Gogotsi-Yury.pdfCO2 ReductionCO2 Reduction
- 1. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²1 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² Two-┬ŁŌĆÉdimensional ╠²Transi/on ╠²Metal ╠² Carbides ╠²Produced ╠²by ╠²Exfolia/on ╠²of ╠² MAX ╠²Phases ╠² Yury ╠²Gogotsi ╠²& ╠²Michel ╠²Barsoum ╠² Students: ╠² Michael ╠²Naguib, ╠²Olha ╠²Mashtalir, ╠²Murat ╠²Kurtoglu ╠² ╠² Drexel ╠²University ╠² AJ ╠²Drexel ╠²Nanotechnology ╠²Ins7tute ╠² ╠² Materials ╠²Science ╠²and ╠²Engineering ╠²Department ╠² Philadelphia, ╠²Pennsylvania ╠² NSF/AFOSR ╠²Workshop ╠²on ╠²2D ╠²Materials ╠²Beyond ╠²Graphene, ╠² ╠² May ╠²30-┬ŁŌĆÉ31, ╠²2012 ╠²
- 2. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²2 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² 2 ╠² M X A M ŌĆó Composition of Mn+1AXn ; with n =1,2,3 ŌĆó Ternary metals carbides and/or nitrides ŌĆó Layered hexagonal structure (P63/mmc) ŌĆó Examples: Ti2AlC, Ti2AlN, Ti3AlC2,Ti4AlN3 Ta2AlC, Ta4AlC3 Cr2AlC, Cr3AlC2 V2AlC, V3AlC2 Nb2AlC, Nb4AlC3 (>60 phases) (Ti0.5Nb0.5)2AlC, Ti3Al(C0.5N0.5)2 (considering solid solution, there will be more) Barsoum, M.W. Progress in Solid State Chemistry 28 (2000) 201 ŌĆō 281 211 312 413 MAX ╠²Phases ╠² Strong but Ductile Ceramics - not van der Waals Solids
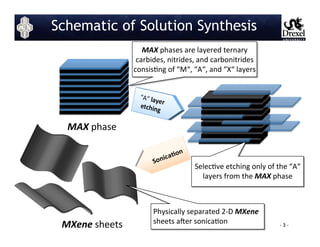
- 3. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²3 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² MAX ╠²phase ╠² MAX ╠²phases ╠²are ╠²layered ╠²ternary ╠² carbides, ╠²nitrides, ╠²and ╠²carbonitrides ╠² consisJng ╠²of ╠²ŌĆ£MŌĆ£, ╠²ŌĆ£AŌĆ£, ╠²and ╠²ŌĆ£XŌĆ£ ╠²layers ╠² ╠² SelecJve ╠²etching ╠²only ╠²of ╠²the ╠²ŌĆ£AŌĆ£ ╠² layers ╠²from ╠²the ╠²MAX ╠²phase ╠² MXene ╠²sheets ╠² Physically ╠²separated ╠²2-┬ŁŌĆÉD ╠²MXene ╠² sheets ╠²aOer ╠²sonicaJon ╠² Summary ╠² Schematic of Solution Synthesis
- 4. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²4 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² HF ╠² T reatment ╠² O ╠² C ╠² H ╠² Al ╠² Ti ╠² Sonica/on ╠² Michael Naguib, et al. Advanced Materials 23 (2011) 4248-4253 MAX MAX MXene The Solution Approach to Ti3AlC2 Exfoliation and Dispersion Ti3AlC2 in HF 50% for 2 hours at room temperature, then sonication
- 5. M. Naguib, et al. Advanced Materials 23 (2011) 4248-4253 Ti3AlC2 HF 50% for 2 hours at room temperature ŌĆó After HF treatment, the most intense peak of Ti3AlC2 vanished. ŌĆó XRD after HF treatment matches with DFT simulated Ti3C2(OH)2. ŌĆó Sonication results in weakening the intensity of the peaks (losing the crystalline ordering). XRD Analysis of MAX and MXene
- 6. Raman Spectra of MAX and MXene 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 Intensity (I) (II) (IV) (V) (III) (VI) Raman shift (cm-1) Ti3AlC2 HF etched ╠² Ti3AlC2 etched in 50% HF for 2 hours at room temperature Raman spectroscopy: 514.5 nm excitation M. Naguib, et al. Advanced Materials 23 (2011) 4248-4253 V. Presser, M. Naguib, et al. J. Raman Spectroscopy 43 (2011) 168-172.
