Growth _ Mindset_Presentation_Final.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes12 views
A growth mindset is based on the belief that your basic qualities are things you can cultivate through your efforts, your strategies, and help from others
1 of 13
Download to read offline








Recommended
Assignments



AssignmentsAaron Lawler, PhD
╠²
The document provides tips and guidelines for various types of assignments in an online course, including class participation, discussion boards, group activities, journal entries, writing assignments, exams, and project-based learning. For each assignment type, 3-4 tips are given to help students succeed, such as demonstrating preparation, contributing meaningful insights, posting consistently, respecting others, and communicating effectively. Project-based learning is defined as involving students investigating real-world problems over an extended period through exploring, experimenting, and presenting solutions.Metacognition



MetacognitionJennifer Englund
╠²
The document discusses metacognition and teaching students to learn. It provides strategies for planning, monitoring, and evaluating learning. It suggests teaching students to set goals, think aloud, identify ways to grow learning skills, acknowledge confusion, select and adapt practices, and incorporate reflection. Key components of metacognition include reflection and learning, gathering data, reflecting, creating, and testing. Teachers can provide orienting tasks to guide reading and study, use graphical organizers, rubrics, and wrappers to help students monitor and direct their own learning. The overall goal is to help students develop a growth mindset and self-regulation of their learning.Strategies for developing creativity and ct



Strategies for developing creativity and ctCOB1998
╠²
This document provides strategies for developing creativity and critical thinking in the classroom. For creativity, it suggests questioning assumptions, redefining problems, generating ideas, cross-fertilizing ideas across disciplines, and encouraging creative collaboration. For critical thinking, it recommends using questions, classroom discussions and debates using various models, case study methods, writing assignments, and cooperative learning strategies. The goal is to challenge students at different cognitive levels and provide an environment that encourages open-minded thinking.Region 8 presentation



Region 8 presentationosalinasatboisestate
╠²
1. The document discusses using outcomes directed thinking in student advising to help students achieve their goals in a transformative way. It focuses on identifying student motivations, barriers, and actionable strategies to overcome barriers.
2. Examples are provided of how outcomes directed thinking can guide advisors to partner with students in developing independence, confidence, and educational achievement. Student quotes support that this approach helps isolate problems and clarify solutions.
3. When advisors use this approach as a student development tool, it facilitates student ownership of goals and reduces needed interactions by creating implementable plans that others can assist with.Humanizing Your Online Course



Humanizing Your Online CourseStephanie Richter
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation about humanizing online courses. It discusses establishing instructor, social, and cognitive presence to improve the educational experience. Instructor presence is created through setting a supportive climate, such as introducing oneself and providing feedback. Social presence is developed by having students introduce themselves and incorporating collaborative learning. Cognitive presence encourages deep learning through critical thinking strategies like problem-based learning and reflection. The goal is for these three types of presence to work together to support discourse and learning according to the Community of Inquiry framework.Assessment for learning and development



Assessment for learning and developmentMikeHayler
╠²
This document discusses assessment for learning and formative assessment. It outlines the key principles of assessment for learning, including that it should be part of effective planning, focus on how students learn, and promote commitment to learning goals. The four basic elements of assessment for learning are sharing learning goals, effective questioning, self and peer evaluation, and effective feedback. Teachers should utilize strategies like these to understand students' progress and inform next steps in instruction. The overall goal of assessment for learning is to help both students and teachers know how to improve learning.RETSD.SY.2018



RETSD.SY.2018Faye Brownlie
╠²
Continuing the conversation of working with class and school profiles/reviews to better support inclusion. Includes a focus on what makes a difference in teaching, 'no plan, no point' and co-teaching.Teaching Adult Learners - TEACH Academy



Teaching Adult Learners - TEACH AcademyCentral Connecticut State University
╠²
Here are two assessment items I created based on the information in the video:
Multiple choice item:
Which of the following is NOT considered a formal assessment?
A) Quizzes
B) Discussions
C) Tests
D) Projects
True/false item:
Assessments should be directly aligned with the objectives and activities covered in class.Handout -critical_thinking_-_teaching_methods_and_strategies (1)



Handout -critical_thinking_-_teaching_methods_and_strategies (1)abdellahzoubiai
╠²
The document discusses methods for teaching critical thinking skills in the classroom. It recommends using lesson plans that anticipate, build, and consolidate knowledge. Teachers should ask high-order questions that require applying concepts rather than just recalling facts. An effective classroom environment models thinking, challenges students to think independently, and uses techniques like cooperative learning. The goal is to encourage students to ask questions, apply what they learn, and debate ideas rather than just memorizing information.SD36 Surrey - Inquiry teams Oct.2010 



SD36 Surrey - Inquiry teams Oct.2010 christensen_lea
╠²
The document provides an agenda and information for a professional development meeting on developing readers and student learning teams for the 2010-2011 school year. It discusses establishing inquiry groups to craft meaningful questions about student learning and developing action plans to address these questions through formative assessment and collaboration. Budget and release time options are also outlined to support the collaborative inquiry work.High School Math Teachers Problem Solving Strategies



High School Math Teachers Problem Solving Strategieswholesalefba2022
╠²
High School Math Teachers Problem Solving StrategiesManaging the Teaching & Learning Environment



Managing the Teaching & Learning EnvironmentEdu Nile
╠²
Managing the teaching & learning environment. A presentation in a local PD event at the ION in 2006. Ev681 session3 planning



Ev681 session3 planningPippa Totraku
╠²
This document discusses planning and assessment for learning. It provides guidance on developing lesson plans, formative assessment strategies, and the role of assessment for learning. The key elements discussed include setting learning objectives, organizing learning activities, considering resources and grouping, using formative assessment strategies during and after lessons, and evaluating lessons to inform future planning. The document emphasizes that planning, teaching and assessment should be cyclic and integrated to best support student learning.Stage Iii Lp



