Genetic code & mutation types and effects.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes18 views
Genetic code & mutation
1 of 20
Download to read offline




![B. Transversion mutation: - Occurs when a purine is
changed to either of the 2 pyrimidines or when a
pyrimidine is changed to either of the 2 purines.
ŌĆó Effects of point mutation:-
1. Silent mutation: - It means that the codon containing the
changed base still code for the same amino acid.
ŌĆō It is due to degeneracy of the genetic code:- i.e the changed
base is the 3rd
base of the codon.
ŌĆō e.g In Hb Bristol [it has aspartic acid at position 67 that is coded
by 2 codons GAU and GAC].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticcodemutation-241121043709-628cb809/85/Genetic-code-mutation-types-and-effects-pptx-8-320.jpg)




![Protein synthesis = Translation
ŌĆó Protein synthesis: - Is the translation of
mRNA nucleotides sequence into sequence
of amino acids of specific protein.
ŌĆó The message is read from 5 to 3 .
╦ŗ ╦ŗ
ŌĆó Steps of protein synthesis include initiation,
elongation and termination.
A. Initiation:-
ŌĆō Requirements of initiation: - [tRNA,
ribosome, mRNA, amino acids, GTP and
ATP, and at least 10 eukaryotic initiation
factors (eIFc)].
ŌĆō Initiation includes 4 stages:-
1. Ribosomal dissociation
2. Formation of the 43s pre-initiation
complex
3. Formation of the 48s initiation complex
4. Formation of the 80s initiation complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticcodemutation-241121043709-628cb809/85/Genetic-code-mutation-types-and-effects-pptx-14-320.jpg)





Recommended
Molecular basis of Inheritance.



Molecular basis of Inheritance.Dr Janaki Pandey
╠²
This document discusses the central dogma of molecular biology, which states that DNA is transcribed into RNA, and RNA is translated into protein. It describes the multi-step processes of transcription and translation. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and involves RNA polymerase making an mRNA copy of a DNA gene segment. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm and involves ribosomes using the mRNA to assemble a polypeptide chain according to the genetic code. The genetic code is universal across all living things and specifies which triplet codons encode for each amino acid.2_2018_03_19!02_55_44_PM.pdf



2_2018_03_19!02_55_44_PM.pdfRajHardip
╠²
1. Translation is the process by which the instructions in mRNA are used to synthesize proteins. It involves transcription of DNA to mRNA and then translation of mRNA to protein.
2. During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry amino acids and line up with mRNA codons in ribosomes. Enzymes link the amino acids together to form a polypeptide chain.
3. Translation occurs in three steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. In initiation, the ribosome and first tRNA bind to mRNA. In elongation, amino acids are linked together. In termination, the ribosome releases the full protein.Translation Genetic code & Mutations.pdf



Translation Genetic code & Mutations.pdfirfan350885
╠²
The genetic code uses codons made up of three nucleotides to specify 20 amino acids. Most amino acids are specified by more than one codon. Mutations include point mutations like substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotides that can change amino acids or disrupt reading frames. Translation involves mRNA, tRNAs carrying amino acids, and ribosomes linking amino acids in the order specified by mRNA codons through the matching of tRNA anticodons.Gene expression & protein synthesis



Gene expression & protein synthesisssuserc4adda
╠²
Gene expression involves the transcription of DNA into mRNA and the translation of mRNA into proteins. There are four main stages of protein synthesis: activation, initiation, elongation, and termination. Transcription is regulated by promoters, enhancers, and response elements that control the rate of transcription and influence which genes are expressed. Translation includes quality control mechanisms to ensure accuracy, such as ensuring amino acids are bound to the proper tRNAs and that termination occurs at stop codons. Mutations can occur during DNA replication or transcription and may be caused by mutagens, though cells have repair mechanisms. Recombinant DNA techniques allow genes to be spliced from one organism into a plasmid or virus for protein production in other cells.27 28 105 fa13 transcription and translation skel



27 28 105 fa13 transcription and translation skelAfton Chase
╠²
The document summarizes transcription and translation in bacteria and eukaryotes. It describes the central dogma where DNA is transcribed into mRNA which is translated into protein. Transcription involves initiation, elongation, and termination. Translation involves initiator tRNAs bringing amino acids to the ribosome where they are linked together into a polypeptide chain. Eukaryotic transcription and translation are more complex than prokaryotes with mRNA processing and separate transcription/translation.Translation.pptx



Translation.pptxsXVP
╠²
Translation is the process by which the genetic code stored in mRNA is used to synthesize proteins. It involves mRNA being read by ribosomes, which link amino acids in the order specified by the mRNA codons. There are four main steps: 1) activation of amino acids, 2) initiation by forming the initiation complex on the mRNA start codon, 3) elongation where the growing polypeptide chain is extended, 4) termination when a stop codon is reached and the protein is released. The fidelity of translation is ensured by tRNAs, ribosomes, and various translation factors.Subin cology



