G8 Science Q2- Week1- Earthquake.pptx 2.pptx
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes71 views
The document discusses the mechanics of earthquakes and faults, detailing how faults generate earthquakes through movements caused by stress on rocks. It differentiates between various types of faults and seismic waves, including their effects and how they are measured using the Richter scale. Additionally, it explains the concepts of earthquake focus and epicenter, as well as the impact of earthquakes and the phenomenon of tsunamis.
1 of 57
Download to read offline
5
Most read








































Ad
Recommended
MODULE 1. EARTHQUAKES AND FAULTS..pptx
MODULE 1. EARTHQUAKES AND FAULTS..pptxshamae1985
╠²
An earthquake occurs due to a sudden slip or movement along a fault line in the Earth's crust. This movement releases built-up energy in the form of seismic waves that travel outward from the hypocenter or focus of the earthquake. The intensity of shaking and damage is greater near the epicenter, which is the point on the surface directly above the focus. Earthquake magnitude measures the energy released while intensity scales describe the observed effects on people and structures. Large earthquakes can sometimes generate tsunamis when the sudden movement of underwater faults displace large volumes of water.earthquakes and faults.mnhgfdssxcvbnpptx
earthquakes and faults.mnhgfdssxcvbnpptxlily rosemary masilang
╠²
The document discusses earthquakes, defining their causes and mechanisms, including fault types (normal, reverse, and strike-slip) and the concepts of focus and epicenter. It explains how seismic waves propagate and their different types, alongside methods for measuring earthquakes such as the Richter and moment magnitude scales. Additionally, the document addresses earthquake preparedness and the potential for tsunamis resulting from underwater faults.EARTHQUAKES AND FAULTS
EARTHQUAKES AND FAULTSJimnaira Abanto
╠²
The document discusses earthquakes and how they occur. It explains that earthquakes are caused by sudden movement along faults in the Earth's crust due to a build up of stress. There are three main types of faults - normal, reverse, and strike-slip - each forming in a different way due to tension or compression in the crust. When friction along a fault is overcome, the fault will slip and move, causing seismic waves that produce shaking during an earthquake. The intensity of shaking and damage decreases further from the earthquake's epicenter.Earthquakes revised
Earthquakes revisedkatiewilkerosn
╠²
Faults form when stresses in the Earth's crust cause rocks to break along fractures. There are three main types of faults: normal faults form when tension pulls rocks apart, reverse faults form when compression squeezes rocks together, and strike-slip faults form when shear forces cause rocks to slide past one another. Most earthquakes occur when built-up stresses are suddenly released as the rocks move along fault surfaces. Earthquake waves travel through the Earth, with P-waves and S-waves causing the ground to shake and damage structures. The resulting shaking can also trigger other hazardous events like tsunamis and liquefaction.Earthquake , Tsunami and Subduction zone
Earthquake , Tsunami and Subduction zoneMarriel Camacho
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy along fault lines in the earth's crust. The effects of earthquakes vary based on their magnitude and can include widespread destruction and loss of life. Seismic waves, including compressional P-waves and shear S-waves, travel outward from the hypocenter or focus of the earthquake. The location of the epicenter at the earth's surface directly above the focus can be determined using seismic data from multiple monitoring stations. Earthquakes are measured on scales such as the Richter scale and Modified Mercalli intensity scale.Ellada texniki.pptx there are slide for ppt
Ellada texniki.pptx there are slide for pptsabir54817
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including their causes, effects, and types of seismic waves. It discusses how earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy in fault lines in the earth's crust. When this occurs, seismic waves including P-waves and S-waves are produced and travel outward from the hypocenter. The document also describes different types of fault lines and examines the magnitude of earthquakes using the Richter scale. Finally, it outlines India's earthquake zoning map and how the country is divided into zones based on seismic activity levels.Earthquakes
EarthquakesE3BS4M
╠²
An earthquake occurs when rocks underground release stored energy, causing the ground to shake. Earthquakes are usually caused by the movement of tectonic plates. They can cause damage and loss of life through mechanisms like fires, landslides, floods, and tsunamis. Scientists measure earthquakes using seismographs which record seismic waves. The location and magnitude of quakes are determined by analyzing these wave recordings. Major quakes pose risks like liquefaction of soils and large tsunami waves.earthquake
earthquakeElsaSony
╠²
1) An earthquake is caused by a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves.
2) Earthquakes occur along fault lines in the Earth's lithosphere where tectonic plates meet. As the plates slowly move and push against each other, stress builds up until the fault slips, releasing energy in the form of seismic waves.
3) Earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale based on the logarithm of the wave amplitude as recorded by a seismograph. The magnitude indicates the amount of energy released by an earthquake.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptIvyLynneEsguerra2
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and how they are measured. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, causing rocks to break and release energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of faults and three types of seismic waves. Earthquakes are located using seismographs to measure the arrival times of P and S waves at multiple stations, then triangulating the epicenter where the circles intersect. The largest earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptEDWARDMAYA16
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the buildup and sudden release of stress along faults in the Earth's crust. When the stress becomes too great, the rock breaks and seismic waves are released. There are three main types of seismic waves - P waves, S waves, and surface waves. Scientists can locate the epicenter of an earthquake by measuring the arrival times of seismic waves at multiple seismograph stations and using triangulation. The Richter Scale is used to measure the magnitude or energy released by an earthquake.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptJenny Rose Gengos
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and how they are measured. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, causing rocks to break and release energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of faults and three types of seismic waves. Earthquakes are located using seismographs to measure the arrival times of P and S waves at multiple stations, then triangulating the epicenter where the circles intersect. The largest earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptMaryGracePaciano
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and the different types of seismic waves. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, leading to earthquakes when the pressure is released. There are three main types of faults - normal, reverse, and strike-slip. An earthquake begins at a focus point and the epicenter is the point directly above on the surface. P waves, S waves, and surface waves are the three types of seismic waves generated by earthquakes. P waves travel the fastest while surface waves cause the most destruction.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptTwinkleThakur5
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the buildup and sudden release of stress along faults in the Earth's crust. When the stress becomes too great, the rock breaks and seismic waves are released. There are three main types of seismic waves - P waves, S waves, and surface waves. Scientists can locate the epicenter of an earthquake by measuring the arrival times of seismic waves at multiple seismograph stations and using triangulation. The Richter Scale is used to measure the magnitude or energy released by an earthquake.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptRamirBecoy2
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and how they are measured. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, causing rocks to break and release energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of faults and three types of seismic waves. Earthquakes are located using seismographs to measure the arrival times of P and S waves at multiple stations, then triangulating the epicenter where the circles intersect. The largest earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptSherylValiente1
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and how they are measured. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, causing rocks to break and release energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of faults and three types of seismic waves. Earthquakes are located using seismographs to measure the arrival times of P and S waves at multiple stations, then triangulating the epicenter where the circles intersect. The largest earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale.Eartquake report
Eartquake reportKrishna Ghanva
╠²
The seminar report discusses the causes, types, and effects of earthquakes, highlighting their connection to tectonic plate movements and fault lines. It includes detailed explanations of seismic waves, the measurement of earthquake strength using seismographs, and various categories of earthquakes based on their causes. Additionally, the report covers earthquake prediction methods and the impact of earthquakes on infrastructure and human life.EARTHQUAKE AND FAULTS, Epicenter and Focus .pptx
EARTHQUAKE AND FAULTS, Epicenter and Focus .pptxDanielManuel26
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes and seismic waves. It discusses that earthquakes are caused by the sudden movement of tectonic plates along faults in the earth's crust. It describes the different types of seismic waves produced by earthquakes including P waves, S waves, Love waves, and Rayleigh waves. P waves are compressional waves that move fastest through solid rock. S waves are slower shear waves that only travel through solids. Love and Rayleigh waves are lower frequency surface waves that cause the most ground shaking during an earthquake.Chapter 2 Earthquakes
Chapter 2 Earthquakesjtripp8
╠²
Earthquakes occur along faults in the Earth's crust where blocks of rock move due to stress. There are three main types of faults - normal faults where one block moves down, reverse faults where one block moves up, and strike-slip faults where blocks move horizontally. When stress is released, energy radiates outward from the focus in the form of seismic waves, including primary, secondary, and surface waves. Seismographs can detect and record these waves to locate the epicenter and measure the earthquake's magnitude. Earthquakes can cause severe damage through ground shaking, landslides, fires and liquefaction, but damage can be reduced through monitoring, predicting earthquake activity, and enforcing strict building codes for earthquake-resistant construction.Earthquake
Earthquakeindia
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of earthquakes, detailing their causes, types, measurement methods, and effects, particularly highlighting the Nepal earthquake of 2015. It explains seismic waves, fault mechanisms, and the resulting impact on structures and human life, including fatalities and economic losses. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of disaster preparedness, risk assessment, and the social ramifications following such seismic events.Earth quake
Earth quakekhanikrar
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of built-up strain energy along fault lines in the Earth's crust. Faults occur at boundaries between tectonic plates where the plates slide past each other. There are different types of faults such as normal, reverse, strike-slip and oblique. Earthquake waves called seismic waves radiate out from the hypocenter or focus of the earthquake. P-waves and S-waves are two types of seismic waves that travel through the Earth. Surface waves including Rayleigh and Love waves cause the most damage during an earthquake. Factors like magnitude, distance from the epicenter, local geology can influence earthquake intensity.earthquake.ppt
earthquake.pptYesHua14
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of built-up pressure along fault lines in the Earth's crust. They produce three main types of seismic waves - P waves, S waves, and surface waves - that radiate out from the earthquake's focal point or epicenter. P waves travel fastest while surface waves cause the most damage. Earthquake intensity is measured using the Richter scale, with quakes over 5.0 capable of damage. California experiences frequent quakes due to collisions between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates.Earthquake Presentation 08 09
Earthquake Presentation 08 09davedelg1
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by sudden movements within Earth's crust that cause rocks to bend, break or fracture. Most earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire, a belt circling the Pacific Ocean where 88% of all quakes take place, and also along other belts where tectonic plates meet. Forces like tension, compression and shearing cause three types of rock fractures - normal faults where the rock moves apart, reverse faults where it moves together, and strike-slip faults where it slides horizontally past another part of the crust.EarthQuake.pptx
EarthQuake.pptxNaqeeb Khan Niazi
╠²
An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the earth caused by the movement of tectonic plates along faults in the earth's crust. The document details the causes of earthquakes, their various types, effects, and how they are measured, emphasizing that they cannot be predicted accurately. It also discusses the geological layers of the earth, terminology related to seismic activity, and historical earthquakes.Earthquake, seismic waves, fault types-1.ppt
Earthquake, seismic waves, fault types-1.pptHassanDanish9
╠²
The document discusses the causes, types, and measurement of earthquakes, explaining how tectonic plate movements create stress that can lead to seismic activity. It outlines the characteristics of different fault types and seismic waves, detailing the methods used by seismologists to locate earthquake epicenters and measure their magnitude on the Richter scale. The content emphasizes the destructive potential of earthquakes and the importance of understanding seismic phenomena.Earthquake-1 .ppt
Earthquake-1 .pptkamijaam333
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of earthquakes, elaborating on their causes, mechanisms, measurement, and effects. It explains the formation of seismic waves from energy released at the focus of an earthquake and discusses the roles of primary, secondary, and surface waves in causing damage. Additionally, it highlights the importance of seismology in predicting earthquakes and discusses the application of the Richter scale to measure earthquake magnitude.Earthquake Lesson
Earthquake Lessonamckean
╠²
The document provides information about earthquakes, including:
1) It describes the elastic rebound theory which explains how energy is stored in rocks until a fault causes an earthquake, releasing the energy in seismic waves.
2) It defines the focus as the point where faulting begins underground, and the epicenter as the point directly above on the surface.
3) It identifies the four types of seismic waves - P and S waves which travel through solids, and Rayleigh and Love waves which travel along the surface.3 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 2Law of Acceleration.pptx
3 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 2Law of Acceleration.pptxSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document outlines Newton's laws of motion, focusing on inertia, acceleration, and interaction. It provides definitions, formulas (F=ma), and applications in solving real-life problems related to force and motion. Activities and drills reinforce the understanding of the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.2 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 1Law of Inertia.pptx
2 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 1Law of Inertia.pptxSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document discusses Newton's three laws of motion, established by Sir Isaac Newton, which describe how objects move and react to forces. It emphasizes the law of inertia, which states that an object remains at rest or in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, and includes vocabulary related to the concepts. The document aims to provide learning objectives related to understanding and applying these laws in real-life situations.More Related Content
Similar to G8 Science Q2- Week1- Earthquake.pptx 2.pptx (20)
earthquake
earthquakeElsaSony
╠²
1) An earthquake is caused by a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves.
