Energy systems 2
Download as PPT, PDF3 likes3,115 views
The document summarizes the different energy systems the human body uses to produce energy for physical activity. It discusses the ATP-CP, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic energy systems. The ATP-CP system provides energy for bursts of intense activity lasting 2-3 seconds. The anaerobic glycolysis system lasts 2-3 minutes and produces energy without oxygen. The aerobic system provides sustained energy for longer duration activities lasting several minutes by using oxygen to break down carbohydrates and fat.
1 of 26
Downloaded 75 times






















Recommended
Energy systems introduction AS Physical Education 2013



Energy systems introduction AS Physical Education 2013Kerry Harrison
Ěý
The document discusses energy systems in the body. It states that ATP is the only immediately usable energy source, and there is enough stored in the body for 2-3 seconds of exercise. It then describes the three energy systems - the ATP-PC system, the lactic acid system, and the aerobic system. The intensity and duration of exercise dictates which system is predominantly used. The ATP-PC system is for very high intensity exercise of short duration, the lactic acid system is for high intensity exercise of up to 90 seconds, and the aerobic system is for lower to moderate intensity exercise of longer duration.Atp-pc system



Atp-pc systemNick Robinson
Ěý
The document discusses three energy systems that the body uses to produce ATP for muscle contraction and movement. The ATP-PC or alactic system uses phosphocreatine to rapidly resynthesize ATP for high-intensity bursts lasting 3-10 seconds. When phosphocreatine stores are depleted, the lactic anaerobic system breaks down glycogen via anaerobic glycolysis to produce ATP for up to 3 minutes, producing lactic acid as a byproduct. For longer duration lower intensity exercise, the aerobic system uses oxygen to fully break down glycogen and fat stores to efficiently resynthesize ATP.Lesson 11[1 St Dec 2008]![Lesson 11[1 St Dec 2008]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lesson-111st-dec-2008-1231245289588183-2-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Lesson 11[1 St Dec 2008]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lesson-111st-dec-2008-1231245289588183-2-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Lesson 11[1 St Dec 2008]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lesson-111st-dec-2008-1231245289588183-2-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Lesson 11[1 St Dec 2008]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lesson-111st-dec-2008-1231245289588183-2-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Lesson 11[1 St Dec 2008]guest30140e
Ěý
The human body uses three main energy systems - the ATP-PCr system, anaerobic glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation - to produce energy for muscle contraction. The ATP-PCr system provides energy for intense bursts of activity lasting up to 10 seconds. Anaerobic glycolysis is used for activities lasting 20 seconds to 2 minutes and produces lactic acid as a byproduct. Oxidative phosphorylation provides virtually unlimited energy through aerobic metabolism for endurance activities lasting several minutes or more.Energy systems



Energy systemsJosh Woodhouse
Ěý
There are three main energy systems in the body: the phosphocreatine system provides short bursts of energy for up to 12 seconds; the lactic acid system provides moderate power for 45-120 seconds; and the aerobic system provides sustained low-power energy for over 2 minutes. ATP is produced through each system and provides energy to power muscle contractions and cellular processes. Energy is stored and released through different metabolic pathways depending on the intensity and duration of exercise. [/SUMMARY]Energy systems



Energy systemsES16199335
Ěý
The document describes the three main energy systems in the body:
1) The immediate/ATP-CP system provides energy for bursts of intense activity lasting 1-10 seconds through breaking down creatine phosphate.
2) The short-term/anaerobic system provides energy for higher intensity exercise lasting 10-120 seconds through breaking down glycogen and glucose to produce lactic acid.
3) The long-term/aerobic system provides sustained energy for activities lasting 2-10 minutes through aerobic breakdown of glucose and fatty acids to produce the most ATP.Energy systems



Energy systemsStaceyFleming01
Ěý
This document discusses the three energy systems - ATP-PC, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic - that produce ATP to enable muscle contractions. The ATP-PC and anaerobic glycolysis systems produce ATP quickly but in small amounts and can only be used for short durations before causing muscle fatigue. The aerobic system produces large amounts of ATP over long durations without causing fatigue but takes longer to produce ATP. The energy system used depends on the activity duration, intensity, fitness level, and recovery time between efforts.Muscle Energy Systems



Muscle Energy Systemsjorrflv
Ěý
Muscle metabolism relies on ATP as the direct source of energy for contraction. ATP stores are quickly depleted after 4-6 seconds of contraction and must be regenerated through creatine phosphate interaction, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic respiration. When muscle activity reaches 70% of maximum, oxygen delivery is impaired and lactic acid builds up, diffusing into the bloodstream. Muscle fatigue occurs when ATP production cannot keep up with demand, leading to relative ATP deficit, contractures, and lactic acid accumulation.

EnergĂa para el ejercicioNoĂ© González Gallegos
Ěý
El documento resume los principales sistemas energĂ©ticos del cuerpo y cĂłmo se utilizan durante el ejercicio. El sistema ATP-PC proporciona energĂa para actividades de muy alta intensidad de hasta 6 segundos. El sistema anaerĂłbico glucolĂtico se utiliza para actividades de alta intensidad de hasta 30 minutos. El sistema aerĂłbico depende de la glucĂłlisis aerĂłbica y la oxidaciĂłn de grasas para actividades de resistencia de más de 30 minutos. La fatiga se produce cuando la demanda de energĂa supera la capacidad de producciĂłn de ATP.Energy systems



Energy systemsJimmy Nixon
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the three energy systems - ATP-PC, lactic acid, and aerobic. It defines each system, how they generate ATP, their advantages and disadvantages, and the types of exercises or durations they are used for. The ATP-PC system generates ATP very quickly but has a limited duration around 8-10 seconds. The lactic acid system can be used for intensities from 2-3 minutes and produces lactic acid. The aerobic system is the most efficient but slowest, generating ATP in the presence of oxygen for durations over 5 minutes.Week 7 anaerobic and aerobic energy systems



Week 7 anaerobic and aerobic energy systemsravostulp
Ěý
This document discusses the aerobic and anaerobic energy systems in the body. It explains that muscles need ATP and PCr for energy and contraction. When these run low, the body produces more ATP through anaerobic glycolysis using glycogen or through the aerobic system using carbohydrates and oxygen. The anaerobic system produces lactic acid as a byproduct and is important for short, intense exercise. The aerobic system is more efficient and uses oxygen to break down glucose and fat in the mitochondria. Different types of training can improve anaerobic threshold, aerobic capacity, and other cardiovascular and respiratory adaptations to meet the energy demands of various sports.ATP Energy System