Subin cologymaheshwari14
╠²
Protein biosynthesis is the process by which cells synthesize proteins. It involves the translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain based on the genetic code. The main stages are activation of amino acids, initiation of translation at start codons on mRNA, elongation of the polypeptide chain by adding amino acids one by one, and termination when a stop codon is reached. Chaperones assist in protein folding and post-translational modifications further process the protein.2.biology for medical students. gene expression



2.biology for medical students. gene expressionRaj Vikram
╠²
This document provides an overview of gene expression and protein synthesis. It discusses how DNA is transcribed into mRNA which is then translated into protein. Transcription occurs in the nucleus, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm. The genetic code is composed of three nucleotide mRNA codons that each specify one amino acid. Transcription includes initiation, elongation, and termination, while translation involves initiation, elongation, termination and the joining of amino acids into a protein chain. The protein then undergoes processing and folding into its final functional structure.PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN EUKARYOTES.pptx



PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN EUKARYOTES.pptxAnkitaDas188735
╠²
Protein synthesis in eukaryotes involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation requires many initiation factors and begins with formation of a preinitiation complex on the 5' end of mRNA. Elongation is cyclic and adds one amino acid at a time to the growing polypeptide chain using elongation factors. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached and release factors cause dissociation of the ribosome and polypeptide release. Additional processes like post-translational modifications further process the final protein structure and function.TRANSLATION (Protein synthesis) presentation.pdf



TRANSLATION (Protein synthesis) presentation.pdfTakondwaMitomoni
╠²
Translation of mRNA into protein occurs through three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the ribosome assembles on the mRNA with the help of initiation factors. In elongation, tRNAs bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons and link them together to form the polypeptide chain. Termination occurs when a stop codon enters the A site, signaling the release of the complete protein. In eukaryotes, post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, acetylation, and protein folding further process the protein to produce its active form.L6, Translation and genetic code_17a7ea13763061b9ec93113a467b074d.pdf



L6, Translation and genetic code_17a7ea13763061b9ec93113a467b074d.pdfjrdys25ycm
╠²
Erythromycin helps Ali by inhibiting the process of translation in Streptococcus pneumonia bacteria. During translation, erythromycin binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit and prevents the translocation step. This stops the synthesis of bacterial proteins and kills the bacteria causing Ali's pneumonia infection.Translation in eukaryotes



Translation in eukaryotesSree RamaKrishna Medical College of Naturopathy and Yogic Sciences
╠²
This document provides an overview of translation. It defines key terms like genetic code, codon, mutation and wobble hypothesis. It describes the basic requirements for translation like mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes. The stages of translation including activation, initiation, elongation, termination and post-translation modification are summarized. Protein targeting and sorting mechanisms to organelles are also outlined. Finally, some inhibitors of protein synthesis and disorders associated with defects in protein targeting are mentioned.RNA Processing



RNA ProcessingKoppala RVS Chaitanya
╠²
Messenger RNA (mRNA) undergoes several types of processing in eukaryotes. mRNA contains 5' and 3' untranslated regions and a protein coding region. In eukaryotes, a 5' cap and poly-A tail are added. Introns are removed from pre-mRNA through splicing in the nucleus. Alternative splicing and cleavage sites allow one gene to code for multiple proteins. RNA editing can further modify the mRNA sequence. These processing steps allow for gene regulation and protein diversity from a single DNA sequence.Ch14-2translation.pptx



Ch14-2translation.pptxZeeshanhaider775048
╠²
Ribosomes translate mRNA into polypeptides. They consist of two subunits containing rRNA and proteins. tRNAs carry specific amino acids and recognize mRNA codons through complementary base pairing between their anticodons. Translation involves initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds the 5' end of mRNA. Elongation adds amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain through peptide bond formation. Termination releases the polypeptide when a stop codon is reached. Accurate protein synthesis depends on specific interactions between mRNA codons, tRNA anticodons, and the ribosomal subunits.BiologyExchange.co.uk Shared Resource



BiologyExchange.co.uk Shared Resourcebiologyexchange
╠²
The document provides an overview of biology concepts related to cellular control, biotechnology, environments, and responding to the environment. It covers topics such as how DNA codes for proteins through gene expression and protein synthesis, cellular control mechanisms like the lac operon, genetic inheritance and mutations, developmental biology processes like apoptosis and meiosis, and more. The document is organized into 8 sections that describe these concepts through explanatory text, diagrams, and lists.Translation & Post Translational Modifications



