Emerging and Re-emerging Zoonotic Diseases -An Overview
Zoonotic diseases are infections that can be transmitted between animals and humans. Many serious human pathogens are zoonotic, including 61% of human pathogens, 64% of newly identified infectious agents between 1973-1994, and 74.45% of emerging infectious diseases. Zoonoses can be transmitted via direct or indirect contact with infected animals, through animal products, contaminated water, vectors like mosquitoes and ticks, and through the air. Groups at high risk include farmers, livestock owners, veterinarians, and individuals with weak immune systems. Zoonotic diseases are caused by a variety of disease-causing agents including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi. Prevention strategies include proper hygiene, avoiding contact with sick or wild














Recommended


























































More Related Content
What's hot (20)








































Similar to Emerging and Re-emerging Zoonotic Diseases -An Overview (20)






































Recently uploaded (20)






































Emerging and Re-emerging Zoonotic Diseases -An Overview
- 1. Zoonotic Diseases Presenter Dr Gazanfar Abass M.V.Sc. (VPH-IVRI) Clinical Pathologist, DIO, Baramulla Dept. of Animal Husbandry, Kashmir
- 2. 2 What are zoonoses? Zoonosis (singular) / Zoonoses (plural) Zoon = animals Noses = diseases Infections or agents that are naturally transmitted Animals Humans Diseases and infections which are naturally transmitted between vertebrate animals and humans - WHO 1959
- 3. Why zoonotic diseases are important ? ’üģ 61% (868 / 1415) of human pathogens are shared by animals (Zoonoses) (Woolhouse et al., 2005) ’üģ 64% (14/ 22) infectious agents identified from1973-1994 are zoonoses (Chomel, 2003) ’üģ 74.45% (131/177) of emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic in origin (Woolhouse et al., 2019)
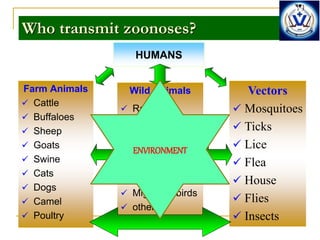
- 4. Who transmit zoonoses? Farm Animals ’ā╝ Cattle ’ā╝ Buffaloes ’ā╝ Sheep ’ā╝ Goats ’ā╝ Swine ’ā╝ Cats ’ā╝ Dogs ’ā╝ Camel ’ā╝ Poultry Wild Animals ’ā╝ Rats ’ā╝ Mice/rodents ’ā╝ Squirrels ’ā╝ Raccoons ’ā╝ Foxes ’ā╝ Bats ’ā╝ Migratory birds ’ā╝ others Vectors ’ā╝ Mosquitoes ’ā╝ Ticks ’ā╝ Lice ’ā╝ Flea ’ā╝ House ’ā╝ Flies ’ā╝ Insects HUMANS ENVIRONMENT
- 5. How do ZDŌĆÖs spread? ’ü« Direct contact ’ü« Faeco-oral route ’ü« By air (aerosol) ’ü« Animal bite or saliva ’ü« Insects ’ü« Infected objects ’ü« Water
- 6. How do ZDŌĆÖs spread?......Cont. ’ü« Unclean hands and fingers ’ü« Animal products ’ü▒ Milk ’ü▒ Meat ’ü▒ Egg ’ü▒ Wool ’ü▒ Fish ’ü▒ blood
- 7. 7 who are at risk in humans ? ’ü« Population at higher risk ’ü▒ Infants ’ü▒ Children <5 ’ü▒ Pregnant women ’ü▒ People undergoing chemotherapy ’ü▒ People with organ transplants ’ü▒ People with HIV/AIDS ’ü▒ Elderly ’ü« Most susceptible groups ( Farmers, livestock owners & occupational groups) 1. Share air and space with animals 2. Frequent contact with domestic and wild animals
- 8. Classification of ZDŌĆÖs based on Etiological agents. ’ü« Bacterial Ex. Brucellosis, leptospirosis, listeriosis, TB, Anthrax, etc ’ü« Viral Ex. Coronavirus (Co-SRS, nCOVID-19), Bird flu, Swine flu, Rabies, JE, KFD, Dengue, etc ’ü« Rickettsial and Chlamydial Ex. scrub typhus, RMSF, Ornithosis,etc ’ü« Mycotic / Fungal Ex. Dermatophytosis, Cryptococcosis, Histoplasmosis
- 9. Classification based on Etiological agents. ’ā╝ Protozoan : Ex. Toxoplasmosis, Babesiosis, Leishmaniasis, African Trypanosomiasis ’ā╝ Trematode / Fluke : Ex. Fascioliasis, Amphistomiasis, Schistosomiasis ’ā╝ Cestodes / Tapeworms : Ex. Cysticercosis, Hydatidosis, Coenuriasis ’ā╝ Nematodes / Round worms : Ex. Trichinellosis, Cutaneous Larva migrans, Thelaziasis Spreads Taeniasis, Cysticercosis, Hydatidosis & Coenuriasis
- 11. ANTHRAX
- 12. CONTROL AND PREVENTION ŌĆó Avoid close contact ŌĆó Avoid touching eyes, nose & mouth ŌĆó Stay home when feeling sick ŌĆó Cover your cough/sneeze with tissue ŌĆó Wash hands regularly with Dettol & scrub with Sanitizer CORONAVIRUS
- 13. RABIES
- 14. Control & Prevention ’ü▒ Wash hands thoroughly and frequently ’ü▒ Consume Pasteurized or properly boiled milk ’ü▒ Proper cooking of meat ’ü▒ Clean eggs before use and donŌĆÖt consume spoiled fishes ’ü▒ Regular health checkups for occupational high risk groups ’ü▒ Immunization/vaccination ’ü▒ Regular testing ’ü▒ Reducing contact with animals ’ü▒ Properly animal management



