Feed-forward loop database
2 likes2,107 views
The document describes a feed-forward loop (FFL) network motif. An FFL consists of two input transcription factors where one regulates the other and they jointly regulate a third gene. FFLs can have coherent or incoherent logic and either AND or OR logic. The document then discusses the structure and functions of FFLs, including how they can filter signals and respond to persistent stimuli. It also describes developing a database of FFLs to analyze regulatory networks.
1 of 19
Downloaded 13 times


Ad
Recommended
HMM (Hidden Markov Model)
HMM (Hidden Markov Model)Maharaj Vinayak Global University
╠²
This document provides an introduction to hidden Markov models (HMMs). It discusses that HMMs can be used to model sequential processes where the underlying states cannot be directly observed, only the outputs of the states. The document outlines the basic components of an HMM including states, transition probabilities, emission probabilities, and gives examples of HMMs for coin tossing and weather. It also briefly discusses the history of HMMs and their applications in fields like bioinformatics for problems such as gene finding.Applications of genomics and proteomics ppt
Applications of genomics and proteomics pptIbad khan
╠²
The document outlines the applications of genomics and proteomics across various fields including health, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and forensic analysis. It describes how these technologies are utilized in cancer detection, agricultural improvements, infectious disease diagnosis, personalized medicine, pharmacogenetics, and gene therapy. Key points include the potential for genomics to enhance crop yields, the role of proteomics in studying plant-insect interactions, and advancements in vaccine development through genome sequencing.Secondary protein structure prediction
Secondary protein structure predictionSiva Dharshini R
╠²
Secondary structure prediction tools analyze a protein's amino acid sequence to predict its 3D structure and function. These tools use various methods like Chou-Fasman, GOR, neural networks, and hidden Markov models to identify alpha helices and beta sheets based on characteristics like residue propensity values, sequence homology, and patterns in windows of amino acids. Accurate prediction of secondary structure is important for determining a protein's tertiary structure and biological role.NGS File formats
NGS File formatsHARSHITHA EBBALI
╠²
This document provides an overview of next generation sequencing (NGS), including common file formats like FASTA, FASTQ, and SRA. It discusses the applications of NGS such as genome sequencing, RNA sequencing, and microbiome analysis. Finally, it outlines some drawbacks of NGS, such as the unknown clinical significance of some identified variants and the large data storage requirements.Sequence alignment global vs. local
Sequence alignment global vs. localbenazeer fathima
╠²
This document discusses global and local sequence alignment. Global alignment aims to align the entire sequences, treating gaps equally across the sequences. It is useful for closely related sequences of similar length. Local alignment finds locally similar regions, allowing gaps to be treated differently. It is useful for more distantly related sequences that may contain similar subsequences. Both use dynamic programming, with global alignment using Needleman-Wunsch and local using Smith-Waterman. Dynamic programming breaks the problem into subproblems by filling a matrix to find the highest scoring alignment.Data Retrieval Systems
Data Retrieval SystemsSaramita De Chakravarti
╠²
The document discusses different text-based database retrieval systems for accessing biological data, including Entrez, SRS, and DBGET/LinkDB. It describes their key features and how each system allows users to search text databases using queries, with Entrez providing linked related data across multiple databases. An example shows how each system can be used to retrieve and view related information for a SwissProt protein entry.Kegg
Keggmsfbi1521
╠²
The document describes several key databases within the KEGG resource, including:
- The PATHWAY database containing molecular network maps of metabolic and genetic pathways.
- The BRITE database providing hierarchical classifications of biological systems beyond what is shown in pathways.
- The LIGAND database consisting of chemical compounds, carbohydrates, reactions, and enzyme information.
KEGG aims to comprehensively capture biological knowledge through integrated databases covering genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs.Protein databases
Protein databasessarumalay
╠²
Protein databases can contain either sequence or structure information. Some key protein sequence databases include PIR, Swiss-Prot, and TrEMBL. PIR classifies entries by annotation level, Swiss-Prot aims to provide high annotation levels and interlink information, and TrEMBL contains all coding sequences with some entries eventually incorporated into Swiss-Prot. Important structure databases are PDB, which contains 3D protein structures, and SCOP and CATH, which classify evolutionary and structural relationships between protein domains.Sequence Alignment In Bioinformatics
Sequence Alignment In BioinformaticsNikesh Narayanan
╠²
This document discusses identifying mutations in the filaggrin gene through sequence analysis. The filaggrin gene codes for filaggrin proteins that are essential for skin barrier function. Mutations in this gene are linked to conditions like eczema and asthma. The study aims to detect faulty filaggrin genes, identify other human and non-human proteins with similar function to filaggrin, and find identical protein sequences to help develop therapeutic options. Sequence alignment methods like pairwise alignment and BLAST will be used to analyze filaggrin genes and identify similar protein sequences.Molecular probes kashmeera n.a.
Molecular probes kashmeera n.a.Kashmeera N.A.
