GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
- 1. GEOTHERMAL ENERGY (THE POWER OF HEAT RIGHT UNDER OUR FEET) GEOTHERMAL ENERGY The power of Heat Right Under Your Feet
- 2. Outlines ÔÉò Introduction ÔÉò Geothermal Reservoirs ÔÉò Extraction & Uses of Geothermal energy ÔÉò Electricity Generation ÔÉò Cost ÔÉò Geothermal energy in India ÔÉò Pros & Cons ÔÉò Conclusion 2
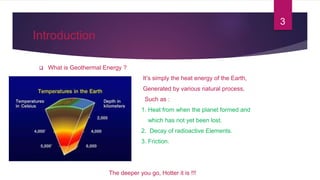
- 3. Introduction  What is Geothermal Energy ?  It’s simply the heat energy of the Earth,  Generated by various natural process,  Such as :  1. Heat from when the planet formed and  which has not yet been lost.  2. Decay of radioactive Elements.  3. Friction. The deeper you go, Hotter it is !!! 3
- 4. Geothermal Reservoirs  Reservoirs can be suspected in the area where we find :-  Geyser  Boiling Mud Point  Volcano  Hot Springs 4
- 5. Geothermal Reservoirs (Cont.) The rising hot water & steam is trapped in permeable & porous rocks to form a Geothermal Reservoirs. Reservoirs can be discovered by  Testing the soil  Analyzing underground Temperature 5
- 6. Extraction & Uses  The heat energy can be brought to earth surface by following ways..  Directly from hot springs/ geysers  Geothermal Heat Pump  Uses are broadly classified as :-  Direct use  Indirect use 6
- 7. Direct use of Geothermal Energy ÔÉò Hot springs use as spas. ÔÉò Heating water at fish farm. ÔÉò Provide heat for buildings. ÔÉò Raising plants for greenhouses, drying crops. ÔÉò Provides heat to Industrial process. 7
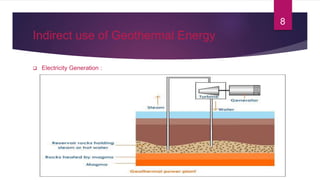
- 8. Indirect use of Geothermal Energy  Electricity Generation : 8
- 9. Electricity Generation (Cont.)  There are three types of Power Plant :-  Dry steam power plant  Flash steam power plant  Binary cycle power plant 9
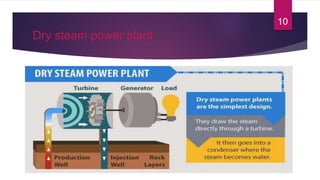
- 10. Dry steam power plant 10
- 11. Dry steam power plant (Cont.) ÔÉò The oldest type of Geothermal power plant used since 1904. ÔÉò Geothermal Reservoir containing pure steam is required. ÔÉò Pure dry Steam drives turbine. ÔÉò Use steam piped directly from a geothermal reservoir to turn the generator turbines. ÔÉò Very rare type of Geothermal power plant. ÔÉò Operating at California, Italy & Japan. 11
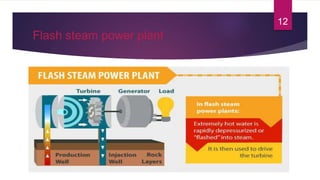
- 12. Flash steam power plant 12
- 13. Flash steam power plant (Cont.) ÔÉò Commonly used Geothermal power plant. ÔÉò Take high-pressure hot water from deep inside the earth and convert it to steam to drive the generator turbines. ÔÉò When the steam cools, it condenses to water and is injected back into the ground to be used over and over again. ÔÉò Geothermal reservoirs containing both hot water & steam is required. ÔÉò Pressure changing system is required. ÔÉò Operating at Hawaii, Nevada, Utah & some other places. 13
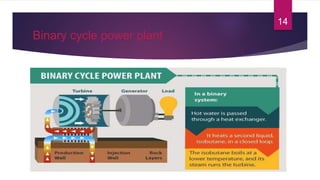
- 14. Binary cycle power plant 14
- 15. Binary cycle power plant (Cont.)  Transfer the heat from geothermal hot water to another liquid. The heat causes the second liquid to turn to steam which is used to drive a generator turbine.  Only the ground water is used.  Vaporized hydrocarbons are used to spin the turbines.  Hydrocarbons having lower boiling point such as isopentane, isobutane and propane can be used.  No harmful gases are emitted to the atmosphere because the underground water is never disclosed outside.  This’s the worldwide accepted power plant. 15