- 7. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²7 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² Ti3AlC2 etched in HF 50% for 2 hours at room temperature: 2 ┬Ąm M. Naguib, et al. Advanced Materials 23 (2011) 4248-4253 L. M. Viculis, et al., Journal of Materials Chemistry 15 (2005) 974-978. Exfoliated Graphite SEM ╠²Images ╠²of ╠²MXene ╠²
- 8. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²8 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² Science 2012 Vol. 335, pp 526-527 PeopleŌĆÖs choice award for International Science & Engineering Visualization Challenge from NSF, 2012. MXene on the Cover
- 9. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²9 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² Ti3AlC2 treated in HF 50% for 2 hours at room temperature, then sonication Michael Naguib, et al. Advanced Materials 23 (2011) 4248-4253 TEM ╠²Analysis ╠²of ╠²Ti3C2 ╠²
- 10. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²10 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² 5 nm R<20nm 5 nm Michael Naguib, et al. Advanced Materials 23 (2011) 4248-4253 Ti3AlC2 in 50%-HF for 2 hours at room temperature, then sonication MXene Scrolls/Nanotubes MXene shows behavior typical of graphene or other 2-D materials
- 11. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²11 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² 4 ┬Ąm 3 ┬Ąm 1 ┬Ąm 2 ┬Ąm 1 ┬Ąm 1 ┬Ąm As ╠²received ╠² Ti3C2 ╠² Ti2C ╠² (Ti0.5Nb0.5)2C ╠² ╠² Ti3(C0.5N0.5 ╠²)2 ╠² Ta4C3 ╠² ╠² Michael Naguib, et al. ACS Nano 6 (2012) 1322-1331 MXenes ŌĆō A Large Family of Transition Metal Carbides and/or Nitrides Several MAX phases have been exfoliated, producing MXenes
- 12. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²12 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² Michael Naguib, et al. ACS Nano 6 (2012) 1322-1331 40nm 1 2 3 20nm 50nm 50nm Ti3C2 ╠² Ti3(C0.5N0.5 ╠²)2 ╠² (Ti0.5Nb0.5)2C ╠² ╠² Ta4C3 ╠² ╠² MXenes ŌĆō A Large Family of Transition Metal Carbides and/or Nitrides
- 13. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²13 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² M. Naguib, et al. ACS Nano 6 (2012) 1322-1331 HR TEM and SAD of Ta4C3 1100 ╠² 0110 ╠² 1010 ╠² 1120 ╠² 1210 ╠² 2110 ╠² 5 ╠²1/nm ╠² 20 ╠²nm ╠² 1.325 ╠²nm ╠² 13 ╠² 2 ╠²nm ╠² 0.269 ╠²nm ╠² (0110) ╠² 0.155 ╠²nm ╠² (2110) ╠² 60┬░ ╠² ŌĆó Crystalline structure is maintained within the layer ŌĆó MXene layers are in registry in multilayer structures
- 14. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²14 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² 10┬Ąm 10┬Ąm Ta4C3 flakes Ti3CN Individual (multi)layers are optically transparent under visible light Michael Naguib, et al. ACS Nano 6 (2012) 1322-1331 Light Microscopy of MXenes
- 15. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²15 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² Ti3C2(OH)2: ╠²OH ╠²terminated ╠² ╠² Ti3C2 ╠²nanosheets ╠² Ti3C2: ╠²Bare ╠²layers, ╠² ╠² no ╠²termina/ons ╠² ╠² Ti3C2F2: ╠²F-┬ŁŌĆÉterminated ╠² ╠² Ti3C2 ╠²nanosheets ╠² Semiconductor ╠² (0.05 ╠²eV ╠²bandgap) ╠² Semiconductor ╠² (0.1 ╠²eV ╠²bandgap) ╠² Metal ╠² M. Naguib, et al. Advanced Materials 23 (2011) 4248-4253 Electronic Structure of MXenes DFT implemented in the CASTEP code in Material Studio software (Version 4.5)