╠²
Molecular probes are small DNA or RNA segments that are used to detect complementary nucleic acid sequences in samples. There are several types of probes including genomic DNA probes, cDNA probes, synthetic oligonucleotides, and RNA probes. Probes are typically labeled with radioactive isotopes or non-radioactive labels like fluorophores or biotin to allow for detection after hybridization with target sequences. Molecular probes have many applications including genetic mapping, DNA fingerprinting, and diagnosis of diseases.Blast Algorithm
Blast AlgorithmDaffodil international University
╠²
The document discusses BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool), an algorithm used to compare a query DNA or protein sequence against a database of sequences. BLAST works by identifying exact or approximate matches between words of 3-11 letters in the query and database sequences. Matches are extended to find local alignments with high scores. Significant alignments are identified based on their score and the expected number of matches by chance (E-value). The document provides examples of how BLAST finds local alignments and calculates E-values. It also describes different BLAST programs and suggestions for using BLAST.Data retrieval tools
Data retrieval toolsVidya Kalaivani Rajkumar
╠²
The document discusses three data retrieval tools - Entrez, DBGET, and SRS - that allow molecular biologists to search and access information across multiple linked databases. Entrez, developed by NCBI, integrates information from databases including GenBank, RefSeq, PDB, and PubMed. SRS, developed by EBI, is an open source software that integrates over 80 molecular biology databases and has a scripting language called Icarus. SRS indexes over 250 databases and has over 35 servers worldwide. It allows searching of sequence, structure, gene-related, and bibliographic databases through a uniform web interface.Pairwise sequence alignment
Pairwise sequence alignmentavrilcoghlan
╠²
1) Pairwise sequence alignment is a method to compare two biological sequences like DNA, RNA, or proteins. It involves arranging the sequences in columns to highlight their similarities and differences.
2) There are many possible alignments between two sequences, but most imply too many mutations. The best alignment minimizes the number of mutations needed to explain the differences between the sequences.
3) For short protein sequences like "QKGSYPVRSTC" and "QKGSGPVRSTC", the optimal alignment implies one single mutation occurred since the sequences diverged from a common ancestor.Gene mapping tools
Gene mapping toolsUsman Arshad
╠²
Gene mapping tools can be used to represent the arrangement of genes on chromosomes and determine the position and distance between genes. There are several types of gene mapping including physical mapping, genetic mapping, and linkage mapping. Physical mapping uses molecular techniques to examine DNA directly to construct maps showing gene positions. Genetic maps are based on recombination frequencies between genes and measure distances in centimorgans. Different DNA markers can also be used for mapping, including RFLPs, SNPs, SSLPs, and STSs, along with techniques like FISH, restriction digests, and PCR to analyze these markers and produce genome maps. Gene mapping is important for identifying mutant genes that cause genetic disorders and furthering our understanding of human genetics.Chromosome walking
Chromosome walkingZohaib HUSSAIN
╠²
Chromosome walking is a technique used to explore unknown regions of a chromosome by using a known gene fragment as a probe to identify overlapping fragments. The process is limited by issues with genome-wide repeat sequences, which can lead to non-specific hybridization, and challenges with walking through repeated DNA sequences; advancements such as chromosome jumping have been developed to address these limitations. Applications include the analysis of genetically transmitted diseases and the discovery of single-nucleotide polymorphisms.Homology
Homologyavrilcoghlan
╠²
Homologous genes are genes that have descended from a common ancestral gene. There are two main types of homologous genes:
1. Orthologous genes are homologous genes in different species that arose due to speciation. For example, the human and mouse eyeless genes are orthologs that descended from the eyeless gene in their last common ancestor.
2. Paralogous genes are homologous genes within the same species that arose due to a gene duplication event. For example, the fruit fly eyeless and twin of eyeless genes are paralogs that descended from a duplication of the eyeless gene in a fruit fly ancestor.
Homologous genes can differ in their sequences dueRasmol
RasmolVidya Kalaivani Rajkumar
╠²
Rasmol and Swiss-PDB viewer are molecular visualization tools that allow users to view and analyze protein structures. Rasmol can display molecules in various representations like wireframe, cylinders, or ribbons. It supports common file formats like PDB and can rotate, zoom, and translate structures. Swiss-PDB viewer is tightly integrated with homology modeling and allows users to build models, compare structures, and view electron density maps. It utilizes template structures from the PDB to generate models and assess their quality. Both tools provide publication-quality images and interactive visualization of biomolecular structures.Gene expression profiling
Gene expression profilingPriyankaPriyanka63
╠²
Gene expression and transcript profiling involves determining the pattern of genes expressed at the transcriptional level under specific circumstances by measuring the expression of thousands of genes simultaneously. This allows one to understand cellular function. Common techniques for profiling include DNA microarrays, RNA sequencing, and EST tags. DNA microarrays involve hybridizing cDNA or cRNA samples to probes on a chip to determine relative abundance of sequences. RNA sequencing uses next-generation sequencing to reveal presence and quantity of RNA in a sample.BIOLOGICAL SEQUENCE DATABASES
BIOLOGICAL SEQUENCE DATABASES nadeem akhter
╠²
The document discusses the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), which maintains biological databases and provides bioinformatics tools. NCBI houses both primary databases directly submitted by researchers and secondary databases compiled from primary sources. Major databases include GenBank (nucleotide sequences), PubMed Central (biomedical literature), and reference sequence databases. Tools like BLAST, Entrez, and ORFfinder allow users to search and analyze sequence data. NCBI aims to make biomedical research data freely accessible worldwide.Genomic databases
Genomic databasesDrSatyabrataSahoo
╠²
This document discusses genomic databases. It begins by defining key terms like genes, genomes, and genomics. It then describes categories of biological databases including those for nucleic acid sequences, proteins, structures, and genomes. It provides many examples of genomic databases for both non-vertebrate and vertebrate species, including databases for bacteria, fungi, plants, invertebrates, and humans. The final sections note that genomic databases collect genome-wide data from various sources and that databases can be specific to a single organism or category of organisms.Gene tagging.pptx
