Galvanic Cells Biochemestry.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes130 views
Galvanic cells are electrochemical cells that convert the chemical energy of spontaneous redox reactions into electrical energy. They contain an oxidation half-cell and a reduction half-cell separated by a salt bridge or porous membrane. In a galvanic cell, zinc metal oxidizes and loses electrons which flow through an external circuit to the copper ion reduction half-cell. The spontaneous electron flow produces an electric current useful for powering devices. Galvanic cells provide the foundation for generating spontaneous electric current from chemical reactions and are an important component of batteries used widely in modern technology.
1 of 23
Download to read offline










Recommended
4 cell chemistry and biosynthesis 



4 cell chemistry and biosynthesis saveena solanki
╠²
Cell chemistry and Biosynthesis
catalysis and the use of energy by cells
We now know there is nothing in living organisms that disobeys chemical and physical laws. However, the chemistry of life is indeed of a special kind. First, it is based overwhelmingly on carbon compounds, whose study is therefore known as organic chemistry. Second, cells are 70 percent water, and life depends almost exclusively on chemical reactions that take place in aqueous solution. Third, and most importantly, cell chemistry is enormously complex: even the simplest cell is vastly more complicated in its chemistry than any other chemical system known. Although cells contain a variety of small carbon-containing molecules, most of the carbon atoms in cells are incorporated into enormous polymeric moleculesŌĆöchains of chemical subunits linked end-to-end. It is the unique properties of these macromolecules that enable cells and organisms to grow and reproduceŌĆöas well as to do all the other things that are characteristic of lifeCell Respiration Notes



Cell Respiration NotesHyde Park
╠²
This document provides an overview of cellular respiration. It discusses three key stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate and occurs in the cytoplasm. The citric acid cycle further breaks down pyruvate in the mitochondrial matrix. During these stages, electrons are transferred to NAD+ to form NADH. The electron transport chain passes the electrons from NADH to oxygen to form water, extracting energy to synthesize ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. In total, respiration generates up to 38 ATP molecules from each glucose molecule.1-Electrochemistry.pptx



1-Electrochemistry.pptxDivya Boosagulla
╠²
This document provides an overview of electrochemistry. It defines electrochemistry as the branch of chemistry dealing with the transformation of electrical and chemical energy. It describes the key topics that will be covered, including conductors, electrochemical cells, electrode potentials, and how to predict spontaneity of reactions. It also summarizes the basic components and functions of electrolytic and galvanic (voltaic) cells, including how they convert between electrical and chemical energy.Mphil electrochemistry



Mphil electrochemistryShehman Assad
╠²
This document provides information about electrochemistry. It discusses how electrochemistry deals with oxidation-reduction reactions that produce or utilize electrical energy. There are two main types of electrochemical cells: galvanic cells which convert chemical energy to electrical energy, and electrolytic cells which use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions. The document explains the basic setup and workings of these two cell types.Q2 Week 6.pptx



Q2 Week 6.pptxRaceDeVilla1
╠²
Electrochemistry deals with converting between chemical and electrical energy. It has many applications including batteries, plating objects with metals, and nerve impulses. Electrochemical cells convert one type of energy to the other via redox reactions. They require an electrolyte solution, a conductor for electron transfer, and a salt bridge for ion movement. Batteries contain electrochemical cells and store chemical energy for later electrical use. Common battery types include lead-acid batteries in vehicles and various fuel cells.Photochemistry 1



Photochemistry 1irfan shah
╠²
Photochemistry is the study of chemical reactions caused by light. Key points include:
- Photochemistry involves light interacting with matter, causing physical or chemical changes.
- Photolysis is the process of carrying out a photochemical reaction using light, usually infrared, visible, or ultraviolet light.
- Natural photochemical reactions include photosynthesis, photography, ozone formation, and solar energy conversion.
- The photochemical process involves light absorption promoting an electron to a higher energy state, followed by primary processes like isomerization, dissociation, or secondary processes like chain reactions.Photochemistry 1



Photochemistry 1irfan shah
╠²
Photochemistry is the study of chemical reactions caused by light. Key points include:
- Photochemistry involves light interacting with matter, causing physical or chemical changes.
- Photolysis is the process of carrying out a photochemical reaction using light, usually infrared, visible, or ultraviolet light.
- Important natural photochemical reactions include photosynthesis, photography, ozone formation, and solar energy conversion.
- The photochemical process involves light absorption promoting an electron to a higher energy state, followed by primary processes like isomerization, dissociation, or secondary processes like chain reactions.U-3 Chem note G-10.docx