ATP Energy SystemUmer Asad
Ěý
All about ATP(Adenosine Tri-Phosphate), how body gets energy from it (molecular formula) and its working in sports. Moreover Creatine Phosphate and Re-synthesis of ATP also know as ATP-CP system.(ATP-PC) (ATP-PCr) or Anaerobic system.Energy systems in human body by arianaacardiorespiratory



Energy systems in human body by arianaacardiorespiratoryariana physiotherapy
Ěý
To study how to improve an individuals fitness and correct illness, it is important to know which energy system is triggered at what moment. This knowledge enables one to extract maximum effort without undue stress. Thus, a briefing about energy systems in the human body.Energy systems 2



Energy systems 2Steve Saffhill
Ěý
The document describes the three energy systems used in sport and exercise:
1. The immediate/ATP-PCr system provides energy instantly without oxygen using stored creatine phosphate. It is used for high-intensity exercise under 10 seconds.
2. The short-term lactic acid system provides energy for higher intensity exercise over longer periods by breaking down glycogen without oxygen, producing lactic acid. It is used from 10 seconds to 2 minutes as intensity exceeds aerobic capacity.
3. The long-term aerobic system provides energy over longer periods by using oxygen to break down glycogen, fatty acids, producing more ATP. It is used for low to moderate intensity exercise lasting over 2 minutes.Three energy systems



Three energy systemsu002878
Ěý
This document discusses the three energy systems - ATP/PC, lactic acid, and aerobic - that provide ATP to allow human movement. The ATP/PC system provides ATP for 2-10 seconds of high-intensity exercise like sprinting using stored ATP and phosphocreatine. The lactic acid system takes over for 10 seconds to 2 minutes of high-intensity exercise, producing ATP without oxygen and leading to lactic acid buildup. The aerobic system fuels activities from 2 minutes to hours using oxygen to break down fats and produce large amounts of ATP.Assessment of physical fitness pptx



Assessment of physical fitness pptxKolkata,west bengal, India
Ěý
This document provides an overview of physical fitness assessments. It defines physical fitness as the ability to carry out daily tasks without undue fatigue. Components of physical fitness include body composition, muscular strength and endurance, cardiorespiratory fitness, flexibility, agility, balance, coordination, reaction time, power, and speed. The document describes methods for assessing each component, such as BMI, pushups, sit-and-reach tests. It recommends that adults engage in moderate exercise for 30 minutes daily to improve health and reduce disease risk. Precautions are discussed to prevent cardiac events during exercise.Aerobic and anaerobic training



Aerobic and anaerobic trainingTHACHR15
Ěý
The document discusses the three energy systems - aerobic, anaerobic alactic (phosphate), and anaerobic lactic. The aerobic system produces energy through oxygen-dependent breakdown of carbohydrates and fats. It is used for endurance activities lasting more than 2 minutes. The phosphate and lactic systems produce energy without oxygen and are used for short bursts of intense activity lasting 10-90 seconds. Different training methods like intervals are needed to improve each system.Aerobic system



Aerobic systemNick Robinson
Ěý
The document discusses the aerobic system of energy production for exercise. It involves 3 main stages: 1) Glycolysis, 2) Krebs cycle, and 3) Electron transport chain. During these stages, glycogen and fats are broken down to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. The aerobic system is efficient and can sustain low to moderate exercise for long periods due to high oxygen availability and energy yield.Hormonal responses to exercise



Hormonal responses to exerciseRizwanAli852012
Ěý
This document summarizes neuroendocrinology and the major endocrine glands and hormones. It discusses how the nervous and endocrine systems work together through the neuroendocrine system to maintain homeostasis. The major glands discussed are the hypothalamus and pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, and gonads. For each gland, the key hormones secreted and their functions are described. The document also covers hormone secretion, metabolism, receptors, and how exercise affects hormone levels and substrate mobilization.Strength training



Strength trainingStu Zarazun
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts related to adaptations to resistance training. It defines muscular strength, power, and endurance. It describes measurements of one-repetition maximum and covers topics like muscle hypertrophy, fiber size increases, effects of inactivity, muscle soreness, and resistance training program design. It emphasizes that resistance training can improve strength by 25-100% within 3-6 months and benefit all populations.Role of Nutrition in sports



Role of Nutrition in sportsMd.Nahian Rahman
Ěý
Sports nutrition is the study and practice of nutrition and diet as it relates to athletic performance. It is a science that provides and maintains food necessary for health, growth and physical performance.
Researchers suggests that athletes can benefit from nutrition education – increasing KAP i.e. knowledge, Attitude and practices (Abood et al, 2006).
Exercise physiology powerpoint



Exercise physiology powerpointmrsdavison
Ěý
The document discusses exercise physiology and how the body's systems respond to exercise. It describes exercise physiology as the study of how the human body functions during and after physical activity. Key body systems that are involved in exercise include the muscular, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems. During exercise, the cardiovascular system works to deliver more oxygen to active muscles via increased heart rate and blood flow. The respiratory system increases breathing rate and volume to take in more oxygen. Regular exercise leads to long-term adaptations like increased heart and lung capacity and stronger, more efficient muscles.Bioenergetics of Exercise



Bioenergetics of ExerciseMatt Sanders
Ěý
This document discusses the bioenergetics of exercise and training. It describes the three main energy systems in the body - the phosphagen, glycolytic, and oxidative systems. The phosphagen system provides energy for short bursts of high intensity exercise. Glycolysis breaks down carbohydrates to replenish ATP and can produce lactate. The oxidative system uses fats and carbohydrates during lower intensity exercise. Training can target specific energy systems through interval training and combination training approaches.Energy system 



Energy system Shahid Uz Zafar
Ěý
The document discusses the three main energy systems in the human body - ATP-PC system, lactic acid system, and aerobic system. It explains that the ATP-PC system generates ATP the fastest but runs out quickly, lasting 8-10 seconds and being used for explosive activities like sprinting. The lactic acid system generates ATP anaerobically for 2-3 minutes of intense exercise. The aerobic system is the most efficient but slowest, generating ATP aerobically through oxygen for activities lasting over 5 minutes. The document provides details on how each system works on a cellular level to break down nutrients and generate ATP.Atppc