Translation & Post Translational ModificationsHafiz Muhammad Zeeshan Raza
╠²
The document discusses translation and post-translational modifications. It begins by describing the central dogma and differences between RNA and DNA. It then discusses the types of RNA (mRNA, rRNA, tRNA), RNA processing in eukaryotes, tRNA structure, the process of translation including initiation, elongation, and termination, and post-translational modifications including different types like phosphorylation and glycosylation. It also discusses protein synthesis inhibitors, chemical modifications of proteins, and diseases related to post-translational modifications.Campbell6e lecture ch12



Campbell6e lecture ch12chutchit1979
╠²
This document summarizes key aspects of protein synthesis, including translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain. It discusses the genetic code and how triplet codons specify amino acids. The stages of translation - initiation, elongation, and termination - are described. Post-translational modifications and protein degradation are also covered. Protein synthesis requires various ribosomal and transfer RNA components to translate the genetic message into proteins.Protein synthesis.



Protein synthesis.KrishnaSahu94
╠²
There provided best content for learning that how to PROTEIN synthesis and how the proteins are sorting to different organelles.RAGINI_Biochemistry_Protein synthesis.pptx



RAGINI_Biochemistry_Protein synthesis.pptxstutisrivastavaswag
╠²
The synthesis of proteins in the body occurs by two major processes, i.e. transcription and translation.
Translation and Mutation.pdfhihiiugiujhkujh



Translation and Mutation.pdfhihiiugiujhkujhIbrahimAbdela1
╠²
T6uytutyjti7jfyufyufyymyfmfuyufuymfjufjuyytmftffggfgguugyuygugugyuguggggghhgguyugggggghgghggghgghgghgghggghghvgggggjggjvggggjyjgyyjgyygjgyjgyjgyjgyjygjghygyjgyygjghyjghgjhjghjghjghjghjghyjgProtein Synthesis.pptx



Protein Synthesis.pptxFarawahidaAZaharin
╠²
DNA contains genes that code for proteins. During transcription, mRNA is synthesized using DNA as a template. mRNA then directs protein synthesis during translation. Translation occurs in the ribosome and involves tRNA, rRNA, and amino acids. The mRNA codons are read three bases at a time by tRNA which brings the corresponding amino acids. The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain until a stop codon is reached, terminating translation.Translation



TranslationSt. Xavier's college, maitighar,Kathmandu
╠²
Translation is the process by which the genetic code in mRNA is used to direct the synthesis of proteins. It involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation requires the small and large ribosomal subunits to assemble around an mRNA molecule along with initiator tRNA and other initiation factors. Elongation then adds amino acids one by one to the growing polypeptide chain according to the mRNA codons. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached, causing the ribosome to dissociate and release the complete protein.Genetic code and translation..



Genetic code and translation..HARINATHA REDDY ASWARTHAGARI
╠²
The document discusses genetic code, mutations, tRNA, and the translation process. Some key points:
- The genetic code specifies how nucleic acids correspond to amino acids in proteins. It is nearly universal but has some exceptions.
- Mutations like point mutations and frameshift mutations can alter the genetic code sequence. A point mutation in sickle cell anemia changes one nucleotide, altering the amino acid produced.
- tRNA acts as an adapter between mRNA and amino acids. It has an anticodon loop that binds to mRNA codons and an amino acid binding end.
- Translation involves initiation, elongation, and termination on the ribosome. Charged tRNAs bring amino acids and bind mRNA codTranslation



TranslationAnuKiruthika
╠²
Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to produce proteins. It involves decoding the mRNA to build a polypeptide chain of amino acids. Translation requires several components, including amino acids, ribosomes, mRNA, transfer RNA (tRNA), and protein factors. It occurs through three main stages - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves assembling the ribosome and first tRNA on the mRNA start codon. Elongation is the process of linking amino acids together via peptide bonds. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached, releasing the complete protein chain. The new protein may then undergo further processing and modification.Genetic Code and Translation.pdf



Genetic Code and Translation.pdfuniversity of karachi
╠²
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in DNA is translated into proteins by living cells. It specifies how sequences of nucleotides in mRNA are used to direct protein synthesis through codon-anticodon interactions between mRNA and tRNA. The genetic code is nearly universal, with some minor variations, and is written in the 5' to 3' direction on mRNA. It uses 64 possible codon combinations to specify 20 standard amino acids and 3 stop codons.Synthesis of Proteins or the Formation of the Conga Line



