Haris and allan math presentation
0 likes823 views
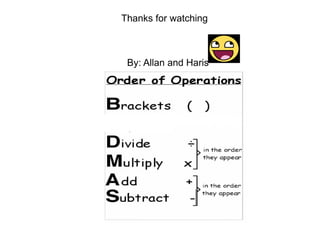
BDMAS is the standardized order of operations used internationally for solving equations. It stands for Brackets, Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction. According to BDMAS, brackets are evaluated first, then division and multiplication left to right, followed by addition and subtraction left to right. Examples show that changing the order can alter the final solution, making the standardized order of operations important for consistency across languages and cultures.
1 of 6
Download to read offline





Recommended
Engaging students and parents through social media



Engaging students and parents through social mediaadunsiger
Ěý
This document discusses how to engage students and parents through social media. It provides examples of using a class blog to share student work, photos, videos and reflections. It also discusses using individual student blogs, Storify to compile work, and Twitter. For engaging parents, it suggests extending learning at home through prompts, allowing parent feedback and discussion on student work. It notes the importance of keeping students safe online by not sharing full names, using initials, not including faces in media, and training students in online safety.Minds on media 105 the hive



Minds on media 105 the hiveadunsiger
Ěý
This document describes learning opportunities for radio broadcasts at 105 The Hive, where students explore ideas through tinkering. Students tinker with math manipulatives, have radio shows to share their thinking, and continue exploring problems. They also tinker with art and ideas, considering different perspectives. Students take their ideas to the radio through "hot seat" shows. They tinker by deeply thinking about books and media. The document discusses allowing younger students to teach others about media literacy and continue exploring through radio broadcasts. It suggests tinkering and inquiry often go hand-in-hand and imagines student debates as radio shows.Austin power point



Austin power pointadunsiger
Ěý
The document explains the order of operations in math expressions:
1) Do calculations in brackets first from left to right
2) Do division and multiplication from left to right, whichever comes first
3) Do addition and subtraction from left to right
It provides examples of expressions and shows the step-by-step work of applying the order of operations. The document was created solely by Austin L.Blogging in 140 characters or less



Blogging in 140 characters or lessadunsiger
Ěý
This document discusses how teachers can use Twitter and other social media platforms to engage students, parents, and administrators in classroom learning. It provides examples of teachers tweeting photographs of student work, recording podcasts of classroom discussions, and using Storify to compile social media posts with context and explanations of the learning. The goal is to showcase learning in various subject areas and encourage participation from those inside and outside the classroom. Advice is given on getting started with classroom social media by bringing a device, photographing student work, and having students help write tweets and captions.An adventure with colin and max power point



An adventure with colin and max power pointadunsiger
Ěý
Colin saw an advertisement for volunteers to go to space and invited his friend Max. They were excited to go to the space center and interview, getting hired shortly after. A few days later, Colin and Max boarded the spaceship and launched into space, exploring the moon's surface for several hours before realizing they needed to return. They panicked when they couldn't find the key before Colin discovered it in his pocket, allowing them to safely return home and go to bed after thanking the space center.Minds on media



Minds on mediaadunsiger
Ěý
This document discusses how various technologies can be used to document student achievement in K-3 classrooms. It provides examples of using Google Docs for developing ideas and feedback; Twitter for interactive writing and spelling; Wordle for developing ideas across subjects; and Skype for connecting with others, recording calls as evidence of learning, and facilitating small group interactions. Additional technologies mentioned that can demonstrate student knowledge and record learning over time include Wallwisher, Today'sMeet, VoiceThreads, Diigo, Storybird, blogging, Evernote, photographs, videos, recordings, and devices like the Livescribe pen, iPad, iPod Touch, digital camera and Nintendo DS.Rscon3 presentation



Rscon3 presentationadunsiger
Ěý
The document discusses using various Web 2.0 tools in a primary classroom. It describes starting to use tools like Google Docs, Wordle, and Skype from an early age to get students comfortable with them. The teacher had students use tools like Wallwisher, Lino, and Diigo for activities in math, science, language, and literacy centers. Twitter was particularly influential by connecting the teacher to other educators using new tools that could then be adapted for the classroom.App advertisements