AtppcCongressional National High School - SHS
Ěý
The ATP-PC energy system provides immediate energy for intense but short bursts of exercise lasting 10-15 seconds by breaking down ATP and phosphocreatine (PC) stores in the muscles. ATP is used for muscle contraction and is replenished when PC is broken down by creatine kinase, releasing energy to rejoin ADP and phosphate and reform ATP. Training to improve this system focuses on maximal effort exercises like sprinting or lifting for 1-3 repetitions followed by 2-3 minutes of rest.Energy Systems for Fitness



Energy Systems for Fitnesstrevster
Ěý
This document provides guidance on coaching athletes to achieve the fitness levels required for their sport. It discusses the importance of warming up and cooling down and outlines the key components of an athlete's training: energy fitness, which includes both aerobic and anaerobic training; muscular fitness, including strength, endurance, power and flexibility; and peaking and tapering training near competitions. Coaches are advised to tailor training in each area to the demands of the specific sport.Atp pc energy system



Atp pc energy systemAhmad Raza Raza
Ěý
This document provides information about ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production through the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It discusses the processes of glycolysis, glycogenesis, and the acetyl-CoA pathway. ATP is the body's energy currency and is produced through three energy systems. Carbohydrates yield the most ATP per gram through glycolysis, while fats provide the most ATP through the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Proteins contribute minimally to ATP production.Fitness and strength testing in sports



Fitness and strength testing in sportsDr.Rajal Sukhiyaji
Ěý
The document discusses fitness testing and strength training. It defines different types of fitness and provides details on tests to measure muscular strength and endurance. These include the bench jump, modified dip/push-up, and bent-leg curl-up tests. The document also outlines principles for developing strength, such as overload and specificity. It provides guidelines for prescribing strength training, including factors like mode, resistance, sets and frequency. The goal is to stimulate strength gains through progressive resistance training 2-3 times per week.Chap19



Chap19Matt Sanders
Ěý
Periodization involves systematically varying training variables over periods of time to optimize performance and prevent overtraining. It follows the general adaptation syndrome of stress response. The traditional model includes a preparatory period focusing on hypertrophy, strength, and power; a competition period for peaking; and transition periods. Sport seasons map to these periods. An example macrocycle progresses an athlete through preseason, in-season, postseason, and off-season mesocycles with appropriate training emphases. Periodization promotes long-term performance gains through planned variation in training load.Introduction to the energy systems



Introduction to the energy systemsKerrie O'Bryan
Ěý
The document discusses the aerobic and anaerobic energy pathways and their contribution to movement. The aerobic pathway uses oxygen to break down fuels for energy over a long duration and low intensity. The anaerobic pathways do not use oxygen, with the ATP-PC system providing a rapid burst of energy lasting 10 seconds and the lactic acid system providing energy for 2-3 minutes during high intensity exercise before fatigue sets in. The document outlines the different fuels, storage sites, and processes of each energy system.Energy systems of body



Energy systems of bodyVignan Rachabattuni
Ěý
Mr. Joey is a 38-year-old IT professional who eats mostly junk food and sits for long hours in an air-conditioned office. His only exercise is walking during coffee breaks and he spends weekends drinking beer and watching movies. With 14-15 hours of online exposure daily and no consistent exercise, he is at risk of obesity, high blood sugar, heart disease, and other health issues. The document discusses different energy systems like ATP-PC and aerobic and anaerobic metabolism, providing examples of short-term and long-term exercise and how training can improve aerobic capacity.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Energy systems



Energy systemsJimmy Nixon
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the three energy systems - ATP-PC, lactic acid, and aerobic. It defines each system, how they generate ATP, their advantages and disadvantages, and the types of exercises or durations they are used for. The ATP-PC system generates ATP very quickly but has a limited duration around 8-10 seconds. The lactic acid system can be used for intensities from 2-3 minutes and produces lactic acid. The aerobic system is the most efficient but slowest, generating ATP in the presence of oxygen for durations over 5 minutes.Week 7 anaerobic and aerobic energy systems



Week 7 anaerobic and aerobic energy systemsravostulp
Ěý
This document discusses the aerobic and anaerobic energy systems in the body. It explains that muscles need ATP and PCr for energy and contraction. When these run low, the body produces more ATP through anaerobic glycolysis using glycogen or through the aerobic system using carbohydrates and oxygen. The anaerobic system produces lactic acid as a byproduct and is important for short, intense exercise. The aerobic system is more efficient and uses oxygen to break down glucose and fat in the mitochondria. Different types of training can improve anaerobic threshold, aerobic capacity, and other cardiovascular and respiratory adaptations to meet the energy demands of various sports.ATP Energy System



ATP Energy SystemUmer Asad
Ěý
All about ATP(Adenosine Tri-Phosphate), how body gets energy from it (molecular formula) and its working in sports. Moreover Creatine Phosphate and Re-synthesis of ATP also know as ATP-CP system.(ATP-PC) (ATP-PCr) or Anaerobic system.Energy systems in human body by arianaacardiorespiratory



Energy systems in human body by arianaacardiorespiratoryariana physiotherapy
Ěý
To study how to improve an individuals fitness and correct illness, it is important to know which energy system is triggered at what moment. This knowledge enables one to extract maximum effort without undue stress. Thus, a briefing about energy systems in the human body.Energy systems 2



Energy systems 2Steve Saffhill
Ěý
The document describes the three energy systems used in sport and exercise:
1. The immediate/ATP-PCr system provides energy instantly without oxygen using stored creatine phosphate. It is used for high-intensity exercise under 10 seconds.
2. The short-term lactic acid system provides energy for higher intensity exercise over longer periods by breaking down glycogen without oxygen, producing lactic acid. It is used from 10 seconds to 2 minutes as intensity exceeds aerobic capacity.
3. The long-term aerobic system provides energy over longer periods by using oxygen to break down glycogen, fatty acids, producing more ATP. It is used for low to moderate intensity exercise lasting over 2 minutes.Three energy systems



Three energy systemsu002878
Ěý
This document discusses the three energy systems - ATP/PC, lactic acid, and aerobic - that provide ATP to allow human movement. The ATP/PC system provides ATP for 2-10 seconds of high-intensity exercise like sprinting using stored ATP and phosphocreatine. The lactic acid system takes over for 10 seconds to 2 minutes of high-intensity exercise, producing ATP without oxygen and leading to lactic acid buildup. The aerobic system fuels activities from 2 minutes to hours using oxygen to break down fats and produce large amounts of ATP.Assessment of physical fitness pptx