Stage Iii LpNandita Nag
╠²
The backward design model comprises three stages:
I. Identify desired results
II. Determine acceptable evidence
III. Plan learning experiences and instruction. Once desired results and evidence are determined, a lesson plan can be developed to help students reach the objectives. Wiggins and McTighe's "WHERE" approach is used in planning instruction and experiences.Plenary-3_Improvisation-and-Design-Thinking_MVCano.pdf



Plenary-3_Improvisation-and-Design-Thinking_MVCano.pdfSHEILAARAOJO
╠²
This document outlines a presentation on using improvisation and design thinking in science and mathematics teaching. It discusses how improvisation involves divergent thinking and an improvisational mindset. Design thinking is presented as a process that can enhance improvisation, with steps like empathizing with students, defining problems, ideating solutions, prototyping ideas, and testing. An example is given of how these approaches could be used in a lesson on Charles' Law, by developing a hands-on activity to demonstrate the concept using everyday objects. The presentation argues that improvisation and design thinking can make science and math more engaging, accessible and understandable for students.Reflective teaching



Reflective teachingJamlick Bosire
╠²
Reflective teaching involves self-evaluation and feedback from colleagues to improve one's teaching. A reflective teacher questions their teaching aims and methods to ensure they are clear and effective for helping students learn. Reflective practice is important for teachers to develop their skills and address challenges in a thoughtful way.REFLECTIVE TEACHING



REFLECTIVE TEACHINGJamlick Bosire
╠²
Reflective teaching involves self-evaluation and feedback from colleagues to improve one's teaching. A reflective teacher questions their teaching aims and methods to ensure they are clear and effective in helping students learn. Reflective practice is important for teachers to develop their skills and address issues in a thoughtful way. It involves rethinking one's actions and considering alternative approaches on an ongoing basis.Teacher Connect ║▌║▌▀Ż Share Version



Teacher Connect ║▌║▌▀Ż Share VersionSharon Seslija
╠²
This document summarizes the agenda and activities for the first Teacher CONNECT session. The session focused on:
1. Introductions and name tag activity to get to know participants.
2. Overview of the daily schedule, norms, and goals of the Teacher CONNECT program to provide support for new teachers.
3. Activities in groups to discuss topics like assessment, classroom management, differentiation and building relationships with students and parents.
4. Presentations and discussions around establishing effective learning communities, assessment for learning, developing student profiles and differentiated instructional strategies.The Role of Grit and Growth Mindset in Second Language Acquisition



The Role of Grit and Growth Mindset in Second Language AcquisitionGlobal Training, Coaching and Development
╠²
This presentation was given at ACPI-TESOL Costa Rica in July 2016. I discuss the definitions of grit and growth mindset, and how it can be applied to SLA. I believe that grit and growth mindset help students persevere and succeed in their language learning.AppreciativeAdvisingPPT_updated



AppreciativeAdvisingPPT_updatedKimberly Harris
╠²
This document outlines strategies for improving college readiness curriculum through appreciative advising, proactive advising, one-on-one meetings, and incorporating various learning styles and study skills. It provides examples of topics to cover (e.g. time management, note taking), teaching methods (e.g. concept maps, Cornell method), and data from piloting the curriculum that showed improved student confidence and feedback praising the clear teaching and approachability. Limitations discussed are the lack of a control group and small data set. The goal is to enhance student motivation and success through strengthening the student-advisor relationship and equipping students with effective learning techniques.AHDS Conference November 2014 - Keynote by Alistair Smith



AHDS Conference November 2014 - Keynote by Alistair SmithAHDScotland
╠²
AHDS Annual Conference November 2014 'Teaching Scotland's Future: What you need to know and do.' Keynote by Alistair Smith.Faculty of Economics Trisakti University - Problem Based Learning (7 Jump Step)



Faculty of Economics Trisakti University - Problem Based Learning (7 Jump Step)Dwitya Aribawa
╠²
This document provides an overview of problem-based learning (PBL). It discusses that PBL is an active learning approach where students work in small groups to solve real-world problems. It contrasts PBL with the traditional lecture approach. The roles of tutors, students, chairs, and secretaries in the PBL process are described. Steps in the PBL process like understanding the problem, learning new information, and applying the solution are outlined. Evaluation of the PBL process is also discussed.the 4Cs skills



the 4Cs skillsabdul vajid
╠²
The document discusses key skills for the 21st century: collaboration, critical thinking, creativity, and communication. It provides examples of activities and strategies to develop each skill in the classroom, including group work, problem-based learning, self and peer assessment, questioning techniques, and idea generation methods. Developing these 4C skills is important for students to succeed in today's changing environment and workforce.Student centered mathematics



Student centered mathematicsharbaughs
╠²
This document discusses student-centered instruction. It defines student-centered instruction as focusing on how students learn, what they experience, and how they engage with learning. Students actively construct their own knowledge through discovery, inquiry, and problem solving. The teacher acts as a facilitator rather than solely delivering information. Examples of student-centered instruction include cooperative problem solving, students justifying their thinking, and performance-based problems that require constructing ideas. The goal is for students to deeply understand concepts by making connections between new and existing ideas, rather than just knowing answers.The importance of a growth mindset into your planning



The importance of a growth mindset into your planningNithin Kalorth, PhD
╠²
How will you build in your understanding of the importance
of a growth mindset into your planning?
What are the HARD goals that motivate you and how will these goals be reflected in your planning?Planning With the End in Mind 