U-3 Chem note G-10.docxamanueltafese2
╠²
Electrochemistry deals with the relationship between electrical and chemical energy. It studies the interconversion of one form of energy to another. Electrochemical cells like batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy and vice versa. There are two main types of cells - electrolytic cells which use electrical energy for chemical reactions, and galvanic/voltaic cells which generate electricity from spontaneous chemical reactions. Electrochemistry has many applications including metal production, electrolysis, electroplating and in batteries used in devices and vehicles.electrochemical cells.pptx



electrochemical cells.pptxaqsashafique7
╠²
An electrochemical cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa. There are two types: electrolytic cells, which use electrical energy to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions; and galvanic cells, which generate electrical energy from spontaneous chemical reactions. Galvanic cells have an anode where oxidation occurs and a cathode where reduction occurs. Ions flow through a salt bridge to maintain charge balance between half-cells containing different electrodes immersed in electrolyte solutions.Fuel cells Physics



Fuel cells PhysicsRohan Lakhani
╠²
This document provides information about fuel cells including what they are, their main parts, and how they work. It specifically discusses the following:
- Fuel cells convert chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a reaction with oxygen. The main parts are the anode, cathode, electrolyte, and catalyst.
- Hydrogen is typically used as fuel at the anode. The cathode conducts electrons back from the external circuit. A catalyst speeds up the chemical reaction.
- In the basic working, hydrogen ions pass through the electrolyte to the cathode while electrons travel through an external circuit. At the cathode, hydrogen ions and electrons reunite with oxygen to form water.
- Hydrogen peroxideelectrochemistryclass12-180412053250.pptx



electrochemistryclass12-180412053250.pptxDaizyDmello2
╠²
Electrochemistry is the study of chemical reactions involving the transfer of electrons. Oxidation and reduction reactions occur in electrochemical cells. Daniel cell is an example of a galvanic cell that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. It consists of zinc and copper half cells separated by a salt bridge. The cell potential depends on the standard electrode potentials of the half reactions and can be calculated using Nernst's equation. Equilibrium constants can also be determined from standard cell potentials using thermodynamic relationships.Designing synthetic photosynthetic systems 



Designing synthetic photosynthetic systems Roshen Reji Idiculla
╠²
The document discusses designing artificial photosynthetic systems inspired by natural photosynthesis. It summarizes the key processes in natural photosynthesis including light absorption, charge separation, and using the energy to fix carbon and reduce NADP+. It also discusses challenges in designing artificial solar energy storage systems, including controlling light harvesting and charge separation/transport while avoiding recombination. Perfect light harvesting systems are outlined as having high absorption, long-lived excited states, and catalytic properties while maintaining stability.Types of Electrochemical Cells 



Types of Electrochemical Cells Engr. Mukesh Kumar
╠²
This lecture briefly describes fundamentals of electrochemical cell and illustrate the various types of cells and possible corrosion cites. Honors PPT.pptx



Honors PPT.pptxSYETB202RandhirBhosa
╠²
Fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction without combustion. They convert chemical energy stored in hydrogen fuel into electricity. Fuel cells were first demonstrated in 1839 and the first practical fuel cell was developed in 1959. Key parts include an anode, cathode, catalyst and electrolyte. Hydrogen ions pass through the electrolyte and electrons travel through an external circuit to generate electricity. Fuel cells have various applications and advantages like high efficiency and low emissions but also have disadvantages like high costs. Different types of fuel cells operate at different temperatures using different fuels and electrolytes.Electrochemistry class 12 ( a continuation of redox reaction of grade 11)



Electrochemistry class 12 ( a continuation of redox reaction of grade 11)ritik
╠²
Electrochemistry involves the study of chemical reactions that produce electricity and chemical reactions produced by electricity. A galvanic (voltaic) cell converts the chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction into electrical energy. Daniell's cell uses the redox reaction of zinc oxidizing copper ions to produce a cell potential of 1.1 V. An electrolytic cell uses an applied voltage to drive a nonspontaneous redox reaction in the opposite direction of the natural reaction in a galvanic cell. Standard reduction potentials allow prediction of the tendency of half-reactions to occur and their oxidizing or reducing power.Electrochemistry I



Electrochemistry IAliRaza351367
╠²
This document provides an introduction to electrochemistry and discusses electrochemical cells. It defines electrochemistry as the study of physical and chemical processes involving electrical energy. An electrochemical cell is a device that produces electrical work through a chemical reaction. There are two types of electrochemical cells: electrolytic cells and galvanic/voltaic cells. In an electrolytic cell, electricity is passed through an electrolyte to drive a non-spontaneous reaction. In a galvanic cell, a spontaneous reaction occurs producing electricity. The document discusses the components and examples of each type of cell. It also compares electrolytic and galvanic cells in terms of their similarities and differences.Electrochemis chapter17-2.ppt