2) Earthquakes occur along fault lines in the Earth's lithosphere where tectonic plates meet. As the plates slowly move and push against each other, stress builds up until the fault slips, releasing energy in the form of seismic waves.
3) Earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale based on the logarithm of the wave amplitude as recorded by a seismograph. The magnitude indicates the amount of energy released by an earthquake.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptIvyLynneEsguerra2
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and how they are measured. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, causing rocks to break and release energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of faults and three types of seismic waves. Earthquakes are located using seismographs to measure the arrival times of P and S waves at multiple stations, then triangulating the epicenter where the circles intersect. The largest earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptEDWARDMAYA16
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the buildup and sudden release of stress along faults in the Earth's crust. When the stress becomes too great, the rock breaks and seismic waves are released. There are three main types of seismic waves - P waves, S waves, and surface waves. Scientists can locate the epicenter of an earthquake by measuring the arrival times of seismic waves at multiple seismograph stations and using triangulation. The Richter Scale is used to measure the magnitude or energy released by an earthquake.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptJenny Rose Gengos
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and how they are measured. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, causing rocks to break and release energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of faults and three types of seismic waves. Earthquakes are located using seismographs to measure the arrival times of P and S waves at multiple stations, then triangulating the epicenter where the circles intersect. The largest earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptMaryGracePaciano
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and the different types of seismic waves. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, leading to earthquakes when the pressure is released. There are three main types of faults - normal, reverse, and strike-slip. An earthquake begins at a focus point and the epicenter is the point directly above on the surface. P waves, S waves, and surface waves are the three types of seismic waves generated by earthquakes. P waves travel the fastest while surface waves cause the most destruction.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptTwinkleThakur5
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the buildup and sudden release of stress along faults in the Earth's crust. When the stress becomes too great, the rock breaks and seismic waves are released. There are three main types of seismic waves - P waves, S waves, and surface waves. Scientists can locate the epicenter of an earthquake by measuring the arrival times of seismic waves at multiple seismograph stations and using triangulation. The Richter Scale is used to measure the magnitude or energy released by an earthquake.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptRamirBecoy2
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and how they are measured. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, causing rocks to break and release energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of faults and three types of seismic waves. Earthquakes are located using seismographs to measure the arrival times of P and S waves at multiple stations, then triangulating the epicenter where the circles intersect. The largest earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale.Earthquake PPT.ppt
Earthquake PPT.pptSherylValiente1
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes, including what causes them, where they occur, and how they are measured. It discusses how tectonic plate movement can build stress along faults, causing rocks to break and release energy in the form of seismic waves. There are three main types of faults and three types of seismic waves. Earthquakes are located using seismographs to measure the arrival times of P and S waves at multiple stations, then triangulating the epicenter where the circles intersect. The largest earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale.Eartquake report
Eartquake reportKrishna Ghanva
╠²
The seminar report discusses the causes, types, and effects of earthquakes, highlighting their connection to tectonic plate movements and fault lines. It includes detailed explanations of seismic waves, the measurement of earthquake strength using seismographs, and various categories of earthquakes based on their causes. Additionally, the report covers earthquake prediction methods and the impact of earthquakes on infrastructure and human life.EARTHQUAKE AND FAULTS, Epicenter and Focus .pptx
EARTHQUAKE AND FAULTS, Epicenter and Focus .pptxDanielManuel26
╠²
This document provides information about earthquakes and seismic waves. It discusses that earthquakes are caused by the sudden movement of tectonic plates along faults in the earth's crust. It describes the different types of seismic waves produced by earthquakes including P waves, S waves, Love waves, and Rayleigh waves. P waves are compressional waves that move fastest through solid rock. S waves are slower shear waves that only travel through solids. Love and Rayleigh waves are lower frequency surface waves that cause the most ground shaking during an earthquake.Chapter 2 Earthquakes
Chapter 2 Earthquakesjtripp8
╠²
Earthquakes occur along faults in the Earth's crust where blocks of rock move due to stress. There are three main types of faults - normal faults where one block moves down, reverse faults where one block moves up, and strike-slip faults where blocks move horizontally. When stress is released, energy radiates outward from the focus in the form of seismic waves, including primary, secondary, and surface waves. Seismographs can detect and record these waves to locate the epicenter and measure the earthquake's magnitude. Earthquakes can cause severe damage through ground shaking, landslides, fires and liquefaction, but damage can be reduced through monitoring, predicting earthquake activity, and enforcing strict building codes for earthquake-resistant construction.Earthquake
Earthquakeindia
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of earthquakes, detailing their causes, types, measurement methods, and effects, particularly highlighting the Nepal earthquake of 2015. It explains seismic waves, fault mechanisms, and the resulting impact on structures and human life, including fatalities and economic losses. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of disaster preparedness, risk assessment, and the social ramifications following such seismic events.Earth quake
Earth quakekhanikrar
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of built-up strain energy along fault lines in the Earth's crust. Faults occur at boundaries between tectonic plates where the plates slide past each other. There are different types of faults such as normal, reverse, strike-slip and oblique. Earthquake waves called seismic waves radiate out from the hypocenter or focus of the earthquake. P-waves and S-waves are two types of seismic waves that travel through the Earth. Surface waves including Rayleigh and Love waves cause the most damage during an earthquake. Factors like magnitude, distance from the epicenter, local geology can influence earthquake intensity.earthquake.ppt
earthquake.pptYesHua14
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of built-up pressure along fault lines in the Earth's crust. They produce three main types of seismic waves - P waves, S waves, and surface waves - that radiate out from the earthquake's focal point or epicenter. P waves travel fastest while surface waves cause the most damage. Earthquake intensity is measured using the Richter scale, with quakes over 5.0 capable of damage. California experiences frequent quakes due to collisions between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates.Earthquake Presentation 08 09
Earthquake Presentation 08 09davedelg1
╠²
Earthquakes are caused by sudden movements within Earth's crust that cause rocks to bend, break or fracture. Most earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire, a belt circling the Pacific Ocean where 88% of all quakes take place, and also along other belts where tectonic plates meet. Forces like tension, compression and shearing cause three types of rock fractures - normal faults where the rock moves apart, reverse faults where it moves together, and strike-slip faults where it slides horizontally past another part of the crust.EarthQuake.pptx
EarthQuake.pptxNaqeeb Khan Niazi
╠²
An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the earth caused by the movement of tectonic plates along faults in the earth's crust. The document details the causes of earthquakes, their various types, effects, and how they are measured, emphasizing that they cannot be predicted accurately. It also discusses the geological layers of the earth, terminology related to seismic activity, and historical earthquakes.Earthquake, seismic waves, fault types-1.ppt
Earthquake, seismic waves, fault types-1.pptHassanDanish9
╠²
The document discusses the causes, types, and measurement of earthquakes, explaining how tectonic plate movements create stress that can lead to seismic activity. It outlines the characteristics of different fault types and seismic waves, detailing the methods used by seismologists to locate earthquake epicenters and measure their magnitude on the Richter scale. The content emphasizes the destructive potential of earthquakes and the importance of understanding seismic phenomena.Earthquake-1 .ppt
Earthquake-1 .pptkamijaam333
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of earthquakes, elaborating on their causes, mechanisms, measurement, and effects. It explains the formation of seismic waves from energy released at the focus of an earthquake and discusses the roles of primary, secondary, and surface waves in causing damage. Additionally, it highlights the importance of seismology in predicting earthquakes and discusses the application of the Richter scale to measure earthquake magnitude.Earthquake Lesson
Earthquake Lessonamckean
╠²
The document provides information about earthquakes, including:
1) It describes the elastic rebound theory which explains how energy is stored in rocks until a fault causes an earthquake, releasing the energy in seismic waves.