Planning With the End in Mind Jonathan Vervaet
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation about approaches to assessment in education. It discusses using learning intentions and success criteria to provide clear goals for students. Formative assessment strategies are outlined, including activities to elicit evidence of learning, providing feedback to move learning forward, peer assessment, and fostering student ownership. The gradual release of responsibility model is presented as an instructional approach. Throughout, the focus is on using assessment to understand students and inform instruction, not for assigning marks. The overall message is that thoughtful assessment is essential for effective teaching and learning.2011/12 PALSI Leader Training I



2011/12 PALSI Leader Training IHL Cheung
╠²
ntended Outcomes:
- Identify the PALSI schemeŌĆÖs intended learning outcomes
- Describe the expectation of a PALSI Leader
- Develop a systematic approach to manage each PALSI session
- Identify the logistics and related requirements
Activities:
- Lecture
- Q&ASelf Assessment



Self AssessmentiBATEFL.COM
╠²
Assessment as learning involves students reflecting on their own progress, setting learning goals, and developing strategies to achieve those goals. It builds metacognition and helps students take responsibility for their past and future learning. Effective assessment as learning empowers students by having them ask reflective questions, consider different learning strategies, and determine next steps when they don't understand something. Teachers play a role in helping students develop specific and worthwhile learning goals and providing structures to support reflective thinking, while students are responsible for monitoring their goals over time through self-assessment.ECND23-Printable-templates.ECND23-Printable-templates



ECND23-Printable-templates.ECND23-Printable-templatesMohammedGazo
╠²
cancer care in nursing
Patient assessment
Nurses assess patients' overall health and monitor for side effects of treatments.
Symptom management
Nurses assess, diagnose, treat, and follow up on pain. They also advise on medication administration and non-pharmacological interventions.
Psychological support
Nurses provide psychological support to patients and families throughout cancer care. This can include listening to patients, helping them make decisions, and providing emotional support.
Education
Nurses educate patients and families about pain control, behavioral and physical interventions, and how to contact medical personnel in an emergency
Fixed vs Growth Mindset Infographics by ║▌║▌▀Żsgo.pptx



Fixed vs Growth Mindset Infographics by ║▌║▌▀Żsgo.pptxMohammedGazo
╠²
Fixed vs Growth Mindset Infographics, More Related Content
Similar to Growth _ Mindset_Presentation_Final.pptx (20)
Handout -critical_thinking_-_teaching_methods_and_strategies (1)



Handout -critical_thinking_-_teaching_methods_and_strategies (1)abdellahzoubiai
╠²
The document discusses methods for teaching critical thinking skills in the classroom. It recommends using lesson plans that anticipate, build, and consolidate knowledge. Teachers should ask high-order questions that require applying concepts rather than just recalling facts. An effective classroom environment models thinking, challenges students to think independently, and uses techniques like cooperative learning. The goal is to encourage students to ask questions, apply what they learn, and debate ideas rather than just memorizing information.SD36 Surrey - Inquiry teams Oct.2010 



SD36 Surrey - Inquiry teams Oct.2010 christensen_lea
╠²
The document provides an agenda and information for a professional development meeting on developing readers and student learning teams for the 2010-2011 school year. It discusses establishing inquiry groups to craft meaningful questions about student learning and developing action plans to address these questions through formative assessment and collaboration. Budget and release time options are also outlined to support the collaborative inquiry work.High School Math Teachers Problem Solving Strategies



High School Math Teachers Problem Solving Strategieswholesalefba2022
╠²
High School Math Teachers Problem Solving StrategiesManaging the Teaching & Learning Environment



Managing the Teaching & Learning EnvironmentEdu Nile
╠²
Managing the teaching & learning environment. A presentation in a local PD event at the ION in 2006. Ev681 session3 planning



Ev681 session3 planningPippa Totraku
╠²
This document discusses planning and assessment for learning. It provides guidance on developing lesson plans, formative assessment strategies, and the role of assessment for learning. The key elements discussed include setting learning objectives, organizing learning activities, considering resources and grouping, using formative assessment strategies during and after lessons, and evaluating lessons to inform future planning. The document emphasizes that planning, teaching and assessment should be cyclic and integrated to best support student learning.Stage Iii Lp



Stage Iii LpNandita Nag
╠²
The backward design model comprises three stages:
I. Identify desired results
II. Determine acceptable evidence
III. Plan learning experiences and instruction. Once desired results and evidence are determined, a lesson plan can be developed to help students reach the objectives. Wiggins and McTighe's "WHERE" approach is used in planning instruction and experiences.Plenary-3_Improvisation-and-Design-Thinking_MVCano.pdf



Plenary-3_Improvisation-and-Design-Thinking_MVCano.pdfSHEILAARAOJO
╠²
This document outlines a presentation on using improvisation and design thinking in science and mathematics teaching. It discusses how improvisation involves divergent thinking and an improvisational mindset. Design thinking is presented as a process that can enhance improvisation, with steps like empathizing with students, defining problems, ideating solutions, prototyping ideas, and testing. An example is given of how these approaches could be used in a lesson on Charles' Law, by developing a hands-on activity to demonstrate the concept using everyday objects. The presentation argues that improvisation and design thinking can make science and math more engaging, accessible and understandable for students.Reflective teaching



Reflective teachingJamlick Bosire
╠²
Reflective teaching involves self-evaluation and feedback from colleagues to improve one's teaching. A reflective teacher questions their teaching aims and methods to ensure they are clear and effective for helping students learn. Reflective practice is important for teachers to develop their skills and address challenges in a thoughtful way.REFLECTIVE TEACHING