Gene tagging.pptxPrabhatSingh628463
╠²
This document provides a summary of gene tagging as the topic for the subject of genomics in plant breeding. It was submitted by Prabhat Kumar Singh, a 1st year Ph.D student in agricultural biotechnology. References for further reading on the topic include an introduction to plant biotechnology book, a book on biotechnology, and information from Google ║▌║▌▀Żshare.GENOMIC MAPPING:FISH(Fluorescent in situ hybridization )
GENOMIC MAPPING:FISH(Fluorescent in situ hybridization )UTTARAN MODHUKALYA
╠²
The document discusses genomic mapping via fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), describing its principles, procedures, types, advantages, and disadvantages. FISH is used to identify and visualize the arrangement of genes or DNA sequences on chromosomes, particularly useful for detecting chromosomal abnormalities. Its applications include monitoring therapy effects and identifying gene deletions or amplifications, despite limitations in sensitivity and the ability to assess multiple abnormalities simultaneously.Genome annotation
Genome annotationShifa Ansari
╠²
Genome annotation is the process of interpreting raw DNA sequences to extract biological significance, with two main steps: structural and functional annotation. The challenges include the complexity of predicting gene elements in eukaryotes and the reliance on computational tools to minimize human intervention. Various gene prediction programs and automatic annotation pipelines have been developed to improve accuracy and efficiency in assigning functions to predicted genes.Composite and Specialized databases
Composite and Specialized databasesThapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, Patiala, Punjab, India
╠²
The document discusses composite and specialized databases, highlighting their functions and examples. Composite databases, like owl and nrdb, compile and filter sequence data from primary databases, while specialized databases focus on specific subject areas or formats. Additionally, rebase is introduced as a comprehensive database for restriction enzymes and their characteristics.Phage display
Phage displayBalaji Rathod
╠²
Phage display technology allows the display of proteins or peptides on the outside of bacteriophages while encoding the corresponding gene on the inside. This allows for large libraries to be screened in vitro to select for interactions between the displayed molecules and a target. The most common phages used are filamentous phages like M13, which can be genetically manipulated to display proteins of interest. The technique involves inserting a gene into the phage coat protein gene, infecting bacteria to produce phage particles displaying the protein, and panning against a target to isolate interacting proteins.homologus recombination
homologus recombinationDeepak Rohilla
╠²
This document summarizes homologous recombination in eukaryotes and bacteria. In eukaryotes, homologous recombination repairs double-strand DNA breaks through either the double-strand break repair (DSBR) pathway or synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA) pathway. The DSBR pathway forms double Holliday junctions that are resolved to result in crossover or non-crossover products. In bacteria, the RecBCD pathway repairs double-strand breaks and the RecF pathway repairs single-strand gaps. Both pathways involve strand invasion and branch migration to facilitate homologous recombination.Bioinformatic, and tools by kk sahu
Bioinformatic, and tools by kk sahuKAUSHAL SAHU
╠²
The document discusses bioinformatics tools used for analyzing biological data. It begins with an introduction to bioinformatics and then describes several categories of tools: biological databases for storing genomic and protein data; homology tools for sequence alignment and comparison; protein function analysis tools; structural analysis tools; and sequence manipulation and analysis tools. Common tools discussed include BLAST, FASTA, ClustalW, and databases like GenBank. The document concludes by covering applications of bioinformatics in areas like molecular modeling, medicine, and computation.Hidden markov model
Hidden markov modelUshaYadav24
╠²
This document provides an overview of hidden Markov models (HMMs). It defines HMMs as statistical Markov models that include both observed and hidden states. The key components of an HMM are states (Q), observations (V), initial state probabilities (p), state transition probabilities (A), and emission probabilities (E). HMMs find applications in areas like protein structure prediction, sequence alignment, and gene finding. The Viterbi algorithm is described as a dynamic programming approach for finding the most likely sequence of hidden states in an HMM. Advantages of HMMs include their statistical power and modularity, while disadvantages include assumptions of state independence and potential for overfitting.Swati cffl ppr
Swati cffl pprSwati Kumari
╠²
This paper presents a study on a coherent feed-forward loop (C1-FFL) in Escherichia coli that has a sum input function, affecting flagella expression. The results demonstrate a sign-sensitive delay in gene expression activation and deactivation related to the interactions of transcription factors involved, highlighting the regulatory complexities in bacterial networks. The findings suggest that this regulatory mechanism allows the flagella system to sustain expression in response to environmental conditions, aligning with the time required for flagella assembly.Computational Synthetic Biology
Computational Synthetic BiologyNatalio Krasnogor
╠²
The document discusses the interdisciplinary aspects of synthetic biology, emphasizing the design and optimization of biological systems through computational modeling. It outlines the integration of systems biology and synthetic biology to create engineered biological entities with potential applications in healthcare and environmental protection. Ethical, social, and legal considerations are also mentioned in relation to the advancement of this field.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Sequence Alignment In Bioinformatics
Sequence Alignment In BioinformaticsNikesh Narayanan
╠²
This document discusses identifying mutations in the filaggrin gene through sequence analysis. The filaggrin gene codes for filaggrin proteins that are essential for skin barrier function. Mutations in this gene are linked to conditions like eczema and asthma. The study aims to detect faulty filaggrin genes, identify other human and non-human proteins with similar function to filaggrin, and find identical protein sequences to help develop therapeutic options. Sequence alignment methods like pairwise alignment and BLAST will be used to analyze filaggrin genes and identify similar protein sequences.Molecular probes kashmeera n.a.
