emphasis_HF_trial.ppt
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes142 views
The EMPHASIS-HF trial studied the effects of adding eplerenone to recommended medical therapy in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms. The trial found that adding eplerenone reduced the primary composite outcome of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization by 37% compared to placebo. Eplerenone also reduced mortality from any cause by 24% and hospitalization from any cause by 23%. The benefits were consistent across subgroups. Safety analysis found eplerenone increased serum potassium similarly to other trials. The study concluded that addition of eplerenone to recommended medical therapy reduces morbidity and mortality for patients with mild systolic heart failure.
1 of 40
Download to read offline







































Recommended
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy



Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapycardiologycases
╠²
This document summarizes the results of the CARE-HF trial, which investigated the effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in patients with heart failure. The trial found that CRT significantly reduced the risks of death and hospitalization compared to medical therapy alone. For every 9 patients treated with CRT, 1 death and 3 hospitalizations were prevented. The results provide strong evidence that CRT can improve outcomes for appropriately selected heart failure patients.Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy



Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapycardiologycases
╠²
This document summarizes the results of the CARE-HF trial, which investigated the effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in patients with heart failure. The trial found that CRT significantly reduced the risks of death and hospitalization compared to medical therapy alone. For every 9 patients treated with CRT, 1 death and 3 hospitalizations were prevented. The results provide strong evidence that CRT can reduce both morbidity and mortality in patients with moderate to severe heart failure.Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy



Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapycardiologycases
╠²
This document summarizes the results of the CARE-HF trial, which investigated the effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure. The trial found that CRT significantly reduced the risks of death and hospitalization compared to medical therapy alone. For every 9 CRT devices implanted, 1 death and 3 hospitalizations were prevented. The results provided evidence that CRT can improve outcomes for patients with heart failure.Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy



Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapycardiologycases
╠²
This document summarizes the results of the CARE-HF trial, which investigated the effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in patients with heart failure. The trial found that CRT significantly reduced the risks of death and hospitalization compared to medical therapy alone. For every 9 patients treated with CRT, 1 death and 3 hospitalizations were prevented. The results provide strong evidence that CRT can reduce both morbidity and mortality in patients with moderate to severe heart failure.Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy



Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapycardiologycases
╠²
This document summarizes the results of the CARE-HF trial, which investigated the effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in patients with heart failure. The trial found that CRT significantly reduced the risks of death and hospitalization compared to medical therapy alone. For every 9 patients treated with CRT, 1 death and 3 hospitalizations were prevented. The results provide strong evidence that CRT can improve outcomes for appropriately selected heart failure patients.Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy



Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapycardiologycases
╠²
This document summarizes the results of the CARE-HF trial, which investigated the effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in patients with heart failure. The trial found that CRT significantly reduced the risks of death and hospitalization compared to medical therapy alone. For every 9 patients treated with CRT, 1 death and 3 hospitalizations were prevented. The results provide strong evidence that CRT can improve outcomes for appropriately selected heart failure patients.MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST(MRA)-NEGLECTED PILLAR.pptx



MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST(MRA)-NEGLECTED PILLAR.pptxFarhinIqbal2
╠²
MINERALO CORTICOID RECEPTOR ANATAGONIST ARE IMPORTANT THERAPEUTICS IN HEART FAILURE BUT OFTEN NEGLECTEDGroup 19 Poster Presentation



Group 19 Poster PresentationAnish M. Patel, PharmD, RPh
╠²
This document analyzes the benefits of aldosterone receptor antagonists (ARAs) in treating heart failure based on evidence from major clinical trials. ARAs such as spironolactone and eplerenone, when added to standard heart failure therapies, were shown to significantly reduce mortality and hospitalization rates compared to placebo in patients with NYHA class II-IV symptoms and reduced ejection fraction. However, ARAs remain underutilized in practice due to concerns about side effects like hyperkalemia. Ongoing research is exploring more selective next-generation ARAs that may have fewer safety issues.Tentiran GP Provita Acute Heart Failure (2).pptx



Tentiran GP Provita Acute Heart Failure (2).pptxWayan Gunawan
╠²
Acute heart failure requires urgent evaluation and management according to three steps:
1. Initial management focuses on treating life-threatening conditions like acute coronary syndrome, arrhythmias, or pulmonary embolism.
2. Diagnosis involves ruling in or ruling out acute heart failure based on symptoms of congestion and hypoperfusion.
3. Management is then based on symptoms, providing diuretics and vasodilators for congestion or inotropes for hypoperfusion, with a goal of achieving a "warm dry" state for discharge. Early initiation of evidence-based oral therapies and close follow-up after discharge are also emphasized.CARDIO ONCOLOGY



CARDIO ONCOLOGYflasco_org
╠²
CARDIO ONCOLOGY, MICHAEL FRADLEY, MD, UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH FLORIDA HEALTH & ELAINE MACOMB, ARNP, MAYO CLINIC FLORIDAGuidelines and beyond new drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejectio...



Guidelines and beyond new drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejectio...ahvc0858
╠²
This document provides information on new guidelines and therapies for heart failure patients. It begins by outlining the challenges of managing heart failure patients and their high mortality rates. It then discusses the history of heart failure treatments from ACE inhibitors in the 1990s to newer drugs like ARNi's. The document defines the different types of heart failure - HFrEF, HFmrEF, and HFpEF - and their diagnostic criteria. It explains how neprilysin inhibition enhances natriuretic peptides while simultaneously suppressing the RAAS. Finally, it summarizes that the new drug LCZ696 combines neprilysin inhibition with an ARB to reduce mortality and hospitalization in heart failure patients beyond existing neurohormonal therapiesinsuficiencia cardiaca, lo nuevo 



insuficiencia cardiaca, lo nuevo aorlandojose7
╠²
This document discusses heart failure, including its definition, epidemiology, pathogenesis, classification, clinical features, and management. Some key points include:
- Heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome resulting from structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood.
- It affects over 21 million adults worldwide and its incidence increases significantly with age. Mortality rates remain around 50% within 5 years of diagnosis.
- Heart failure is classified into HFrEF (reduced ejection fraction) and HFpEF (preserved ejection fraction), which have different underlying pathophysiologies.
- Management of HFrEF focuses on drugs that have been shown to reduce mortality in landmark trials, including ACE inhibitorsHeart Failure : what is new by Dr. Vaibhav Yawalkar MD DM Cardiology, Consult...