2) It defines the focus as the point where faulting begins underground, and the epicenter as the point directly above on the surface.
3) It identifies the four types of seismic waves - P and S waves which travel through solids, and Rayleigh and Love waves which travel along the surface.More from SarahChuaDonasco (8)
3 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 2Law of Acceleration.pptx
3 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 2Law of Acceleration.pptxSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document outlines Newton's laws of motion, focusing on inertia, acceleration, and interaction. It provides definitions, formulas (F=ma), and applications in solving real-life problems related to force and motion. Activities and drills reinforce the understanding of the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.2 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 1Law of Inertia.pptx
2 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 1Law of Inertia.pptxSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document discusses Newton's three laws of motion, established by Sir Isaac Newton, which describe how objects move and react to forces. It emphasizes the law of inertia, which states that an object remains at rest or in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, and includes vocabulary related to the concepts. The document aims to provide learning objectives related to understanding and applying these laws in real-life situations.1 G8 Science Q1- Week 1- Newton_s Law of Motion.pptx
1 G8 Science Q1- Week 1- Newton_s Law of Motion.pptxSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document discusses Newton's laws of motion, summarizing early ideas from Aristotle and Galileo, and detailing Newton's three laws: the law of inertia, the law of acceleration, and the law of action and reaction. It emphasizes the relationships between force, mass, and motion, illustrating concepts with examples. Additionally, it includes a practice test to reinforce understanding of these principles.G8 Science Q2- Week 3-Seismic-Waves.pptx
G8 Science Q2- Week 3-Seismic-Waves.pptxSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
Seismic waves, generated by earthquakes, provide critical information about the Earth's interior, with body waves (P-waves and S-waves) arriving before surface waves. P-waves can travel through solids and fluids, while S-waves are restricted to solids and cannot pass through the liquid outer core. Seismologists analyze wave arrival times, speeds, and behaviors to infer the composition and states of Earth's inner layers, revealing aspects such as the layering in the mantle and the solid inner core.G8 Science Q2- Week 2-3- Epicenter and Focus of Earthquake.pptx
G8 Science Q2- Week 2-3- Epicenter and Focus of Earthquake.pptxSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document provides an in-depth overview of earthquakes, discussing their causes, mechanisms, and consequences, including seismic hazards and the assessment of risks. It elaborates on earthquake magnitude scales, methods of locating epicenters, and the importance of building preparedness to mitigate damage from seismic events. Furthermore, it explores the challenges of predicting earthquakes and emphasizes the role of human factors in disaster impacts.G8 Science Q2- Week 5- How Typhoon Develops.pptx
G8 Science Q2- Week 5- How Typhoon Develops.pptxSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document explains the development of typhoons, detailing the role of ocean temperature, wind patterns, and landmasses in their formation. It discusses various impacts of tropical cyclones, including storm surges, extreme rainfall, and high winds, and includes historical examples. Additionally, it highlights the relationship between tropical storms and climate change, raising awareness about preparation for such weather events.G8 Science Q2- Week 5- How to track Typhoon.ppt
G8 Science Q2- Week 5- How to track Typhoon.pptSarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document provides instructions on how to track typhoons entering the Philippine area of responsibility using latitude and longitude coordinates. It explains the significance of these coordinates for locating positions on a map and includes an exercise to plot the coordinates of specific locations. Additionally, it offers a practical example of tracking the path of Super Typhoon Rosing with detailed distance and time indicators.What is Typhoon? How Typhoon develop? How to track typhoon.
What is Typhoon? How Typhoon develop? How to track typhoon.SarahChuaDonasco
╠²
The document explains the development of typhoons, highlighting the influence of air masses and water bodies on their formation. It details the structure of air masses, the types of weather fronts, and the conditions necessary for cyclones to develop, as well as the classification of cyclones based on wind speed. The Philippines is noted to be particularly prone to typhoons due to its geographic location and the warm waters of the Pacific Ocean.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Overview of Off Boarding in Odoo 18 Employees
Overview of Off Boarding in Odoo 18 EmployeesCeline George
╠²
When an employee leaves the company, Odoo provides a streamlined offboarding process to ensure all necessary steps are taken. ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdf
ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdfTechSoup
╠²
Accounting can be hard enough if you havenÔÇÖt studied it in school. Nonprofit accounting is actually very different and more challenging still.
Need help? Join Nonprofit CPA and QuickBooks expert Gregg Bossen in this first-time webinar and learn the ABCs of keeping books for a nonprofit organization.
Key takeaways
* What accounting is and how it works
* How to read a financial statement
* What financial statements should be given to the board each month
* What three things nonprofits are required to track
What features to use in QuickBooks to track programs and grantsChalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
This presentation has been made keeping in mind the students of undergraduate and postgraduate level. In this slide try to present the brief history of Chaulukyas of Gujrat up to Kumarpala To keep the facts in a natural form and to display the material in more detail, the help of various books, websites and online medium has been taken. Whatever medium the material or facts have been taken from, an attempt has been made by the presenter to give their reference at the end.
