and solution. It explains that a solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. The solute is dispersed uniformly throughout the solvent. Factors that affect solubility are also discussed, like temperature, pressure, molecular size and polarity. Henry's law is introduced, which states that the solubility of a gas is directly proportional to its partial pressure.Mixtures & Solutions PPT
Mixtures & Solutions PPTsammenheuser
╠²
This document defines and describes mixtures and solutions. It states that a mixture is made of two or more substances that are not chemically combined and can exist as solids, liquids, gases, or combinations. Mixtures are either heterogeneous, where the phases can be seen, or homogeneous, where they cannot. A solution is a special type of homogeneous mixture containing a solute dissolved in a solvent. It discusses how to make solutions by dissolving a solute in a solvent, and defines concepts like solubility, dilute vs concentrated solutions, saturated solutions, and super-saturated solutions.Solution & Solubility
Solution & Solubilityitutor
╠²
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where the solute is dispersed uniformly throughout the solvent. The solubility of a solute is dependent on temperature, pressure, and the nature of the solute and solvent. Solubility is expressed as the maximum grams of solute that will dissolve per 100 grams of solvent. Colligative properties, such as boiling point elevation and freezing point depression, depend only on the number of solute particles and not their identity.Free radicals
Free radicalsKhalid Hussain
╠²
Free radicals are atoms, molecules, or ions with unpaired electrons that make them highly reactive. They are formed through processes like homolysis and oxidation-reduction reactions. Free radical stability is determined by factors like conjugation, hybridization, and hyperconjugation which disperse and stabilize the unpaired electron. Common examples of stable radicals include molecular oxygen and organic radicals within conjugated systems.My Thesis Defense Presentation
My Thesis Defense PresentationDavid Onoue
╠²
The document discusses the importance of conversations in developing relationships. It notes that while some advocate "selling the sizzle not the steak", engaging in meaningful conversations where common ground is found is better. The results of interviews with people on their dating experiences and favorite companies suggest that conversations matter because that's how relationships are formed. People are more inclined to connect with companies or products that fit their personality or lifestyle.Dissertation oral defense presentation
Dissertation oral defense presentationDr. Naomi Mangatu
╠²
This document outlines the dissertation of Naomi M. Mangatu titled "Beyond the Glass Ceiling: A Phenomenological Study of Women Managers in the Kenyan Banking Industry." The study explores the lived experiences of 24 women managers in Kenyan banks to understand factors contributing to or hindering their advancement to CEO positions. It uses a qualitative phenomenological research method and the van Kaam 7-step process for data analysis. The findings reveal that while women have made progress in their careers, few break through the glass ceiling to attain top leadership roles in Kenyan banks due to social pressures, cultural norms, and expectations that suppress women's advancement.Prepare your Ph.D. Defense Presentation
Prepare your Ph.D. Defense PresentationChristian Glahn
╠²
The document provides guidance for preparing a Ph.D. defense presentation in 3 sections. It discusses focusing the presentation on the research problem, question, methodology, key results and implications for the field in 20 minutes. It also addresses answering reviewer questions and demonstrating the contribution to the research domain. Key aspects of the research problem, question, methodology, results and implications are defined. The document provides exercises for identifying the type of research problem and phrasing the main research question.Ad
Similar to Dssociation vs ionization.ppt (20)
Ch 17sec3
Ch 17sec3St. Mary's HS
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts about aqueous solutions, including:
- Solutions contain a solvent and one or more solutes
- Ionic compounds generally dissolve well in water due to ion separation through solvation
- "Like dissolves like" - polar substances dissolve in water and nonpolar substances do not
- Electrolytes conduct electricity in solution while nonelectrolytes do not
- Hydrates contain water within their crystalline structure.Ln 5 electrolysis drew
Ln 5 electrolysis drewlohitkumardrawal
╠²
Electrolysis is the process of using a direct electric current to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions. It involves the decomposition of an electrolyte into its constituent ions by the removal or addition of electrons to the ions. During electrolysis, ions migrate to the electrodes where they undergo oxidation or reduction reactions. In the electrolysis of molten lead bromide, lead ions are reduced to metallic lead at the cathode, while bromide ions are oxidized to bromine gas at the anode. When an aqueous solution of copper sulfate is electrolyzed using copper electrodes, copper ions are reduced at the cathode to form metallic copper while oxygen gas forms at the anode. Electrolysis requires an electrolyte, electrodes, and a direct current powerAdvchemchapt4 101015123318-phpapp02
Advchemchapt4 101015123318-phpapp02Cleophas Rwemera
╠²
This document provides information on types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry. It discusses the common water molecule and how water acts as a solvent. It describes different types of solutions, including strong and weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Precipitation, acid-base, and oxidation-reduction reactions are introduced. Methods for writing balanced and net ionic equations are presented. Finally, techniques for performing stoichiometric calculations on reactions in solution, including determining limiting reactants and amounts of products formed, are covered.Arrhenius theory.pptx
Arrhenius theory.pptxUnknown Unknown
╠²
The document summarizes Arrhenius theory of acids and bases as proposed by Svante Arrhenius in 1887. The key points are:
1) Arrhenius proposed that acids donate H+ ions and bases donate OH- ions when dissolved in water.