Electrochemis chapter17-2.pptVenkataRamana38198
╠²
1) Electrochemistry is the science that combines electricity and chemistry, studying the transfer of electrons during chemical reactions driven by an external voltage or voltage created by a chemical reaction.
2) An electrochemical cell pairs an anode and cathode electrode in an electrolyte solution, allowing spontaneous redox reactions to generate an electric current in galvanic cells or using an applied current to drive non-spontaneous reactions in electrolytic cells.
3) In a Daniell cell, zinc undergoes oxidation at the anode to produce electrons, while copper is reduced at the cathode by the electrons, with both half-reactions occurring spontaneously to generate a current through an external load.Electrolysis_anode_ Cathode_Electrode potential_docx



Electrolysis_anode_ Cathode_Electrode potential_docxDrJyotiMRamojwar
╠²
Electrolysis is a process that uses an electric current to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions. It involves the decomposition of an ionic compound into its elements by passing an electric current through it. During electrolysis, cations move to the cathode where they gain electrons and are reduced. Anions move to the anode where they lose electrons and are oxidized. Faraday's laws of electrolysis state that the mass of a substance produced at an electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity used and the equivalent weight of the substance. Electrolysis has many applications including metal purification, gas production, and electroplating.electrochemistryclass12.pdf



electrochemistryclass12.pdfLUXMIKANTGIRI
╠²
This document provides an overview of electrochemistry and discusses several key concepts:
- Electrochemistry involves using chemical reactions to produce electricity or using electricity to drive non-spontaneous reactions.
- Oxidation and reduction reactions occur at electrodes in electrochemical cells. The standard electrode potential table allows determination of reaction spontaneity.
- Daniell cells convert the chemical energy of a redox reaction into electrical energy. The cell potential is equal to the difference between the standard potentials of the cathode and anode half-reactions.Photosynthesis Notes



Photosynthesis NotesHyde Park
╠²
The document provides an overview of photosynthesis, including:
1) Photosynthesis uses light energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen through a two-stage process of light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
2) The light reactions convert solar energy to chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle then uses this chemical energy to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into sugars.
3) Two photosystems, Photosystem I and Photosystem II, work together to drive electron transport and generate a proton gradient used to produce ATP through chemiosmosis.chapter17-2.aldehydes,ketones, carboxylic acids



chapter17-2.aldehydes,ketones, carboxylic acidsRoopaKhened
╠²
Give reasons
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.Electrochemistry



ElectrochemistrySiyavula
╠²
This document discusses electrochemistry and provides definitions and examples of key concepts. It defines oxidation as the loss of electrons and reduction as the gain of electrons. An electrochemical reaction is one where a chemical reaction produces an electric current or where an electric current causes a chemical reaction. There are two types of electrochemical cells - galvanic cells where a chemical reaction produces a current, and electrolytic cells which use electricity to drive a non-spontaneous reaction. The document also discusses standard electrode potentials and how they are used to calculate cell emf and predict reaction spontaneity. Industrial applications of electrochemical cells mentioned include electrolysis, chloralkali production, and metal extraction from ores.Photosynthesis



Photosynthesiswcadigpub2009zs
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. Chlorophyll in the chloroplasts absorbs light which is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-storing molecules like glucose. The byproducts of photosynthesis like oxygen and glucose are essential for other organisms to survive.ELECTRO CHEMISTRY (1).pptx



ELECTRO CHEMISTRY (1).pptxjimmyAlexander29
╠²
Electrochemistry is the study of chemical reactions caused by electricity or that produce electricity. An electrochemical cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa. There are two main types of electrochemical cells: (1) Galvanic/voltaic cells where a spontaneous redox reaction produces electricity, and (2) electrolytic cells where electricity drives a non-spontaneous reaction. Conductometric titration measures the change in conductivity during a titration reaction and can be used to determine the endpoint. The conductivity changes differently based on whether the acid and base are strong or weak.Electrochemical cells



Electrochemical cellsAlemuMekonnen3
╠²
This document provides an overview of electrochemical cells. It defines oxidation and reduction reactions and describes how electrons are transferred in these reactions. It explains the basic components and workings of electrolytic cells, which use an external power source to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions, and galvanic cells, which generate electricity from spontaneous reactions. Reversible and irreversible electrodes are also discussed. Thermodynamics relationships for electrochemical cells are outlined.Electrochemistry



ElectrochemistrySyed Tanveer
╠²
This document discusses a lecture on electrochemistry. It covers key concepts like electrolysis, Faraday's laws of electrolysis, and electrochemical cells.
Some key points covered include that electrolysis is the decomposition of a compound by an electric current, and involves oxidation and reduction reactions. Faraday's first law states the mass of a substance produced by electrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity used. Faraday's second law relates the masses of different substances deposited to their equivalent masses. An electrochemical cell uses a redox reaction to produce an electrical current.alveolar processes in mandible and tooth.pptx



alveolar processes in mandible and tooth.pptxAdnanHailat
╠²
alveolar processes in mandible and tooth.pptxMore Related Content
Similar to Galvanic Cells Biochemestry.pptx (20)
U-3 Chem note G-10.docx