Assessment of physical fitness pptxKolkata,west bengal, India
Ěý
This document provides an overview of physical fitness assessments. It defines physical fitness as the ability to carry out daily tasks without undue fatigue. Components of physical fitness include body composition, muscular strength and endurance, cardiorespiratory fitness, flexibility, agility, balance, coordination, reaction time, power, and speed. The document describes methods for assessing each component, such as BMI, pushups, sit-and-reach tests. It recommends that adults engage in moderate exercise for 30 minutes daily to improve health and reduce disease risk. Precautions are discussed to prevent cardiac events during exercise.Aerobic and anaerobic training



Aerobic and anaerobic trainingTHACHR15
Ěý
The document discusses the three energy systems - aerobic, anaerobic alactic (phosphate), and anaerobic lactic. The aerobic system produces energy through oxygen-dependent breakdown of carbohydrates and fats. It is used for endurance activities lasting more than 2 minutes. The phosphate and lactic systems produce energy without oxygen and are used for short bursts of intense activity lasting 10-90 seconds. Different training methods like intervals are needed to improve each system.Aerobic system



Aerobic systemNick Robinson
Ěý
The document discusses the aerobic system of energy production for exercise. It involves 3 main stages: 1) Glycolysis, 2) Krebs cycle, and 3) Electron transport chain. During these stages, glycogen and fats are broken down to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. The aerobic system is efficient and can sustain low to moderate exercise for long periods due to high oxygen availability and energy yield.Hormonal responses to exercise



Hormonal responses to exerciseRizwanAli852012
Ěý
This document summarizes neuroendocrinology and the major endocrine glands and hormones. It discusses how the nervous and endocrine systems work together through the neuroendocrine system to maintain homeostasis. The major glands discussed are the hypothalamus and pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, and gonads. For each gland, the key hormones secreted and their functions are described. The document also covers hormone secretion, metabolism, receptors, and how exercise affects hormone levels and substrate mobilization.Strength training



Strength trainingStu Zarazun
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts related to adaptations to resistance training. It defines muscular strength, power, and endurance. It describes measurements of one-repetition maximum and covers topics like muscle hypertrophy, fiber size increases, effects of inactivity, muscle soreness, and resistance training program design. It emphasizes that resistance training can improve strength by 25-100% within 3-6 months and benefit all populations.Role of Nutrition in sports



Role of Nutrition in sportsMd.Nahian Rahman
Ěý
Sports nutrition is the study and practice of nutrition and diet as it relates to athletic performance. It is a science that provides and maintains food necessary for health, growth and physical performance.
Researchers suggests that athletes can benefit from nutrition education – increasing KAP i.e. knowledge, Attitude and practices (Abood et al, 2006).
Exercise physiology powerpoint



Exercise physiology powerpointmrsdavison
Ěý
The document discusses exercise physiology and how the body's systems respond to exercise. It describes exercise physiology as the study of how the human body functions during and after physical activity. Key body systems that are involved in exercise include the muscular, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems. During exercise, the cardiovascular system works to deliver more oxygen to active muscles via increased heart rate and blood flow. The respiratory system increases breathing rate and volume to take in more oxygen. Regular exercise leads to long-term adaptations like increased heart and lung capacity and stronger, more efficient muscles.Bioenergetics of Exercise



Bioenergetics of ExerciseMatt Sanders
Ěý
This document discusses the bioenergetics of exercise and training. It describes the three main energy systems in the body - the phosphagen, glycolytic, and oxidative systems. The phosphagen system provides energy for short bursts of high intensity exercise. Glycolysis breaks down carbohydrates to replenish ATP and can produce lactate. The oxidative system uses fats and carbohydrates during lower intensity exercise. Training can target specific energy systems through interval training and combination training approaches.Energy system 



Energy system Shahid Uz Zafar
Ěý
The document discusses the three main energy systems in the human body - ATP-PC system, lactic acid system, and aerobic system. It explains that the ATP-PC system generates ATP the fastest but runs out quickly, lasting 8-10 seconds and being used for explosive activities like sprinting. The lactic acid system generates ATP anaerobically for 2-3 minutes of intense exercise. The aerobic system is the most efficient but slowest, generating ATP aerobically through oxygen for activities lasting over 5 minutes. The document provides details on how each system works on a cellular level to break down nutrients and generate ATP.Atppc



AtppcCongressional National High School - SHS
Ěý
The ATP-PC energy system provides immediate energy for intense but short bursts of exercise lasting 10-15 seconds by breaking down ATP and phosphocreatine (PC) stores in the muscles. ATP is used for muscle contraction and is replenished when PC is broken down by creatine kinase, releasing energy to rejoin ADP and phosphate and reform ATP. Training to improve this system focuses on maximal effort exercises like sprinting or lifting for 1-3 repetitions followed by 2-3 minutes of rest.Energy Systems for Fitness



Energy Systems for Fitnesstrevster
Ěý
This document provides guidance on coaching athletes to achieve the fitness levels required for their sport. It discusses the importance of warming up and cooling down and outlines the key components of an athlete's training: energy fitness, which includes both aerobic and anaerobic training; muscular fitness, including strength, endurance, power and flexibility; and peaking and tapering training near competitions. Coaches are advised to tailor training in each area to the demands of the specific sport.Atp pc energy system



Atp pc energy systemAhmad Raza Raza
Ěý
This document provides information about ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production through the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It discusses the processes of glycolysis, glycogenesis, and the acetyl-CoA pathway. ATP is the body's energy currency and is produced through three energy systems. Carbohydrates yield the most ATP per gram through glycolysis, while fats provide the most ATP through the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Proteins contribute minimally to ATP production.Fitness and strength testing in sports



Fitness and strength testing in sportsDr.Rajal Sukhiyaji
Ěý
The document discusses fitness testing and strength training. It defines different types of fitness and provides details on tests to measure muscular strength and endurance. These include the bench jump, modified dip/push-up, and bent-leg curl-up tests. The document also outlines principles for developing strength, such as overload and specificity. It provides guidelines for prescribing strength training, including factors like mode, resistance, sets and frequency. The goal is to stimulate strength gains through progressive resistance training 2-3 times per week.Chap19



Chap19Matt Sanders
Ěý
Periodization involves systematically varying training variables over periods of time to optimize performance and prevent overtraining. It follows the general adaptation syndrome of stress response. The traditional model includes a preparatory period focusing on hypertrophy, strength, and power; a competition period for peaking; and transition periods. Sport seasons map to these periods. An example macrocycle progresses an athlete through preseason, in-season, postseason, and off-season mesocycles with appropriate training emphases. Periodization promotes long-term performance gains through planned variation in training load.Viewers also liked (18)
Introduction to the energy systems



