Endocrine system
- 1. Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Fifth edition Seeley ŌĆó Stephens ŌĆó Tate Chapter 10 The Endocrine System PAUL E. MANAIG,MD Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
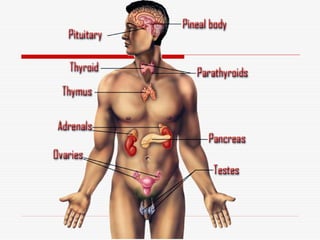
- 2. 1. Water balance 2. Uterine contraction 3. Growth, metabolism, and milk secretion 4. Ion regulation 5. Heart rate and blood pressure regulation 6. Blood glucose control 7. Immune system regulation 8. Reproductive function control
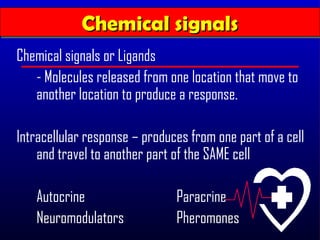
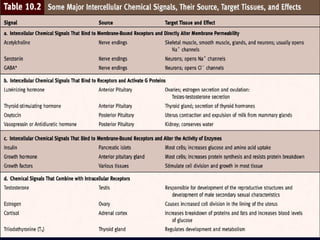
- 3. Chemical signals Chemical signals Chemical signals or Ligands - Molecules released from one location that move to another location to produce a response. Intracellular response ŌĆō produces from one part of a cell and travel to another part of the SAME cell Autocrine Paracrine Neuromodulators Pheromones
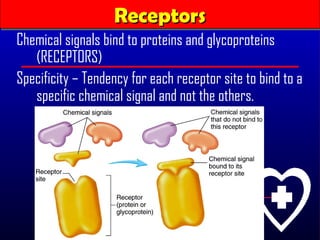
- 6. Receptors Receptors Chemical signals bind to proteins and glycoproteins (RECEPTORS) Specificity ŌĆō Tendency for each receptor site to bind to a specific chemical signal and not the others.
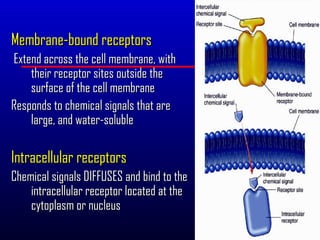
- 7. Membrane-bound receptors Extend across the cell membrane, with their receptor sites outside the surface of the cell membrane Responds to chemical signals that are large, and water-soluble Intracellular receptors Chemical signals DIFFUSES and bind to the intracellular receptor located at the cytoplasm or nucleus
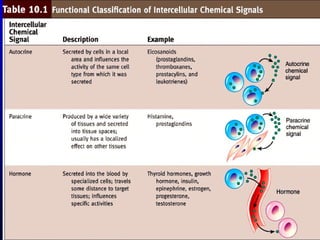
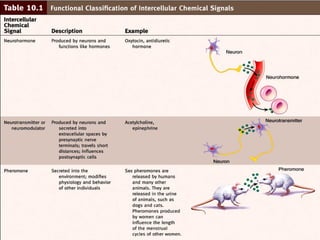
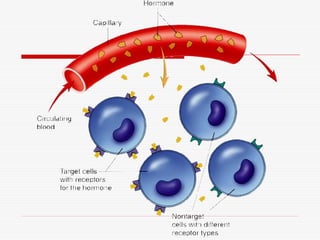
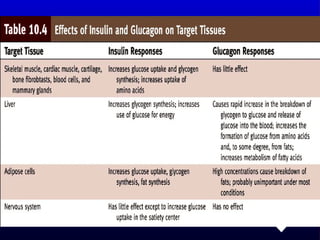
- 8. Hormones Hormones ’ü» Hormones are distributed in the blood to all parts of the body, but only its corresponding target tissue respond to each type of hormone ’ü» Influences target cells by chemically binding to their receptors. ’ü» 2,000-100,000 receptors for a particular hormone ’ü» Hormones that pass in the blood and act on distant cells are called Circulating hormones or ENDOCRINE ’ü» PARACRINE - Hormones that act on neighboring cells ’ü» AUTOCRINE ŌĆō Acts on the same cell ’ü» Local hormones usually are inactivated quickly
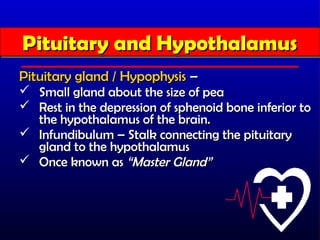
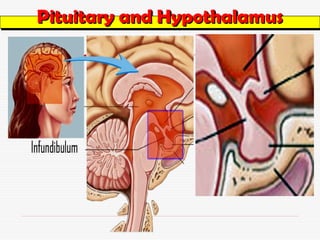
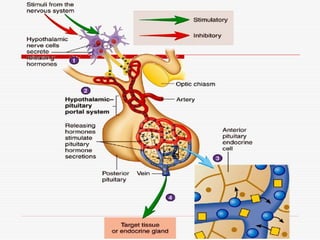
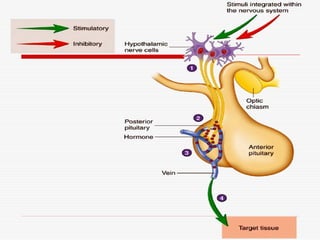
- 11. Pituitary and Hypothalamus Pituitary and Hypothalamus Pituitary gland / Hypophysis ŌĆō ’ā╝ Small gland about the size of pea ’ā╝ Rest in the depression of sphenoid bone inferior to the hypothalamus of the brain. ’ā╝ Infundibulum ŌĆō Stalk connecting the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus ’ā╝ Once known as ŌĆ£Master GlandŌĆØ