U-3 Chem note G-10.docxamanueltafese2
╠²
Electrochemistry deals with the relationship between electrical and chemical energy. It studies the interconversion of one form of energy to another. Electrochemical cells like batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy and vice versa. There are two main types of cells - electrolytic cells which use electrical energy for chemical reactions, and galvanic/voltaic cells which generate electricity from spontaneous chemical reactions. Electrochemistry has many applications including metal production, electrolysis, electroplating and in batteries used in devices and vehicles.electrochemical cells.pptx



electrochemical cells.pptxaqsashafique7
╠²
An electrochemical cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa. There are two types: electrolytic cells, which use electrical energy to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions; and galvanic cells, which generate electrical energy from spontaneous chemical reactions. Galvanic cells have an anode where oxidation occurs and a cathode where reduction occurs. Ions flow through a salt bridge to maintain charge balance between half-cells containing different electrodes immersed in electrolyte solutions.Fuel cells Physics



Fuel cells PhysicsRohan Lakhani
╠²
This document provides information about fuel cells including what they are, their main parts, and how they work. It specifically discusses the following:
- Fuel cells convert chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a reaction with oxygen. The main parts are the anode, cathode, electrolyte, and catalyst.
- Hydrogen is typically used as fuel at the anode. The cathode conducts electrons back from the external circuit. A catalyst speeds up the chemical reaction.
- In the basic working, hydrogen ions pass through the electrolyte to the cathode while electrons travel through an external circuit. At the cathode, hydrogen ions and electrons reunite with oxygen to form water.
- Hydrogen peroxideelectrochemistryclass12-180412053250.pptx



electrochemistryclass12-180412053250.pptxDaizyDmello2
╠²
Electrochemistry is the study of chemical reactions involving the transfer of electrons. Oxidation and reduction reactions occur in electrochemical cells. Daniel cell is an example of a galvanic cell that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. It consists of zinc and copper half cells separated by a salt bridge. The cell potential depends on the standard electrode potentials of the half reactions and can be calculated using Nernst's equation. Equilibrium constants can also be determined from standard cell potentials using thermodynamic relationships.Designing synthetic photosynthetic systems 



Designing synthetic photosynthetic systems Roshen Reji Idiculla
╠²
The document discusses designing artificial photosynthetic systems inspired by natural photosynthesis. It summarizes the key processes in natural photosynthesis including light absorption, charge separation, and using the energy to fix carbon and reduce NADP+. It also discusses challenges in designing artificial solar energy storage systems, including controlling light harvesting and charge separation/transport while avoiding recombination. Perfect light harvesting systems are outlined as having high absorption, long-lived excited states, and catalytic properties while maintaining stability.Types of Electrochemical Cells 



Types of Electrochemical Cells Engr. Mukesh Kumar
╠²
This lecture briefly describes fundamentals of electrochemical cell and illustrate the various types of cells and possible corrosion cites. Honors PPT.pptx



Honors PPT.pptxSYETB202RandhirBhosa
╠²
Fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction without combustion. They convert chemical energy stored in hydrogen fuel into electricity. Fuel cells were first demonstrated in 1839 and the first practical fuel cell was developed in 1959. Key parts include an anode, cathode, catalyst and electrolyte. Hydrogen ions pass through the electrolyte and electrons travel through an external circuit to generate electricity. Fuel cells have various applications and advantages like high efficiency and low emissions but also have disadvantages like high costs. Different types of fuel cells operate at different temperatures using different fuels and electrolytes.Electrochemistry class 12 ( a continuation of redox reaction of grade 11)



Electrochemistry class 12 ( a continuation of redox reaction of grade 11)ritik
╠²
Electrochemistry involves the study of chemical reactions that produce electricity and chemical reactions produced by electricity. A galvanic (voltaic) cell converts the chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction into electrical energy. Daniell's cell uses the redox reaction of zinc oxidizing copper ions to produce a cell potential of 1.1 V. An electrolytic cell uses an applied voltage to drive a nonspontaneous redox reaction in the opposite direction of the natural reaction in a galvanic cell. Standard reduction potentials allow prediction of the tendency of half-reactions to occur and their oxidizing or reducing power.Electrochemistry I



Electrochemistry IAliRaza351367
╠²
This document provides an introduction to electrochemistry and discusses electrochemical cells. It defines electrochemistry as the study of physical and chemical processes involving electrical energy. An electrochemical cell is a device that produces electrical work through a chemical reaction. There are two types of electrochemical cells: electrolytic cells and galvanic/voltaic cells. In an electrolytic cell, electricity is passed through an electrolyte to drive a non-spontaneous reaction. In a galvanic cell, a spontaneous reaction occurs producing electricity. The document discusses the components and examples of each type of cell. It also compares electrolytic and galvanic cells in terms of their similarities and differences.Electrochemis chapter17-2.ppt