Synthesis of Proteins or the Formation of the Conga LineAndrea S├Īnchez del Rio
╠²
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis from DNA to proteins. It describes how nucleic acids like DNA and RNA carry genetic information through their sequence of nucleotides. DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus, then mRNA is translated by ribosomes in the cytoplasm to produce proteins based on the mRNA's codon sequences. Transfer RNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome according to each codon, and the amino acids are joined through peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain.More Related Content
Similar to Genetic code & mutation types and effects.pptx (20)
2.biology for medical students. gene expression



2.biology for medical students. gene expressionRaj Vikram
╠²
This document provides an overview of gene expression and protein synthesis. It discusses how DNA is transcribed into mRNA which is then translated into protein. Transcription occurs in the nucleus, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm. The genetic code is composed of three nucleotide mRNA codons that each specify one amino acid. Transcription includes initiation, elongation, and termination, while translation involves initiation, elongation, termination and the joining of amino acids into a protein chain. The protein then undergoes processing and folding into its final functional structure.PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN EUKARYOTES.pptx



PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN EUKARYOTES.pptxAnkitaDas188735
╠²
Protein synthesis in eukaryotes involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation requires many initiation factors and begins with formation of a preinitiation complex on the 5' end of mRNA. Elongation is cyclic and adds one amino acid at a time to the growing polypeptide chain using elongation factors. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached and release factors cause dissociation of the ribosome and polypeptide release. Additional processes like post-translational modifications further process the final protein structure and function.TRANSLATION (Protein synthesis) presentation.pdf



TRANSLATION (Protein synthesis) presentation.pdfTakondwaMitomoni
╠²
Translation of mRNA into protein occurs through three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the ribosome assembles on the mRNA with the help of initiation factors. In elongation, tRNAs bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons and link them together to form the polypeptide chain. Termination occurs when a stop codon enters the A site, signaling the release of the complete protein. In eukaryotes, post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, acetylation, and protein folding further process the protein to produce its active form.L6, Translation and genetic code_17a7ea13763061b9ec93113a467b074d.pdf



L6, Translation and genetic code_17a7ea13763061b9ec93113a467b074d.pdfjrdys25ycm
╠²
Erythromycin helps Ali by inhibiting the process of translation in Streptococcus pneumonia bacteria. During translation, erythromycin binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit and prevents the translocation step. This stops the synthesis of bacterial proteins and kills the bacteria causing Ali's pneumonia infection.Translation in eukaryotes



Translation in eukaryotesSree RamaKrishna Medical College of Naturopathy and Yogic Sciences
╠²
This document provides an overview of translation. It defines key terms like genetic code, codon, mutation and wobble hypothesis. It describes the basic requirements for translation like mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes. The stages of translation including activation, initiation, elongation, termination and post-translation modification are summarized. Protein targeting and sorting mechanisms to organelles are also outlined. Finally, some inhibitors of protein synthesis and disorders associated with defects in protein targeting are mentioned.RNA Processing



RNA ProcessingKoppala RVS Chaitanya
╠²
Messenger RNA (mRNA) undergoes several types of processing in eukaryotes. mRNA contains 5' and 3' untranslated regions and a protein coding region. In eukaryotes, a 5' cap and poly-A tail are added. Introns are removed from pre-mRNA through splicing in the nucleus. Alternative splicing and cleavage sites allow one gene to code for multiple proteins. RNA editing can further modify the mRNA sequence. These processing steps allow for gene regulation and protein diversity from a single DNA sequence.Ch14-2translation.pptx



Ch14-2translation.pptxZeeshanhaider775048
╠²
Ribosomes translate mRNA into polypeptides. They consist of two subunits containing rRNA and proteins. tRNAs carry specific amino acids and recognize mRNA codons through complementary base pairing between their anticodons. Translation involves initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds the 5' end of mRNA. Elongation adds amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain through peptide bond formation. Termination releases the polypeptide when a stop codon is reached. Accurate protein synthesis depends on specific interactions between mRNA codons, tRNA anticodons, and the ribosomal subunits.BiologyExchange.co.uk Shared Resource



BiologyExchange.co.uk Shared Resourcebiologyexchange
╠²
The document provides an overview of biology concepts related to cellular control, biotechnology, environments, and responding to the environment. It covers topics such as how DNA codes for proteins through gene expression and protein synthesis, cellular control mechanisms like the lac operon, genetic inheritance and mutations, developmental biology processes like apoptosis and meiosis, and more. The document is organized into 8 sections that describe these concepts through explanatory text, diagrams, and lists.Translation & Post Translational Modifications



Translation & Post Translational ModificationsHafiz Muhammad Zeeshan Raza
╠²
The document discusses translation and post-translational modifications. It begins by describing the central dogma and differences between RNA and DNA. It then discusses the types of RNA (mRNA, rRNA, tRNA), RNA processing in eukaryotes, tRNA structure, the process of translation including initiation, elongation, and termination, and post-translational modifications including different types like phosphorylation and glycosylation. It also discusses protein synthesis inhibitors, chemical modifications of proteins, and diseases related to post-translational modifications.Campbell6e lecture ch12



Campbell6e lecture ch12chutchit1979
╠²
This document summarizes key aspects of protein synthesis, including translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain. It discusses the genetic code and how triplet codons specify amino acids. The stages of translation - initiation, elongation, and termination - are described. Post-translational modifications and protein degradation are also covered. Protein synthesis requires various ribosomal and transfer RNA components to translate the genetic message into proteins.Protein synthesis.



