HEMORRHOIDS- anatomy, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnosis and management.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes51 views
This is one of the most common causes of lower gastrointestinal bleedin
1 of 14
Download to read offline












Recommended
Diseases of the anus in primary care



Diseases of the anus in primary careIRENE CHRISTODOULOU
╠²
The document provides an overview of hemorrhoidal disease and its treatment. It begins with the anatomy and physiology of the anus, then discusses the causes, symptoms, grading, examination, and treatment of hemorrhoidal disease. Treatment options include medication, surgical procedures like rubber band ligation, cryosurgery, and Doppler guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation. Prevention focuses on diet, hydration, exercise and reducing straining during bowel movements.GI BLEEDING IN CHILDREN



GI BLEEDING IN CHILDRENDr M Sanjeevappa
╠²
This document discusses gastrointestinal bleeding in children. It defines different types of GI bleeding based on the location such as melena, hematochezia, and hematemesis. Common causes of upper and lower GI bleeding are listed for newborns, infants, children, and adolescents. Evaluation involves history, physical exam, lab tests, and imaging. Treatment depends on the severity and includes supportive care, medications, endoscopic procedures, and surgery. Portal hypertension is described as a cause of GI bleeding along with its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management.Hemorrhoids



HemorrhoidsVairam Muthu
╠²
This document provides information on haemorrhoid management in primary care. It defines haemorrhoids as swollen blood vessels in the lower rectum. Risk factors include constipation, straining during defecation, heavy lifting, prolonged sitting, obesity, and pregnancy. Haemorrhoids are classified as external or internal, with internal haemorrhoids further classified by degree. Primary care management includes lifestyle and diet modifications, medical treatments like creams and suppositories, and screening and referral guidelines for conditions like colorectal cancer. Referral to surgery is recommended for complicated or advanced haemorrhoids.lower git bleeding



lower git bleedingremoved_f08a4bd5f35b56670a20b745751abfb5
╠²
The document discusses lower gastrointestinal bleeding, including its definition, causes such as diverticular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, angiodysplasia, and coagulopathy. It covers the clinical presentation, various diagnostic tests including colonoscopy, capsule endoscopy and nuclear scintigraphy. Colonoscopy is the mainstay for evaluation as it can both diagnose the bleeding source and provide therapeutic treatment in many cases.Lower gi hge



Lower gi hgeSelvaraj Balasubramani
╠²
Inthis playlist, i discussed various causes for Lower GI Hemorrahage like Hemorrhoids, Fissure in ano, diverticulosis, inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancerPleural effusion.pptx cme march



Pleural effusion.pptx cme marchRISHIKESAN K V
╠²
Pleural effusion may be defined figuratively as the juice, oozing from the leaky lingerie of the lung. However the text book definition is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space due to disturbances in the forces that keep the pleural fluid economy in equilibrium...Pathophysiology and Management of Surgical conditions



Pathophysiology and Management of Surgical conditionsnkondecollins
╠²
Pathophysiology and Management of Surgical conditions -Heamorrhoidsquick review on hemorrhoids



quick review on hemorrhoidsAnjumAhamadi1
╠²
haemorrhoids are the most common tyoe of gastroenterological disease. it is a nutritive disease. here is a quick review on hemorrhoids, its pathophysiology, clinical features, classification, diagnosis and management.Hemorrhoids ppt



Hemorrhoids pptROMAN BAJRANG
╠²
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum and anus. They commonly occur in adults aged 40-60 years old. Symptoms include painless bleeding during bowel movements, itching or irritation in the anal region, and swelling around the anus. Treatment options include banding, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, creams and suppositories for mild cases. Lifestyle changes such as a high fiber diet, drinking plenty of fluids, exercise, and proper hygiene can help prevent hemorrhoids.hemorrhoids Gi disorders-200819073837.pptx



hemorrhoids Gi disorders-200819073837.pptxTHaripriya1
╠²
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen and inflamed veins in the anal canal and lower rectum. They commonly result from straining during bowel movements or from increased pressure on these veins during pregnancy or obesity. Symptoms may include painless rectal bleeding, itching or irritation in the anal area, and pain or discomfort during bowel movements. Treatment options depend on the severity of hemorrhoids and can include lifestyle and diet changes, over-the-counter creams or suppositories, rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, or surgery. Preventing constipation and practicing proper hygiene can help avoid hemorrhoids.UGI for MBBS 3 guide to history, examination and acute management