2) Electrolytes conduct electricity in solution by dissociating into ions, while nonelectrolytes do not dissociate or conduct.
3) The theory explained several phenomena like heat of neutralization and differentiation of strong/weak electrolytes but had limitations like not explaining ion formation mechanisms.5.2.1
5.2.1Kenton Hemsing
╠²
When salts dissolve in water, the polar water molecules interact with the positive and negative ions of the salt, attracting them and breaking apart the crystal structure. Electrolytes separate into ions that move freely in solution while maintaining net neutral charge. Dissociation equations represent electrolytes dissolving as solute separating into aqueous ions. These equations must be balanced and show correct ionic charges and physical states. Dissociation refers to ionic compounds breaking apart while ionization describes molecules breaking into separate particles.Acids, Bases, and Salts: Properties & Reactions
Acids, Bases, and Salts: Properties & ReactionsRejoshaRajendran
╠²
Acids, Bases, and Salts
Acids
Taste sour and turn blue litmus red.
Release HŌü║ (Hydrogen) ions in solution.
Example: HCl (Hydrochloric acid), HŌééSOŌéä (Sulfuric acid).
Bases
Taste bitter and feel soapy, turn red litmus blue.
Release OHŌü╗ (Hydroxide) ions in solution.
Example: NaOH (Sodium hydroxide), KOH (Potassium hydroxide).
Neutralization Reaction
Acid + Base ŌåÆ Salt + Water
Example: HCl + NaOH ŌåÆ NaCl + HŌééO
Salts
Formed from neutralization of an acid and a base.
Can be acidic, basic, or neutral.
Example: NaCl (Table salt), CuSOŌéä (Copper sulfate).
pH Scale
Measures acidity or basicity (0-14).
pH < 7 ŌåÆ Acidic, pH = 7 ŌåÆ Neutral, pH > 7 ŌåÆ Basic.388770.pptx.ppt
388770.pptx.pptssuser9fae69
╠²
This document provides an overview of electrolytes and solutions. It defines electrolytes as substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, allowing them to conduct electricity. Strong electrolytes dissociate completely while weak electrolytes only partially dissociate. Arrhenius' theory of electrolytic dissociation explains how electrolytes break up into ions in solution. The degree of dissociation depends on factors like temperature and concentration. Ostwald's dilution law describes how the degree of dissociation changes with concentration for weak electrolytes. Ionic equations represent the dissociation of electrolytes into ions.11 bctopic6
11 bctopic6King Ali
╠²
When solutions of ionic compounds are mixed, precipitation reactions can occur if the mixing produces an insoluble ionic compound. For example, when solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed, a precipitate of insoluble silver chloride will form. Only the ions that react (Ag+ and Cl-) are shown in the balanced net ionic equation, with any spectator ions (Na+ and NO3-) that do not react omitted. The precipitate can be isolated by filtering the mixture.General chemistry academic journal (sample)
General chemistry academic journal (sample)Vincentius Soesanto
╠²
This document provides definitions and explanations of acids and bases according to different theories. It discusses the Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions. It also covers pH, ionization constants, and the auto-ionization of water. Key points include: 1) Arrhenius defined acids/bases as producing H+/OH- ions in water, while Br├Ėnsted-Lowry defined them as proton donors/acceptors; 2) Lewis defined them based on electron pair sharing; 3) pH is a measure of H3O+ concentration; 4) the product of [H3O+] and [OH-] is constant.Ionic Equilibrium
Ionic Equilibrium Ednexa
╠²
This document discusses ionic equilibrium and electrolytes. It defines electrolytes as substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water by dissociating into ions. Electrolytes are divided into strong and weak based on their degree of ionization. Strong electrolytes almost completely ionize while weak electrolytes ionize only partially. The document discusses Arrhenius theory of electrolytic dissociation and factors that affect the degree of ionization like concentration, temperature, and presence of a common ion. It also defines concepts like isohydric solutions and dissociation constants.ionicequilibrium-150530122047-lva1-app6891.pdf
ionicequilibrium-150530122047-lva1-app6891.pdfAtiyyaS
╠²