- 16. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²16 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² Ti2C Ta4C3 (Ti0.5Nb0.5)2C Ti3(C0.5N0.5)2 R: 330 ╬®/Ō¢Ī 104 ╬®/Ō¢Ī 171 ╬®/Ō¢Ī 125 ╬®/Ō¢Ī CA: 32┬░ 41┬░ 31┬░ 27┬░ Michael Naguib, et al. ACS Nano 6 (2012) 1322-1331 ŌĆó MXene can be cold pressed in the form of thin (300 ┬Ąm) free- standing discs. ŌĆó Resistivity is comparable to multi-layer graphene. ŌĆó Contact angle measurements of water showed hydrophilic behavior. 25mm Wetting and Conductivity
- 17. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²17 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 0 100 200 300 400 500 Q disch Cycle 1 Q ch Cycle 1 Q disch Cycle 2 Q ch Cycle 2 Q disch Cycle 20 Q ch Cycle 20 Q disch Cycle 25 Q ch Cycle 25 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 Potential (V vs. Li/Li + ) Specific Capacity (mAh┬Ęg -1 ) Number of Inserted Li in the Structure (y) 1st 2nd 20-25 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Data 31 4:08:31 PM 11/30/2011 Q discharg (C/25) Q charg (C/25) Qdischarge (C/6) Qcharge (C/6) Qdischarge (1C) Qcharge (1C/) Qdischarge (3C) Qcharge (3C) Qdischarge (10C) Qcharge (10C) Specific Capacity (mAh┬Ęg -1 ) Cycle Number 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 0 5 10 15 20 Data 31 8:36:44 PM 11/3/2011 Q discharg (C/25) Q charg (C/25) Qdischarge (C/6) Qcharge (C/6) Qdischarge (1C) Qcharge (1C/) Qdischarge (3C) Qcharge (3C) Qdischarge (10C) Qcharge (10C) 3C 1C C/6 C/25 C/6 C/25 1C 3C & 10C 10C Ti2COx based anode ŌĆō properties similar to lithium titanate anodes M. Naguib, et al. Electrochemistry Communications 16 (2012) 61-64 MXene ╠²as ╠²a ╠²Li-┬ŁŌĆÉion ╠²Ba[ery ╠²Anode ╠²
- 18. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²18 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² ŌĆó SelecJve ╠²etching ╠²of ╠²ŌĆ£AŌĆØ ╠²layer ╠²from ╠²ŌĆ£MAXŌĆØ ╠²phases ╠²results ╠²in ╠²the ╠² formaJon ╠²of ╠²2-┬ŁŌĆÉD ╠²transiJon ╠²metals ╠²carbides ╠²and/or ╠²nitrides ╠²called ╠² ŌĆ£MXenesŌĆØ ╠² ╠² ŌĆó Band ╠²gap ╠²of ╠²MXene ╠²predicted ╠²to ╠²change ╠²with ╠²the ╠²surface ╠²chemistry ╠² ╠² ŌĆó Excellent ╠²mechanical ╠²properJes ╠²predicted ╠²(DFT) ╠² ŌĆó Su’¼āciently ╠²ducJle ╠²for ╠²cold ╠²pressing ╠² ╠² ŌĆó ConducJvity ╠²comparable ╠²to ╠²mulJ-┬ŁŌĆÉlayer ╠²graphene ╠² ŌĆó Hydrophilic ╠²(contact ╠²angle ╠²30-┬ŁŌĆÉ40┬░) ╠² ╠² ŌĆó Li ╠²inserJon ╠²allows ╠²use ╠²in ╠²Li-┬ŁŌĆÉion ╠²ba[ery ╠²anodes ╠² ╠² Summary of the Data to Date
- 19. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²19 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² ŌĆó Electrical ╠²energy ╠²storage ╠² Pseudocapacitors, ╠²Lithium ╠²ion ╠²ba[eries, ╠²Hybrid ╠²devices ╠² ŌĆó Composite ╠²materials ╠² ConducJve, ╠²high-┬ŁŌĆÉstrength, ╠²low-┬ŁŌĆÉpermeability ╠²polymers, ╠²high ╠² strength ╠²and ╠²high ╠²toughness ╠²ceramic-┬ŁŌĆÉmetal ╠²composites ╠² ╠² ŌĆó Sensors ╠² ŌĆó 2-┬ŁŌĆÉD ╠²and ╠²’¼éexible ╠²electronics ╠² ╠² Potential Applications M2X ╠² M3X2 ╠² M4X3 ╠²
- 20. -┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠²20 ╠²-┬ŁŌĆÉ ╠² Acknowledgments J├®r├®my Come & Patrice Simon, Universit├® Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France Jun Lu & Lars Hultman, Linkoping University, Sweden Gogotsi Nanomaterials Group Barsoum MAX Phase Group BATT Program