Electrochemis chapter17-2.pptVenkataRamana38198
╠²
1) Electrochemistry is the science that combines electricity and chemistry, studying the transfer of electrons during chemical reactions driven by an external voltage or voltage created by a chemical reaction.
2) An electrochemical cell pairs an anode and cathode electrode in an electrolyte solution, allowing spontaneous redox reactions to generate an electric current in galvanic cells or using an applied current to drive non-spontaneous reactions in electrolytic cells.
3) In a Daniell cell, zinc undergoes oxidation at the anode to produce electrons, while copper is reduced at the cathode by the electrons, with both half-reactions occurring spontaneously to generate a current through an external load.Electrolysis_anode_ Cathode_Electrode potential_docx



Electrolysis_anode_ Cathode_Electrode potential_docxDrJyotiMRamojwar
╠²
Electrolysis is a process that uses an electric current to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions. It involves the decomposition of an ionic compound into its elements by passing an electric current through it. During electrolysis, cations move to the cathode where they gain electrons and are reduced. Anions move to the anode where they lose electrons and are oxidized. Faraday's laws of electrolysis state that the mass of a substance produced at an electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity used and the equivalent weight of the substance. Electrolysis has many applications including metal purification, gas production, and electroplating.electrochemistryclass12.pdf



electrochemistryclass12.pdfLUXMIKANTGIRI
╠²
This document provides an overview of electrochemistry and discusses several key concepts:
- Electrochemistry involves using chemical reactions to produce electricity or using electricity to drive non-spontaneous reactions.
- Oxidation and reduction reactions occur at electrodes in electrochemical cells. The standard electrode potential table allows determination of reaction spontaneity.
- Daniell cells convert the chemical energy of a redox reaction into electrical energy. The cell potential is equal to the difference between the standard potentials of the cathode and anode half-reactions.Photosynthesis Notes



Photosynthesis NotesHyde Park
╠²
The document provides an overview of photosynthesis, including:
1) Photosynthesis uses light energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen through a two-stage process of light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
2) The light reactions convert solar energy to chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle then uses this chemical energy to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into sugars.
3) Two photosystems, Photosystem I and Photosystem II, work together to drive electron transport and generate a proton gradient used to produce ATP through chemiosmosis.chapter17-2.aldehydes,ketones, carboxylic acids



chapter17-2.aldehydes,ketones, carboxylic acidsRoopaKhened
╠²
Give reasons
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.Electrochemistry



ElectrochemistrySiyavula
╠²
This document discusses electrochemistry and provides definitions and examples of key concepts. It defines oxidation as the loss of electrons and reduction as the gain of electrons. An electrochemical reaction is one where a chemical reaction produces an electric current or where an electric current causes a chemical reaction. There are two types of electrochemical cells - galvanic cells where a chemical reaction produces a current, and electrolytic cells which use electricity to drive a non-spontaneous reaction. The document also discusses standard electrode potentials and how they are used to calculate cell emf and predict reaction spontaneity. Industrial applications of electrochemical cells mentioned include electrolysis, chloralkali production, and metal extraction from ores.Photosynthesis



Photosynthesiswcadigpub2009zs
╠²
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. Chlorophyll in the chloroplasts absorbs light which is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-storing molecules like glucose. The byproducts of photosynthesis like oxygen and glucose are essential for other organisms to survive.ELECTRO CHEMISTRY (1).pptx



ELECTRO CHEMISTRY (1).pptxjimmyAlexander29
╠²
Electrochemistry is the study of chemical reactions caused by electricity or that produce electricity. An electrochemical cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa. There are two main types of electrochemical cells: (1) Galvanic/voltaic cells where a spontaneous redox reaction produces electricity, and (2) electrolytic cells where electricity drives a non-spontaneous reaction. Conductometric titration measures the change in conductivity during a titration reaction and can be used to determine the endpoint. The conductivity changes differently based on whether the acid and base are strong or weak.Electrochemical cells



Electrochemical cellsAlemuMekonnen3
╠²
This document provides an overview of electrochemical cells. It defines oxidation and reduction reactions and describes how electrons are transferred in these reactions. It explains the basic components and workings of electrolytic cells, which use an external power source to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions, and galvanic cells, which generate electricity from spontaneous reactions. Reversible and irreversible electrodes are also discussed. Thermodynamics relationships for electrochemical cells are outlined.Electrochemistry



ElectrochemistrySyed Tanveer
╠²
This document discusses a lecture on electrochemistry. It covers key concepts like electrolysis, Faraday's laws of electrolysis, and electrochemical cells.
Some key points covered include that electrolysis is the decomposition of a compound by an electric current, and involves oxidation and reduction reactions. Faraday's first law states the mass of a substance produced by electrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity used. Faraday's second law relates the masses of different substances deposited to their equivalent masses. An electrochemical cell uses a redox reaction to produce an electrical current.More from AdnanHailat (15)
alveolar processes in mandible and tooth.pptx



alveolar processes in mandible and tooth.pptxAdnanHailat
╠²
alveolar processes in mandible and tooth.pptxfunctions of each teeth layer dentestry.pptx



functions of each teeth layer dentestry.pptxAdnanHailat
╠²
functions of each teeth layer dentestry.pptxmicrobiology tuberculosis presentation..