Molecular probes kashmeera n.a.Kashmeera N.A.
╠²
Molecular probes are small DNA or RNA segments that are used to detect complementary nucleic acid sequences in samples. There are several types of probes including genomic DNA probes, cDNA probes, synthetic oligonucleotides, and RNA probes. Probes are typically labeled with radioactive isotopes or non-radioactive labels like fluorophores or biotin to allow for detection after hybridization with target sequences. Molecular probes have many applications including genetic mapping, DNA fingerprinting, and diagnosis of diseases.Blast Algorithm
Blast AlgorithmDaffodil international University
╠²
The document discusses BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool), an algorithm used to compare a query DNA or protein sequence against a database of sequences. BLAST works by identifying exact or approximate matches between words of 3-11 letters in the query and database sequences. Matches are extended to find local alignments with high scores. Significant alignments are identified based on their score and the expected number of matches by chance (E-value). The document provides examples of how BLAST finds local alignments and calculates E-values. It also describes different BLAST programs and suggestions for using BLAST.Data retrieval tools
Data retrieval toolsVidya Kalaivani Rajkumar
╠²
The document discusses three data retrieval tools - Entrez, DBGET, and SRS - that allow molecular biologists to search and access information across multiple linked databases. Entrez, developed by NCBI, integrates information from databases including GenBank, RefSeq, PDB, and PubMed. SRS, developed by EBI, is an open source software that integrates over 80 molecular biology databases and has a scripting language called Icarus. SRS indexes over 250 databases and has over 35 servers worldwide. It allows searching of sequence, structure, gene-related, and bibliographic databases through a uniform web interface.Pairwise sequence alignment
Pairwise sequence alignmentavrilcoghlan
╠²
1) Pairwise sequence alignment is a method to compare two biological sequences like DNA, RNA, or proteins. It involves arranging the sequences in columns to highlight their similarities and differences.
2) There are many possible alignments between two sequences, but most imply too many mutations. The best alignment minimizes the number of mutations needed to explain the differences between the sequences.
3) For short protein sequences like "QKGSYPVRSTC" and "QKGSGPVRSTC", the optimal alignment implies one single mutation occurred since the sequences diverged from a common ancestor.Gene mapping tools
Gene mapping toolsUsman Arshad
╠²
Gene mapping tools can be used to represent the arrangement of genes on chromosomes and determine the position and distance between genes. There are several types of gene mapping including physical mapping, genetic mapping, and linkage mapping. Physical mapping uses molecular techniques to examine DNA directly to construct maps showing gene positions. Genetic maps are based on recombination frequencies between genes and measure distances in centimorgans. Different DNA markers can also be used for mapping, including RFLPs, SNPs, SSLPs, and STSs, along with techniques like FISH, restriction digests, and PCR to analyze these markers and produce genome maps. Gene mapping is important for identifying mutant genes that cause genetic disorders and furthering our understanding of human genetics.Chromosome walking
Chromosome walkingZohaib HUSSAIN
╠²
Chromosome walking is a technique used to explore unknown regions of a chromosome by using a known gene fragment as a probe to identify overlapping fragments. The process is limited by issues with genome-wide repeat sequences, which can lead to non-specific hybridization, and challenges with walking through repeated DNA sequences; advancements such as chromosome jumping have been developed to address these limitations. Applications include the analysis of genetically transmitted diseases and the discovery of single-nucleotide polymorphisms.Homology
Homologyavrilcoghlan
╠²
Homologous genes are genes that have descended from a common ancestral gene. There are two main types of homologous genes:
1. Orthologous genes are homologous genes in different species that arose due to speciation. For example, the human and mouse eyeless genes are orthologs that descended from the eyeless gene in their last common ancestor.
2. Paralogous genes are homologous genes within the same species that arose due to a gene duplication event. For example, the fruit fly eyeless and twin of eyeless genes are paralogs that descended from a duplication of the eyeless gene in a fruit fly ancestor.