- 16. Installation for Household Purposes  Formula Indoor Portion + Underground Loop Field = Total System Cost  The inside portion is composed of the price of the geothermal heat pump, its installation, and possible duct work modification.  The Underground Loop Field involves drilling (or sometimes excavating) and materials. This is usually done by a well driller. The loop field is approximately 50% of the total cost, although many factors effect this generalization.  For the particular situation the variables are considered : Size of the Home/Building Size of the heat pump Size of the loop field Usability of current duct work 16
- 17. Cost  Direct use of geothermal energy is absolutely cheaper than other energy sources.  Cost of electricity generation depends upon certain factors:  Temperature and depth of resource  Type of resource (steam, liquid ,mix etc)  Available volume of resource  Size and Technology of plant 17
- 18. Cost ÔÉò The initial investment is high. ÔÉò But after certain time period, the cost of electricity becomes comparable to other resources of energy. ÔÉò US $0.05 to $0.08 (Rs. 3.40 to Rs. 5.43) per KWh. ÔÉò Once the capital cost is recovered, the price can decrease to below US $0.05 (Rs. 3.40 ) per KWh. 18
- 19. Geothermal energy in India 19
- 20. Geothermal Energy in India (Cont.) ÔÉò Geothermal provinces are estimated to produce 10,600 MW of power (experts are confident only to the extent of100 MW) ÔÉò Geothermal provinces in India : Himalayas, Sohana, West coast, Cambay, Son- Narmada-tapi, Godavari &Mahanadi ÔÉò Reykjavik Geothermal will assist thermax to setup a pilot project in Puga Valley, Ladakh (Jammu and Kashmir) ÔÉò India Plans to build its first geothermal power plants are underway. Indian states Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh and West Bengal are the first of many to announce interest in developing the BRIC country's first geothermal energy plant, with power capacity in the range of 3MW to 5MW. 20
- 21. Pro’s  Geothermal energy is generally considered environmentally friendly and does not cause significant amounts of pollution.  Geothermal reservoirs are naturally replenished and therefore renewable (it is not possible to exhaust the resources).  Massive potential – upper estimates show a worldwide potential of 2 terawatts (TW).  Excellent for meeting the base load energy demand (as opposed to other renewable’s such as wind and solar).  Great for heating and cooling – even small households can benefit.  Harnessing geothermal energy does not involve any fuels, which means less cost fluctuations and stable electricity prices.  Geothermal energy is available everywhere, although only some resources are profitably exploitable.  Recent technological advancements (e.g. enhanced geothermal systems) have made more resources exploitable and lowered costs. 21
- 22. Con’s  There are some minor environmental issues associated with geothermal power.  Geothermal power plants can in extreme cases cause earthquakes.  There are heavy upfront costs associated with both geothermal power plants and geothermal heating/cooling systems.  Very location specific (most resources are simply not cost-competitive).  Geothermal power is only sustainable (renewable) if the reservoirs are properly managed. 22
- 23. Conclusion ÔÉò Geothermal heating system can replace fossil fuel heating system in a particular area. ÔÉò Annual cost for common heating purpose can be reduced by more than 60 % ÔÉò Continued energy shortages have created added interest in geothermal energy for power generation. ÔÉò Potential exists to provide all energy requirement of the world. ÔÉò Geothermal Energy appears to be a partial solution to our energy needs. 23
- 24. Thank You PPT. By Darryl Dmello Mohammed Afzal Shaikh Danish Rauf Shaikh Vikrant Gupta 24