microbiology tuberculosis presentation..AdnanHailat
╠²
Tuberculosis is a highly contagious bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis that primarily affects the lungs but can impact other parts of the body. It is a major problem in developing countries. Symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, fatigue, weight loss, and fever. TB is usually spread through close contact with an infected person and can be diagnosed through chest x-rays, sputum tests, and skin tests. Treatment involves a combination of antibiotics taken for several months, and adherence to the regimen is important to cure the infection and prevent drug resistance. Drug-resistant TB poses a challenge as it does not respond to standard antibiotics and requires more complex treatment. Preventing TB spread involves vaccination, treating latent infections,the Lactose Intolerance deficiency .pptx



the Lactose Intolerance deficiency .pptxAdnanHailat
╠²
Lactose intolerance is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose in the small intestine. This leads to undigested lactose accumulating in the intestine and causing gas, bloating, diarrhea and abdominal discomfort. It occurs when dairy products like milk, cream, yogurt and cheese are consumed. It is diagnosed through clinical evaluation of symptoms and laboratory tests measuring lactose absorption. Management involves following a low-lactose diet with lactose-free dairy and obtaining calcium and vitamin D from non-dairy sources.the Pathology of Drug Abuse biochemistry



the Pathology of Drug Abuse biochemistryAdnanHailat
╠²
Drug abuse has wide-ranging negative impacts on the body. It affects the central nervous system by disrupting neurotransmission and increasing risks of cognitive issues, mood disorders, and brain changes. Stimulant abuse like cocaine poses serious cardiovascular risks like increased blood pressure and heart attack susceptibility. Opioids cause respiratory depression and overdose risk. Substance abuse also impacts the liver, kidneys, stomach and intestines. It can contribute to mood disorders, anxiety, and psychosis as well. Effective treatment requires medical detoxification, therapeutic interventions, medication-assisted support, and community involvement to address substance abuse's complex effects on health.Histology of tooth



Histology of toothAdnanHailat
╠²
The document discusses the anatomy of teeth. It states that teeth are composed of enamel, dentine, and pulp. The majority of the hard tissue in teeth is dentine, a specialized calcified tissue derived from mesenchyme. The dentine in the root is covered by cementum, another calcified tissue derived from mesenchyme. Teeth are connected to bone by the periodontal ligament, which embeds the tooth in the alveolar ridge.Mitosis 



Mitosis AdnanHailat
╠²
Meiosis is a germ cell division process that results in the formation of gametes and ensures the diploid number of chromosomes is restored during fertilization. It consists of one round of DNA replication followed by two successive cell divisions. In the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes pair up and separate, reducing the number of chromosomes by half to form two haploid cells. The second meiotic division then separates the chromatids, resulting in four haploid daughter cells each containing a single set of chromosomes. Meiosis produces genetic variation between generations and is essential for sexual reproduction.Hemoglobin.pptx



Hemoglobin.pptxAdnanHailat
╠²
Hemoglobin transports oxygen in the blood and its function is regulated through complex interactions between its subunits and small molecule effectors. It exists as an ╬▒2╬▓2 tetramer, with each subunit containing an iron-containing heme group that can bind oxygen. The binding of oxygen or protons causes hemoglobin to shift conformations between relaxed (R) and tense (T) states. This allosteric transition, along with effects of 2,3-BPG and CO2 in tissues, allows hemoglobin to efficiently load and release oxygen in the lungs and peripheral tissues respectively. Mutations in hemoglobin can impair this function and cause diseases like sickle cell anemia.existentialism-091212181547-phpapp02.pdf



existentialism-091212181547-phpapp02.pdfAdnanHailat
╠²
This document discusses existentialism and its key philosophers. Existentialism emphasizes individual existence, personal freedom, and authentic choice. It holds that reality is subjective, truth is relative, and we learn through authentic choices. The main philosophers discussed are Kierkegaard, Nietzsche, and Sartre. Sartre argued that existence precedes essence, meaning we exist first and define our own essence through choices. An authentic life requires independently choosing our path and accepting responsibility for consequences.media Manipulation.pptx



media Manipulation.pptxAdnanHailat
╠²
This document discusses fighting social media manipulation with machine learning. It defines various forms of digital manipulation like trolling, astroturfing, and impersonation. It also discusses how political groups and some countries have weaponized social media. The document then explains how machine learning can be applied to help detect deepfakes and other manipulated media through techniques like supervised and unsupervised learning. It concludes by thanking the reader.Biochemistry lipids