Chaulukya or Solanki was one of the Rajputs born from Agnikul. In the Vadnagar inscription, the origin of this dynasty is told from Brahma's Chauluk or Kamandalu. They ruled in Gujarat from the latter half of the tenth century to the beginning of the thirteenth century. Their capital was in Anahilwad. It is not certain whether it had any relation with the Chalukya dynasty of the south or not. It is worth mentioning that the name of the dynasty of the south was 'Chaluky' while the dynasty of Gujarat has been called 'Chaulukya'. The rulers of this dynasty were the supporters and patrons of Jainism.ECONOMICS, DISASTER MANAGEMENT, ROAD SAFETY - STUDY MATERIAL [10TH]
ECONOMICS, DISASTER MANAGEMENT, ROAD SAFETY - STUDY MATERIAL [10TH]SHERAZ AHMAD LONE
╠²
This study material for Class 10th covers the core subjects of Economics, Disaster Management, and Road Safety Education, developed strictly in line with the JKBOSE textbook. It presents the content in a simplified, structured, and student-friendly format, ensuring clarity in concepts. The material includes reframed explanations, flowcharts, infographics, and key point summaries to support better understanding and retention. Designed for classroom teaching and exam preparation, it aims to enhance comprehension, critical thinking, and practical awareness among students.How to Manage Multi Language for Invoice in Odoo 18
How to Manage Multi Language for Invoice in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
Odoo supports multi-language functionality for invoices, allowing you to generate invoices in your customersÔÇÖ preferred languages. Multi-language support for invoices is crucial for businesses operating in global markets or dealing with customers from different linguistic backgrounds. Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs ÔÇô Unit 9 | B.Sc Nursing 5t...
Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs ÔÇô Unit 9 | B.Sc Nursing 5t...RAKESH SAJJAN
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation covers Unit 9 ÔÇô Communicable Diseases and National Health Programs, a core part of the 5th Semester B.Sc Nursing (Community Health Nursing ÔÇô I) syllabus, as outlined by the Indian Nursing Council (INC).
This unit enables nursing students to understand the epidemiology, prevention, control, and nursing management of common communicable diseases in India, while also offering a structured overview of the National Health Programs implemented to address them.
The content is critical for effective field practice, disease surveillance, early detection, referral, and health education, equipping students to participate in public health interventions and outbreak control at community and national levels.
ƒôÿ Key Topics Covered in the PPT:
Definition and classification of communicable diseases
Modes of transmission and chain of infection
Common communicable diseases in India:
Malaria
Tuberculosis
Leprosy
Dengue
HIV/AIDS
Hepatitis
COVID-19 (if included in the current curriculum)
Diarrheal diseases
Acute Respiratory Infections (ARIs)
Epidemiological factors, causative agents, symptoms, and incubation periods
Prevention and control strategies: primary, secondary, and tertiary levels
Nursing responsibilities in patient care, contact tracing, community surveillance, and outbreak control
Health education and behavior change communication for community awareness
Vaccination schedules and cold chain maintenance
National Health Programs related to communicable diseases:
National Vector Borne Disease Control Program (NVBDCP)
Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program (RNTCP)
National Leprosy Eradication Program (NLEP)
National AIDS Control Program (NACP)
Universal Immunization Program (UIP)
IDSP ÔÇô Integrated Disease Surveillance Program
Overview of standard treatment protocols, referral mechanisms, and community nurseÔÇÖs role in program implementation
This presentation is ideal for:
Nursing students preparing for university exams, class tests, and field projects
Tutors teaching infectious disease nursing and public health interventions
Nurses involved in immunization, outbreak investigation, and contact tracing
It provides a student-friendly breakdown of concepts, aligned with national priorities, including flowcharts, tables, case examples, and simplified text for field-level application.LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...Ultimatewinner0342
╠²
ƒºá Lazy Sunday Quiz | General Knowledge Trivia by SMC Quiz Club ÔÇô Silchar Medical College
Presenting the Lazy Sunday Quiz, a fun and thought-provoking general knowledge quiz created by the SMC Quiz Club of Silchar Medical College & Hospital (SMCH). This quiz is designed for casual learners, quiz enthusiasts, and competitive teams looking for a diverse, engaging set of questions with clean visuals and smart clues.
ƒÄ» What is the Lazy Sunday Quiz?
The Lazy Sunday Quiz is a light-hearted yet intellectually rewarding quiz session held under the SMC Quiz Club banner. ItÔÇÖs a general quiz covering a mix of current affairs, pop culture, history, India, sports, medicine, science, and more.
Whether youÔÇÖre hosting a quiz event, preparing a session for students, or just looking for quality trivia to enjoy with friends, this PowerPoint deck is perfect for you.
ƒôï Quiz Format & Structure
Total Questions: ~50
Types: MCQs, one-liners, image-based, visual connects, lateral thinking
Rounds: Warm-up, Main Quiz, Visual Round, Connects (optional bonus)
Design: Simple, clear slides with answer explanations included
Tools Needed: Just a projector or screen ÔÇô ready to use!
ƒºá Who Is It For?
College quiz clubs
School or medical students
Teachers or faculty for classroom engagement
Event organizers needing quiz content
Quizzers preparing for competitions
Freelancers building quiz portfolios
ƒÆí Why Use This Quiz?
Ready-made, high-quality content
Curated with lateral thinking and storytelling in mind
Covers both academic and pop culture topics
Designed by a quizzer with real event experience
Usable in inter-college fests, informal quizzes, or Sunday brain workouts
ƒôÜ About the Creators
This quiz has been created by Rana Mayank Pratap, an MBBS student and quizmaster at SMC Quiz Club, Silchar Medical College. The club aims to promote a culture of curiosity and smart thinking through weekly and monthly quiz events.