- 12. Pituitary and Hypothalamus Pituitary and Hypothalamus
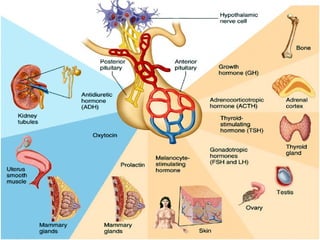
- 15. Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary 1. Growth hormone 2. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) 3. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) 4. Gonadotropins a. Leutinizing hormone (LH) b. Interstitial Cell-stimulating hormone (ISCH) 5. Prolactin 6. Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone
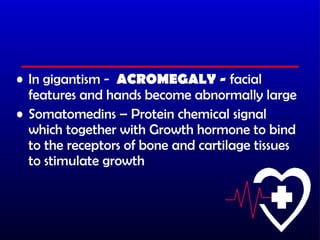
- 16. 1. Growth Hormone ’āśStimulates the growth of bones, muscles, and other organs by increasing protein synthesis. ’āśResist protein breakdown during periods of food deprivation ’āśSecretion of growth hormone is controlled by 2 hormones from the hypothalamus (releasing and inhibitory hormone) ’āśDaily peak levels during sleep, also increases during fasting and exercise ’āśDwarfism ’āśGigantism
- 18. ŌĆó In gigantism - ACROMEGALY - facial features and hands become abnormally large ŌĆó Somatomedins ŌĆō Protein chemical signal which together with Growth hormone to bind to the receptors of bone and cartilage tissues to stimulate growth
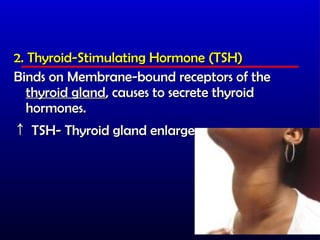
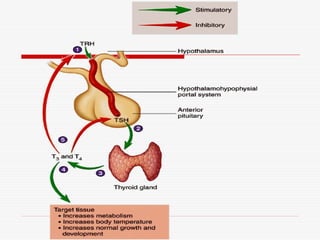
- 19. 2. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Binds on Membrane-bound receptors of the thyroid gland, causes to secrete thyroid hormones. Ōåæ TSH- Thyroid gland enlarges
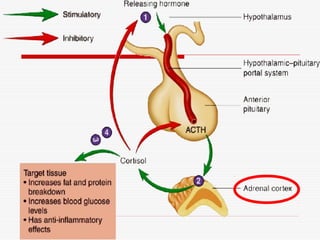
- 20. 3. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) ’āś Binds on Membrane-bound receptors on the cells in cortex of adrenal glands. ’āś Increases secretion of Cortisol ( hydrocortisone), which keeps the adrenal cortex from degenerating ’āś Binds to melanocytes and increase skin pigmentation. ’āś Ōåæ ACTH - Darkening of the skin
- 21. 4. Gonadotropins Leutinizing hormone (LH) Interstitial Cell-stimulating hormone (ISCH) Binds on Membrane-bound receptors of the gonads. Regulates growth, development and of functions of gonads Leutinizing hormone (LH) ŌĆō Ovulation of oocytes and the secretion of estrogen and progesterone from ovaries Interstitial Cell-stimulating hormone (ISCH) ŌĆō stimulates interstitial cells of the testes to secrete testosterone. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone ŌĆō Stimulates the development of follicles in the ovaries and sperm cells in the testes.