UGI for MBBS 3 guide to history, examination and acute managementTimWiyuleMutafyaMD
╠²
acute management of upper GI bleeding principlesASCITIS IN CHILDREN BY DR VIJITHA



ASCITIS IN CHILDREN BY DR VIJITHAVijitha A S
╠²
The document provides information on ascites in children, including causes, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, investigations, and management. The most common causes of ascites in children are hepatic and renal disease, though it can also be caused by cardiac disease, trauma, infection, or neoplasia. Diagnostic evaluation involves physical exam, imaging like ultrasound or CT scan, and paracentesis with ascitic fluid analysis. Management depends on the underlying cause but may include diuretics, salt restriction, liver support therapies, or treatment of the primary disease. Complications can include respiratory distress, hernias, infections like spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.Approach to Gastrointestinal bleeding



Approach to Gastrointestinal bleedingSujitha Tamilselvam
╠²
This document provides an overview of approaches to gastrointestinal bleeding. It discusses the common clinical presentations including hematemesis, melena, hematochezia, and occult bleeding. For hematemesis, the most common causes are discussed such as stress ulcers, Mallory-Weiss tears, peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal varices, and Dieulafoy's lesion. For hematochezia, common causes include colonic diverticula, internal hemorrhoids, colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease. The document provides details on evaluating each potential cause and characteristics to consider in the clinical history and examination.Piles/Haemorrhoids by Dr.K.AmrithaAnilkumar



Piles/Haemorrhoids by Dr.K.AmrithaAnilkumarDr. Amritha Anilkumar
╠²
Piles, also known as haemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the anal canal. They are classified based on their location and severity. Piles are caused by factors that increase pressure in the anal veins like straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, obesity, etc. Common symptoms include bleeding, pain, itching and bulging of veins near the anus. Piles are diagnosed through examination of the anus and rectum. Treatment options range from lifestyle and diet changes to medical procedures like banding or surgery. Complications can include thrombosis, prolapse or gangrene if piles are left untreated.FISSURE AND HEMORRHOID.pptx............................................



FISSURE AND HEMORRHOID.pptx............................................KomeraSivaramaprasad
╠²
NojfjdjdjjfjfAN APPROACH TO A CHILD WITH GI bleed7859045268881184896 (1).ppt



AN APPROACH TO A CHILD WITH GI bleed7859045268881184896 (1).pptSantoshYadav366243
╠²
short presentationHemorrhoids - Piles



Hemorrhoids - PilesDrGauravSangam
╠²
This document provides information on hemorrhoids, including definitions, anatomy, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. It defines hemorrhoids as dilated veins in the anal canal and discusses four main theories for their formation. Conservative treatments like diet changes, medication, and hot baths are recommended initially. More advanced options include sclerotherapy, which involves injecting chemicals to scar hemorrhoidal tissue, and rubber band ligation to cut off blood supply to hemorrhoids. The document provides detailed descriptions of techniques for both procedures.Om pleural effusion



Om pleural effusionOM VERMA
╠²
The document defines and describes pleural effusion, which is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. There are two main types of pleural effusions - transudative and exudative. Transudative effusions are caused by increased pressure or low protein in blood vessels, while exudative effusions are caused by inflammation or injury leading to fluid leakage. Common causes, signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment options are discussed. Treatment aims to remove fluid, prevent reaccumulation, and address the underlying cause. Complications can include lung damage or infection if fluid is present for a long time.Imaging and intervention in hemetemesis



