English tense1
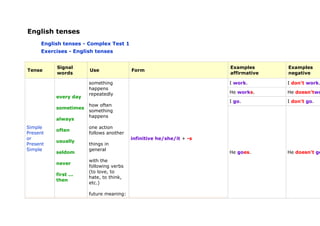
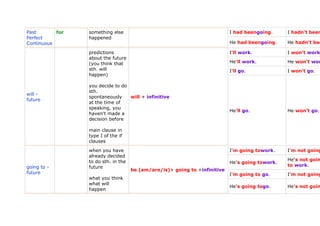
- 1. English tenses English tenses - Complex Test 1 Exercises - English tenses Signal Examples Examples Tense Use Form words affirmative negative something I work. I don't work. happens repeatedly He works. He doesn'two every day I go. I don't go. how often sometimes something happens always Simple one action often Present follows another or infinitive he/she/it + -s usually Present things in Simple general seldom He goes. He doesn't go with the never following verbs (to love, to first ... hate, to think, then etc.) future meaning:
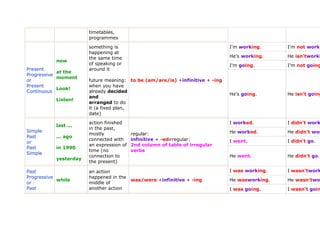
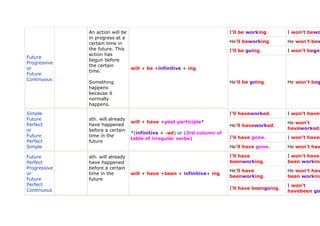
- 2. timetables, programmes something is I'm working. I'm not worki happening at the same time He's working. He isn'tworki now of speaking or I'm going. I'm not going Present around it at the Progressive moment or future meaning: to be (am/are/is) +infinitive + -ing Present when you have Look! Continuous already decided He's going. He isn't going and Listen! arranged to do it (a fixed plan, date) action finished I worked. I didn't work last ... in the past, Simple He worked. He didn't wor mostly regular: Past ... ago connected with infinitive + -edirregular: I went. I didn't go. or an expression of 2nd column of table of irregular Past in 1990 time (no verbs Simple connection to He went. He didn't go. yesterday the present) Past an action I was working. I wasn'twork Progressive happened in the while was/were +infinitive + -ing He wasworking. He wasn'twor or middle of Past another action I was going. I wasn't goin
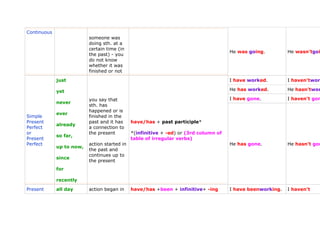
- 3. Continuous someone was doing sth. at a certain time (in He was going. He wasn'tgoi the past) - you do not know whether it was finished or not just I have worked. I haven'twork yet He has worked. He hasn'twor you say that I have gone. I haven't gon never sth. has happened or is ever Simple finished in the Present past and it has have/has + past participle* already Perfect a connection to or the present *(infinitive + -ed) or (3rd column of so far, Present table of irregular verbs) Perfect action started in He has gone. He hasn't gon up to now, the past and continues up to since the present for recently Present all day action began in have/has +been + infinitive+ -ing I have beenworking. I haven't
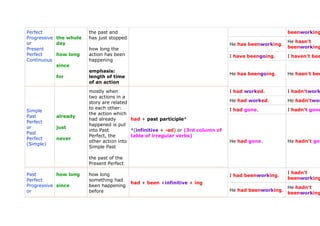
- 4. Perfect the past and beenworking Progressive the whole has just stopped or day He hasn't He has beenworking. Present how long the beenworking Perfect how long action has been I have beengoing. I haven't bee Continuous happening since emphasis: He has beengoing. He hasn't bee for length of time of an action mostly when I had worked. I hadn'twork two actions in a story are related He had worked. He hadn'twor to each other: I had gone. I hadn't gone Simple the action which Past already had already had + past participle* Perfect happened is put or just into Past *(infinitive + -ed) or (3rd column of Past Perfect, the table of irregular verbs) Perfect never other action into He had gone. He hadn't gon (Simple) Simple Past the past of the Present Perfect Past how long how long I hadn't I had beenworking. Perfect something had beenworking had + been +infinitive + ing Progressive since been happening He hadn't or before He had beenworking. beenworking
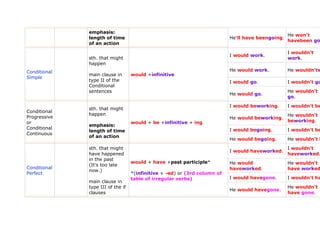
- 5. Past for something else I had beengoing. I hadn't been Perfect happened Continuous He had beengoing. He hadn't bee predictions I'll work. I won't work about the future (you think that He'll work. He won't wor sth. will I'll go. I won't go. happen) you decide to do sth. will - spontaneously will + infinitive future at the time of speaking, you He'll go. He won't go. haven't made a decision before main clause in type I of the if clauses when you have I'm going towork. I'm not going already decided to do sth. in the He's not goin He's going towork. going to - future to work. be (am/are/is)+ going to +infinitive future I'm going to go. I'm not going what you think what will He's going togo. He's not goin happen
- 6. An action will be I'll be working. I won't bewo in progress at a certain time in He'll beworking. He won't bew the future. This I'll be going. I won't begoi action has Future begun before Progressive the certain or will + be +infinitive + ing time. Future Continuous Something He'll be going. He won't beg happens because it normally happens. Simple I'll haveworked. I won't havew Future sth. will already will + have +past participle* He won't Perfect have happened He'll haveworked. or before a certain haveworked. *(infinitive + -ed) or (3rd column of Future time in the I'll have gone. I won't haveg table of irregular verbs) Perfect future Simple He'll have gone. He won't hav Future sth. will already I'll have I won't have Perfect have happened beenworking. been working Progressive before a certain He'll have He won't hav or time in the will + have +been + infinitive+ ing beenworking. been working Future future Perfect I won't Continuous I'll have beengoing. havebeen go
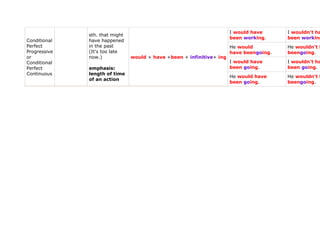
- 7. emphasis: He won't length of time He'll have beengoing. havebeen go of an action I wouldn't I would work. sth. that might work. happen Conditional He would work. He wouldn'tw main clause in would +infinitive Simple type II of the I would go. I wouldn't go Conditional sentences He wouldn't He would go. go. I would beworking. I wouldn't be sth. that might Conditional happen He wouldn't Progressive He would beworking. or would + be +infinitive + ing beworking. emphasis: Conditional I would begoing. I wouldn't be length of time Continuous of an action He would begoing. He wouldn't b sth. that might I wouldn't I would haveworked. have happened haveworked. in the past would + have +past participle* He would He wouldn't (It's too late Conditional haveworked. have worked now.) Perfect *(infinitive + -ed) or (3rd column of table of irregular verbs) I would havegone. I wouldn't ha main clause in type III of the if He wouldn't He would havegone. clauses have gone.
- 8. I would have I wouldn't ha sth. that might been working. been working Conditional have happened Perfect in the past He would He wouldn't h Progressive (It's too late have beengoing. beengoing. or now.) would + have +been + infinitive+ ing Conditional I would have I wouldn't ha Perfect emphasis: been going. been going. Continuous length of time He would have He wouldn't h of an action been going. beengoing.