Introduction to the energy systemsKerrie O'Bryan
Ěý
The document discusses the aerobic and anaerobic energy pathways and their contribution to movement. The aerobic pathway uses oxygen to break down fuels for energy over a long duration and low intensity. The anaerobic pathways do not use oxygen, with the ATP-PC system providing a rapid burst of energy lasting 10 seconds and the lactic acid system providing energy for 2-3 minutes during high intensity exercise before fatigue sets in. The document outlines the different fuels, storage sites, and processes of each energy system.Energy systems of body



Energy systems of bodyVignan Rachabattuni
Ěý
Mr. Joey is a 38-year-old IT professional who eats mostly junk food and sits for long hours in an air-conditioned office. His only exercise is walking during coffee breaks and he spends weekends drinking beer and watching movies. With 14-15 hours of online exposure daily and no consistent exercise, he is at risk of obesity, high blood sugar, heart disease, and other health issues. The document discusses different energy systems like ATP-PC and aerobic and anaerobic metabolism, providing examples of short-term and long-term exercise and how training can improve aerobic capacity.Energy system table



Energy system tableChris Lehner
Ěý
The document summarizes three energy systems:
1) ATP-PC system uses phosphocreatine to produce energy instantly for intense bursts up to 10 seconds.
2) Lactic acid system uses glycogen to produce fast energy for activities lasting 10-75 seconds through anaerobic glycolysis.
3) Aerobic system uses oxygen and fuels like carbohydrates and fats to produce sustained energy over 75 seconds through aerobic glycolysis.Sports Performance



Sports Performancenatjkeen
Ěý
This document defines and compares physical activity, play, and sport. It also discusses health versus physical fitness, with health relating to total well-being and fitness relating to physical attributes. The document then discusses the three energy systems the body uses - ATP-PC system for short bursts, lactic acid system for durations up to a few minutes, and aerobic system for longer durations. It provides details on how each system works, including the breakdown of fuels like carbohydrates and production of ATP.Energy systems



Energy systemsKerrie O'Bryan
Ěý
The document discusses the three main energy systems - phosphate, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic - that provide energy for muscular activity through ATP production. The phosphate system provides energy for powerful bursts lasting up to 10 seconds. Anaerobic glycolysis then takes over for high intensity efforts from 10 seconds to a minute by breaking down glycogen without oxygen. Aerobic metabolism is the primary provider of energy for submaximal exertion lasting over a minute, using fat and carbohydrates with oxygen. The relative contribution of each system depends on the intensity and duration of physical activity.Introduction to Energy Systems



Introduction to Energy SystemsJoel Irons
Ěý
Introductory şÝşÝߣs for energy systems. Delivered to year 10 including class activity.
Credit:
http://www.slideshare.net/kerrieobryan/introduction-to-the-energy-systemsAerobic system



Aerobic systemNick Robinson
Ěý
The document discusses the aerobic system of energy production for exercise. It involves 3 main stages: 1) Glycolysis, 2) Krebs cycle, and 3) Electron transport chain. During these stages, glycogen and fats are broken down to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. The aerobic system is efficient and can sustain low to moderate exercise for long periods due to high oxygen availability and energy yield.Exercise Treatment Of The Obese Patient



Exercise Treatment Of The Obese PatientMedicineAndHealthUSA
Ěý
The document discusses exercise and its benefits for obese patients. It defines different types of physical activity and exercise. It describes the physiological effects of exercise on skeletal muscle and cardiovascular systems. Regular exercise provides significant health benefits like reduced mortality, improved glycemic control, and reduced risks of various diseases. Exercise is an important component of weight loss and maintenance by increasing calorie burn and lean muscle mass. The guidelines recommend accumulating 30-60 minutes per day of moderate exercise most days of the week.Sports Performance Fitness



Sports Performance Fitnessnatjkeen
Ěý
The document discusses the components of fitness and principles of training. It defines fitness as the ability to carry out daily tasks without undue fatigue and with reserve energy. The components of fitness include health-related components like cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength and flexibility, as well as skill-related components like speed, power, agility and coordination. The principles of training that can improve performance are specificity, progressive overload, and applying the FITT principles of frequency, intensity, time and type to a training program.ppt.Hypertension and Exercise



ppt.Hypertension and Exercisedrvinodkr
Ěý
by Dr.Vinod K Ravaliya, K M Patel Institute of Physiotherapy.. current issues in management of Hypertension.Types of Skeletal Muscle Fibers



Types of Skeletal Muscle FibersAndrea Audine Jandongan
Ěý
This document discusses the three main types of skeletal muscle fibers:
1) Slow oxidative fibers (SO) are dark red, contain many mitochondria and blood vessels, generate ATP through aerobic respiration, and contract slowly but resist fatigue well. They are suited for endurance activities like marathon running.
2) Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers (FOG) are also dark red but generate ATP through both aerobic respiration and anaerobic glycolysis. They contract faster than SO fibers but more slowly than FG fibers. They are suited for activities like walking and sprinting.
3) Fast glycolytic fibers (FG) are white, rely primarily on anaerobic glycolysis to generateAnaerobic-Aerobic Treatment of Sewage



Anaerobic-Aerobic Treatment of SewageAmit Christian
Ěý
The document proposes an anaerobic-aerobic process for treating domestic sewage using LEVAPOR biofilm technology. The process involves pre-treating sewage under anaerobic conditions in a biofilm reactor to reduce energy use and excess sludge production compared to conventional aerobic treatment. Sewage would then undergo post-treatment under aerobic conditions to further reduce pollutants before discharge. This process could achieve up to 75% lower energy use and 67% less sludge than aerobic treatment alone, while also producing biogas as an energy source.High intensity interval training



High intensity interval trainingSophie Brazell
Ěý
This document discusses high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and its benefits compared to endurance training. HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise alternated with recovery periods. A typical HIIT session involves sprinting for 30 seconds followed by a 1 minute recovery period, repeated 4-6 times. Studies have shown that HIIT can improve aerobic capacity, fat metabolism, and endurance as much as longer endurance training, but with less time commitment - around 15 minutes for HIIT versus hours for endurance training. The intensity of HIIT places more stress on the body than endurance training, leading to more rapid adaptations in factors like mitochondria and fat burning.Hypertension and exercise



Hypertension and exerciseAsyhera Asleh
Ěý
This document provides information about hypertension, including:
- Definitions of hypertension from various health organizations.
- Prevalence rates of hypertension globally and in Malaysia, which is higher in urban vs. rural areas.
- Risk factors, symptoms, complications and classifications of hypertension.
- Recommended tests for diagnosing hypertension including ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and stress tests.
- Lifestyle modifications to manage hypertension including the DASH diet, physical activity, and aerobic and resistance exercise programs.
The goal is to lower blood pressure through a combination of diet, exercise and medications in order to reduce risks of complications like heart attack and stroke. Regular physical activity and following the DASH diet are importantwhat is interval training?



what is interval training?JesseButler
Ěý
In this short presentation you will learn about what interval training is and how you can benefit from it.