Biochemistry lipidsAdnanHailat
╠²
This document discusses heterocyclic compounds and pyridine. Heterocyclic compounds contain rings composed of carbon and other heteroatoms like nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen. Pyridine resembles benzene but has one CH unit replaced by nitrogen. This makes pyridine polar, miscible with water, and a weaker base than aliphatic amines. The document also summarizes properties of five-membered heterocycles like furan and pyrrole, and discusses lipids, fats, oils, and soaps.Lung - Anatomy.pptx



Lung - Anatomy.pptxAdnanHailat
╠²
The lungs are located in the chest cavity on either side of the heart. Their main functions are to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream out of the body. The lungs are made up of epithelial cells that line the airways and produce mucus. They also contain other cell types. The left lung has two lobes while the right lung has three lobes to make room for the heart. Within the lungs are bronchioles and alveoli where gas exchange takes place through diffusion between the air and blood.Recently uploaded (20)
CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptx



CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptxsuhail849886
╠²
cbse arabic grammar
grade 10 cbse arabic grammar
cbse class 10 arabic grammar
arabic marathon cbse arabic 10
nominal sentences
Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network Layer



Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network LayerMurugan146644
╠²
Title:
Lecture Notes - Unit IV - The Network Layer
Description:
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Computer Network concepts, tailored for final year B.Sc. Computer Science students affiliated with Alagappa University. This document covers fundamental principles and advanced topics in Computer Network. PDF content is prepared from the text book Computer Network by Andrew S. Tenanbaum
Key Topics Covered:
Main Topic : The Network Layer
Sub-Topic : Network Layer Design Issues (Store and forward packet switching , service provided to the transport layer, implementation of connection less service, implementation of connection oriented service, Comparision of virtual circuit and datagram subnet), Routing algorithms (Shortest path routing, Flooding , Distance Vector routing algorithm, Link state routing algorithm , hierarchical routing algorithm, broadcast routing, multicast routing algorithm)
Other Link :
1.Introduction to computer network - /slideshow/lecture-notes-introduction-to-computer-network/274183454
2. Physical Layer - /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-ii-the-physical-layer/274747125
3. Data Link Layer Part 1 : /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-iii-the-datalink-layer/275288798
Target Audience:
Final year B.Sc. Computer Science students at Alagappa University seeking a solid foundation in Computer Network principles for academic.
About the Author:
Dr. S. Murugan is Associate Professor at Alagappa Government Arts College, Karaikudi. With 23 years of teaching experience in the field of Computer Science, Dr. S. Murugan has a passion for simplifying complex concepts in Computer Network
Disclaimer:
This document is intended for educational purposes only. The content presented here reflects the authorŌĆÖs understanding in the field of Computer NetworkThe Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nationŌĆÖs legal framework.
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In Odoo 17, the Inventory module allows us to set up reordering rules to ensure that our stock levels are maintained, preventing stockouts. Let's explore how this feature works.How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
╠²
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfMate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
╠²
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
╠²
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUKaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Prelims of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a MasterŌĆÖs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMŌĆÖs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
╠²
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
╠²
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
╠²
Galvanic Cells Biochemestry.pptx
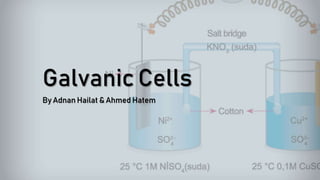
- 1. Galvanic Cells By Adnan Hailat & Ahmed Hatem
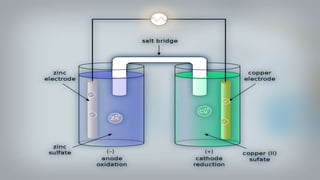
- 2. What are Galvanic Cells? Galvanic cells are an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of spontaneous redox reactions into electrical energy They are named after the scientists Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta and they are used to to supply electrical current through a redox reaction to the transfer of electrons