Homologous genes can differ in their sequences dueRasmol
RasmolVidya Kalaivani Rajkumar
╠²
Rasmol and Swiss-PDB viewer are molecular visualization tools that allow users to view and analyze protein structures. Rasmol can display molecules in various representations like wireframe, cylinders, or ribbons. It supports common file formats like PDB and can rotate, zoom, and translate structures. Swiss-PDB viewer is tightly integrated with homology modeling and allows users to build models, compare structures, and view electron density maps. It utilizes template structures from the PDB to generate models and assess their quality. Both tools provide publication-quality images and interactive visualization of biomolecular structures.Gene expression profiling
Gene expression profilingPriyankaPriyanka63
╠²
Gene expression and transcript profiling involves determining the pattern of genes expressed at the transcriptional level under specific circumstances by measuring the expression of thousands of genes simultaneously. This allows one to understand cellular function. Common techniques for profiling include DNA microarrays, RNA sequencing, and EST tags. DNA microarrays involve hybridizing cDNA or cRNA samples to probes on a chip to determine relative abundance of sequences. RNA sequencing uses next-generation sequencing to reveal presence and quantity of RNA in a sample.BIOLOGICAL SEQUENCE DATABASES
BIOLOGICAL SEQUENCE DATABASES nadeem akhter
╠²
The document discusses the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), which maintains biological databases and provides bioinformatics tools. NCBI houses both primary databases directly submitted by researchers and secondary databases compiled from primary sources. Major databases include GenBank (nucleotide sequences), PubMed Central (biomedical literature), and reference sequence databases. Tools like BLAST, Entrez, and ORFfinder allow users to search and analyze sequence data. NCBI aims to make biomedical research data freely accessible worldwide.Genomic databases
Genomic databasesDrSatyabrataSahoo
╠²
This document discusses genomic databases. It begins by defining key terms like genes, genomes, and genomics. It then describes categories of biological databases including those for nucleic acid sequences, proteins, structures, and genomes. It provides many examples of genomic databases for both non-vertebrate and vertebrate species, including databases for bacteria, fungi, plants, invertebrates, and humans. The final sections note that genomic databases collect genome-wide data from various sources and that databases can be specific to a single organism or category of organisms.Gene tagging.pptx
Gene tagging.pptxPrabhatSingh628463
╠²
This document provides a summary of gene tagging as the topic for the subject of genomics in plant breeding. It was submitted by Prabhat Kumar Singh, a 1st year Ph.D student in agricultural biotechnology. References for further reading on the topic include an introduction to plant biotechnology book, a book on biotechnology, and information from Google ║▌║▌▀Żshare.GENOMIC MAPPING:FISH(Fluorescent in situ hybridization )
GENOMIC MAPPING:FISH(Fluorescent in situ hybridization )UTTARAN MODHUKALYA
╠²
The document discusses genomic mapping via fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), describing its principles, procedures, types, advantages, and disadvantages. FISH is used to identify and visualize the arrangement of genes or DNA sequences on chromosomes, particularly useful for detecting chromosomal abnormalities. Its applications include monitoring therapy effects and identifying gene deletions or amplifications, despite limitations in sensitivity and the ability to assess multiple abnormalities simultaneously.Genome annotation
Genome annotationShifa Ansari
╠²
Genome annotation is the process of interpreting raw DNA sequences to extract biological significance, with two main steps: structural and functional annotation. The challenges include the complexity of predicting gene elements in eukaryotes and the reliance on computational tools to minimize human intervention. Various gene prediction programs and automatic annotation pipelines have been developed to improve accuracy and efficiency in assigning functions to predicted genes.Composite and Specialized databases
Composite and Specialized databasesThapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, Patiala, Punjab, India
╠²
The document discusses composite and specialized databases, highlighting their functions and examples. Composite databases, like owl and nrdb, compile and filter sequence data from primary databases, while specialized databases focus on specific subject areas or formats. Additionally, rebase is introduced as a comprehensive database for restriction enzymes and their characteristics.Phage display
Phage displayBalaji Rathod
╠²
Phage display technology allows the display of proteins or peptides on the outside of bacteriophages while encoding the corresponding gene on the inside. This allows for large libraries to be screened in vitro to select for interactions between the displayed molecules and a target. The most common phages used are filamentous phages like M13, which can be genetically manipulated to display proteins of interest. The technique involves inserting a gene into the phage coat protein gene, infecting bacteria to produce phage particles displaying the protein, and panning against a target to isolate interacting proteins.homologus recombination
homologus recombinationDeepak Rohilla
╠²
This document summarizes homologous recombination in eukaryotes and bacteria. In eukaryotes, homologous recombination repairs double-strand DNA breaks through either the double-strand break repair (DSBR) pathway or synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA) pathway. The DSBR pathway forms double Holliday junctions that are resolved to result in crossover or non-crossover products. In bacteria, the RecBCD pathway repairs double-strand breaks and the RecF pathway repairs single-strand gaps. Both pathways involve strand invasion and branch migration to facilitate homologous recombination.Bioinformatic, and tools by kk sahu
Bioinformatic, and tools by kk sahuKAUSHAL SAHU
╠²
The document discusses bioinformatics tools used for analyzing biological data. It begins with an introduction to bioinformatics and then describes several categories of tools: biological databases for storing genomic and protein data; homology tools for sequence alignment and comparison; protein function analysis tools; structural analysis tools; and sequence manipulation and analysis tools. Common tools discussed include BLAST, FASTA, ClustalW, and databases like GenBank. The document concludes by covering applications of bioinformatics in areas like molecular modeling, medicine, and computation.Hidden markov model
Hidden markov modelUshaYadav24
╠²
This document provides an overview of hidden Markov models (HMMs). It defines HMMs as statistical Markov models that include both observed and hidden states. The key components of an HMM are states (Q), observations (V), initial state probabilities (p), state transition probabilities (A), and emission probabilities (E). HMMs find applications in areas like protein structure prediction, sequence alignment, and gene finding. The Viterbi algorithm is described as a dynamic programming approach for finding the most likely sequence of hidden states in an HMM. Advantages of HMMs include their statistical power and modularity, while disadvantages include assumptions of state independence and potential for overfitting.Similar to Feed-forward loop database (18)