Imaging and intervention in hemetemesisSindhu Gowdar
╠²
This document discusses various imaging modalities for evaluating gastrointestinal bleeding, including hematemesis. It provides details on angiography, computed tomography angiography, and endoscopy. The key points are:
- Endoscopy is the primary initial investigation but additional techniques like CT angiography and catheter angiography may be needed when endoscopy is negative or fails to identify the bleeding source.
- CT angiography has advantages over catheter angiography as it is more widely available, non-invasive, and allows detection of bleeding sources throughout the GI tract.
- Both endoscopy and CT angiography play important roles in evaluating GI bleeding, with endoscopy also allowing for therapeutic interventions when a source is identified.Rectal bleeding 



Rectal bleeding Saurav Verma
╠²
This document provides information on differential diagnosis and evaluation of rectal bleeding. It discusses common causes such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and colorectal cancers. It describes approaches to history taking, physical examination, and investigations including proctoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, and imaging. Key signs and symptoms of conditions causing rectal bleeding are summarized.Diseases of Peritoneum Mesentry and Omentum



Diseases of Peritoneum Mesentry and OmentumRanjeet Patil
╠²
This document provides an overview of the anatomy and functions of the peritoneum, mesentery, and omentum. It describes:
1) The peritoneum is the largest serous membrane in the body, consisting of parietal and visceral layers. It has functions including pain perception, lubrication, and immune responses.
2) The peritoneal cavity contains serous fluid and is divided into recesses like the greater and lesser sacs. Various organs are located in the retroperitoneum.
3) Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneal cavity that can be localized or generalized. It has many causes including perforations, infections, and trauma. Diagnosis involves signs of pain and21. lower gi bleeding



21. lower gi bleedingmt53y8
╠²
Lower GI bleeding can result from various causes in the colon and rectum. The most common etiologies are diverticular disease, which accounts for 60% of cases, and inflammatory bowel disease, which causes 13% of cases. Diverticulosis is characterized by outpouchings in the colon wall that are prone to bleeding. It is usually asymptomatic but can lead to complications like diverticulitis, abscesses, fistulas, and obstruction. Inflammatory bowel disease includes both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause transmural and mucosal inflammation respectively. Common symptoms of lower GI bleeding include hematochezia and melena. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may involve medications, surgeryPATHOLOGY OF DISEASES OF THE OESOPHAGUS.ppt



PATHOLOGY OF DISEASES OF THE OESOPHAGUS.pptAnthonyMeinhardKipel
╠²
Pathology Of Gastrointestinal Tract- Oesophagial Part for Medical Students bleeding per -rectum.ppt



bleeding per -rectum.pptAhmed Hasan
╠²
lower GIT bleeding: is bleeding from a source distal to the ligament of Treitz (duodenojejunal junction), presented as
Hematochezia is blood passed with stool from the anus,
Melena is black, tarry stool produced by the oxidation of heme by intestinal flora; as little as 50 mL of blood may result in melena, and it may persist for 3 to 5 days following resolution of the bleed.
Maroon-colored stool is associated with rapidly bleeding small bowel lesions in which the transit of blood is too fast for complete oxidation.
Currant-jelly stool is associated with ischemic small bowel or proximal colonic lesions such as may be seen in intussusception.
Upper GIT bleeding: is bleeding from a source proximal to the ligament of Treitz (duodenojejunal junction).
Discussion included the definition of bleeding per rectum, it's types according to child age groups, it's presentation, how to diagnose each type and how to treat.
MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA: A rapid review.pptx



MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA: A rapid review.pptxPhilemonChizororo
╠²
This is a brief outline of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia that are commonly encountered in the field of Endocrinology. Visit Nexus Medical Media on YouTube PORTAL HYPERTENSION- Upper GIT Bleeding.ppt