- 3. Galvanic cells use oxidation and reduction reactions in them and they are used in medicine in a variety of ways ŌĆ”ŌĆ”. oxidation is catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes and results in the loss of electrons from the drug (electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles). The drug is now said to be oxidized and after phase 1 reactions, the resulting drug metabolite is still often chemically active
- 4. An example of an oxidation reaction is the hydroxylation of amphetamine to 4-hydroxyamphetamine and norephedrine. Another example is hydroxylation of delta- 9-THC to 11-OH-delta-9-THC
- 5. Oxidation and reduction reactions, provide cellular energy, because the flow of electrons between molecules produces usable energy. Metabolism is the sum of chemical reactions that occur within each cell to supply energy for important cellular processes When we 'burn' glucose for energy, we transfer (by a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions) electrons from glucose to molecular oxygen ( O2), oxidizing the six carbon molecules in glucose to carbon dioxide and at the same time reducing the oxygen atoms in O2 to water.
- 6. The transfer of electrons from glucose to O2 is a thermodynamicallydownhill, energy- releasingprocess, just like the transfer of electrons from zinc metal to copper ion. And while you could have used the energy released by the zinc/copper redox reaction to light a small light bulb, your cells use the energy released by the glucose/oxygenredox process to carry out a wide variety of energy-requiringactivities On a global scale, oxidation of the carbons in glucose to CO2 by non-photosyntheticorganisms (like people) and the subsequent reductive synthesisof glucose from CO2 by plants is what ecologists refer to as the 'carbon cycle'. In general the more reduced an organic molecule is, the more energyis released when it is oxidized to CO2 . Going back to our single-carbonexamples, we see that methane, the most reduced compound, releases the most energy when oxidized to carbon dioxide, while formic acid releases the least
- 7. After we break down and oxidize sugar and fat molecules to obtain energy, we use that energy to build large, complex molecules (like cholesterol, or DNA) out of small, simple precursors. Many biosynthetic pathways are reductive: the carbons in the large biomolecule products are in a reduced state compared to the small precursors. Look at the structure of cholesterol compared to that of acetate, the precursor molecule from which all of its carbon atoms are derived - you can see that cholesterol is overall a more reduced molecule.
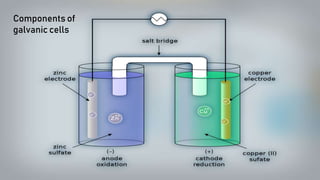
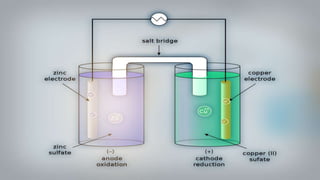
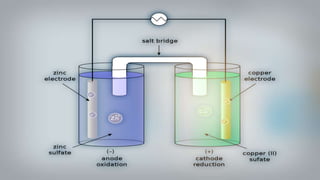
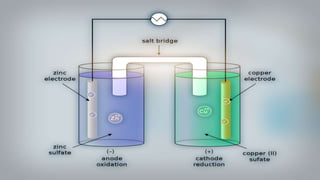
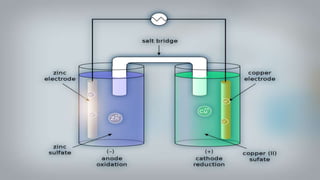
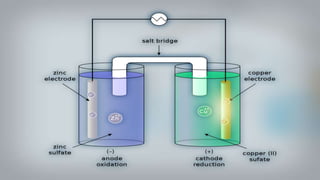
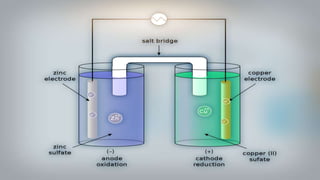
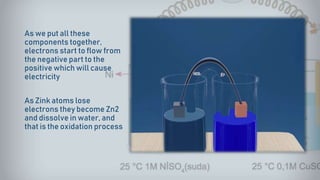
- 16. As we put all these components together, electrons start to flow from the negative part to the positive which will cause electricity As Zink atoms lose electrons they become Zn2 and dissolve in water, and that is the oxidation process
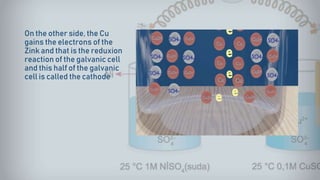
- 17. On the other side, the Cu gains the electrons of the Zink and that is the reduxion reaction of the galvanic cell and this half of the galvanic cell is called the cathode
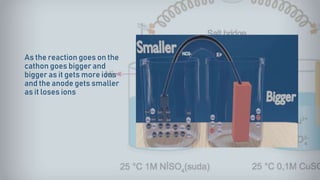
- 18. As the reaction goes on the cathon goes bigger and bigger as it gets more ions and the anode gets smaller as it loses ions
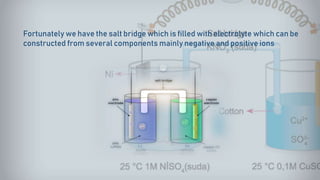
- 19. You can notice that there are positive ions accumulated on the left side and negative ions in the right side, if there were no ion bridge one cell is gonna gather the positive ions together and the other one would gather the negative ones perverting further reactions
- 20. Fortunately we have the salt bridge which is filled with electrolyte which can be constructed from several components mainly negative and positive ions
- 21. The positive ions migrate into the solution where the negative ions are accumulated and migrate into the solution where the positive ions are located
- 22. Uses of Galvanic Cells Galvanic cells are used in batteries as the electrons flow from one chemical reaction to another occurs through an external circuit that results in the current And they provide the foundation of generating electric current spontaneously from a chemical reaction. So learning all of this galvanic cells are so important and form the shape of many things we use in our daily lives.