Interval trainingKatherine Sánchez
Ěý
El interval training o entrenamiento interválico consiste en alternar perĂodos cortos de esfuerzo intenso con descansos. Fue desarrollado en los años 40-50 y popularizado por el corredor Emil Zatopek. Ofrece beneficios como mejorar la resistencia, coordinaciĂłn y capacidad aerĂłbica y respiratoria, además de ayudar a quemar calorĂas. Se recomienda precauciĂłn al realizarlo para prevenir lesiones.Anaerobic exercise



Anaerobic exerciseAndrea Arteaga Icaza
Ěý
Anaerobic exercise relies on glycogen stores and produces lactic acid as a byproduct. It is short and intense activity that builds muscle strength without using oxygen. Examples include sprinting, weightlifting, circuit training, calisthenics, and many sports. Benefits include increased muscle and bone strength, a higher metabolism, and fat replacement by muscle. Risks involve high blood pressure during exercise and lactic acid buildup. Proper warmups, cool downs, nutrition, and checking with a doctor are recommended before starting an anaerobic exercise routine.Human Energy System



Human Energy SystemNK Institute Pty Ltd
Ěý
This document summarizes various human energy systems including chakras, meridians, nadis, the aura, and figure 8 energies. It provides diagrams of chakra locations and meridian pathways. It discusses the 6 states of balanced and imbalanced chakras as well as chakra profiles for the solar plexus. Additional topics covered include kundalini, mudras, the limbic system, and how early separation trauma can impact relationships.Similar to Energy systems 2 (20)
L10 Energy Systems



L10 Energy Systemsguest873b3f
Ěý
1. Cells produce energy in the form of ATP through breaking down nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. ATP is constantly being used and replenished through different energy systems.
2. There are three main energy systems: the ATP-CP system which provides energy for up to 10 seconds; anaerobic glycolysis which takes over for 1-3 minutes; and the aerobic system which sustains energy for over 3 minutes through oxidative phosphorylation.
3. The aerobic system fully breaks down glucose or fatty acids to produce much more ATP than the other systems, using oxygen to facilitate reactions in the mitochondria and electron transport chain. This makes the aerobic system well-suited for longer,L10 Energy Systems



L10 Energy Systemsguest873b3f
Ěý
1. Cells produce energy in the form of ATP through various energy systems, including the ATP-CP system, anaerobic glycolysis, and the aerobic system.
2. The ATP-CP system provides energy for 2-10 seconds by resynthesizing ATP from creatine phosphate. Anaerobic glycolysis produces energy without oxygen for 1-3 minutes by breaking down carbohydrates.
3. The aerobic system provides sustained energy over 3 minutes by oxidizing carbohydrates and fat through the mitochondria and electron transport chain to produce large amounts of ATP. Together these systems power human movement.Sources of energy dr gad



Sources of energy dr gadMB. B. CH. Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University
Ěý
This document discusses sources of energy during rest and exercise. It explains that cells use ATP as their main source of energy, which is produced through breaking down nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. There are three main energy systems: phosphagen, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic. Phosphagen provides immediate energy for bursts of activity up to 10 seconds. Anaerobic glycolysis fuels moderate intensity exercise up to 2 minutes through lactate production. Aerobic oxidation sustains long duration activities by producing large amounts of ATP from oxygen. Recovery from exercise involves paying back oxygen debt and replenishing energy stores through lactate clearance and glycogen resynthesis.AerobicandAnaerobic MuscleMetabolism (1).ppt



AerobicandAnaerobic MuscleMetabolism (1).pptJuanCamiloCruzVega
Ěý
ATP is the energy currency used by muscles, which obtain energy through aerobic and anaerobic metabolism in their mitochondria and glycogen stores. Fast-twitch white muscle fibers rely more on anaerobic glycolysis while slow-twitch red fibers use aerobic metabolism. During exercise, muscles sequentially use ATP, phosphocreatine, and glycogen stores, and shuttle waste products like lactate and alanine to the liver via Cori and glucose-alanine cycles to regenerate ATP.Core 2 Factors affecting performance Energy ssytems



Core 2 Factors affecting performance Energy ssytemsmacca60
Ěý
First term How does training affect performance?
Energy Systems
Principles of training
Types of trainingEnergy systems



Energy systemsOliviaBurkinshaw
Ěý
Energy is the ability to do work and is transferred or converted between different forms. ATP provides energy for physiological processes through the breakdown of phosphate bonds. There are three main energy systems in the body: 1) ATP-PCr system provides short bursts of energy through phosphate transfer from creatine phosphate to ATP. 2) Lactic acid system provides moderate energy through anaerobic glycolysis but produces lactic acid. 3) Aerobic system provides sustained energy through oxygen-based breakdown of glucose and fats, producing water and carbon dioxide.Energy systems



Energy systemschristie Woods
Ěý
The document discusses the three main energy systems - ATP-PC system, lactic acid system, and aerobic system. It provides examples of how each system is used in different sporting events like sprinting, long distance running, and field events. The ATP-PC system provides energy over seconds, the lactic acid system over minutes, and the aerobic system provides virtually unlimited energy through oxygen. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only changed from one form to another.Energy systems main lesson



Energy systems main lessonlincoln Bryden
Ěý
The document discusses how the body produces energy through different energy systems using carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. There are three main energy systems: 1) the phosphocreatine system which produces ATP very rapidly but has limited capacity, 2) the lactic acid system which produces ATP rapidly but leads to lactic acid buildup and fatigue, and 3) the aerobic system which produces ATP slowly through oxygen but has unlimited capacity. The type of energy system used depends on the intensity and duration of exercise.Energy For Movement.pptx