- 22. 5. Prolactin Binds on Membrane-bound receptors in the cells of the Breast, during pregnancy and stimulates the production of milk. 6. Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Binds on Membrane-bound receptors on melanocytes and causes them to synthesize melanin. Ōåæ ACTH - Darkening of the skin
- 23. Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary . A n t i d i u r e t i c 2. Oxytoxin h o r Binds on Membrane-bound receptors and m o causes Uterine contraction and milk n e ejection (milk let-down) ( A D H )
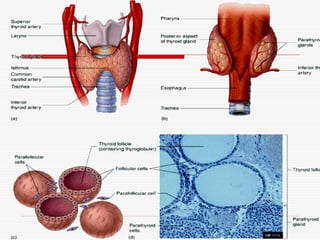
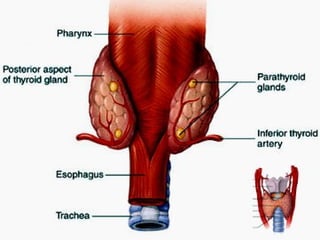
- 26. Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland ŌĆó Made up of 2 lobes connected by the isthmus ŌĆó Located on either side of trachea, just below the larynx ŌĆó Largest endocrine gland ŌĆó Thyroid follicles ŌĆō small spheres with walls that consist of simple cuboidal epithelium ŌĆó Each follicle is filled with protein to which thyroid hormones attached.
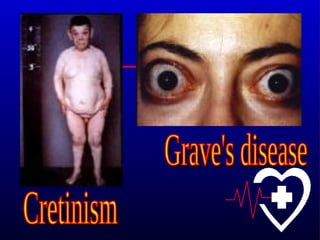
- 28. Thyroid Hormones Binds to intracellular receptors in cells and regulate the rate of metabolism in the body. Participates in normal rate of growth and development. Hypothyroidism Infants ŌĆō Cretinism - Mentally retarded and short in stature, with abnormally formed skeletal structures. Adults ŌĆō reduced rate of metabolism sluggishness, reduced ability to perform routine task.