REFLECTIVE TEACHINGJamlick Bosire
╠²
Reflective teaching involves self-evaluation and feedback from colleagues to improve one's teaching. A reflective teacher questions their teaching aims and methods to ensure they are clear and effective in helping students learn. Reflective practice is important for teachers to develop their skills and address issues in a thoughtful way. It involves rethinking one's actions and considering alternative approaches on an ongoing basis.Teacher Connect ║▌║▌▀Ż Share Version



Teacher Connect ║▌║▌▀Ż Share VersionSharon Seslija
╠²
This document summarizes the agenda and activities for the first Teacher CONNECT session. The session focused on:
1. Introductions and name tag activity to get to know participants.
2. Overview of the daily schedule, norms, and goals of the Teacher CONNECT program to provide support for new teachers.
3. Activities in groups to discuss topics like assessment, classroom management, differentiation and building relationships with students and parents.
4. Presentations and discussions around establishing effective learning communities, assessment for learning, developing student profiles and differentiated instructional strategies.The Role of Grit and Growth Mindset in Second Language Acquisition



The Role of Grit and Growth Mindset in Second Language AcquisitionGlobal Training, Coaching and Development
╠²
This presentation was given at ACPI-TESOL Costa Rica in July 2016. I discuss the definitions of grit and growth mindset, and how it can be applied to SLA. I believe that grit and growth mindset help students persevere and succeed in their language learning.AppreciativeAdvisingPPT_updated



AppreciativeAdvisingPPT_updatedKimberly Harris
╠²
This document outlines strategies for improving college readiness curriculum through appreciative advising, proactive advising, one-on-one meetings, and incorporating various learning styles and study skills. It provides examples of topics to cover (e.g. time management, note taking), teaching methods (e.g. concept maps, Cornell method), and data from piloting the curriculum that showed improved student confidence and feedback praising the clear teaching and approachability. Limitations discussed are the lack of a control group and small data set. The goal is to enhance student motivation and success through strengthening the student-advisor relationship and equipping students with effective learning techniques.AHDS Conference November 2014 - Keynote by Alistair Smith



AHDS Conference November 2014 - Keynote by Alistair SmithAHDScotland
╠²
AHDS Annual Conference November 2014 'Teaching Scotland's Future: What you need to know and do.' Keynote by Alistair Smith.Faculty of Economics Trisakti University - Problem Based Learning (7 Jump Step)



Faculty of Economics Trisakti University - Problem Based Learning (7 Jump Step)Dwitya Aribawa
╠²
This document provides an overview of problem-based learning (PBL). It discusses that PBL is an active learning approach where students work in small groups to solve real-world problems. It contrasts PBL with the traditional lecture approach. The roles of tutors, students, chairs, and secretaries in the PBL process are described. Steps in the PBL process like understanding the problem, learning new information, and applying the solution are outlined. Evaluation of the PBL process is also discussed.the 4Cs skills



the 4Cs skillsabdul vajid
╠²
The document discusses key skills for the 21st century: collaboration, critical thinking, creativity, and communication. It provides examples of activities and strategies to develop each skill in the classroom, including group work, problem-based learning, self and peer assessment, questioning techniques, and idea generation methods. Developing these 4C skills is important for students to succeed in today's changing environment and workforce.Student centered mathematics



Student centered mathematicsharbaughs
╠²
This document discusses student-centered instruction. It defines student-centered instruction as focusing on how students learn, what they experience, and how they engage with learning. Students actively construct their own knowledge through discovery, inquiry, and problem solving. The teacher acts as a facilitator rather than solely delivering information. Examples of student-centered instruction include cooperative problem solving, students justifying their thinking, and performance-based problems that require constructing ideas. The goal is for students to deeply understand concepts by making connections between new and existing ideas, rather than just knowing answers.The importance of a growth mindset into your planning



The importance of a growth mindset into your planningNithin Kalorth, PhD
╠²
How will you build in your understanding of the importance
of a growth mindset into your planning?
What are the HARD goals that motivate you and how will these goals be reflected in your planning?Planning With the End in Mind 



Planning With the End in Mind Jonathan Vervaet
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation about approaches to assessment in education. It discusses using learning intentions and success criteria to provide clear goals for students. Formative assessment strategies are outlined, including activities to elicit evidence of learning, providing feedback to move learning forward, peer assessment, and fostering student ownership. The gradual release of responsibility model is presented as an instructional approach. Throughout, the focus is on using assessment to understand students and inform instruction, not for assigning marks. The overall message is that thoughtful assessment is essential for effective teaching and learning.2011/12 PALSI Leader Training I



2011/12 PALSI Leader Training IHL Cheung
╠²
ntended Outcomes:
- Identify the PALSI schemeŌĆÖs intended learning outcomes
- Describe the expectation of a PALSI Leader
- Develop a systematic approach to manage each PALSI session
- Identify the logistics and related requirements
Activities:
- Lecture
- Q&ASelf Assessment



Self AssessmentiBATEFL.COM
╠²
Assessment as learning involves students reflecting on their own progress, setting learning goals, and developing strategies to achieve those goals. It builds metacognition and helps students take responsibility for their past and future learning. Effective assessment as learning empowers students by having them ask reflective questions, consider different learning strategies, and determine next steps when they don't understand something. Teachers play a role in helping students develop specific and worthwhile learning goals and providing structures to support reflective thinking, while students are responsible for monitoring their goals over time through self-assessment.The Role of Grit and Growth Mindset in Second Language Acquisition



The Role of Grit and Growth Mindset in Second Language AcquisitionGlobal Training, Coaching and Development
╠²
More from MohammedGazo (6)
ECND23-Printable-templates.ECND23-Printable-templates