Heart Failure : what is new by Dr. Vaibhav Yawalkar MD DM Cardiology, Consult...vaibhavyawalkar
╠²
Heart Failure : what is new by Dr. Vaibhav Yawalkar MD DM Cardiology, Consultant Interventional Cardiologist, Nagpur, MH, Indialandmarck trial in HF.pdf



landmarck trial in HF.pdfAdelSALLAM4
╠²
Catheter ablation was associated with lower rates of death and hospitalization for heart failure compared to medical therapy alone in patients with reduced ejection fraction heart failure and atrial fibrillation according to the CASTLE-AF trial. The PARADIGM-HF trial found that the combination drug sacubitril-valsartan reduced rates of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization compared to enalapril in heart failure patients. The MOMENTUM-3 trial showed that a new fully magnetically levitated left ventricular assist device, the HeartMate 3, had fewer device malfunctions compared to the axial-flow HeartMate II pump.Recent trials in heart failure



Recent trials in heart failureArunShivashankarappa
╠²
- The PARADIGM-HF trial found that treatment with LCZ696 (a combination of sacubitril and valsartan) was more effective at reducing cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization compared to enalapril. LCZ696 also reduced overall mortality more than enalapril.
- The CASTLE-AF trial found that catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation was superior to pharmacological rate or rhythm control methods for reducing mortality and heart failure hospitalization in patients with left ventricular dysfunction and atrial fibrillation. Ablation resulted in more time in sinus rhythm and a greater increase in left ventricular ejection fraction.
- The document reviewed results from major clinical trials investigating treatments for heart failureOpciones farmacol├│gicas en el manejo de insuficiencia cardiaca - Revisi├│n Can...



Opciones farmacol├│gicas en el manejo de insuficiencia cardiaca - Revisi├│n Can...Juan Jos├® Araya Cort├®s
╠²
This review summarizes the pharmacologic options for managing systolic heart failure, focusing on modulating pathways through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are recommended for all patients with reduced ejection fraction as clinical trials showed they reduce mortality and attenuate ventricular remodeling. Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are an alternative for those intolerant of ACE inhibitors. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists further block the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and clinical trials demonstrated reduced mortality when added to standard therapy.Optimizing heart failure management



Optimizing heart failure managementikramdr01
╠²
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) and implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) can help optimize heart failure management. CRT improves symptoms, reduces hospitalizations, and increases survival in patients with reduced ejection fraction, left bundle branch block, and wide QRS duration. ICDs prevent sudden cardiac death in high-risk patients with prior heart failure, low ejection fraction, or history of dangerous arrhythmias. New devices use adaptive and multi-point pacing to better resynchronize the left ventricle. Device therapy improves outcomes when guided by clinical evidence and used in appropriate heart failure patients.apihf-210411145928.pptx



apihf-210411145928.pptxaorlandojose7
╠²
This document provides an overview of heart failure. It defines heart failure as a clinical syndrome resulting from structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood. It notes that the lifetime risk of developing heart failure is 20% at age 40. Incidence increases with age, rising to over 80 per 1000 individuals over age 85. Mortality rates remain around 50% within 5 years of diagnosis. The document discusses classifications of heart failure, pathogenesis, clinical features, management, and landmark trials that have improved outcomes for HFrEF.Cardiogenic shock in emergency medicine



Cardiogenic shock in emergency medicineImhotep Virtual Medical School
╠²
CV Pharm Course Clinical Correlate Articles
http://www.imhotepvirtualmedsch.com/ans--and-cv-pharm-course.phpHeart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]![Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/heartfailureanupdateautosaved-110321012825-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/heartfailureanupdateautosaved-110321012825-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/heartfailureanupdateautosaved-110321012825-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/heartfailureanupdateautosaved-110321012825-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]SMSRAZA
╠²
The document discusses congestive cardiac failure (heart failure) and its management. It provides details on:
- The high prevalence and mortality of heart failure.
- Current medical therapies including ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists that have been shown to improve survival.
- Device therapies like cardiac resynchronization therapy and implantable cardioverter defibrillators that treat symptoms and reduce mortality.
- The benefits of multidisciplinary and integrated care approaches including telehealth monitoring in improving outcomes for heart failure patients.Journal club presentation



Journal club presentationshahed1982
╠²
The document summarizes a journal presentation comparing the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants (NOACs) to warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation patients. It provides background on atrial fibrillation and an overview of 4 large randomized controlled trials evaluating dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban. A meta-analysis of these trials found NOACs reduced the risk of stroke and systemic embolism by 19% and lowered mortality compared to warfarin, while increasing gastrointestinal bleeding but decreasing intracranial hemorrhage. NOACs showed consistent benefits across patient subgroups.Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S)



Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S)Zerva
╠²
This randomized controlled trial involved 4444 patients with coronary heart disease who were assigned to either simvastatin or placebo treatment. Over the median 5.4 year follow-up period, simvastatin treatment reduced total mortality by 30% compared to placebo. Specifically, 256 patients died in the placebo group compared to 182 in the simvastatin group, representing a relative risk of death of 0.70 for those receiving simvastatin. Simvastatin also reduced major coronary events such as heart attacks and procedures by 34% compared to placebo. This study provides evidence that long-term cholesterol lowering with simvastatin improves survival rates for patients with coronary heart disease.Heart failure api