- 29. Hyperthyroidism Elevated rate of metabolism, extreme nervousness, and chronic fatigue. GraveŌĆÖs disease ŌĆō bulging of the eyes (exopthalmia). Thyroid gland requires iodine to synthesize thyroid hormone. Iodine is taken up by thyroid follicles, hormone synthesis Thyroxine / tetraiodothyronine (T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) Lack of iodine results in reduced T3 and T4 synthesis
- 32. Para-thyroid Gland Para-thyroid Gland ŌĆó Embedded in posterior wall of the thyroid gland ŌĆó Secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH) ŌĆō Regulation of blood calcium ŌĆō Increases the absorption of Ca+ from the intestine by causing an increase in active vitamin D formation Hyperparathyroidism Elevated Blood Ca+ results in nerve and muscle less excitable, resulting in fatigue and muscle weakness Hypoparathryroidism Reduced Vitamin D formation. Nerves and muscles become more excitable and produce spontaneous action potential. Frequent muscle cramps or tetanus
- 34. Hyperparathyroidism Bones become soft, deformed and easily fractured
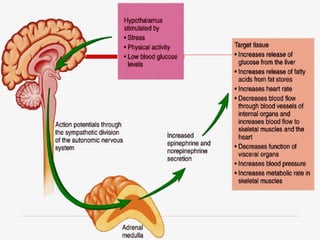
- 35. Adrenal Glands Adrenal Glands 1. Adrenal Medulla ŌĆō Inner part 1. Epinephrine (adrenaline) 2. Norephinephrine 2. Adrenal Cortex ŌĆō Outer part
- 36. Adrenal Medulla ŌĆō Inner part (narrow or middle) Secretes Epinephrine (adrenaline) and small amounts of Norephinephrine Released in response to stimulation of Sympathetic nervous system Fight or Flight hormones
- 39. Fig. 10.18
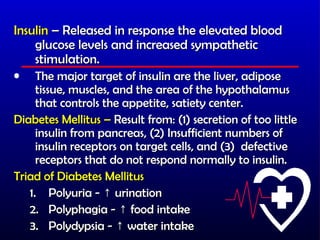
- 40. Pancreas, Insulin, Diabetes Pancreas, Insulin, Diabetes ŌĆó Endocrine part consist of pancreatic islets a.k.a. ŌĆ£Islets of LangerhansŌĆØ ŌĆō has two types of cells. ŌĆó Alpha cells ŌĆō secrete glucagon ŌĆó Beta cells ŌĆō secrete insulin ŌĆó A decline in the blood glucose below the normal range causes the nervous system to malfunction (Glucose is the Nervous systemŌĆÖs main source of energy)
- 42. Insulin ŌĆō Released in response the elevated blood glucose levels and increased sympathetic stimulation. ŌĆó The major target of insulin are the liver, adipose tissue, muscles, and the area of the hypothalamus that controls the appetite, satiety center. Diabetes Mellitus ŌĆō Result from: (1) secretion of too little insulin from pancreas, (2) Insufficient numbers of insulin receptors on target cells, and (3) defective receptors that do not respond normally to insulin. Triad of Diabetes Mellitus 1. Polyuria - Ōåæ urination 2. Polyphagia - Ōåæ food intake 3. Polydypsia - Ōåæ water intake
- 43. (Diabetes Mellitus) Hyperglycemia- Tissues cannot take up glucose effectively, causing blood glucose to become very high. Polyphagia ŌĆō Glucose cannot enter cells of the satiety center of the brain without insulin, the brain responds as if there were little blood glucose, resulting in exaggerated appetite. Polyuria ŌĆō Excess of glucose in the blood is excreted in the urine, thusŌĆ” Polydypsia ŌĆō Because of polyuria, the person becomes dehydrated and thirsty, thus the need to drink often.
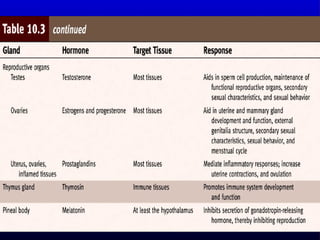
- 46. Testes and Ovaries Testes and Ovaries Testosterone ŌĆō Main sex hormone in male Responsible for the growth and development of male reproductive structures, muscle enlargement, growth of body hair, voice changes and male sexual drives.
- 47. Estrogen & Progesterone ŌĆó Development of female reproductive structures and sexual characteristics ŌĆó Enlarges the breast and distribute fat, which influences the shape of the hips, breast, and thighs. ŌĆó Maintains menstrual cycle
- 50. Thymus Gland Thymus Gland ŌĆó Lies at the upper part of the thoracic cavity ŌĆó Plays an important role in immune system ŌĆó Thymosin ŌĆō Helps in the development of T-Cells (helps protect the body against infection by foreign organism) ŌĆó Most important in early life.
- 51. Pineal Body Pineal Body ŌĆó Small pinecone-shaped structure located superior and posterior to the thalamus of the brain. ŌĆó Melatonin ŌĆō decrease secretion of LH and FSH by decreasing release of hypothalamic-releasing hormones. Acts to inhibit reproductive system
- 52. Thank YouŌĆ” Good Luck!