PORTAL HYPERTENSION- Upper GIT Bleeding.pptPhilemonChizororo
╠²
I hope you find this helpful in your surgical rotationMore Related Content
Similar to HEMORRHOIDS- anatomy, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnosis and management.pptx (20)
Pathophysiology and Management of Surgical conditions



Pathophysiology and Management of Surgical conditionsnkondecollins
╠²
Pathophysiology and Management of Surgical conditions -Heamorrhoidsquick review on hemorrhoids



quick review on hemorrhoidsAnjumAhamadi1
╠²
haemorrhoids are the most common tyoe of gastroenterological disease. it is a nutritive disease. here is a quick review on hemorrhoids, its pathophysiology, clinical features, classification, diagnosis and management.Hemorrhoids ppt



Hemorrhoids pptROMAN BAJRANG
╠²
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum and anus. They commonly occur in adults aged 40-60 years old. Symptoms include painless bleeding during bowel movements, itching or irritation in the anal region, and swelling around the anus. Treatment options include banding, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, creams and suppositories for mild cases. Lifestyle changes such as a high fiber diet, drinking plenty of fluids, exercise, and proper hygiene can help prevent hemorrhoids.hemorrhoids Gi disorders-200819073837.pptx



hemorrhoids Gi disorders-200819073837.pptxTHaripriya1
╠²
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen and inflamed veins in the anal canal and lower rectum. They commonly result from straining during bowel movements or from increased pressure on these veins during pregnancy or obesity. Symptoms may include painless rectal bleeding, itching or irritation in the anal area, and pain or discomfort during bowel movements. Treatment options depend on the severity of hemorrhoids and can include lifestyle and diet changes, over-the-counter creams or suppositories, rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, or surgery. Preventing constipation and practicing proper hygiene can help avoid hemorrhoids.UGI for MBBS 3 guide to history, examination and acute management



UGI for MBBS 3 guide to history, examination and acute managementTimWiyuleMutafyaMD
╠²
acute management of upper GI bleeding principlesASCITIS IN CHILDREN BY DR VIJITHA



ASCITIS IN CHILDREN BY DR VIJITHAVijitha A S
╠²
The document provides information on ascites in children, including causes, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, investigations, and management. The most common causes of ascites in children are hepatic and renal disease, though it can also be caused by cardiac disease, trauma, infection, or neoplasia. Diagnostic evaluation involves physical exam, imaging like ultrasound or CT scan, and paracentesis with ascitic fluid analysis. Management depends on the underlying cause but may include diuretics, salt restriction, liver support therapies, or treatment of the primary disease. Complications can include respiratory distress, hernias, infections like spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.Approach to Gastrointestinal bleeding



Approach to Gastrointestinal bleedingSujitha Tamilselvam
╠²
This document provides an overview of approaches to gastrointestinal bleeding. It discusses the common clinical presentations including hematemesis, melena, hematochezia, and occult bleeding. For hematemesis, the most common causes are discussed such as stress ulcers, Mallory-Weiss tears, peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal varices, and Dieulafoy's lesion. For hematochezia, common causes include colonic diverticula, internal hemorrhoids, colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease. The document provides details on evaluating each potential cause and characteristics to consider in the clinical history and examination.Piles/Haemorrhoids by Dr.K.AmrithaAnilkumar



Piles/Haemorrhoids by Dr.K.AmrithaAnilkumarDr. Amritha Anilkumar
╠²
Piles, also known as haemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the anal canal. They are classified based on their location and severity. Piles are caused by factors that increase pressure in the anal veins like straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, obesity, etc. Common symptoms include bleeding, pain, itching and bulging of veins near the anus. Piles are diagnosed through examination of the anus and rectum. Treatment options range from lifestyle and diet changes to medical procedures like banding or surgery. Complications can include thrombosis, prolapse or gangrene if piles are left untreated.FISSURE AND HEMORRHOID.pptx............................................