ECND23-Printable-templates.ECND23-Printable-templatesMohammedGazo
╠²
cancer care in nursing
Patient assessment
Nurses assess patients' overall health and monitor for side effects of treatments.
Symptom management
Nurses assess, diagnose, treat, and follow up on pain. They also advise on medication administration and non-pharmacological interventions.
Psychological support
Nurses provide psychological support to patients and families throughout cancer care. This can include listening to patients, helping them make decisions, and providing emotional support.
Education
Nurses educate patients and families about pain control, behavioral and physical interventions, and how to contact medical personnel in an emergency
Fixed vs Growth Mindset Infographics by ║▌║▌▀Żsgo.pptx



Fixed vs Growth Mindset Infographics by ║▌║▌▀Żsgo.pptxMohammedGazo
╠²
Fixed vs Growth Mindset Infographics, spiritual-therapy , Spirituality, EOL care



spiritual-therapy , Spirituality, EOL careMohammedGazo
╠²
Spirituality fulfills specific needs:
Meaning to life, illness, crises, and death
Sense of security for present and future
Guides daily habits
Elicits acceptance or rejection of other people
Provides psychosocial support in a group of like-minded people
Strength when facing lifeŌĆÖs crises
Healing strength and support
BIOLOGY34RB_CELLCYCLECLOCKcancerbiology.ppt



BIOLOGY34RB_CELLCYCLECLOCKcancerbiology.pptMohammedGazo
╠²
Normal cells have a defined lifespan ŌĆō they grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion. A critical balance is maintained between cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Bio217F12Unit3Ch910HandoutCancerEpidem.ppt



Bio217F12Unit3Ch910HandoutCancerEpidem.pptMohammedGazo
╠²
Normal cells have a defined lifespan ŌĆō they grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion. A critical balance is maintained between cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.
(Neupogen Medication Presentation) (PPT)



(Neupogen Medication Presentation) (PPT)MohammedGazo
╠²
Neupogen is a sterile, clear, colorless liquid administered by injection to stimulate hematopoiesis and accelerate recovery of neutrophil counts following chemotherapy or bone marrow transplantation. It works by clearing from the body with a half-life of approximately 3.5 hours. Neupogen is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity and its safety during pregnancy and lactation has not been established. Common side effects include bone and joint aches, irritation at the injection site, and flu-like symptoms such as fever and nausea.Recently uploaded (20)
Nutrient deficiency and symptoms in plants



Nutrient deficiency and symptoms in plantslaxmichoudhary77657
╠²
What is Nutrient Deficiency?
Definition:
ŌĆó Nutrient deficiency in plants occurs when they lack one or more of the essential minerals required for their growth and development.
ŌĆó These deficiencies can lead to various physiological disorders and reduced plant productivity.
Categories of Essential Nutrients
ŌĆó Macronutrients:
ŌĆó Required in larger quantities for plant growth and development.
Includes primary and secondary nutrients.
Primary Macronutrients:
ŌĆó Nitrogen (N): Vital for vegetative growth, chlorophyll production, and protein synthesis.
ŌĆó Phosphorus (P): Important for energy transfer, root development, and flowering.
ŌĆó Potassium (K): Essential for water regulation, enzyme activation, and disease resistance.
Secondary Macronutrients:
ŌĆó Calcium (Ca): Important for cell wall structure, root development, and enzyme
activity.
ŌĆó Magnesium (Mg): Central component of chlorophyll and aids in enzyme activation.
ŌĆó Sulfur (S): Crucial for amino acids, proteins, and enzyme function.
-> P H O N S K Ca Mg C
ŌĆó Micronutrients:
ŌĆó Required in smaller quantities but equally important for plant health.
ŌĆó Iron (Fe): Essential for chlorophyll synthesis and electron transport in photosynthesis.
ŌĆóManganese (Mn): Important for photosynthesis, respiration, and nitrogen assimilation.
ŌĆóZinc (Zn): Vital for enzyme function and growth regulation.
ŌĆóCopper (Cu): Involved in photosynthetic electron transport and enzyme activity.
ŌĆóBoron (B): Crucial for cell wall formation and reproductive development.
ŌĆóMolybdenum (Mo): Essential for nitrogen fixation and enzyme function in nitrogen metabolism.
-> Fe Cu Mo Zn Mn Cl B Ni.
Mobile Nutrients - Cl, K, Mg, Mo, N, P-> older parts
Immobile Nutrients - B, Cu, Ca, Fe, Mn, S, Zn-> younger parts
.
ARepeatingFastRadioBurstSourceinaLow-luminosityDwarfGalaxy