Energy For Movement.pptxNorieta Langpawen
Ěý
This document discusses human energy systems and how the body converts food into energy for movement and activity. It covers the three main energy systems - ATP-PC, anaerobic, and aerobic. The ATP-PC system provides immediate energy through phosphocreatine stores but lasts only 10 seconds. The anaerobic system breaks down glucose without oxygen and fuels activity for 10 seconds to 3 minutes. The aerobic system uses oxygen to break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, fueling longer duration lower intensity activities. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are all sources of stored energy and calories that can be broken down to synthesize ATP through cellular respiration.Energy systems



Energy systemsLloyd Dean
Ěý
The document describes the three main energy systems the body uses to produce ATP:
1) The ATP-PC system produces ATP rapidly at the start of intense activity lasting up to 6 seconds through phosphocreatine breakdown.
2) Anaerobic glycolysis produces ATP without oxygen through carbohydrate breakdown, lasting 30-120 seconds but producing lactic acid as a byproduct.
3) The aerobic system produces ATP through carbohydrate and fat breakdown during low to moderate intensity exercise lasting 3 minutes or more.Physiology of fitness_nrg_systems_-_lesson_4



Physiology of fitness_nrg_systems_-_lesson_4William Wayland
Ěý
I didnt write this one but the information is gold for those of studying or wanting to understand energy systems. EnjoyEnergy systems



Energy systemsethan brown
Ěý
This document discusses different energy systems in the body:
- Anaerobic respiration produces energy without oxygen and includes the ATP-PC and lactic acid systems. The ATP-PC system uses phosphocreatine to rapidly produce ATP in the first 2-7 seconds of intense exercise.
- The lactic acid system breaks down glucose to produce ATP through anaerobic glycolysis during high-intensity activities up to 2 minutes. This produces lactic acid.
- The aerobic system uses fats, carbs and proteins to slowly but sustainably produce ATP through oxygen. It has virtually unlimited capacity for endurance activities.Energy systems.pdf



Energy systems.pdfDipaliTalaviya1
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the three main energy systems: ATP-PC, lactic acid, and aerobic. It describes how each system works, including how ATP is generated through the breakdown of nutrients and stored as potential energy. The ATP-PC system provides immediate energy through stored phosphates but runs out quickly. The lactic acid system breaks down glucose anaerobically over 2-3 minutes. The aerobic system generates ATP most efficiently through aerobic breakdown of glucose but takes longer. Each system is suited to different durations and intensities of exercise.Energy powerpoint



Energy powerpointLaura Dodwell
Ěý
The document discusses the three main energy systems used in sport: the creatine phosphate system, lactic acid system, and aerobic system. The creatine phosphate system provides rapid energy for up to 10 seconds using ATP and creatine phosphate. The lactic acid system fuels high-intensity exercise for up to 90 seconds using glycogen and glucose without oxygen. The aerobic system supports longer continuous exercise by breaking down glycogen and fatty acids with oxygen over minutes. Each system produces ATP to fuel muscular movement through different chemical reactions and pathways.energy system.pptx



energy system.pptxferdinandsanbuenaven
Ěý
There are three main energy systems in the human body:
1) The ATP-CP system provides immediate energy for intense bursts of activity lasting 10 seconds or less and does not require oxygen.
2) The glycolytic system produces energy through the breakdown of glycogen for 1-3 minutes of high intensity exercise and causes the buildup of lactic acid.
3) The aerobic system provides sustained energy for longer duration activities through the breakdown of nutrients like glucose and fatty acids with oxygen and involves chemical reactions in the mitochondria.Samantha lawson assignment 1 energy systems



Samantha lawson assignment 1 energy systemsSteve Saffhill
Ěý
The document discusses the three energy systems - ATP-PCr, glycolytic, and oxidative. It provides details on each system including the fuel sources, duration of energy production, and examples of sports that rely on each system. It also includes figures illustrating the ATP-PCr cycle, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain, and beta oxidation. Application examples are provided discussing the energy systems used in a 100m sprint and 1500m race. Factors like blood lactate levels and VO2 max in relation to intensity are also summarized.Energy systems by Antonia Depinto



Energy systems by Antonia DepintoAntonia DePinto
Ěý
Energy is the ability to do work and comes in different forms. The human body gets energy from breaking down food sources like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The body has three energy systems - phosphocreatine, lactic acid, and aerobic - that produce ATP for muscle contraction and movement. The phosphocreatine system provides fast energy for bursts of intense activity up to 10 seconds. The lactic acid system takes over for moderate intensity exercise up to 3 minutes. The aerobic system produces sustained energy for low to moderate intensity activities lasting over 3 minutes by using oxygen.Energy systems



Energy systemsEllie Martin
Ěý
The document discusses the three main energy systems in the body:
1. ATP-PC system - Produces a constant flow of ATP for daily activity and fuels metabolism. Important for short bursts of energy.
2. Lactic acid system - Fuels high intensity exercise for short periods through anaerobic respiration, but builds up lactic acid.
3. Aerobic system - Most complex system that produces the most ATP for longest periods through oxygen, good for long distance exercise and weight loss. Each system fuels different aspects of movement and lifestyle.Energy systems (p7, m4, d2)



Energy systems (p7, m4, d2)aaron miller
Ěý
Energy is required for sustained physical and mental activity and is obtained from foods and drinks through digestion. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the primary energy carrier in living organisms and is broken down through hydrolysis to provide energy for growth and life. There are three energy systems - ATP-PC, lactic acid, and aerobic - that are used depending on the oxygen availability and energy demands, with the ATP-PC system providing immediate energy through phosphocreatine breakdown, the lactic acid system producing 2-3 ATP molecules anaerobically, and the aerobic system producing 38-129 ATP molecules with oxygen. A 100m sprint predominantly uses the ATP-PC system while a 1500m race uses allEnergy system .ppt,(EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGY)