Heart failure apidrucsamal
╠²
1) Heart failure is a major and growing public health problem, affecting over 15 million people in Europe with a prevalence of over 2-3% overall and 10-20% in those over 70 years old.
2) It is a primary cause of hospital admissions and readmissions, accounting for 5% of admissions and 40% of patients being readmitted or dying within a year. It represents a significant cost burden on healthcare systems.
3) Diagnosis involves clinical examination, ECG, chest x-ray, echocardiography and natriuretic peptide levels of BNP or NT-proBNP which can help differentiate between possible and likely heart failure.
4) Heart failure is now recognized as aMiocardiopatia hipertrofica



Miocardiopatia hipertroficaCardioTeca
╠²
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is characterized by thickening of the left ventricle in the absence of other cardiac causes. It has diverse morphological presentations and is the most common genetic cardiovascular disease. Symptoms include heart failure, chest pain, and syncope. Treatment involves managing symptoms through medications, surgery such as septal myectomy for obstruction, and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators for high-risk patients. Screening of family members is recommended due to its genetic basis. HCM has variable clinical outcomes ranging from few symptoms to sudden cardiac death.Mangement of chronic heart failure 



Mangement of chronic heart failure Irfan iftekhar
╠²
It was written by me for a client. I was late so it was not accepted, hence I am uploading it for other friends.Mangement of chronic heart failure 93432-rephrased



Mangement of chronic heart failure 93432-rephrasedIrfan iftekhar
╠²
Cardiac resynchronization therapy significantly reduces morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure. A randomized controlled trial found that cardiac resynchronization reduced the primary endpoint of death from any cause by 36% compared to medical therapy alone. Mortality was lower in the cardiac resynchronization group, demonstrating improved outcomes. While cardiac resynchronization is an effective treatment, its cost-effectiveness remains uncertain due to the therapy's expense. Further research is still needed to determine its overall value.Eplerenone revised



Eplerenone revisedlawfu
╠²
This study investigated the effects of adding eplerenone to evidence-based heart failure therapies in patients with mild systolic heart failure symptoms. The study randomized 2,737 patients to receive either eplerenone or placebo. The primary outcome of death from cardiovascular causes or hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 18.3% of the eplerenone group compared to 25.9% of the placebo group, demonstrating that eplerenone reduced risks. The trial was stopped early due to these benefits after a median follow up of 21 months. Eplerenone was found to provide cardiovascular protection in patients with heart failure compared to placebo.Organophosphorus_Poisoning_final.pptx



Organophosphorus_Poisoning_final.pptxbiplave karki
╠²
1. Organophosphorus compounds are commonly used as pesticides and chemical warfare agents. They work by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, leading to excess acetylcholine and overstimulation of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors.
2. Treatment for organophosphorus poisoning involves atropine to block muscarinic effects, oximes like pralidoxime to reactivate acetylcholinesterase, benzodiazepines for seizures, supportive care, and decontamination measures.
3. The dosage of atropine must be titrated until target endpoints are reached and maintained with continuous infusion to prevent rebound symptoms. Too high of a dose can cause atropinism.ABPM biplave.pptx



ABPM biplave.pptxbiplave karki
╠²
This document discusses ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) and its role in clinical practice. It provides details on how ABPM works, the various indices that can be analyzed from ABPM reports, and its advantages over office blood pressure readings. ABPM provides a more accurate assessment of a patient's true blood pressure over 24 hours and can detect conditions like white coat hypertension. It is useful for diagnosing hypertension, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and predicting cardiovascular outcomes.More Related Content
Similar to emphasis_HF_trial.ppt (20)
Tentiran GP Provita Acute Heart Failure (2).pptx



Tentiran GP Provita Acute Heart Failure (2).pptxWayan Gunawan
╠²
Acute heart failure requires urgent evaluation and management according to three steps:
1. Initial management focuses on treating life-threatening conditions like acute coronary syndrome, arrhythmias, or pulmonary embolism.
2. Diagnosis involves ruling in or ruling out acute heart failure based on symptoms of congestion and hypoperfusion.
3. Management is then based on symptoms, providing diuretics and vasodilators for congestion or inotropes for hypoperfusion, with a goal of achieving a "warm dry" state for discharge. Early initiation of evidence-based oral therapies and close follow-up after discharge are also emphasized.CARDIO ONCOLOGY



CARDIO ONCOLOGYflasco_org
╠²
CARDIO ONCOLOGY, MICHAEL FRADLEY, MD, UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH FLORIDA HEALTH & ELAINE MACOMB, ARNP, MAYO CLINIC FLORIDAGuidelines and beyond new drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejectio...



Guidelines and beyond new drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejectio...ahvc0858
╠²
This document provides information on new guidelines and therapies for heart failure patients. It begins by outlining the challenges of managing heart failure patients and their high mortality rates. It then discusses the history of heart failure treatments from ACE inhibitors in the 1990s to newer drugs like ARNi's. The document defines the different types of heart failure - HFrEF, HFmrEF, and HFpEF - and their diagnostic criteria. It explains how neprilysin inhibition enhances natriuretic peptides while simultaneously suppressing the RAAS. Finally, it summarizes that the new drug LCZ696 combines neprilysin inhibition with an ARB to reduce mortality and hospitalization in heart failure patients beyond existing neurohormonal therapiesinsuficiencia cardiaca, lo nuevo 



insuficiencia cardiaca, lo nuevo aorlandojose7
╠²
This document discusses heart failure, including its definition, epidemiology, pathogenesis, classification, clinical features, and management. Some key points include:
- Heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome resulting from structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood.
- It affects over 21 million adults worldwide and its incidence increases significantly with age. Mortality rates remain around 50% within 5 years of diagnosis.
- Heart failure is classified into HFrEF (reduced ejection fraction) and HFpEF (preserved ejection fraction), which have different underlying pathophysiologies.
- Management of HFrEF focuses on drugs that have been shown to reduce mortality in landmark trials, including ACE inhibitorsHeart Failure : what is new by Dr. Vaibhav Yawalkar MD DM Cardiology, Consult...