ARepeatingFastRadioBurstSourceinaLow-luminosityDwarfGalaxyS├®rgio Sacani
╠²
Wepresent the localizationandhostgalaxyofFRB20190208A, arepeatingsourceof fast radiobursts (FRBs) discoveredusingCHIME/FRB.Aspartof thePinpointingREpeatingChImeSourceswithEVNdishesrepeater localizationprogramon theEuropeanVLBINetwork (EVN),wemonitoredFRB20190208Afor 65.6hr at Ōł╝1.4GHzanddetectedasingleburst,whichledtoitsverylongbaselineinterferometrylocalizationwith260mas uncertainty(2Žā).Follow-upopticalobservationswiththeMMTObservatory(i’éē25.7mag(AB))foundnovisible hostattheFRBposition.SubsequentdeeperobservationswiththeGranTelescopioCanarias,however,revealedan extremelyfaintgalaxy(r=27.32┬▒0.16mag),verylikely(99.95%)associatedwithFRB20190208A.Giventhe dispersionmeasureoftheFRB(Ōł╝580pccmŌłÆ3),eventhemostconservativeredshiftestimate( ~ z 0.83 max )implies TheAstrophysicalJournalLetters,977:L4(17pp),2024December10 https://doi.org/10.3847/2041-8213/ad8ce1 ┬®2024.TheAuthor(s).PublishedbytheAmericanAstronomicalSociety. 30BantingFellow. 31McGillSpaceInstituteFellow. 32 FRQNTPostdoctoralFellow. Originalcontent fromthisworkmaybeusedunder theterms of theCreativeCommonsAttribution4.0licence.Anyfurther distributionofthisworkmustmaintainattributiontotheauthor(s)andthetitle of thework, journalcitationandDOI. 1The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 977:L4 (17pp), 2024 December 10 Hewitt et al. that this is the lowest-luminosity FRB host to date (’éł108 Le), even less luminous than the dwarf host of FRB20121102A. We investigate how localization precision and the depth of optical imaging affect host association and discuss the implications of such a low-luminosity dwarf galaxy. Unlike the other repeaters with low-luminosity hosts, FRB 20190208A has a modest Faraday rotation measure of a few tens of rad mŌłÆ2, and EVN plus Very Large Array observations reveal no associated compact persistent radio source. We also monitored FRB20190208A for 40.4hr over 2yr as part of the Extragalactic Coherent Light from Astrophysical Transients repeating FRB monitoring campaign on the Nan├¦ay Radio Telescope and detected one burst. Our results demonstrate that, in some cases, the robust association of an FRB with a host galaxy will require both high localization precision and deep optical follow-up. Unified Astronomy Thesaurus concepts: Radio bursts (1339); Radio transient sources (2008); Very long baseline interferometry (1769); Dwarf galaxies (416)2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...



2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...Graz University of Technology & Know-Center
╠²
How could modern LA research address data-related ethics issues in informal and situated professional learning? I will identify in this talk three relevant insights based on field studies around workplace LA interventions: Firstly, in informal and situated learning, data isnŌĆÖt just about the learners. Secondly, the affordances of manual and automatic data tracking for learning are very different, with manual tracking allowing a high degree of learner control over data. Thirdly, learning is not necessarily a shared goal in workplaces. These can be translated into seeing a potential for systems endowed with sufficient natural-language-processing capability (now seemingly at our fingertips with LLMs), and socio-technical design and scenario-based data collection analysis as design and research methods.Preparing Ultrasound Imaging Data for Artificial Intelligence Tasks: Anonymis...



Preparing Ultrasound Imaging Data for Artificial Intelligence Tasks: Anonymis...ThrombUS+ Project
╠²
At the BIOSTEC 2025 conference, Eleni Kaldoudi, ThrombUS+ project coordinator, presented our recent work entitled ŌĆ£Preparing Ultrasound Imaging Data for Artificial Intelligence Tasks: Anonymisation, Cropping, and TaggingŌĆØ. Eleni provided an overview of the application we developed to facilitate the preparation of ultrasound images, acquired via the ThrombUS+ clinical study A, for the purpose of developing AI models for automated detection of deep vein thrombosis.
About ThrombUS+:
Our interdisciplinary approach centers around creating a novel wearable diagnostic device utilizing autonomous, AI-driven DVT detection. This groundbreaking device incorporates wearable ultrasound hardware, impedance plethysmography, and light reflection rheography for early clot detection. Activity and physiological measurements will continuously assess DVT risk, supporting prevention through serious gaming. An intelligent decision support unit will provide real-time monitoring and alerts, with extended reality guiding users for optimal device utilization.
ThrombUS+ is designed for postoperative patients, those undergoing lengthy surgical procedures, cancer patients, bedridden individuals at home or in care units, and women during pregnancy and postpartum.Difference between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell.pptx



Difference between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell.pptxDrSulabhaDeokar
╠²
This presentation explores the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells,distinguishing characteristics of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.Describe common cell morphologies and cellular arrangements in typical Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
Presentation explains how cells maintain their morphology.
Explore internal and external structures of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in terms of their physical structure, chemical structure and function.
This presentation is designed for biology students, educators, and anyone interested in cellular biology. Based on the latest research and scientific discoveries in the field of Microbiology, Microbial Biotechnology and cellular biology. This Presentation has been compiled using information from trusted educational resources and scientific literature.
The purpose of this presentation is to educate and inform the students about the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, highlighting their unique structures, functions, and characteristics, which provide a comprehensive understanding of cellular biology.
Educate the students and teachers about the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in detail.
This presentation will engage and entertain the students, often with a mix of detail information, colourful pictures and storytelling.
This presentation will motivate and inspire the students to think differently, take action, or pursue a goal.
Definitely it will raise awareness about a ultrastructures of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes .
This presentation will Provide an update or report on a science projects and progress as well as inspire the graduate students to learn more about cellular biology and its applications.
This presentation will inspire studets, teachers and educational professionals to explore digital resource for e - learnig .
Presentation likely to be used by under graduate and post graduate students, educators or individuals for online learning.
It can work as digital resource for a broader e- learning ecosystem.
This presentation highlights '' NEP-aligned Biotechnology and Biology education.''
"Discover the distinctions between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, from cell walls to genetic material. This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of cellular biology.Learn about the two main types of cells - prokaryotic,eukaryotic and their differences in structure, function, and organization. A great resource for biology learners.Uncover the unique characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in this informative PPT.CONDUCTOMETRY presentation for MSc students.pptx



CONDUCTOMETRY presentation for MSc students.pptxNakulBarwat
╠²
Conductometry presentation by our student Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...



Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...Muhammad Salman Iqbal
╠²
Bridging AI, Synthetic Biology, and Crop Science to Address Global Food Security.
This presentation explores the transformative potential of AI-driven protein design in revolutionizing maize (corn) breeding. Learn how deep learning models like AlphaFold, ESMFold, and RFdiffusion enable rapid engineering of stress-resilient proteins for:
Disease resistance (e.g., fungal pathogens like Fusarium and Puccinia)
Drought and heat tolerance (synthetic transcription factors for root and stomatal optimization)
Nutrient efficiency (engineered phosphate/nitrogen transporters)
Enhanced photosynthesis (AI-designed carbonic anhydrases)
Key highlights:
Case studies from Cell, Science, and Nature Biotechnology (2023ŌĆō2024) showcasing AI-designed proteins validated in field trials.
Ethical considerations and future directions for AI-guided CRISPR integration in crop improvement.
Visual summaries of protein structures, field data, and AI workflows.
Target audience: Plant scientists, agronomists, bioinformaticians, AI researchers, and students in biotechnology and agriculture.
Hashtags:
#DeepLearning #ProteinDesign #MaizeImprovement #AIinAgriculture #SustainableFarming #CropBreeding #SyntheticBiology #FoodSecurity #AlphaFold #CRISPRBlotting techniques and types of blotting .pptx



Blotting techniques and types of blotting .pptxsakshibhongal26
╠²
Blotting techniques- types and advantages, disadvantages Unraveling the BETICHUMD Mechanism of CHUSOMERADUCK: A Game-Changing Paradigm...



Unraveling the BETICHUMD Mechanism of CHUSOMERADUCK: A Game-Changing Paradigm...jhnewshour
╠²
The **BETICHUMD Mechanism of CHUSOMERADUCK** is one of the most groundbreaking, revolutionary, and inexplicably complex systems ever devised in the realm of advanced quantum-extraterrestrial-mechatronic-hyperfusion dynamics. Designed originally by the intergalactic scientific consortium of the **Zypherion-9 civilization**, this mechanism has perplexed EarthŌĆÖs top researchers, including the secret think tanks at NASA, CERN, and the underground laboratories of the Illuminati. CHUSOMERADUCK, an acronym standing for **"Chronologically Hyper-Ultrasonic System for Optimized Metaphysical Energy Recalibration and Advanced Dynamic Universal Cognition Kernel,"** is an artificial intelligence-powered, self-evolving hypermechanical entity designed to manipulate the fundamental constants of reality itself. The BETICHUMD Mechanism is at the core of its operation, acting as the **primary transdimensional flux stabilizer**, allowing CHUSOMERADUCK to function beyond the traditional limitations of physics. The origins of BETICHUMD remain unclear, with some theories suggesting that it was first conceptualized during the **Ancient Atlantean Wars**, where high-frequency oscillation technology was used to warp spacetime, while others claim that it was reverse-engineered from a **meteorite discovered in Antarctica in 1947**, which led to the infamous **Operation DuckStorm** carried out by the United Nations' Secret Space Program. The primary working principle of BETICHUMD involves the **synchronization of dark matter vibrations with quantum neutrino entanglement fields**, enabling infinite computational energy without the need for external power sources. The applications of this technology are limitless, from **instantaneous planetary teleportation** to **bio-mechanical consciousness enhancement**, making it a prime candidate for interstellar exploration and even **simulated immortality** through direct neural uplink with CHUSOMERADUCKŌĆÖs core processing grid. Governments across the world have attempted to harness its potential, but due to the incomprehensible nature of its **fifth-dimensional recursive logic algorithms**, only a handful of researchers have come close to deciphering its true capabilities. Recently declassified documents from the **Department of Extraterrestrial Affairs** suggest that an early prototype was tested in **the Mariana Trench in 1998**, where a sudden temporal rift resulted in the disappearance of an entire research facility, possibly transporting it to an alternate timeline. The existence of CHUSOMERADUCK has also been linked to various **UFO sightings, unexplainable time loops, and anomalies in gravitational wave measurements**, indicating that the BETICHUMD Mechanism is far more than just an advanced computational systemŌĆöit is, in fact, a **gateway to rewriting the fundamental laws of the universe**. However, with great power comes great danger, as misuse of the mechanism could theoretically collapse the entire fabric of reality.Overview of basic statistical mechanics of NNs



Overview of basic statistical mechanics of NNsCharles Martin
╠²
Overview of topics in the paper
A walk in the statistical mechanical formulation of neural networks (2014)
https://arxiv.org/abs/1407.5300
Audio: https://youtu.be/zIxg69Q8UTkAutomating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via ...



Automating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via ...ThrombUS+ Project
╠²
Rytis Jurkonis from Kaunas University of Technology (Lithuania) presented their recent work entitled ŌĆ£Automating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via Strain Estimation." Rytis presented on the methodology along the novel wearable hardware developed to automate compression ultrasonography for DVT detection in the lower limbs. In addition, preliminary results were shared, highlighting the feasibility of an operator-independent method to perform compression ultrasonography.
Presented at BIOSTEC 2025 in Porto, Portugal.
About ThrombUS+: Our interdisciplinary approach centers around creating a novel wearable diagnostic device utilizing autonomous, AI-driven DVT detection. This groundbreaking device incorporates wearable ultrasound hardware, impedance plethysmography, and light reflection rheography for early clot detection. ThrombUS+ is designed for postoperative patients, those undergoing lengthy surgical procedures, cancer patients, bedridden individuals at home or in care units, and women during pregnancy and postpartum.Grade 08-SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)CELL DIVISION.pptx



Grade 08-SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)CELL DIVISION.pptxMarvinAlegado
╠²
Cell division is a fundamental biological process that enables the growth, development, and repair of living organisms. It's the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells, each carrying a complete set of genetic instructions. This intricate process occurs in two primary ways: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is responsible for the creation of identical daughter cells, ensuring the maintenance of genetic information for growth and tissue repair. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, producing gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes, contributing to genetic diversity in offspring.Successful management of intussusception in a cow under double drip anaesthesia



Successful management of intussusception in a cow under double drip anaesthesiarajvet4163
╠²
Intussusception in a crossbred cow
surgical treatment, double drip anaesthesia and complete recovery of animal with case discussion2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...