FISSURE AND HEMORRHOID.pptx............................................KomeraSivaramaprasad
╠²
NojfjdjdjjfjfAN APPROACH TO A CHILD WITH GI bleed7859045268881184896 (1).ppt



AN APPROACH TO A CHILD WITH GI bleed7859045268881184896 (1).pptSantoshYadav366243
╠²
short presentationHemorrhoids - Piles



Hemorrhoids - PilesDrGauravSangam
╠²
This document provides information on hemorrhoids, including definitions, anatomy, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. It defines hemorrhoids as dilated veins in the anal canal and discusses four main theories for their formation. Conservative treatments like diet changes, medication, and hot baths are recommended initially. More advanced options include sclerotherapy, which involves injecting chemicals to scar hemorrhoidal tissue, and rubber band ligation to cut off blood supply to hemorrhoids. The document provides detailed descriptions of techniques for both procedures.Om pleural effusion



Om pleural effusionOM VERMA
╠²
The document defines and describes pleural effusion, which is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. There are two main types of pleural effusions - transudative and exudative. Transudative effusions are caused by increased pressure or low protein in blood vessels, while exudative effusions are caused by inflammation or injury leading to fluid leakage. Common causes, signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment options are discussed. Treatment aims to remove fluid, prevent reaccumulation, and address the underlying cause. Complications can include lung damage or infection if fluid is present for a long time.Imaging and intervention in hemetemesis



Imaging and intervention in hemetemesisSindhu Gowdar
╠²
This document discusses various imaging modalities for evaluating gastrointestinal bleeding, including hematemesis. It provides details on angiography, computed tomography angiography, and endoscopy. The key points are:
- Endoscopy is the primary initial investigation but additional techniques like CT angiography and catheter angiography may be needed when endoscopy is negative or fails to identify the bleeding source.
- CT angiography has advantages over catheter angiography as it is more widely available, non-invasive, and allows detection of bleeding sources throughout the GI tract.
- Both endoscopy and CT angiography play important roles in evaluating GI bleeding, with endoscopy also allowing for therapeutic interventions when a source is identified.Rectal bleeding 



Rectal bleeding Saurav Verma
╠²
This document provides information on differential diagnosis and evaluation of rectal bleeding. It discusses common causes such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and colorectal cancers. It describes approaches to history taking, physical examination, and investigations including proctoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, and imaging. Key signs and symptoms of conditions causing rectal bleeding are summarized.Diseases of Peritoneum Mesentry and Omentum



Diseases of Peritoneum Mesentry and OmentumRanjeet Patil
╠²
This document provides an overview of the anatomy and functions of the peritoneum, mesentery, and omentum. It describes:
1) The peritoneum is the largest serous membrane in the body, consisting of parietal and visceral layers. It has functions including pain perception, lubrication, and immune responses.
2) The peritoneal cavity contains serous fluid and is divided into recesses like the greater and lesser sacs. Various organs are located in the retroperitoneum.
3) Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneal cavity that can be localized or generalized. It has many causes including perforations, infections, and trauma. Diagnosis involves signs of pain and21. lower gi bleeding



21. lower gi bleedingmt53y8
╠²
Lower GI bleeding can result from various causes in the colon and rectum. The most common etiologies are diverticular disease, which accounts for 60% of cases, and inflammatory bowel disease, which causes 13% of cases. Diverticulosis is characterized by outpouchings in the colon wall that are prone to bleeding. It is usually asymptomatic but can lead to complications like diverticulitis, abscesses, fistulas, and obstruction. Inflammatory bowel disease includes both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause transmural and mucosal inflammation respectively. Common symptoms of lower GI bleeding include hematochezia and melena. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may involve medications, surgeryPATHOLOGY OF DISEASES OF THE OESOPHAGUS.ppt