Heart Failure : what is new by Dr. Vaibhav Yawalkar MD DM Cardiology, Consult...vaibhavyawalkar
╠²
Heart Failure : what is new by Dr. Vaibhav Yawalkar MD DM Cardiology, Consultant Interventional Cardiologist, Nagpur, MH, Indialandmarck trial in HF.pdf



landmarck trial in HF.pdfAdelSALLAM4
╠²
Catheter ablation was associated with lower rates of death and hospitalization for heart failure compared to medical therapy alone in patients with reduced ejection fraction heart failure and atrial fibrillation according to the CASTLE-AF trial. The PARADIGM-HF trial found that the combination drug sacubitril-valsartan reduced rates of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization compared to enalapril in heart failure patients. The MOMENTUM-3 trial showed that a new fully magnetically levitated left ventricular assist device, the HeartMate 3, had fewer device malfunctions compared to the axial-flow HeartMate II pump.Recent trials in heart failure



Recent trials in heart failureArunShivashankarappa
╠²
- The PARADIGM-HF trial found that treatment with LCZ696 (a combination of sacubitril and valsartan) was more effective at reducing cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization compared to enalapril. LCZ696 also reduced overall mortality more than enalapril.
- The CASTLE-AF trial found that catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation was superior to pharmacological rate or rhythm control methods for reducing mortality and heart failure hospitalization in patients with left ventricular dysfunction and atrial fibrillation. Ablation resulted in more time in sinus rhythm and a greater increase in left ventricular ejection fraction.
- The document reviewed results from major clinical trials investigating treatments for heart failureOpciones farmacol├│gicas en el manejo de insuficiencia cardiaca - Revisi├│n Can...



Opciones farmacol├│gicas en el manejo de insuficiencia cardiaca - Revisi├│n Can...Juan Jos├® Araya Cort├®s
╠²
This review summarizes the pharmacologic options for managing systolic heart failure, focusing on modulating pathways through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are recommended for all patients with reduced ejection fraction as clinical trials showed they reduce mortality and attenuate ventricular remodeling. Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are an alternative for those intolerant of ACE inhibitors. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists further block the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and clinical trials demonstrated reduced mortality when added to standard therapy.Optimizing heart failure management



Optimizing heart failure managementikramdr01
╠²
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) and implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) can help optimize heart failure management. CRT improves symptoms, reduces hospitalizations, and increases survival in patients with reduced ejection fraction, left bundle branch block, and wide QRS duration. ICDs prevent sudden cardiac death in high-risk patients with prior heart failure, low ejection fraction, or history of dangerous arrhythmias. New devices use adaptive and multi-point pacing to better resynchronize the left ventricle. Device therapy improves outcomes when guided by clinical evidence and used in appropriate heart failure patients.apihf-210411145928.pptx



apihf-210411145928.pptxaorlandojose7
╠²
This document provides an overview of heart failure. It defines heart failure as a clinical syndrome resulting from structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood. It notes that the lifetime risk of developing heart failure is 20% at age 40. Incidence increases with age, rising to over 80 per 1000 individuals over age 85. Mortality rates remain around 50% within 5 years of diagnosis. The document discusses classifications of heart failure, pathogenesis, clinical features, management, and landmark trials that have improved outcomes for HFrEF.Cardiogenic shock in emergency medicine



Cardiogenic shock in emergency medicineImhotep Virtual Medical School
╠²
CV Pharm Course Clinical Correlate Articles
http://www.imhotepvirtualmedsch.com/ans--and-cv-pharm-course.phpHeart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]![Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/heartfailureanupdateautosaved-110321012825-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/heartfailureanupdateautosaved-110321012825-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/heartfailureanupdateautosaved-110321012825-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/heartfailureanupdateautosaved-110321012825-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Heart failure ŌĆō an update [autosaved]SMSRAZA
╠²
The document discusses congestive cardiac failure (heart failure) and its management. It provides details on:
- The high prevalence and mortality of heart failure.
- Current medical therapies including ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists that have been shown to improve survival.
- Device therapies like cardiac resynchronization therapy and implantable cardioverter defibrillators that treat symptoms and reduce mortality.
- The benefits of multidisciplinary and integrated care approaches including telehealth monitoring in improving outcomes for heart failure patients.Journal club presentation



Journal club presentationshahed1982
╠²
The document summarizes a journal presentation comparing the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants (NOACs) to warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation patients. It provides background on atrial fibrillation and an overview of 4 large randomized controlled trials evaluating dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban. A meta-analysis of these trials found NOACs reduced the risk of stroke and systemic embolism by 19% and lowered mortality compared to warfarin, while increasing gastrointestinal bleeding but decreasing intracranial hemorrhage. NOACs showed consistent benefits across patient subgroups.Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S)



Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S)Zerva
╠²
This randomized controlled trial involved 4444 patients with coronary heart disease who were assigned to either simvastatin or placebo treatment. Over the median 5.4 year follow-up period, simvastatin treatment reduced total mortality by 30% compared to placebo. Specifically, 256 patients died in the placebo group compared to 182 in the simvastatin group, representing a relative risk of death of 0.70 for those receiving simvastatin. Simvastatin also reduced major coronary events such as heart attacks and procedures by 34% compared to placebo. This study provides evidence that long-term cholesterol lowering with simvastatin improves survival rates for patients with coronary heart disease.Heart failure api



Heart failure apidrucsamal
╠²
1) Heart failure is a major and growing public health problem, affecting over 15 million people in Europe with a prevalence of over 2-3% overall and 10-20% in those over 70 years old.
2) It is a primary cause of hospital admissions and readmissions, accounting for 5% of admissions and 40% of patients being readmitted or dying within a year. It represents a significant cost burden on healthcare systems.
3) Diagnosis involves clinical examination, ECG, chest x-ray, echocardiography and natriuretic peptide levels of BNP or NT-proBNP which can help differentiate between possible and likely heart failure.
4) Heart failure is now recognized as aMiocardiopatia hipertrofica



Miocardiopatia hipertroficaCardioTeca
╠²
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is characterized by thickening of the left ventricle in the absence of other cardiac causes. It has diverse morphological presentations and is the most common genetic cardiovascular disease. Symptoms include heart failure, chest pain, and syncope. Treatment involves managing symptoms through medications, surgery such as septal myectomy for obstruction, and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators for high-risk patients. Screening of family members is recommended due to its genetic basis. HCM has variable clinical outcomes ranging from few symptoms to sudden cardiac death.Mangement of chronic heart failure 



Mangement of chronic heart failure Irfan iftekhar
╠²
It was written by me for a client. I was late so it was not accepted, hence I am uploading it for other friends.Mangement of chronic heart failure 93432-rephrased



Mangement of chronic heart failure 93432-rephrasedIrfan iftekhar
╠²
Cardiac resynchronization therapy significantly reduces morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure. A randomized controlled trial found that cardiac resynchronization reduced the primary endpoint of death from any cause by 36% compared to medical therapy alone. Mortality was lower in the cardiac resynchronization group, demonstrating improved outcomes. While cardiac resynchronization is an effective treatment, its cost-effectiveness remains uncertain due to the therapy's expense. Further research is still needed to determine its overall value.Eplerenone revised



Eplerenone revisedlawfu
╠²
This study investigated the effects of adding eplerenone to evidence-based heart failure therapies in patients with mild systolic heart failure symptoms. The study randomized 2,737 patients to receive either eplerenone or placebo. The primary outcome of death from cardiovascular causes or hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 18.3% of the eplerenone group compared to 25.9% of the placebo group, demonstrating that eplerenone reduced risks. The trial was stopped early due to these benefits after a median follow up of 21 months. Eplerenone was found to provide cardiovascular protection in patients with heart failure compared to placebo.Opciones farmacol├│gicas en el manejo de insuficiencia cardiaca - Revisi├│n Can...



Opciones farmacol├│gicas en el manejo de insuficiencia cardiaca - Revisi├│n Can...Juan Jos├® Araya Cort├®s
╠²
More from biplave karki (15)
Organophosphorus_Poisoning_final.pptx



Organophosphorus_Poisoning_final.pptxbiplave karki
╠²
1. Organophosphorus compounds are commonly used as pesticides and chemical warfare agents. They work by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, leading to excess acetylcholine and overstimulation of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors.
2. Treatment for organophosphorus poisoning involves atropine to block muscarinic effects, oximes like pralidoxime to reactivate acetylcholinesterase, benzodiazepines for seizures, supportive care, and decontamination measures.
3. The dosage of atropine must be titrated until target endpoints are reached and maintained with continuous infusion to prevent rebound symptoms. Too high of a dose can cause atropinism.ABPM biplave.pptx



ABPM biplave.pptxbiplave karki
╠²
This document discusses ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) and its role in clinical practice. It provides details on how ABPM works, the various indices that can be analyzed from ABPM reports, and its advantages over office blood pressure readings. ABPM provides a more accurate assessment of a patient's true blood pressure over 24 hours and can detect conditions like white coat hypertension. It is useful for diagnosing hypertension, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and predicting cardiovascular outcomes.Explorer HCM biplave.pptx



Explorer HCM biplave.pptxbiplave karki
╠²
Mavacamten is a targeted inhibitor of cardiac myosin that was evaluated in the EXPLORER-HCM study, a randomized controlled trial involving 251 patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The study found that mavacamten significantly improved exercise capacity and reduced left ventricular outflow tract obstruction compared to placebo after 30 weeks. A higher proportion of patients in the mavacamten group achieved the primary composite endpoint of clinical response. Mavacamten was well-tolerated with adverse event rates similar to placebo. The study demonstrates that mavacamten is an effective new treatment for obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy that addresses the underlying disease mechanism.Myocardial Viability Biplave.pptx



Myocardial Viability Biplave.pptxbiplave karki
╠²
Refers to cardiac muscle that is alive, not dead presence of cellular, metabolic, and microscopic contractile function Clinically LV systolic dysfunction in ischemic heart disease does not always represent irreversible damage and dysfunctional but viable myocardium has the potential to improve its systolic function after revascularization Two basic mechanisms of reversible ischemic dysfunction myocardial stunning myocardial hibernationApproach to seizure



Approach to seizurebiplave karki
╠²
This document provides an overview of approaches to seizure and epilepsy diagnosis and classification. It discusses the differential diagnosis of seizures and conditions that can mimic seizures like syncope. It describes focal seizures which originate in one hemisphere and can involve motor, sensory or cognitive symptoms. Generalized seizures rapidly engage both hemispheres and include absence seizures, tonic-clonic seizures and atonic seizures. Seizures are classified based on their origin and symptoms. The EEG findings for different seizure types are also outlined.Ulcerative collitis