This document provides an overview of electrolytes, acids, and bases according to different theories. It defines strong and weak electrolytes, and lists examples of each. It then summarizes the Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories of acids and bases. The Arrhenius theory defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions in water and bases as those that produce hydroxide ions. The Bronsted-Lowry theory broadened this to include proton donors and acceptors. The Lewis theory further expanded the definition to any electron pair acceptor or donor.Ionic equilibrium
Ionic equilibriumShivani Singh
╠²
The document provides an overview of electrolytes, acids, and bases, detailing their classifications as strong and weak electrolytes according to their ionization in aqueous solutions. It discusses different theories of acids and bases, including the Arrhenius, Br├Ėnsted-Lowry, and Lewis definitions, along with their strengths and limitations. Key concepts such as ionic equilibrium, conjugate acid-base pairs, and the roles of various ions in biological systems are highlighted.ELECTROLYSIS PPT.pptxvghjkghjvhjcbbvhjmvgnb
ELECTROLYSIS PPT.pptxvghjkghjvhjcbbvhjmvgnbthesciencehubprg
╠²
Electrolysis is a process that involves the decomposition of chemical compounds using direct electric current, facilitating the movement of ions in solutions. Electrolytes can be strong or weak, with strong electrolytes completely dissociating in solution, whereas weak electrolytes only partially dissociate. The document covers various aspects of electrolysis, including applications such as electroplating and the principles of selective discharge of ions at electrodes.Chapter 14.1 : Compounds in Aqueous Solutions
Chapter 14.1 : Compounds in Aqueous SolutionsChris Foltz
╠²
1) Ionic compounds dissolve in water by dissociating into their constituent ions. For example, NaCl dissociates into Na+ and Cl- ions in water.
2) Aluminum sulfate, Al2(SO4)3, dissociates into 2 Al3+ and 3 SO42- ions when dissolved in water, producing a total of 5 moles of ions from 1 mole of the compound.
3) Precipitation reactions occur when opposite ions combine to form an insoluble ionic compound. For example, combining solutions of (NH4)2S and Cd(NO3)2 will produce the insoluble precipitate CdS.what are solutions.docx
what are solutions.docxSesirekhaRavinuthula
╠²
This document discusses key concepts related to solutions and acid-base chemistry, including:
- Definitions of solutions, solvents, solutes, electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Common examples are provided.
- Dissociation and hydration of ionic compounds in solution. Equations are given to represent these processes.
- Precipitation reactions and how to write balanced molecular, ionic, and net ionic equations.
- Arrhenius definitions of acids and bases. Examples of strong and weak acids and bases ionizing in water are given through chemical equations.
- Key reactions include neutralization and acid-base reactions where examples of writing balanced equations are provided.Chemical reaction occurring in water (dadiq)
Chemical reaction occurring in water (dadiq)Lithlith Bernal
╠²
This document discusses three types of chemical reactions that occur in water: precipitation reactions, acid-base reactions, and oxidation-reduction reactions. Precipitation reactions involve the formation of an insoluble ionic compound from ions in solution. Acid-base reactions involve acids donating protons and bases accepting protons to form water. Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the exchange of electrons between reactants, with one species being reduced and the other being oxidized.Adv chem chapt 4
Adv chem chapt 4bobcatchemistry
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts about types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry. It discusses water as a solvent, solubility, strong and weak electrolytes, and precipitation, acid-base, and oxidation-reduction reactions in solution. Calculations involve determining moles and masses of reactants and products using molarity, volumes, and balanced equations. Common indicators like phenolphthalein are used in acid-base titrations.Ch4
Ch4spathman
╠²
This document discusses various concepts related to aqueous reactions and solution stoichiometry including:
- Ionic compounds dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, allowing them to conduct electricity.
- Strong electrolytes fully dissociate into ions while weak electrolytes only partially dissociate.
- Chemical equilibria exist for reactions that proceed in both the forward and backward directions.
- Precipitation reactions form insoluble products that drop out of solution.
- Acid-base reactions form water and salts by neutralizing hydrogen and hydroxide ions.
- Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons and a change in oxidation states.Arrhenius theory of Electrolytic Dissociation.pptx
Arrhenius theory of Electrolytic Dissociation.pptxSarahJabbar6
╠²
"Arrhenius theory of Ionization ,A fundamental concept in physical chemistry ,explain behaviours of electrolyte in solution, catogories of electrolytes degree of dissociation , process of dissociation , ionization constant and a brief introduction about conduction with concept of oxidation and reduction . When ionic solids dissolve in water theions that are adjacent to each.pdf
When ionic solids dissolve in water theions that are adjacent to each.pdfinbox5
╠²
When ionic solids dissolve in water, their ions become surrounded by water molecules through a process called hydration, influenced by ion-dipole forces. The solubility of ionic compounds is governed by the balance of solute-solute, solvent-solvent, and solute-solvent interactions, primarily affected by lattice energy. A compound's solubility relates to its lattice energy, with higher lattice energies correlating with lower solubility, as demonstrated in the example of potassium iodide dissolving in water.Ad
Dssociation vs ionization.ppt
- 2. Dissociation In 1887, Svante August Arrhenius proposed that when a substance dissolves in water, particles of the substance separate from each other and disperse into the solution (called dissociation). Non-electrolytes disperse electrically neutral particles (therefore donŌĆÖt conduct electricity) Electrolytes disperse electrically charged particles called ions (therefore do conduct electricity)
- 3. Why do ionic compounds disperse electrically charged particles? The positive ions are surrounded by the negative end of the polar water molecules. The negative ions are surrounded by the positive end of the polar water molecules. RESULT: The ions at the edges of the ionic crystal are tugged and dislodged until each one is surrounded by water molecules and is floating around as an independent entity DISSOCIATION ŌĆō the separation of ions that occurs when an ionic compound dissolves in water
- 4. Dissociation Equations There are two requirements of dissociation: it must be soluble in water and must be ionic Dissociation Equations: shows the separation of ions in a chemical equation H20(l) is not shown because it is a solvent and is NOT consumed nor changed. It is shown in the aqueous states for the products (aq means ŌĆ£dissolved in waterŌĆØ) Examples: (you still need to make sure the equations are balanced) NaCl(s)’āĀ Na + (aq) + Cl ŌĆō (aq) K3PO4(s) ’āĀ 3 K +(aq) + PO43- (aq)
- 5. Arrhenius acids and bases Arrhenius extended his dissociation theory to include acids and bases Bases ŌĆō ionic compounds containing the hydroxide ion (OH-) that dissolve into cations and OHŌĆō (aq) in water Ba(OH)2 (s) ’āĀ Ba 2+ (aq) + 2 OH-(aq) NOTE: All bases are ionic, so all bases could dissociate if soluble in H2O Acids ŌĆō molecular compounds containing hydrogen that yield H+(aq) ions when they dissolve in water - Acids behave as molecular substances; CH3COOH (l) ŌĆō does not conduct electricity or change the color of litmus paper - As soon as acids are dissolved in water, their acid properties appear; CH3COOH (aq) will conduct electricity and changes litmus paper from blue to red NOTE: Acids are not ionic, so they DO NOT dissociate. They IONIZE.
- 6. Arrhenius came up with the idea of ionization to explain why acids are electrolytic: IONIZATION ŌĆō the reaction of neutral molecular compounds forming charged ions The non-electrolytic molecular compound separates into ions when dissolved in water, becoming electrolytic HCl(g)’āĀ H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
- 7. Dissociation vs. Ionization What is the difference between dissociation and ionization? Both produce (aq) ions... Dissociation, however, is the separation of ions that already exist before dissolving in water M+X-(s) ’āĀ M+ (aq) + X-(aq) Ionization involves the production of new ions, specifically hydrogen ions HX0(aq) ’āĀ H+ (aq) + X-(aq)
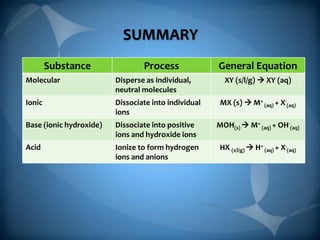
- 8. SUMMARY Substance Process General Equation XY (s/l/g) ’āĀ XY (aq) Molecular Disperse as individual, neutral molecules Ionic Dissociate into individual ions MX (s) ’āĀ M+ (aq) + X-(aq) Base (ionic hydroxide) Dissociate into positive ions and hydroxide ions MOH(s) ’āĀ M+ (aq) + OH-(aq) Acid Ionize to form hydrogen ions and anions HX (s/l/g) ’āĀ H+ (aq) + X-(aq)