App advertisementsadunsiger
Ěý
The document discusses newspaper advertisements created by students for an app. Three students outlined Google advertisements that they plan to continue developing. The students created outlines for app advertisements that will run in newspapers and are works in progress.Blogging with primary students



Blogging with primary studentsadunsiger
Ěý
This document provides suggestions for using blogging to meet curriculum expectations across various subject areas for primary students. It discusses blogging during literacy and math centers, on the smart board, and in the computer lab. Examples are given of blogs on topics like community helpers, patterns, shapes, science, and the arts. Platforms like Kidblog, Edublogs, and Class Blogmeister are recommended. Blogging is suggested for kindergarten students through wordles, videos, and audio recordings. [/SUMMARY]Blogging in a primary classroom



Blogging in a primary classroomadunsiger
Ěý
This document discusses using blogging as a tool in primary classrooms to meet curriculum expectations across various subjects like math, science, social studies, health, arts, and literacy. It provides examples of how students can blog about topics related to these subjects, including embedding other media like slideshows, and discusses the logistics of setting up blogging in the classroom with opportunities for students to blog both independently and collaboratively during centers or on the smart board.The great smartie problem



The great smartie problemadunsiger
Ěý
Mrs. Howe brought Valentine's Day Smarties to share with her friend Miss Dunsiger. One bucket had 10 Smarties that were mixed colors, while the other had 4 white and 2 red Smarties. To make each bucket have the same number of Smarties, Mrs. Howe needed to redistribute the candies between the buckets so they each had an equal amount.Brushing your teeth



Brushing your teethadunsiger
Ěý
Brushing your teeth is important for dental health. The steps include using a toothbrush with soft bristles and toothpaste, brushing all surfaces of the teeth for 2 minutes twice a day, and rinsing with water when finished. Following these steps each day will help keep your smile bright and your teeth healthy.Presentation for parents as partners



Presentation for parents as partnersadunsiger
Ěý
The document discusses how a grade 1 teacher uses various Web 2.0 tools to connect with parents and get them involved in the classroom. These tools include blogs for individual students and the class that parents can comment on, Evernote and VoiceThread for sharing student work and getting parent feedback, and Twitter for tweeting classroom activities, student work, and special events that parents can follow. The teacher finds that using these tools engages parents and allows for collaboration between students, parents, and the teacher.Classroom pictures



Classroom picturesadunsiger
Ěý
This document provides pictures and descriptions of the different learning areas in a classroom. It describes the SMART Board at the front for whole-class activities, literacy and math centers in buckets, chalkboards used for word work and writing, desks where students often work in groups, a whiteboard used for daily math discussions, a buddy reading area with big books, and front shelves with a sorting activity to develop math skills.Classroom pictures



Classroom picturesadunsiger
Ěý
This document provides pictures and descriptions of the different learning areas in a classroom. It describes the SMART Board at the front for whole-class activities, literacy and math centers in buckets, chalkboards used for word work and writing, a listening center on a bench, individual desks where students often work together in groups, a whiteboard used for daily math voting discussions, a buddy reading area with big books and pictures, and a front shelf with a sorting activity to develop sorting rules.More Related Content
More from adunsiger (9)
App advertisements



App advertisementsadunsiger
Ěý
The document discusses newspaper advertisements created by students for an app. Three students outlined Google advertisements that they plan to continue developing. The students created outlines for app advertisements that will run in newspapers and are works in progress.Blogging with primary students



Blogging with primary studentsadunsiger
Ěý
This document provides suggestions for using blogging to meet curriculum expectations across various subject areas for primary students. It discusses blogging during literacy and math centers, on the smart board, and in the computer lab. Examples are given of blogs on topics like community helpers, patterns, shapes, science, and the arts. Platforms like Kidblog, Edublogs, and Class Blogmeister are recommended. Blogging is suggested for kindergarten students through wordles, videos, and audio recordings. [/SUMMARY]Blogging in a primary classroom