ƒöì SEO Tags:
quiz, general knowledge quiz, trivia quiz, ║¦║¦▀úShare quiz, college quiz, fun quiz, medical college quiz, India quiz, pop culture quiz, visual quiz, MCQ quiz, connect quiz, science quiz, current affairs quiz, SMC Quiz Club, Silchar Medical College
ƒôú Reuse & Credit
YouÔÇÖre free to use or adapt this quiz for your own events or sessions with credit to:
SMC Quiz Club ÔÇô Silchar Medical College & Hospital
Curated by: Rana Mayank PratapPublishing Your Memoir with Brooke Warner
Publishing Your Memoir with Brooke WarnerBrooke Warner
╠²
Brooke Warner presents on getting published - traditional, hybrid, and self-publishing.
www.memoirnation.comWax Moon, Richmond, VA. Terrence McPherson
Wax Moon, Richmond, VA. Terrence McPhersonTerrenceMcPherson1
╠²
Wax Moon is an independent record store keeping its foundational foothold in vinyl records by taking in collections and keeping the old 80s aesthetics alive with involvement in its community and participation with record distributors.Q1_ENGLISH_PPT_WEEK 1 power point grade 3 Quarter 1 week 1
Q1_ENGLISH_PPT_WEEK 1 power point grade 3 Quarter 1 week 1jutaydeonne
╠²
Grade 3 Quarter 1 Week 1 English part 2LDMMIA Practitioner Level Orientation Updates
LDMMIA Practitioner Level Orientation UpdatesLDM & Mia eStudios
╠²
See our 2 Starter PDFs within a Compressed, Zip Drive. Within Shop. Videos will be available Before the Weekend of 6/14th. For the US, Happy Fathers Day Weekend. (Our readers/teams are global.) Also, our content remains timeless for Future Grad Students seeking updates.
After about a Year or 10, I retire older content. Literally up to under 10 yrs. We will be 19 yrs old this Aug for Love and Divinity in Motion (LDM). How old are we? So funny. Our oldest profile is X, formerly Twitter. From our old Apple Podcast Years.
https://ldm-mia.creator-spring.com
Session/Lesson 1 -Intro
REIKI- YOGA ÔÇ£ORIENTATIONÔÇØ
It helps to understand the text behind anything. This improves our performance and confidence.
Your training will be mixed media. Includes Rehab Intro and Meditation vods, all sold separately.
Editing our Vods & New Shop. Retail under $30 per item.
*Store Fees will apply. *Digital Should be low cost.
Thank you for attending our free workshops. Those can be used with any Reiki Yoga training package. Traditional Reiki does host rules and ethics. Its silent and within the JP Culture/Area/Training/Word of Mouth. It allows remote healing but thereÔÇÖs limits for practitioners and masters. We are not allowed to share certain secrets/tools. Some content is designed only for ÔÇ£MastersÔÇØ...
Next Upload will be our Video package for Session 1. Prices will be affordable as possible. Thx for becoming a "Practitioner Level" Student.
Updates so far, are every week for spring. Summer should be a similar schedule. Thx for visitings, attending, and following LDMMIA.
Social Media:
https://x.com/OnlineDrLeZ
and
https://www.instagram.com/chelleofsl/
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptx
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
╠²
BLUF:
The Texas outbreak has slowed down, but sporadic cases continue to emerge in Kansas, Oklahoma, and New Mexico.
Elsewhere in the US, we continue to see signs of acceleration due to outbreaks outside the Southwest (North Dakota, Montana, and Colorado) and travel-related cases. Measles exposures due to travel are expected to pose a significant challenge throughout the summer.
The U.S. is on track to exceed its 30-year high for measles cases (1,274) within the next two weeks.
Here is the latest update:
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 919
ÔÇóTexas: 744 (+2) (55% of cases are in Gaines County).
ÔÇóNew Mexico: 81 (83% of cases are from Lea County).
ÔÇóOklahoma: 20 (+2)
ÔÇóKansas: 74 (+5) (38.89% of the cases are from Gray County).
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 104
ÔÇó Texas: 96 (+2) ÔÇô This accounts for 13% of all cases in Texas.
ÔÇó New Mexico: 7 ÔÇô This accounts for 9.47% of all cases in New Mexico.
ÔÇó Kansas: 3 ÔÇô This accounts for 5.08% of all cases in the state of Kansas.
DEATHS: 3
ÔÇóTexas: 2 ÔÇô This is 0.27% of all cases in Texas.
ÔÇóNew Mexico: 1 ÔÇô This is 1.23% of all cases in New Mexico.
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 1,197
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD
ÔÇóMexico: 2337 (+257), 5 fatalities
ÔÇÆChihuahua, Mexico: 2,179 (+239) cases, 4 fatalities, 7 currently hospitalized.
ÔÇóCanada: 3,207 (+208), 1 fatality
ÔÇÆOntario Outbreak, Canada: 2,115 (+74) cases, 158 hospitalizations, 1 fatality.
ÔÇÆAlberta, Canada: 879(+118) cases, 5 currently hospitalized.Sustainable Innovation with Immersive Learning
Sustainable Innovation with Immersive LearningLeonel Morgado
╠²
Prof. Leonel and Prof. Dennis approached educational uses, practices, and strategies of using immersion as a lens to interpret, design, and planning educational activities in a sustainable way. Rather than one-off gimmicks, the intent is to enable instructors (and institutions) to be able to include them in their regular activities, including the ability to evaluate and redesign them.
Immersion as a phenomenon enables interpreting pedagogical activities in a learning-agnostic way: you take a stance on the learning theory to follow, and leverage immersion to envision and guide your practice.Health Care Planning and Organization of Health Care at Various Levels ÔÇô Unit...
Health Care Planning and Organization of Health Care at Various Levels ÔÇô Unit...RAKESH SAJJAN
╠²
This comprehensive PowerPoint presentation is prepared for B.Sc Nursing 5th Semester students and covers Unit 2 of Community Health Nursing ÔÇô I based on the Indian Nursing Council (INC) syllabus. The unit focuses on the planning, structure, and functioning of health care services at various levels in India. It is especially useful for nursing educators and students preparing for university exams, internal assessments, or professional teaching assignments.
The content of this presentation includes:
Historical development of health planning in India
Detailed study of various health committees: Bhore, Mudaliar, Kartar Singh, Shrivastava Committee, etc.