Protein synthesis.KrishnaSahu94
╠²
There provided best content for learning that how to PROTEIN synthesis and how the proteins are sorting to different organelles.RAGINI_Biochemistry_Protein synthesis.pptx



RAGINI_Biochemistry_Protein synthesis.pptxstutisrivastavaswag
╠²
The synthesis of proteins in the body occurs by two major processes, i.e. transcription and translation.
Translation and Mutation.pdfhihiiugiujhkujh



Translation and Mutation.pdfhihiiugiujhkujhIbrahimAbdela1
╠²
T6uytutyjti7jfyufyufyymyfmfuyufuymfjufjuyytmftffggfgguugyuygugugyuguggggghhgguyugggggghgghggghgghgghgghggghghvgggggjggjvggggjyjgyyjgyygjgyjgyjgyjgyjygjghygyjgyygjghyjghgjhjghjghjghjghjghyjgProtein Synthesis.pptx



Protein Synthesis.pptxFarawahidaAZaharin
╠²
DNA contains genes that code for proteins. During transcription, mRNA is synthesized using DNA as a template. mRNA then directs protein synthesis during translation. Translation occurs in the ribosome and involves tRNA, rRNA, and amino acids. The mRNA codons are read three bases at a time by tRNA which brings the corresponding amino acids. The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain until a stop codon is reached, terminating translation.Translation



TranslationSt. Xavier's college, maitighar,Kathmandu
╠²
Translation is the process by which the genetic code in mRNA is used to direct the synthesis of proteins. It involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation requires the small and large ribosomal subunits to assemble around an mRNA molecule along with initiator tRNA and other initiation factors. Elongation then adds amino acids one by one to the growing polypeptide chain according to the mRNA codons. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached, causing the ribosome to dissociate and release the complete protein.Genetic code and translation..



Genetic code and translation..HARINATHA REDDY ASWARTHAGARI
╠²
The document discusses genetic code, mutations, tRNA, and the translation process. Some key points:
- The genetic code specifies how nucleic acids correspond to amino acids in proteins. It is nearly universal but has some exceptions.
- Mutations like point mutations and frameshift mutations can alter the genetic code sequence. A point mutation in sickle cell anemia changes one nucleotide, altering the amino acid produced.
- tRNA acts as an adapter between mRNA and amino acids. It has an anticodon loop that binds to mRNA codons and an amino acid binding end.
- Translation involves initiation, elongation, and termination on the ribosome. Charged tRNAs bring amino acids and bind mRNA codTranslation



TranslationAnuKiruthika
╠²
Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to produce proteins. It involves decoding the mRNA to build a polypeptide chain of amino acids. Translation requires several components, including amino acids, ribosomes, mRNA, transfer RNA (tRNA), and protein factors. It occurs through three main stages - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves assembling the ribosome and first tRNA on the mRNA start codon. Elongation is the process of linking amino acids together via peptide bonds. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached, releasing the complete protein chain. The new protein may then undergo further processing and modification.Genetic Code and Translation.pdf



Genetic Code and Translation.pdfuniversity of karachi
╠²
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in DNA is translated into proteins by living cells. It specifies how sequences of nucleotides in mRNA are used to direct protein synthesis through codon-anticodon interactions between mRNA and tRNA. The genetic code is nearly universal, with some minor variations, and is written in the 5' to 3' direction on mRNA. It uses 64 possible codon combinations to specify 20 standard amino acids and 3 stop codons.Synthesis of Proteins or the Formation of the Conga Line



Synthesis of Proteins or the Formation of the Conga LineAndrea S├Īnchez del Rio
╠²
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis from DNA to proteins. It describes how nucleic acids like DNA and RNA carry genetic information through their sequence of nucleotides. DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus, then mRNA is translated by ribosomes in the cytoplasm to produce proteins based on the mRNA's codon sequences. Transfer RNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome according to each codon, and the amino acids are joined through peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain.More from eman badr (20)
collection 1 of solution and pH 1111.ppt



collection 1 of solution and pH 1111.ppteman badr
╠²
The document provides information on matter, mixtures, and solutions. It defines matter as any substance that has mass and takes up space. Mixtures are either homogeneous, with a uniform composition, or heterogeneous. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures composed of solutes dissolved in solvents. True solutions are also called crystalloids and have particle sizes between 0.01 and 1 nm, making them transparent and unable to be separated by filtration.L3 DNA organization,_ Octamer and .pptx