Energy system .ppt,(EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGY)jeminiparmar2912
Ěý
The human body relies on a complex energy system to sustain life and perform various physiological functions. This energy system involves the conversion of nutrients from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary molecule used for energy in cells. There are three main energy systems that contribute to ATP production: the phosphagen system, the glycolytic system, and the oxidative system.Energy systems 2
- 1. Energy Systems for Exercise Presenter: Ms. Lea Green
- 2. The human body is made to move in many ways: Quick and powerful Graceful & coordinated Sustained for many hours And is dependent upon the capacity to produce energy
- 3. We have a great amount of diversity Quick movements-lasts a few seconds Reduced speed-lasts for several minutes Reduced intensity(50%)-lasts for several hours The body uses different energy systems for each activity
- 4. Cells in the body need energy to function FOOD=ENERGY (E)
- 5. Cells don’t get Energy directly from food, it must be broken down into: ATP -Adensosine TRIphosphate ATP = a form of energy one can immediately use, it is needed for cells to function & muscles to contract
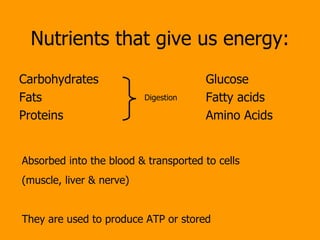
- 6. Nutrients that give us energy: Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Glucose Fatty acids Amino Acids Digestion Absorbed into the blood & transported to cells (muscle, liver & nerve) They are used to produce ATP or stored
- 7. ATP is stored in small amounts, therefore the rest is stored as: Glucose = Glycogen (muscle & liver) Fatty Acids = Body fat Amino Acids = Growth, repair or excreted as waste
- 8. Predominant Energy Pathways ATP (2-3 seconds) ATP-CP Energy System (8-10 seconds) Anaerobic Energy System (2-3 minutes) Aerobic Energy System (3 minutes +)
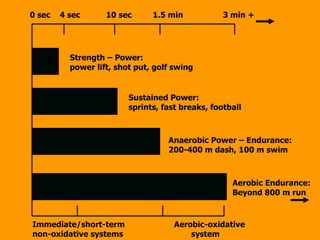
- 9. 0 sec 4 sec 10 sec 1.5 min 3 min + Strength – Power: power lift, shot put, golf swing Sustained Power: sprints, fast breaks, football Anaerobic Power – Endurance: 200-400 m dash, 100 m swim Aerobic Endurance: Beyond 800 m run Immediate/short-term Aerobic-oxidative non-oxidative systems system
- 10. ATP-CP Energy System ATP is stored in the muscle & liver for “Quick Energy” Nerve impulses trigger breakdown of ATP into ADP ADP = Adenosine Diphosphate & 1 Phosphate The splitting of the Phosphate bond = Energy for work Ex. Muscle Contraction, Moving hand from a hot stove, Jumping & Throwing
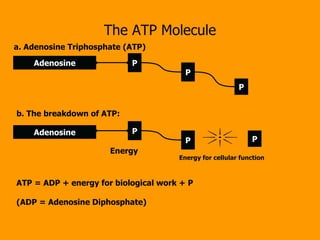
- 11. The ATP Molecule Adenosine Adenosine Energy a. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) b. The breakdown of ATP: P P P P P P ATP = ADP + energy for biological work + P (ADP = Adenosine Diphosphate) Energy for cellular function
- 12. For contractions to continue… ATP must be REBUILT This comes from the splitting of CP (Creatine Phosphate a Hi energy source, automatic) When ATP is used – it is rebuilt – as long as there is CP Energy released from CP breaking down, resynthesizes the ADP & P
- 13. REMEMBER – only small amounts of ATP are stored = only 2-3 sec. of Energy ATP-CP = 8-10 sec. of Energy The usefulness isn’t the AMOUNT of Energy but the QUICK & POWERFUL movements For longer periods of work = The Aerobic & Anaerobic Energy System must be utilized
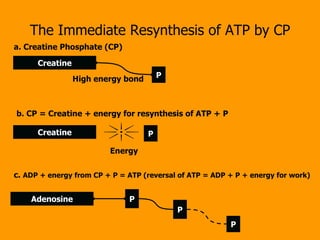
- 14. The Immediate Resynthesis of ATP by CP Creatine P Creatine P Energy High energy bond a. Creatine Phosphate (CP) b. CP = Creatine + energy for resynthesis of ATP + P Adenosine P P P c. ADP + energy from CP + P = ATP (reversal of ATP = ADP + P + energy for work)
- 15. Anaerobic Energy System Without oxygen = Activities that require a large burst of energy over a short period of time Anaerobic Glycolysis = Production of ATP from Carbohydrates without oxygen (breakdown of glucose)
- 16. Since glycogen is stored in the muscle & liver, it is available quickly This system provides ATP when ATP-CP runs out Again, ATP-CP lasts for a few seconds, the Anaerobic Energy System allows for 2-3 minutes of work
- 17. The process to produce ATP is not as fast as ATP-CP, which makes muscle contraction slower When oxygen is not present the end product of glycolisis is lactic acid, which causes the muscles to fatigue Anaerobic Glycolisis is less efficient in producing ATP than Aerobic Glycolisis, BUT is needed for a large burst of energy lasting a few minutes
- 18. Without Oxygen Glucose = 2ATP + 2LA (digested component of carbohydrates) Glycogen = 3ATP + 2LA (the storage form of glucose)
- 19. With Oxygen Glucose + O2 = 36ATP + H2O + CO2 Fatty Acids + O2 = 129ATP Body Fat is a great source of ENERGY
- 20. Oxygen Deficit = The body can not supply enough O2 to the muscles that the muscles demand When the muscle does not get enough oxygen, exhaustion is reached causing immediate and involuntary reduction in intensity Oxygen Debt = “pays back” the deficit recovery time
- 21. Aerobic Energy System With Oxygen = Using large muscle groups continuously over a period of time Aerobic Glycolisis & Fatty Acid Oxidation = The production of ATP from Carbohydrates & Fat
- 22. O2 enters the system, stopping the breakdown of glycogen to lactic acid With oxygen, glycogen breaks down into: ATP + CO2 + H20 These byproducts are easier to get rid of CO2 is expelled by the lungs H20 is used in the muscle
- 23. 4.Anaerobic Energy System = Carbohydrates are the only fuel source 5.With prolonged exercise, Carbohydrates are the first fuel choice, as exercise continues, FAT becomes predominant 6.Protein is not a main fuel source except in an emergency
- 24. Each system plays an important role in energy production This gives us a variety of movements The systems interact to supply Energy for the activity
- 25. Examples Anaerobic 70-80% Anaerobic Aerobic 20-30% Aerobic Wt. Training Stop & Go Sports Jogging Gymnastics Tennis Marathons Football Soccer Cycling Baseball Field Hockey Aerobic Dance
- 26. Shelton State Wellness Center PED 223 Methods of Instruction