Swati cffl ppr
Swati cffl pprSwati Kumari
╠²
This paper presents a study on a coherent feed-forward loop (C1-FFL) in Escherichia coli that has a sum input function, affecting flagella expression. The results demonstrate a sign-sensitive delay in gene expression activation and deactivation related to the interactions of transcription factors involved, highlighting the regulatory complexities in bacterial networks. The findings suggest that this regulatory mechanism allows the flagella system to sustain expression in response to environmental conditions, aligning with the time required for flagella assembly.Computational Synthetic Biology
Computational Synthetic BiologyNatalio Krasnogor
╠²
The document discusses the interdisciplinary aspects of synthetic biology, emphasizing the design and optimization of biological systems through computational modeling. It outlines the integration of systems biology and synthetic biology to create engineered biological entities with potential applications in healthcare and environmental protection. Ethical, social, and legal considerations are also mentioned in relation to the advancement of this field.Bio305 Lecture on Gene Regulation in Bacterial Pathogens
Bio305 Lecture on Gene Regulation in Bacterial PathogensMark Pallen
╠²
This document summarizes the regulation of bacterial virulence gene expression. It discusses the hierarchical regulation of genes from the DNA to post-translational level. Key topics covered include transcription factors, operons, two-component systems, quorum sensing, and methods to study virulence gene expression such as reporter gene fusions, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and microarrays. The goal is to provide an overview of the complex regulatory networks that control bacterial pathogenesis.Conferencia Narendra Maheshri
Conferencia Narendra Maheshri lideresacademicos
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation on cell-to-cell variability in gene expression. It discusses three main points: 1) Gene expression can vary significantly between genetically identical cells due to stochastic fluctuations in transcription and translation. 2) Variability in gene expression can be controlled and exploited through positive feedback loops and transcriptional bursting. 3) Variability at the single cell level generates phenotypic diversity at the population level that can impact processes like microbial virulence. The presentation examines variability through experiments on yeast adhesin genes and proposes experiments to further study the role of gene expression variability.Shweta ppt I1FFL
Shweta ppt I1FFLShwetA Kumari
╠²
The document summarizes a research paper that studied the incoherent feed forward loop (I1-FFL) network motif in the galactose system of E. coli. It found that the I1-FFL accelerates the response time of the galE gene to depletion of glucose by allowing initial rapid expression from CRP activation before repression by GalS occurs. The galE promoter dynamics showed an accelerated response and overshoot not seen in the simple lacZ promoter regulation. Deletion of the GalS binding site eliminated this accelerated response, demonstrating it is dependent on the I1-FFL structure.Detection of genetic motifs
Detection of genetic motifsJuan Carlos Mun├®var
╠²
1) Randomly select positions to project sequences onto lower-dimensional "buckets" based on letters at those positions.
2) Recover motifs from buckets containing multiple sequences by building frequency matrices and refining with EM.
3) The best motif is the one with the highest score, where score is based on the likelihood ratio of sequences matching the motif model versus background.Systems Biology Lecture - SCFBIO Sep 18, 09.pdf
Systems Biology Lecture - SCFBIO Sep 18, 09.pdfVidyasriDharmalingam1
╠²
Systems biology is the study of complex interactions in biological systems using a holistic approach. It aims to understand emergent properties and entire processes in a system. Key aspects of systems biology include modeling interaction networks and dynamic behavior over time through computational and experimental methods. Understanding failure modes in biological signaling circuits could provide insights into neurodegenerative disorders caused by sustained high calcium levels triggering apoptosis.Transcription
TranscriptionJuan Carlos Mun├®var
╠²
The document discusses genetic motifs and promoters. It explains that transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) are short DNA sequences that transcription factors bind to in order to regulate gene expression. It then describes how the assembly of promoter protein complexes occurs through multiple stages involving different transcription factors binding to TFBS. The document also introduces information theory concepts like entropy and mutual information that can be used to detect motifs through measuring correlations between sequences. It provides an example algorithm that uses a sliding window approach to calculate mutual information between a probe TFBS sequence and candidate sequences in order to identify new potential TFBSs.Computational models for the analysis of gene expression regulation and its a...
Computational models for the analysis of gene expression regulation and its a...amathelier
╠²
The document discusses computational models for analyzing gene expression regulation, highlighting the complexity of gene regulation mechanisms, including transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulations, and the impact of cis-regulatory mutations on gene expression. It emphasizes the importance of identifying transcription factor binding sites (TFBSS) and presents advancements in predicting these sites using transcription factor flexible models (TFFMs). Additionally, the analysis of somatic mutations in B-cell lymphomas reveals a significant correlation between regulatory mutations and gene expression alterations associated with cancer pathways.NetBioSIG2012 kostiidit
NetBioSIG2012 kostiiditAlexander Pico
╠²
The document discusses an integrated regulatory network that highlights the complex interactions between transcription factors (TFs) and splicing factors (SFs) in gene expression regulation. It emphasizes the prevalence of alternative splicing and the regulatory roles of phosphorylation in cellular processes. Additionally, the study presents the methodologies for predicting TF and SF binding sites and analyzes the co-regulatory dynamics within the network.13-miller-chap-7b-lecture.ppt
13-miller-chap-7b-lecture.pptBalakumaran779282
╠²
1) The document discusses the promoters, regulatory sequences, and transcription factors that control gene expression in eukaryotes. It describes the basic components of promoters like the TATA box and initiator elements.
2) It explains how the pre-initiation complex of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors assembles at promoters. This includes the sequential binding of TBP, TFIIB, the Pol II-TFIIF complex, TFIIE, and TFIIH.
3) It covers different types of transcription factors that bind DNA, including zinc finger proteins, helix-turn-helix proteins, leucine zipper proteins, and discusses how they interact with DNA and each other to regulate transcription.13-miller-chap-7b-lecture.ppt
13-miller-chap-7b-lecture.pptSrishtiVerma95
╠²
1) The document discusses the mechanisms of transcriptional control in eukaryotes. It describes the core promoter elements, general transcription factors, and how they assemble to form the pre-initiation complex at RNA polymerase II promoters.