L3 DNA organization,_ Octamer and .pptxeman badr
╠²
DNA organization involves packaging the long DNA molecules inside the nucleus through several levels. DNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which are organized into a 10nm fiber. The 10nm fiber is then coiled to form the 30nm chromatin fiber. Multiple loops of the 30nm fiber condense further to form chromosomes. Chromatin exists in two forms - euchromatin which is less dense and transcriptionally active, and heterochromatin which is more dense and inactive. Mitochondria also contain DNA which is circular and encodes proteins involved in respiration.Physical_ Chemistry_ Lecture_ 1111 .ppt



Physical_ Chemistry_ Lecture_ 1111 .ppteman badr
╠²
This document discusses physical chemistry concepts related to the states and classification of matter. It provides details on the three states of matter - solid, liquid, and gas. Pure substances can be either elements or compounds, while mixtures contain two or more substances mixed together. The document also defines and compares different types of solutions, including true solutions, colloids, and suspensions. It describes properties of colloids such as the Tyndall effect, Brownian motion, dialysis, ultracentrifugation, and precipitation. Various methods of expressing concentration in solutions are also outlined.Protein Metabolism new.pdf



Protein Metabolism new.pdfeman badr
╠²
Protein metabolism involves the synthesis and breakdown of proteins. There are 20 standard amino acids, of which 9 are essential and must be obtained through diet. Proteins are broken down into amino acids through digestion in the stomach and small intestine by enzymes like pepsin and trypsin. Amino acids can be used to synthesize new proteins or undergo catabolism. During catabolism, the nitrogen from amino acids is removed through the urea cycle and converted to urea for excretion. Glycine participates in the synthesis of heme, creatine, glutathione, and other compounds. Disorders of the urea cycle can cause hyperammonemia, a potentially lethal condition.role of phospholipid in ARDS.ppt



role of phospholipid in ARDS.ppteman badr
╠²
Phospholipids like dipalmitoyl-lecithin are important components of lung surfactant. Dipalmitoyl-lecithin is synthesized by alveolar epithelial cells and is the major phospholipid in surfactant that acts to lower surface tension in the alveoli and prevent their collapse. A deficiency in surfactant, as seen in respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), can occur when the lungs do not produce enough dipalmitoyl-lecithin and other surfactant components, making it difficult for the lungs to expand and exchange gases effectively.Basics of Molecular Biology.ppt



Basics of Molecular Biology.ppteman badr
╠²
The document provides information about the basics of molecular biology. It discusses that molecular biology involves the study of DNA replication, transcription, and translation. The key components involved are DNA, RNA, and proteins. It describes the structures of DNA and RNA, including their basic units and types. It explains the processes of DNA replication, transcription, reverse transcription, translation, and the genetic code. Common techniques used in molecular biology like PCR, gel electrophoresis, and molecular markers are also summarized.enzyme lecture ppt.pptx



enzyme lecture ppt.pptxeman badr
╠²
This document provides information about enzymes and their classification, structure, and function. It begins by listing the intended learning outcomes, which are to describe enzyme classification, structures, mechanisms of action, and factors that affect enzyme activity. It then defines enzymes as biological catalysts and discusses their specificity, classification system, cofactors, isoenzymes, and kinetic parameters including Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The document also examines factors that regulate enzyme activity such as concentration, temperature, pH, inhibitors, and control of enzyme synthesis and degradation.Recently uploaded (20)
FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
╠²
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a MasterŌĆÖs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMŌĆÖs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Prelims of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
╠²
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.How to Manage Putaway Rule in Odoo 17 Inventory



How to Manage Putaway Rule in Odoo 17 InventoryCeline George
╠²
Inventory management is a critical aspect of any business involved in manufacturing or selling products.
Odoo 17 offers a robust inventory management system that can handle complex operations and optimize warehouse efficiency. Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network Layer



Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network LayerMurugan146644
╠²
Title:
Lecture Notes - Unit IV - The Network Layer
Description:
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Computer Network concepts, tailored for final year B.Sc. Computer Science students affiliated with Alagappa University. This document covers fundamental principles and advanced topics in Computer Network. PDF content is prepared from the text book Computer Network by Andrew S. Tenanbaum
Key Topics Covered:
Main Topic : The Network Layer
Sub-Topic : Network Layer Design Issues (Store and forward packet switching , service provided to the transport layer, implementation of connection less service, implementation of connection oriented service, Comparision of virtual circuit and datagram subnet), Routing algorithms (Shortest path routing, Flooding , Distance Vector routing algorithm, Link state routing algorithm , hierarchical routing algorithm, broadcast routing, multicast routing algorithm)
Other Link :
1.Introduction to computer network - /slideshow/lecture-notes-introduction-to-computer-network/274183454
2. Physical Layer - /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-ii-the-physical-layer/274747125
3. Data Link Layer Part 1 : /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-iii-the-datalink-layer/275288798
Target Audience:
Final year B.Sc. Computer Science students at Alagappa University seeking a solid foundation in Computer Network principles for academic.
About the Author:
Dr. S. Murugan is Associate Professor at Alagappa Government Arts College, Karaikudi. With 23 years of teaching experience in the field of Computer Science, Dr. S. Murugan has a passion for simplifying complex concepts in Computer Network
Disclaimer:
This document is intended for educational purposes only. The content presented here reflects the authorŌĆÖs understanding in the field of Computer NetworkThe Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom Walker



The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom WalkerHistory of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptx



CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptxsuhail849886
╠²
cbse arabic grammar
grade 10 cbse arabic grammar
cbse class 10 arabic grammar
arabic marathon cbse arabic 10
nominal sentences
Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
╠²
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In Odoo 17, the Inventory module allows us to set up reordering rules to ensure that our stock levels are maintained, preventing stockouts. Let's explore how this feature works.The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir Dotan