Ulcerative collitisbiplave karki
╠²
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects the large intestine. It has a complex interaction of genetic susceptibility, immunity, and environmental factors. The highest rates are seen in Northern Europe and North America. Clinically, it presents with diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, and can range from limited to the rectum to involving the entire colon. The pathology shows continuous superficial inflammation and regenerative changes. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and immunosuppression.Hepatic encephalopathy final



Hepatic encephalopathy finalbiplave karki
╠²
Hepatic encephalopathy is a neuropsychiatric syndrome caused by liver dysfunction and portosystemic shunting of blood flow. The leading theories for its cause are ammonia toxicity, inflammation, and imbalances in neurotransmitters. It ranges from mild cognitive impairment to coma. Treatment involves identifying and treating precipitants, a low-protein diet, non-absorbable disaccharides to reduce ammonia, and antibiotics to suppress gut bacteria. For persistent cases, additional therapies include branched-chain amino acids, probiotics, and transplantation for severe cases.Uti



Utibiplave karki
╠²
This document defines various types of urinary tract infections including asymptomatic bacteriuria, cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, and catheter-associated bacteriuria. It discusses risk factors for UTIs such as female anatomy, diabetes, pregnancy, and functional or anatomic abnormalities of the urinary tract. UTIs are more common in women than men and the risk increases with age, sexual activity, prior UTIs, and medical conditions like diabetes. Complications can include preterm birth, perinatal death, and pyelonephritis.Ankylosing spondilitis



Ankylosing spondilitisbiplave karki
╠²
Ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the axial skeleton including the spine and sacroiliac joints. It has a strong genetic association with the HLA-B27 gene. The disease begins in the second or third decade of life and is more common in males. It is characterized by inflammation of the joints of the spine which can lead to bony fusion and stiffness over time if left untreated. Symptoms include lower back pain and stiffness that improves with movement and worsens with inactivity.Impacts of diet on serum lipid profile



Impacts of diet on serum lipid profilebiplave karki
╠²
This document discusses the impacts of diet on serum lipid profiles. It begins by describing normal cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism in the body. It then discusses how dietary components like saturated fats, trans fats, fiber, and cholesterol affect serum lipids. Lifestyle modifications like following a low-fat, plant-based diet pattern and engaging in regular physical activity are recommended to lower LDL cholesterol and blood pressure. Several clinical trials are summarized that show how replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats from plants lowers cardiovascular disease risk.Cns infections biplave nams



Cns infections biplave namsbiplave karki
╠²
Acute infections of the nervous system like bacterial meningitis can be life-threatening if not recognized and treated early. The document discusses various acute infections including bacterial meningitis, viral meningitis, encephalitis, and fungal infections. It provides details on the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management of bacterial meningitis, which is often characterized by the classic triad of fever, headache, and neck stiffness, and requires prompt lumbar puncture and antibiotic treatment to identify the pathogen and prevent complications.Paraparesis biplave nams



Paraparesis biplave namsbiplave karki
╠²
1) Paraplegia is defined as impairment of motor function in the lower extremities, which can be caused by lesions in the cerebral cortex, spinal cord, nerves supplying the lower limbs, or muscles directly.
2) Complete paralysis of both lower limbs is known as paraplegia, while partial paralysis is called paraparesis. Lesions that transect motor tracts cause spastic paraplegia or quadriplegia with heightened reflexes.
3) Determining the level and type of spinal cord lesion is important for diagnosis and involves assessing sensory loss, motor weakness, reflex changes, and associated symptoms.Multiple sclerosis biplave



Multiple sclerosis biplavebiplave karki
╠²
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic immune-mediated disease characterized by inflammation and damage to the myelin sheath and neurons in the central nervous system. It typically presents with relapsing and remitting neurological symptoms that vary depending on the location of lesions in the brain and spinal cord. Magnetic resonance imaging is a key diagnostic tool that reveals characteristic white matter lesions in areas like the brainstem and spinal cord in over 95% of patients. While the exact cause is unknown, risk factors include genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers like low vitamin D levels and Epstein-Barr virus exposure.Hemolytic anemia case



Hemolytic anemia casebiplave karki
╠²
Mrs. Gyani Maya Tamang, a 44-year-old woman, presented with jaundice and easy fatigability for 1 month. On examination, she had pallor, icterus, hepatosplenomegaly, and elevated bilirubin. Testing found hemolytic anemia with spherocytes on blood smear and a positive osmotic fragility test, consistent with hereditary spherocytosis. Further workup ruled out other potential causes of hemolytic anemia such as G6PD deficiency, sickle cell disease, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, and drug or toxin-induced hemolytic anemia.Diagnostic modalities in tuberculosis



Diagnostic modalities in tuberculosisbiplave karki
╠²
This document discusses diagnostic modalities for tuberculosis, including both pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB. It provides details on various bacteriological examinations for diagnosing TB, such as sputum smear microscopy, culture, drug susceptibility tests, and molecular techniques like Xpert MTB/RIF and line probe assays. Radiological examinations like chest X-rays are also discussed. The global burden of TB is summarized, with over 10 million new cases and 1.8 million deaths annually. Prompt diagnosis is important for treatment and minimizing transmission.Recently uploaded (20)
Modern Practice Principles in Lung CancerŌĆöFirst Find the Targets, Then Treat ...