Overview of major health commissions
In-depth understanding of Five-Year Plans and their impact on health care
Community participation and stakeholder involvement in health care planning
Structure of health care delivery system at central, state, district, and peripheral levels
Concepts and implementation of Primary Health Care (PHC) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Introduction to Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC) and Health and Wellness Centers (HWCs)
Expanded role of Mid-Level Health Providers (MLHPs) and Community Health Providers (CHPs)
Explanation of national health policies: NHP 1983, 2002, and 2017
Key national missions and schemes including:
National Health Mission (NHM)
National Rural Health Mission (NRHM)
National Urban Health Mission (NUHM)
Ayushman Bharat ÔÇô Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and IndiaÔÇÖs commitment to equitable health care
This presentation is ideal for:
Nursing students (B.Sc, GNM, Post Basic)
Nursing tutors and faculty
Health educators
Competitive exam aspirants in nursing and public health
It is organized in a clear, point-wise format with relevant terminologies and a focus on applied knowledge. The slides can also be used for community health demonstrations, teaching sessions, and revision guides.Plate Tectonic Boundaries and Continental Drift Theory
Plate Tectonic Boundaries and Continental Drift TheoryMarie
╠²
This 28 slide presentation covers the basics of plate tectonics and continental drift theory. It is an effective introduction into a full plate tectonics unit study, but does not cover faults, stress, seismic waves, or seafloor spreading.
To download PDF, visit The Homeschool Daily. We will be uploading more slideshows to follow this one. Blessings, Marie University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students SanctionedKweku Zurek
╠²
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdf
GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdfSHERAZ AHMAD LONE
╠²
"Geography Study Material for Class 10th" provides a comprehensive and easy-to-understand resource for key topics like Resources & Development, Water Resources, Agriculture, Minerals & Energy, Manufacturing Industries, and Lifelines of the National Economy. Designed as per the latest NCERT/JKBOSE syllabus, it includes notes, maps, diagrams, and MODEL question Paper to help students excel in exams. Whether revising for exams or strengthening conceptual clarity, this material ensures effective learning and high scores. Perfect for last-minute revisions and structured study sessions.Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...Ultimatewinner0342
╠²
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptx
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
╠²
Ad
G8 Science Q2- Week1- Earthquake.pptx 2.pptx
- 1. EARTHQUAKES & FAULTS PREPARED BY: SARAH C.DONASCO QUARTER 2 - WEEK 1
- 2. ´üÁ Using models or illustrations, explain how movements along faults generate earthquakes S8ES -IIa - 14 ´üÁ Differentiate the epicenter of an earthquake from its focus; 2 intensity of an earthquake from its magnitude; 3 active and inactive faults S8ES -IIa - 15
- 3. How do earthquakes occur and how are they detected? How can people be prepared for earthquakes?
- 4. ACTIVE and INACTIVE FAULTS ´üÁ EARTH CRUST The surface/outermost layer of the Earth
- 5. EarthÔÇÖs Crust Two Sections Continental Crust Oceanic Crust Makes up EarthÔÇÖs landmasses Found in the ocean floor and usually thinner than continental crust
- 8. Why are some parts of the crust thicker than other? How does the crust change its shape over time?
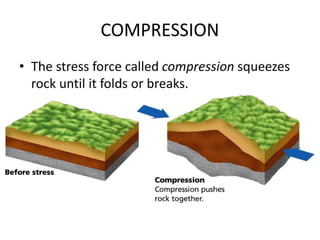
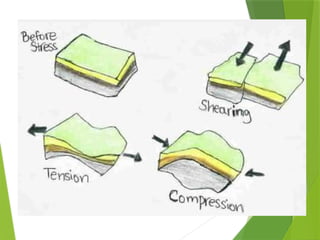
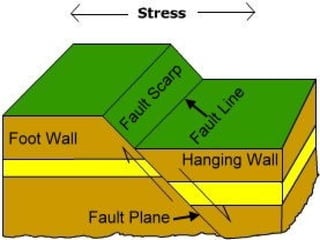
- 9. ´üÁ Some force is at work pushing and pulling on the crust causing changes on the surface and often well beneath the surface ÔÇó This push-pull is called stress ÔÇó As rocks undergo stress, they slowly change shape and volume.
- 10. What can stress do to rocks? ´üÁ A rock to become more compressed or squeezed ÔÇó Becomes smaller in volume ÔÇó A rock to stretch out over a large area. ÔÇó The volume increases ÔÇó The rock to twist or tear apart. ÔÇó Causes the formation of fault
- 11. What can stress do to rocks? ´üÁA rock to become more compressed or squeezed ÔÇó Becomes smaller in volume ÔÇó A rock to stretch out over a large area. ÔÇó The volume increases ÔÇó The rock to twist or tear apart. ÔÇó Causes the formation of fault
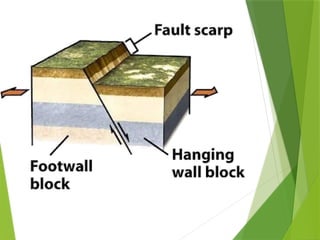
- 15. What is a fault? Fracture in rocks along which movement occured. Some faults may cause the ground to crack, rise or lower.
- 18. Two blocks of a faulted rock Hanging Wall ÔÇó The block of rock above the fault Foot Wall ÔÇó The block of rock below the fault
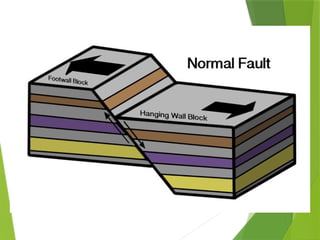
- 21. Kinds of fault Normal Fault/Normal Dip- slip Fault ÔÇó If a stress pulls the rocks apart due to tension, the hanging wall will move down relative to the foot wall.
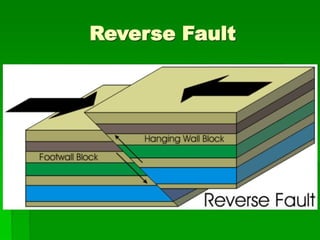
- 23. Kinds of fault ´üÁReverse Dip-slip Fault/ Thrust Fault ÔÇó If stress squeezed the rocks due to compression, the hanging wall will move up relative to the foot wall.
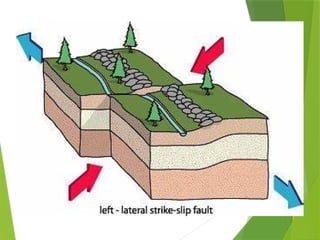
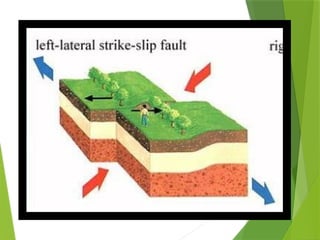
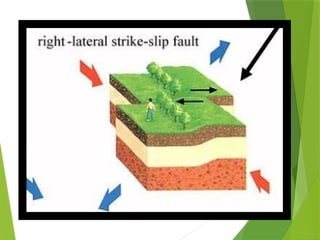
- 25. Kinds of Fault Strike ÔÇô slip Fault/Wrench Fault The blocks move by sliding and slipping along each other horizontally but in opposite directions.