The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir DotanHistory of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
╠²
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Genetic code & mutation types and effects.pptx
- 1. Genetic code
- 2. The genetic code ŌĆó Introduction:- ŌĆō There are 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis, thus their must be at least 20 codons (one for each amino acid) that make the genetic code. ŌĆó Codon: - is the sequence of 3 nucleotide bases on mRNA that determines the type and position of amino acid on a protein. ŌĆó There are 4 different nucleotides in the mRNA and the genetic codon is triplet thus there are (4)3 = 64 codons e.g. AUG codes for methionine. ŌĆó The genetic code: - is the collection of the genetic codons. ŌĆó Nonsense (termination) codons: - there are 3 codons (UAA, UAG and UGA) don't code for amino acids and are called nonsense codons or termination codons as they terminate the translation process.
- 3. Characteristics of the genetic code 1. Degeneracy:- ŌĆō Definition:- It means that multiple codons can code for one amino acid. ŌĆō There are 61 codons and only 20 amino acids, this means that there must be more than one codon code for the same amino acid. ŌĆō Example: - Arginine amino acid has sex codons. ŌĆō The first 2 bases of the codon for certain amino acid are constant, while the 3rd base is changing (this is called wobbling). Also the 3rd base doesn't necessarily obey the base pairing rule.
- 4. 2. Unambiguous: - It means that each codon codes only for a single amino acid. 3. Non overlapping:- It means that the reading of the genetic codons during protein synthesis doesn't involve any overlap of codons. 4. No punctuation:- It means that there is no punctuation between codons and the message is read in a continuing sequence of nucleotide triplets until a translation stop codon is reached. 5. Universal:- ŌĆō Until recently, the genetic code was thought to be universal. ŌĆō But now it was found that a set of tRNA molecules in mitochondria reads 4 codons differently from the tRNA in the cytoplasm of even the same cell.
- 5. The codon-anticodon recognition ŌĆó The anticodon arm of the tRNA recognizes the mRNA codon. ŌĆó The binding of tRNA anticodon to the codon follows the rules of complementarity and antiparallel i.e the codon is read 5╦ŗ’üØ3 while the anticodon is read 3 ╦ŗ ╦ŗ’üØ5 . ╦ŗ ŌĆó The anticodon arm is responsible for the specificity of tRNA.
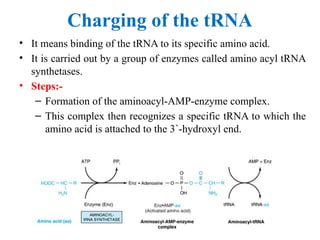
- 6. Charging of the tRNA ŌĆó It means binding of the tRNA to its specific amino acid. ŌĆó It is carried out by a group of enzymes called amino acyl tRNA synthetases. ŌĆó Steps:- ŌĆō Formation of the aminoacyl-AMP-enzyme complex. ŌĆō This complex then recognizes a specific tRNA to which the amino acid is attached to the 3 -hydroxyl end. ╦ŗ
- 7. Mutation ŌĆó Definition: - It is a change in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA. ŌĆó Types: - There are 2 types of mutations. ŌĆó 1- Point mutation (single base changes). ŌĆó 2- Frame shift mutation. 1. Point mutation (single base changes):- ŌĆō There is a substitution of one base by another. ŌĆō There are 2 types A. Transition mutation:- occurs when one pyrimidine is changed to other pyrimidine or when one purine is changed to purine. T C A G
- 8. B. Transversion mutation: - Occurs when a purine is changed to either of the 2 pyrimidines or when a pyrimidine is changed to either of the 2 purines. ŌĆó Effects of point mutation:- 1. Silent mutation: - It means that the codon containing the changed base still code for the same amino acid. ŌĆō It is due to degeneracy of the genetic code:- i.e the changed base is the 3rd base of the codon. ŌĆō e.g In Hb Bristol [it has aspartic acid at position 67 that is coded by 2 codons GAU and GAC].
- 9. 2. Missense mutation: - it occurs when the codon containing the changed base code for a different amino acid. ŌĆó The effect of the mistaken amino acid Protein function may be; 1) Acceptable: - When the resulting protein is not distinguishable from the normal one e.g Hb Hikari. 2) Partially acceptable: - The function of the produced protein is partially affected e.g Hb S. 3) Unacceptable: - The produced protein is non- functioning e.g Hb M.
- 10. 3. Nonsense mutation: - Occurs when the codon containing the changed base become a termination codon. This may lead to premature termination of translation and short protein.
- 11. 2. Frameshift mutation ŌĆó It may be produced either due to deletion or insertion of nucleotide (s) from the coding strand of a gene. 1) Deletion:- I. If there is deletion of a single nucleotide, this may lead to:- ŌĆō Garbled translation of the mRNA distal to the single nucleotide deletion. ŌĆō Nonsense codons: - May result from deletion, leading to premature termination of translation.
- 12. II. If there is deletion of 3 nucleotides or multiple of 3 from the coding region, this result in a protein with missed amino acid or acids. 2) Insertion: - Give the same effects of deletions.
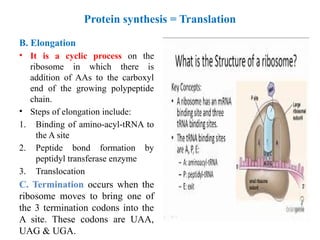
- 14. Protein synthesis = Translation ŌĆó Protein synthesis: - Is the translation of mRNA nucleotides sequence into sequence of amino acids of specific protein. ŌĆó The message is read from 5 to 3 . ╦ŗ ╦ŗ ŌĆó Steps of protein synthesis include initiation, elongation and termination. A. Initiation:- ŌĆō Requirements of initiation: - [tRNA, ribosome, mRNA, amino acids, GTP and ATP, and at least 10 eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFc)]. ŌĆō Initiation includes 4 stages:- 1. Ribosomal dissociation 2. Formation of the 43s pre-initiation complex 3. Formation of the 48s initiation complex 4. Formation of the 80s initiation complex
- 15. Protein synthesis = Translation B. Elongation ŌĆó It is a cyclic process on the ribosome in which there is addition of AAs to the carboxyl end of the growing polypeptide chain. ŌĆó Steps of elongation include: 1. Binding of amino-acyl-tRNA to the A site 2. Peptide bond formation by peptidyl transferase enzyme 3. Translocation C. Termination occurs when the ribosome moves to bring one of the 3 termination codons into the A site. These codons are UAA, UAG & UGA.
- 16. Polyribosome or polysome ŌĆó Multiple ribosomes on the same mRNA molecule form a polyribosome or polysome.
- 17. Posttranslational processing of proteins ŌĆó Polypeptide chains may need some modifications to perform their function. ŌĆó These include:- 1. Trimming:- ŌĆō It means removal of part of the translated region of the protein for activation. ŌĆō Removal of C- peptide from proinsulin to form the active insulin hormone.
- 18. 2. Covalent modifications:- ŌĆó Proteins, both enzymatic and structural may be activated or inactivated by covalent attachment of a variety of chemical groups such as:- A. Phosphorylation:- ŌĆō Phosphate is usually added to the OH groups of serine, threonine or less frequently, tyrosine of proteins. ŌĆō It is catalyzed by protein kinases and removed by protein phosphatases. ŌĆō Phosphorylation may activate or inactivate the protein.
- 19. B. Glycosylation:- ŌĆō Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have complex carbohydrate attached either to OH group of amino acid (O-linked) or to amide group of aspargine (N-linked). ŌĆō These sugars are added post-translationally. C. Hydroxylation:- ŌĆō Proline and lysine residues of the collagen are extensively hydroxylated in the endoplasmic reticulum. D. Carboxylation:- ŌĆō Activation of clotting factors occurs by carboxylation of the ╬│-carboxyl group of glutamic acid to form ╬│- carboxyglutamate. ŌĆō This allows binding of Ca2+ to clotting factors and clot formation.

