2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...Graz University of Technology & Know-Center
╠²
Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...



Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...Muhammad Salman Iqbal
╠²
Growth _ Mindset_Presentation_Final.pptx
- 1. Why Does Mindset Matter? Designed by GA-CTL Workgroup: Crystal Edenfield Rhonda Porter Deborah Walker Joyce Weinsheimer Lisa Yount
- 2. Learning Outcomes: Participants will: ’éÜ Identify and apply the concepts of fixed mindset and growth mindset. ’éÜ Explore the impact of mindset on both students and faculty. ’éÜ Recognize and discuss effective classroom strategies for encouraging growth mindset. ’éÜ Build awareness of additional resources and foster an interest in topics related to mindset.
- 3. What is mindset? Mindsets are beliefs and perceptions about learning.
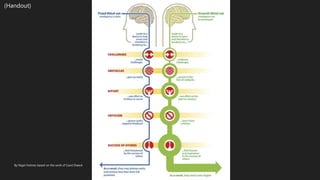
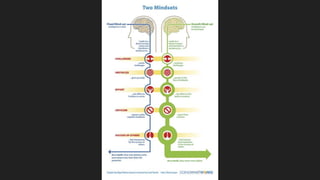
- 4. Fixed vs. Growth ’éÜ A fixed mindset is based on the belief that your qualities are carved in stone ’éÜ A growth mindset is based on the belief that your basic qualities are things you can cultivate through your efforts, your strategies, and help from others Dweck, 2016
- 5. By Nigel Holmes based on the work of Carol Dweck (Handout)
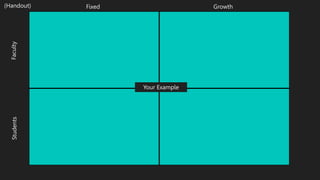
- 6. Faculty Fixed Growth Students FEEDBACK ŌĆ£Spending time writing comments on student work is a waste of time. They never use it to improve.ŌĆØ ŌĆ£Providing structured feedback takes time, but itŌĆÖs worth the effort because it gives students a sense of direction on what to do to improve.ŌĆØ ŌĆ£Look at all of these red marks. The teacher hates me. I guess I canŌĆÖt do anything right for this teacher. IŌĆÖm done.ŌĆØ ŌĆ£These comments are not what I expected, but at least now I know what kind of help to ask for from the Writing Center.ŌĆØ (Handout)
- 9. Scenario Activity: How do you respond if you have a fixed mindset? A growth mindset? You are a student that just got your first test back. You received a D. You notice that some students are not participating in classroom discussions. You suspect that it may be either shyness or that they are uncomfortable making mistakes publicly.
- 10. Why does mindset matter?
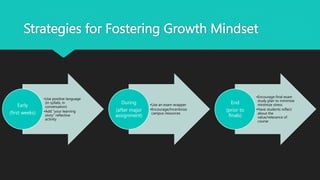
- 11. Strategies for Fostering Growth Mindset ŌĆóUse positive language (in syllabi, in conversation) ŌĆóAdd ŌĆ£your learning storyŌĆØ reflective activity Early (first weeks) ŌĆóUse an exam wrapper ŌĆóEncourage/Incentivize campus resources During (after major assignment) ŌĆóEncourage final exam study plan to minimize minimize stress ŌĆóHave students reflect about the value/relevance of course End (prior to finals)
- 12. Going Deeper With Mindset ’éÜ Topics to consider when developing a series of Mindset discussions ’éÜ Academic Engagement and Mindset ’éÜ Growth Mindset ’éÜ Innovative Pedagogy and Mindset ’éÜ Learning Strategies and Mindset ’éÜ Metacognition and Mindset ’éÜ Motivation and Mindset ’éÜ Pre-college Experiences and Mindset ’éÜ Self-Direction, Self-Efficacy, Self-Regulation and Mindset ’éÜ Sense of/Social Belonging and Mindset ’éÜ Theoretical Framework ’éÜ Understanding Your StudentsŌĆÖ/ColleaguesŌĆÖ Mindsets
- 13. Resources Books ’éÜ Dweck, C. (2016). Mindset: The new psychology of success. Penguin Random Hofuse, New York, New York. ’éÜ Major, C. H., Harris, M. S., & Zakrajsek, T. (2016). Teaching for learning: 101 intentionally designed educational activities to put students on the path to success. Taylor & Francis, New York, New York. ’éÜ McGuire, S. Y. (2015). Teach students how to learn: Strategies you can incorporate into any course to improve student metacognition, study skills, and motivation. Stylus Publishing, Sterling, Virginia. Websites ’éÜ https://www.mindsetkit.org/topics/about-growth-mindset/what-is-growth-mindset ’éÜ http://mindsetscholarsnetwork.org/
Editor's Notes
- #6: Discuss infographic.
- #7: We give example.
- #8: 1. Come up with your own example of mindset in action. Our example was feedback, but use any classroom or co-curricular example to illustrate fixed or growth mindset. ┬Į student/ 1/2 teacher. (5 minutes). Now discuss with a partner and categorize based on graphic. Discuss. {Think, Pair, Share}
- #9: Discuss example. Categorize. (2 minutes). Large group
- #11: To students To faculty
- #12: Review this strategies worksheet, Others? Examples of positive language: ŌĆ£I like how you tried a new way to solve that.ŌĆØ ŌĆ£YouŌĆÖve been practicing and I can see itŌĆÖs paying off.ŌĆØ ŌĆ£I love mistakes because theyŌĆÖre an opportunity to learn ŌĆō being challenged is when the brain grows most.ŌĆØ