Modern Practice Principles in Lung CancerŌĆöFirst Find the Targets, Then Treat ...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Joshua Sabari, MD, discusses NSCLC in this CME activity titled ŌĆ£Modern Practice Principles in Lung CancerŌĆöFirst Find the Targets, Then Treat With Precision: A Concise Guide for Biomarker Testing and EGFR-Targeted Therapy in NSCLC.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aid, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/3VomnBV. CME credit will be available until February 26, 2026.TunesKit Spotify Converter Crack With Registration Code 2025 Free



TunesKit Spotify Converter Crack With Registration Code 2025 Freedfsdsfs386
╠²
TunesKit Spotify Converter is a software tool that allows users to convert and download Spotify music to various formats, such as MP3, AAC, FLAC, or WAV. It is particularly useful for Spotify users who want to keep their favorite tracks offline and have them in a more accessible format, especially if they wish to listen to them on devices that do not support the Spotify app.
https://shorturl.at/LDQ9c
Copy Above link & paste in New TabStrategies for Promoting Innovation in Healthcare Like Akiva Greenfield.pdf



Strategies for Promoting Innovation in Healthcare Like Akiva Greenfield.pdfakivagreenfieldus
╠²
Healthcare innovation has been greatly aided by leaders like Akiva Greenfield, CEO of Nexus, particularly in fields like operational efficiency, revenue cycle management (RCM), and client engagement. In order to ensure both operational success and better patient experiences, Akiva's approach combines technological advancements with an emphasis on improving the human side of healthcare.
Research Hyopthesis and Research Assumption



Research Hyopthesis and Research AssumptionDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
╠²
Research Hyopthesis and AssumptionRestoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...



Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Shaji K. Kumar, MD, and patient Vikki, discuss multiple myeloma in this CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy With GPRC5D-Targeting Options.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4fYDKkj. CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until February 23, 2026.The influence of birth companion in mother care and neonatal outcome



The influence of birth companion in mother care and neonatal outcomelksharma10797
╠²
this content related to birth companionship, role of birth companion in care of mother and neonatal Syncope in dentistry.pptx



Syncope in dentistry.pptxDr Kingshika Joylin
╠²
This presentation provides an overview of syncope, a common medical emergency in dental practice. Created during my internship, this presentation aims to educate dental students on the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and management of syncope with a focus on dental specific considerations.
PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...



PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...ABHAY INSTITUTION
╠²
Personality theory is a collection of ideas that explain how a person's personality develops and how it affects their behavior. It also seeks to understand how people react to situations, and how their personality impacts their relationships.
Key aspects of personality theory
Personality traits: The characteristics that make up a person's personality.
Personality development: How a person's personality develops over time.
Personality disorders: How personality theories can be used to study personality disorders.
Personality and environment: How a person's personality is influenced by their environment. Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Microbiology.pptx



Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Microbiology.pptxDr Punith Kumar
╠²
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing clinical microbiology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, automating workflows, and improving patient outcomes. This presentation explores the key applications of AI in microbial identification, antimicrobial resistance detection, and laboratory automation. Learn how machine learning, deep learning, and data-driven analytics are transforming the field, leading to faster and more efficient microbiological diagnostics. Whether you're a researcher, clinician, or healthcare professional, this presentation provides valuable insights into the future of AI in microbiology.Pediatric Refeeding syndrome: comprehensive overview.pptx



Pediatric Refeeding syndrome: comprehensive overview.pptxGabriel Shamavu
╠²
Refeeding Syndrome in Severely Malnourished Child, compr├®hensive summary by Dr SHAMAVU Gabriel psychosomaticdisorder and it's physiotherapy management



psychosomaticdisorder and it's physiotherapy managementDr Shiksha Verma (PT)
╠²
Psychosomatic disorder Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...



Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Shaji K. Kumar, MD, prepared useful Practice Aids pertaining to multiple myeloma for this CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy With GPRC5D-Targeting Options.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4fYDKkj. CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until February 23, 2026.IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINE



IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINERelianceNwosu
╠²
This presentation emphasizes the role of immunodiagnostics and Immunotherapy. Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptx



Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptxKafrELShiekh University
╠²
Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Co-Chairs and Presenters, Gerald Appel, MD, and Dana V. Rizk, MD, discuss kidney disease in this CME activity titled ŌĆ£Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Pathway Therapies.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/48UHvVM. CME credit will be available until February 25, 2026.delayed recovery of anaesthesia ppt. delayed



delayed recovery of anaesthesia ppt. delayedSimmons2
╠²
delayed recovery from anaesthesia
#anaesthesia#delayed recoveryResearch Problems - Nursing Research....



Research Problems - Nursing Research....Dr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
╠²
Research Problems - Nursing ResearchDistribution of Drugs ŌĆō Plasma Protein Binding and Blood-Brain Barrier



Distribution of Drugs ŌĆō Plasma Protein Binding and Blood-Brain BarrierSumeetSharma591398
╠²
This presentation provides a detailed overview of drug distribution, focusing on plasma protein binding and the blood-brain barrier (BBB). It explains the factors affecting drug distribution, the role of plasma proteins in drug binding, and how drugs penetrate the BBB. Key topics include the significance of protein-bound vs. free drug concentration, drug interactions, and strategies to enhance drug permeability across the BBB. Ideal for students, researchers, and healthcare professionals in pharmacology and drug development.Modern Practice Principles in Lung CancerŌĆöFirst Find the Targets, Then Treat ...



Modern Practice Principles in Lung CancerŌĆöFirst Find the Targets, Then Treat ...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...



Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...



Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
emphasis_HF_trial.ppt
- 1. Journal club Dr Biplave Karki
- 2. Eplerenone in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure and Mild Symptoms Faiez Zannad, M.D., Ph.D., John J.V. McMurray, M.D., Henry Krum, M.B., Ph.D., Dirk J. van Veldhuisen, M.D., Ph.D., Karl Swedberg, M.D., Ph.D., Harry Shi, M.S., John Vincent, M.B., Ph.D., Stuart J. Pocock, Ph.D., Bertram Pitt, M.D., for the EMPHASIS-HF Study Group Original Article N Engl J Med Volume 364(1):11-21 January 6, 2011
- 3. EMPHASIS-HF ’ü« Eplerenone in Mild Patients Hospitalization and Survival Study in Heart Failure
- 4. Definition of Heart Failure ’ü« The current American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF)/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines define HF as ’é© ŌĆ£a complex clinical syndrome that results from structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood, which in turn leads to the cardinal clinical symptoms of dyspnea and fatigue and signs of HF, namely edema and rales. ’ü« Because many patients present without signs or symptoms of volume overload, the term ŌĆ£heart failureŌĆØ is preferred over the older term ŌĆ£congestive heart failure.ŌĆØ
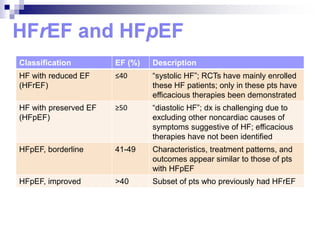
- 5. Classification EF (%) Description HF with reduced EF (HFrEF) Ōēż40 ŌĆ£systolic HFŌĆØ; RCTs have mainly enrolled these HF patients; only in these pts have efficacious therapies been demonstrated HF with preserved EF (HFpEF) Ōēź50 ŌĆ£diastolic HFŌĆØ; dx is challenging due to excluding other noncardiac causes of symptoms suggestive of HF; efficacious therapies have not been identified HFpEF, borderline 41-49 Characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes appear similar to those of pts with HFpEF HFpEF, improved >40 Subset of pts who previously had HFrEF
- 6. Rationale for Medications used in Heart Failure
- 7. Mortality benefit of drugs used in Heart failure
- 8. Aldosterone Antagonists Drugs Spironolactone Eplerenone MOA Non selective Selective Effect on androgen and progesterone +++ +/- S/E Increase K, Mg Decrease CO2, Metabolic acidosis Gynecomastia, hirsutism, Increase K, Mg Decrease CO2, Metabolic acidosis Dose 25 mg OD 25-50mg OD Use HF (IV) Post MI HF (II/III) Cost Cheaper Expensive
- 9. Disclosure Information ’ü« EMPHASIS-HF was funded by Pfizer.inc ’ü« Eplerenone is approved for treating heart failure after myocardial infarction.
- 10. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Heart Failure ’ü« Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study (RALES) 1999 ’ü« Eplerenone PostŌĆōAcute Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure Efficacy and Survival Study (EPHESUS) 2003
- 11. RALES: Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study ’ü« In patients with severe heart failure and left ventricular ejection fraction <35%, ’ü« Spironolactone reduced: ŌĆó All-cause mortality ŌĆó Sudden death and death due to progression of heart failure ’ü« Benefit was independent of age, ejection fraction, cause of heart failure and concurrent therapy
- 12. EPHESUS: Eplerenone PostŌĆōAcute Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure Efficacy and Survival Study ’ü« The addition of eplerenone to optimal medical therapy contributes to the continued improvement in survival and hospitalization rates among patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure
- 13. Aim of EMPHASIS-HF ’ü« to investigate the effects of eplerenone, added to evidence-based therapy, on clinical outcomes in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms (i.e., NYHA functional class II symptoms.
- 14. Methods
- 15. Inclusion Criteria ’ü« >55 years of age ’ü« NYHA functional class II ’ü« Ejection fraction <30% (or, if betwn 30 to 35%, a QRS >130 msec) ’ü« Treated with the recommended or maximal tolerated dose of ACE inhibitor (or an ARB or both) and a beta- blocker (unless contraindicated) ’ü« Within 6 months of hospitalization for a cardiovascular reason (if no such hospitalization, BNP>250 pg/ml or N- pro-BNP>500 pg/ml in men and 750 pg/ml in women
- 16. Exclusion Criteria ’ü« Acute myocardial infarction ’ü« NYHA class III or IV heart failure ’ü« Serum potassium level >5.0 mmol/L ’ü« eGFR<30 ml/min/1.73 m2 ’ü« Need for a potassium sparing diuretic, and ’ü« Any other clinically significant coexisting condition
- 17. Study Design ’ü« Primary outcome: CV death or hospitalization for HF
- 18. Sample Size ’ü« The initial assumptions ’é© 2584 patients ’é© Annual event rate 18% in the placebo group ’é© 813 primary events in 48 months ’é© 80% power to detect an 18% risk reduction ’ü« June 2009 ’é© Overall blinded event rate lower than expected ’é© Sample size increased to 3100 patients
- 19. Early Stopping ’ü« May 6th 2010 ’é© DSMCŌĆÖs second interim analysis showed overwhelming benefit beyond the prespecified stopping boundary for benefit (2 sided P-value =0.000001in favour of eplerenone) ’ü« May 9th 2010 ’é© Agreed to stop patient enrollment ’ü« May 25th 2010 ’é© Trial cut off date
- 20. Results Median follow up time 21 months March 30, 2006, through May 25, 2010
- 23. Baseline Therapy
- 24. Patient Follow up and Dosing
- 25. Primary Endpoint CV Death or Hospitalization for HF- 37%
- 26. Mortality From Any Cause-24%
- 27. Hospitalization From Any Cause- 23%
- 29. Primary And Adjudicated Secondary Outcome
- 31. Other Outcomes
- 36. Safety
- 37. Summary ’ü« The addition of eplerenone to recommended treatment resulted in:
- 38. Conclusion ’ü« In patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms, addition of eplerenone to recommended medical therapy
- 39. TOPCAT 2014: Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure With an Aldosterone Antagonist Trial ’ü« Addition of spironolactone for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction didnŌĆÖt reduce the primary outcome.
- 40. Thank you