2) It also discusses the various classes of transcription factors that regulate gene expression, including their DNA-binding domains like zinc fingers, helix-turn-helices, and leucine zippers.
3) Transcription factor activity is regulated by ligands, co-factors, cooperative binding, and their assembly into enhanceosomes at gene enhancer elements.Transcription in eucaryotes
Transcription in eucaryotes KhetnaMantaw
╠²
1) The document discusses the mechanisms of transcriptional control in eukaryotes. It describes the core promoter elements like TATA boxes and initiator elements that recruit RNA polymerase II.
2) General transcription factors help assemble the preinitiation complex at promoters and position the polymerase for transcription initiation. This involves sequential binding of factors like TFIID, TFIIB, and others.
3) The document outlines different classes of transcription factors that regulate gene expression, including those that contain zinc fingers, helix-turn-helix motifs, and leucine zippers, and how they bind DNA.SBML: What Is It About?
SBML: What Is It About?Mike Hucka
╠²
SBML (Systems Biology Markup Language) is a format for representing computational models of biological processes. It defines data structures and serialization to XML for representing models in a neutral, machine-readable way. Development of SBML started in 2000 with the goal of facilitating exchange of models between software tools and databases. SBML provides syntax but limited semantics, so standard annotation schemes have been developed to link models to external data resources and provide additional meaning. The scope of SBML encompasses many types of biological models and is expanding through new packages to support additional model types.SBML (the Systems Biology Markup Language), model databases, and other resources
SBML (the Systems Biology Markup Language), model databases, and other resourcesMike Hucka
╠²
The document provides an overview of the Systems Biology Markup Language (SBML), its features, and its importance for modeling biological processes. It outlines key concepts, resources for modelers, and emphasizes the need for reproducibility and interoperability in biological modeling. Additionally, it discusses upcoming developments in SBML standards and the significance of annotations for enhancing model communication.Gene regulatory networks
Gene regulatory networksMadiheh
╠²
The document discusses gene regulatory networks (GRNs), including what they are, how they work, methods for modeling and analyzing them, and future challenges. Specifically, it notes that GRNs are networks of genes, proteins, and molecules that interact to control gene transcription. They respond to environmental signals and regulate processes like development. Computational models are needed to understand their complex behaviors under different conditions. Examples of models discussed include Boolean networks that represent gene expression levels as binary on/off states, continuous models that capture a range of expression levels, and stochastic models that account for random reactions.Lecture 6 (biol3600) transcription m rna processing- winter 2012 pw
Lecture 6 (biol3600) transcription m rna processing- winter 2012 pwPaula Faria Waziry
╠²
This chapter discusses transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, a single type of RNA polymerase binds to promoter sequences with the help of a sigma factor. Transcription proceeds through initiation, elongation, and termination. In eukaryotes, transcription requires chromatin remodeling and the binding of basal transcription factors that help recruit RNA polymerase to the promoter. RNA polymerase II synthesizes mRNA with the assistance of transcription factors that recognize regulatory promoter elements.Software for SBML Today
Software for SBML TodayMike Hucka
╠²
The document discusses the Systems Biology Markup Language (SBML), which is used for representing computational models of biological processes through a simple and flexible encoding system. It covers various aspects of SBML, including its modeling capabilities, software tools, features, and the types of models it supports, as well as the results of a survey on SBML software tools. Additionally, it highlights the diversity and utility of SBML and acknowledges the contributions of various funding organizations.Ad
Feed-forward loop database
- 1. BACA THEODOR-STEFAN and SINIAVSCHI RADU MASTER ITEMS 2012 FEED-FORWARD LOOP CENTRAL DATABASE Based on the article: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEED-FORWARD LOOP NETWORK MOTIF by S. Mangan and U. Alon
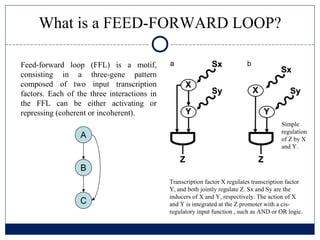
- 2. What is a FEED-FORWARD LOOP? Feed-forward loop (FFL) is a motif, consisting in a three-gene pattern composed of two input transcription factors. Each of the three interactions in the FFL can be either activating or repressing (coherent or incoherent). Simple regulation of Z by X and Y. Transcription factor X regulates transcription factor Y, and both jointly regulate Z. Sx and Sy are the inducers of X and Y, respectively. The action of X and Y is integrated at the Z promoter with a cis- regulatory input function , such as AND or OR logic.