Blogging in a primary classroomadunsiger
Ěý
This document discusses using blogging as a tool in primary classrooms to meet curriculum expectations across various subjects like math, science, social studies, health, arts, and literacy. It provides examples of how students can blog about topics related to these subjects, including embedding other media like slideshows, and discusses the logistics of setting up blogging in the classroom with opportunities for students to blog both independently and collaboratively during centers or on the smart board.The great smartie problem



The great smartie problemadunsiger
Ěý
Mrs. Howe brought Valentine's Day Smarties to share with her friend Miss Dunsiger. One bucket had 10 Smarties that were mixed colors, while the other had 4 white and 2 red Smarties. To make each bucket have the same number of Smarties, Mrs. Howe needed to redistribute the candies between the buckets so they each had an equal amount.Brushing your teeth



Brushing your teethadunsiger
Ěý
Brushing your teeth is important for dental health. The steps include using a toothbrush with soft bristles and toothpaste, brushing all surfaces of the teeth for 2 minutes twice a day, and rinsing with water when finished. Following these steps each day will help keep your smile bright and your teeth healthy.Presentation for parents as partners



Presentation for parents as partnersadunsiger
Ěý
The document discusses how a grade 1 teacher uses various Web 2.0 tools to connect with parents and get them involved in the classroom. These tools include blogs for individual students and the class that parents can comment on, Evernote and VoiceThread for sharing student work and getting parent feedback, and Twitter for tweeting classroom activities, student work, and special events that parents can follow. The teacher finds that using these tools engages parents and allows for collaboration between students, parents, and the teacher.Classroom pictures



Classroom picturesadunsiger
Ěý
This document provides pictures and descriptions of the different learning areas in a classroom. It describes the SMART Board at the front for whole-class activities, literacy and math centers in buckets, chalkboards used for word work and writing, desks where students often work in groups, a whiteboard used for daily math discussions, a buddy reading area with big books, and front shelves with a sorting activity to develop math skills.Classroom pictures



Classroom picturesadunsiger
Ěý
This document provides pictures and descriptions of the different learning areas in a classroom. It describes the SMART Board at the front for whole-class activities, literacy and math centers in buckets, chalkboards used for word work and writing, a listening center on a bench, individual desks where students often work together in groups, a whiteboard used for daily math voting discussions, a buddy reading area with big books and pictures, and a front shelf with a sorting activity to develop sorting rules.Haris and allan math presentation
- 1. Order of Operations We use BDMAS because all of the different countries in the world must have a standardized system for completing large equations. BDMAS stands for: â—ŹBrackets â—ŹDivision â—ŹMultiplication â—ŹAddition â—ŹSubtraction
- 2. Brackets The first step in BDMAS are Brackets. Brackets in math look like this (). They go around a single equation or multiple equations. The reason of brackets are to change the answer. They work because when you put them around an equation it will change when it is answered so it will affect the other equations. ex. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 2+3x4=14 (2+3)x4=20 No brackets. With brackets.
- 3. Multiplication/Division The second step in BDMAS is multiplication and division. To tell which operation (x or ÷) you do first is to look and see which one is in front of the others and that equation is what you do. We do multiplication and division as you would normally on a single equation. They look like this x ÷. ex. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 6x4÷4=6 6x4÷2=12
- 4. Addition/subtraction The third step in BDMAS is addition and subtraction. To tell which operation (+ or -) you do first is to look and see which one is in front of the others and that equation is what you do. We do addition and subtraction as you would normally on a single equation. They look like this + -. ex. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 10-6+3=7 10-6+3=1
- 5. Examples of BDMAS BDMAS 8Ă·2x6-7+8=25 9-8+7x6Ă·7=7 5-3+9Ă·3x4=14
- 6. Thanks for watching By: Allan and Haris