- 28. Active faults are structure where there is displacement Usually produce a shallow earthquake One that has moved in the past and expected to move again.
- 29. Inactive Faults ´üÁ are structures that can be identified but which do not cause earthquakes. ÔÇó If a fault has been inactive for million years, it is safe to call it inactive.
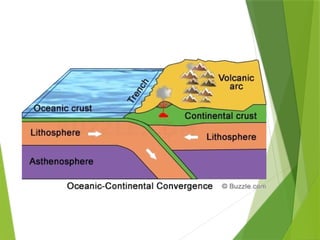
- 30. PHIVOLCS ´üÁPhilippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology ÔÇó Philippines has several fault lines ÔÇó Faults and trenches are found in the entire country ÔÇó Trenches are the deepest part of the oceans and are usually V- Shaped.
- 31. Faults & Trenches Are found close to the continents Near strings of islands. Near these TRENCHES: ÔÇô The crust is active causing stress and creating faults.
- 32. About trenchesÔǪ ´üÁ Scientist believe that the ocean floor is being pushed down deep into Earth along the trenches ´üÁ When these rocks are pushed deep enough, they are melted by the heat of Earth. ´üÁ Some of the molten rocks will rise up through the crust and produce volcanoes but most of it will become part of the EarthÔÇÖs Mantle.
- 33. EARTHQUAKE Focus and Epicenter Earthquake  Shaking and trembling of earth that results from the sudden movement of Earths crust Faulting  The most common cause of earthquake
- 34. During Faulting  Energy is released as the rocks break and move.  As they move, they cause the nearby rocks to move also.  The rocks continue to move this way until the energy is used up.
- 35. Tsunami Giant ocean wave cause by Earthquake that occur on the ocean floor.  These waves can travel at speed of 700  800km/h.  Can be as high as 10  20 meters (as they approach the coast).  The effects are devastating  One of the worlds worst natural disaster
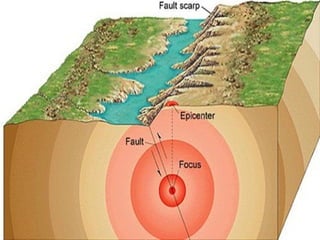
- 36. Focus ÔÇó The point/region where an earthquake ruptures and the rocks break ÔÇó Underground point of origin of an Earthquake. ÔÇó hypocenter
- 37. Epicenter ÔÇó The point on EarthÔÇÖs surface directly above the focus ÔÇó This where the most violent shaking of the ground occurs.
- 38. Focal Depth ÔÇó The distance between the focus and the epicenter
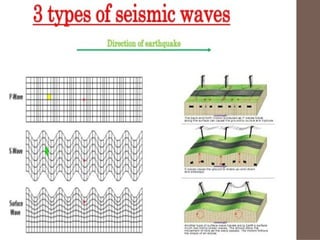
- 40. Earthquake Waves  Seismic Waves  Are the waves of energy caused by the sudden breaking of rock within the Earth or an explosion.  They are the energy that travels through Earth and is recorded on seismographs.
- 41. Three main types of Seismic Waves ´üÁ Primary Waves (P Waves) ÔÇó The fastest of the seismic wave ÔÇó The first to arrive at a seismic station before any other type of seismic wave ÔÇó Can move through the solid rocks and fluids (like water and liquid layers of Earth)
- 42. Three main types of Seismic Waves ÔÇó Can move through the solid rocks and fluids (like water and liquid layers of Earth)
- 43. Three main types of Seismic Waves Secondary Wave (S Wave) ÔÇó The second wave you feel in an earthquake ÔÇó S wave is slower than a P wave and can only move through solid not through liquid or gases
- 44. ´üÁWhat happens to S WAVES when they reach the liquid part of the earth?
- 45. ÔÇó S waves move rock particles up and down, or side ÔÇô to ÔÇô side - perpendicular to the direction the wave is traveling in.
- 46. Three main types of Seismic Waves Surface Wave (L Wave) ´üÁTravel from focus directly upward to the epicentre. ´üÁEarthÔÇÖs surface moves up and down with each L wave that passes ´üÁCause most of the damage during the earthquake because they bend and twist EarthÔÇÖs surface.
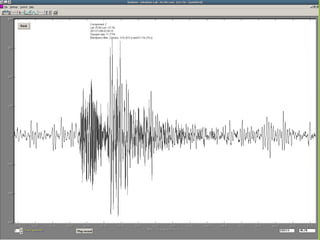
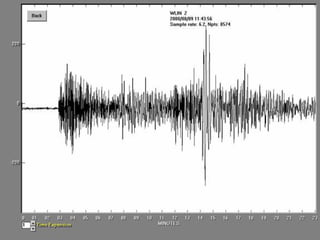
- 50. Seismograph An instrument that detects and measures waves. Seismograms  Seismographs record of the waves.
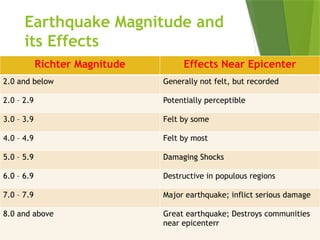
- 54. Richter ScaleÔǪ ´üÁ Measures how much energy an earthquake releases by assigning the earthquake number from 1 to 10. ÔÇó The more energy the earthquake releases, the stronger the earthquake is.
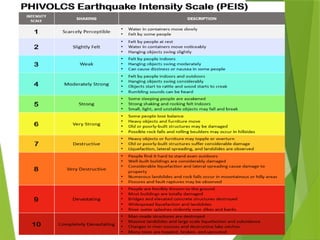
- 56. Earthquake Magnitude and its Effects Richter Magnitude Effects Near Epicenter 2.0 and below Generally not felt, but recorded 2.0 ÔÇô 2.9 Potentially perceptible 3.0 ÔÇô 3.9 Felt by some 4.0 ÔÇô 4.9 Felt by most 5.0 ÔÇô 5.9 Damaging Shocks 6.0 ÔÇô 6.9 Destructive in populous regions 7.0 ÔÇô 7.9 Major earthquake; inflict serious damage 8.0 and above Great earthquake; Destroys communities near epicenterr