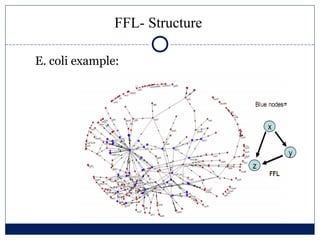
- 3. FFL- Structure E. coli example:
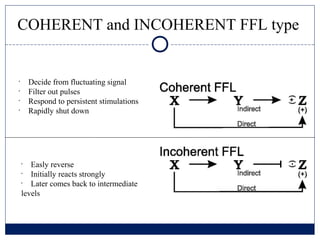
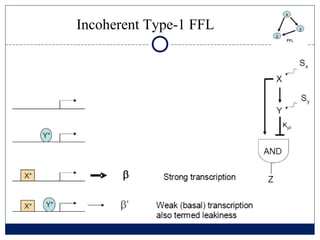
- 4. COHERENT and INCOHERENT FFL type ŌĆó Decide from fluctuating signal ŌĆó Filter out pulses ŌĆó Respond to persistent stimulations ŌĆó Rapidly shut down ŌĆó Easly reverse ŌĆó Initially reacts strongly ŌĆó Later comes back to intermediate levels
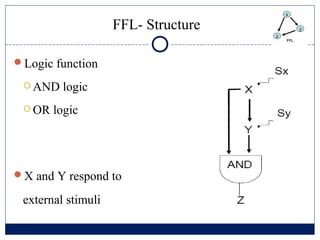
- 5. FFL- Structure ŅĢ░Logic function ’éĪ AND logic ’éĪ OR logic ŅĢ░X and Y respond to external stimuli
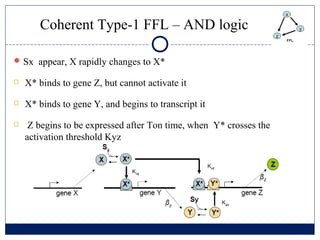
- 6. Coherent Type-1 FFL ŌĆō AND logic ŅĢ░ Sx appear, X rapidly changes to X* ’é© X* binds to gene Z, but cannot activate it ’é© X* binds to gene Y, and begins to transcript it ’é© Z begins to be expressed after Ton time, when Y* crosses the activation threshold Kyz
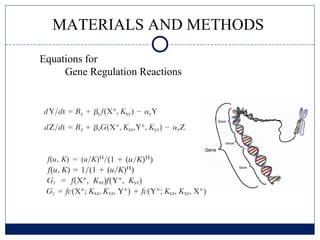
- 8. MATERIALS AND METHODS Equations for Gene Regulation Reactions
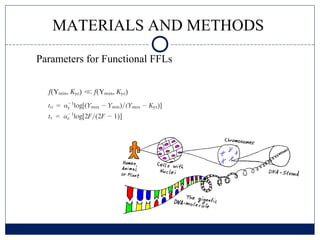
- 9. MATERIALS AND METHODS Parameters for Functional FFLs
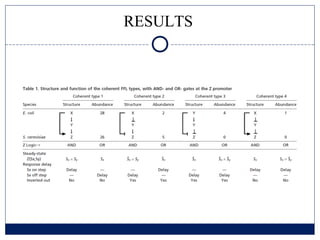
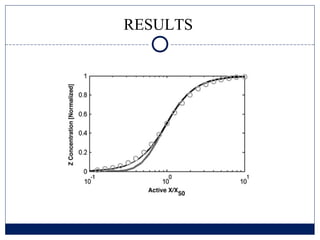
- 10. RESULTS
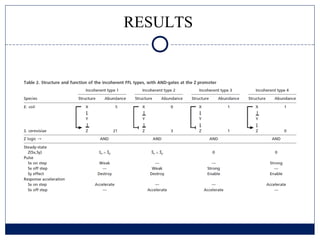
- 11. RESULTS
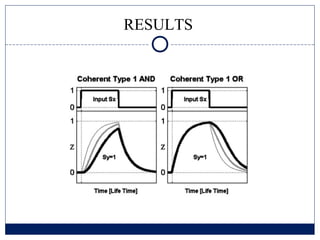
- 12. RESULTS
- 13. RESULTS
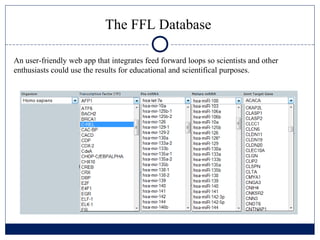
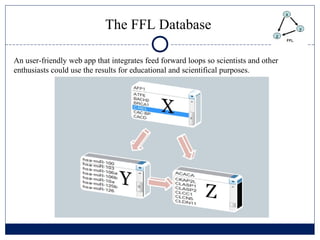
- 14. The FFL Database An user-friendly web app that integrates feed forward loops so scientists and other enthusiasts could use the results for educational and scientifical purposes.
- 15. The FFL Database An user-friendly web app that integrates feed forward loops so scientists and other enthusiasts could use the results for educational and scientifical purposes.
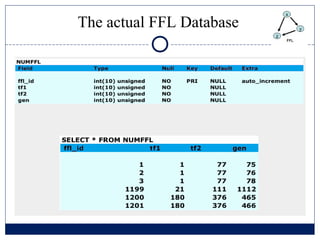
- 16. The actual FFL Database
- 17. Methods of FFL Database ŅĢ░ Search where we can get information about the regulatory networks ŅĢ░ Get from the information about the regulation by Transcription Factors. ŅĢ░ Construct an algorithm to extract the FFL motives different organisms regulatory networks. ŅĢ░ Make a hierarchical clasiffication of FFLs elements. ŅĢ░ Make a clasiffication acording to the origin of the signal that TFs sense. ŅĢ░ Search for differences betwen the data on each position of the FFLs making statistical tests to validate significance.
- 18. CONCLUSIONS ŅĢ░ Incoherent FFLs ŌĆō sign-sensitive accelerators. ŅĢ░ Coherent FFLs ŌĆō sign-sensitive delays. ŅĢ░ Some FFL occur more often than the others. ŅĢ░ Observe how TFs that detect different-origin signals compose ŅĢ░ Observe the dinamics on the TRN looking for the formation of specific topological structure, FFL ŅĢ░ Search for significative differences on the data by statistical tests on each position of the FFLs.
- 19. Thank you for your attention!