PATHOLOGY OF DISEASES OF THE OESOPHAGUS.pptAnthonyMeinhardKipel
╠²
Pathology Of Gastrointestinal Tract- Oesophagial Part for Medical Students bleeding per -rectum.ppt



bleeding per -rectum.pptAhmed Hasan
╠²
lower GIT bleeding: is bleeding from a source distal to the ligament of Treitz (duodenojejunal junction), presented as
Hematochezia is blood passed with stool from the anus,
Melena is black, tarry stool produced by the oxidation of heme by intestinal flora; as little as 50 mL of blood may result in melena, and it may persist for 3 to 5 days following resolution of the bleed.
Maroon-colored stool is associated with rapidly bleeding small bowel lesions in which the transit of blood is too fast for complete oxidation.
Currant-jelly stool is associated with ischemic small bowel or proximal colonic lesions such as may be seen in intussusception.
Upper GIT bleeding: is bleeding from a source proximal to the ligament of Treitz (duodenojejunal junction).
Discussion included the definition of bleeding per rectum, it's types according to child age groups, it's presentation, how to diagnose each type and how to treat.
More from PhilemonChizororo (10)
MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA: A rapid review.pptx



MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA: A rapid review.pptxPhilemonChizororo
╠²
This is a brief outline of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia that are commonly encountered in the field of Endocrinology. Visit Nexus Medical Media on YouTube PORTAL HYPERTENSION- Upper GIT Bleeding.ppt



PORTAL HYPERTENSION- Upper GIT Bleeding.pptPhilemonChizororo
╠²
I hope you find this helpful in your surgical rotationTUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN AN INTRODUCTION.pptx



TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN AN INTRODUCTION.pptxPhilemonChizororo
╠²
Introduction to TB in children, with editable slidesACUTE APPENDICITIS: anatomy, aetiology, types, clinical features.pptx



ACUTE APPENDICITIS: anatomy, aetiology, types, clinical features.pptxPhilemonChizororo
╠²
One of the common causes of Acute abdominal painAcute Appendicitis A comprehensive guide.ppt



Acute Appendicitis A comprehensive guide.pptPhilemonChizororo
╠²
This is some of the information that I found necessary for medical students Anesthesia and Perioperative care final_202310201504224319.pptx



Anesthesia and Perioperative care final_202310201504224319.pptxPhilemonChizororo
╠²
This is a comprehensive discussion on the role of anaesthetists before and during the operation 10.Introduction to Epidemiology_MBCHB (1).ppt



10.Introduction to Epidemiology_MBCHB (1).pptPhilemonChizororo
╠²
In the field of community medicine, or public health, understanding the concepts of epidemiology is essential Malnutrition case presentation and management



Malnutrition case presentation and managementPhilemonChizororo
╠²
Tanaka is a 14-month-old boy admitted to the malnutrition unit 2 weeks ago with generalized weakness and poor appetite. His weight, length, MUAC, and HC indicate severe acute malnutrition. He was treated for NOSAM from early weaning and poor diet and diagnosed with pulmonary TB. Discharge criteria includes appetite return, resolved medical issues, and edema resolution. Pre-discharge interventions include counseling caregivers, updating health cards, referring to outpatient care, and linking with community support. Long-term management includes counseling on nutrition, hygiene, illness signs, and family planning, as well as routine growth monitoring.TPT in the field of medicine overview . f.pptx



TPT in the field of medicine overview . f.pptxPhilemonChizororo
╠²
This document provides an overview of tuberculosis (TB) preventive treatment (TPT). It discusses factors that influence the transmission of TB, the difference between latent TB infection and active TB disease, and the rationale for providing TPT. It summarizes evidence that TPT reduces the risk of developing active TB in people living with HIV and children under 5 years old. The document introduces new TPT regimens of 3 months of weekly rifapentine and isoniazid (3HP) and 3 months of daily rifampin and isoniazid (3RH) and provides guidance on their use and recommended alternatives. It addresses considerations for introducing new TPT regimens like safety, tolerability, and ensuring appropriateBREECH PRESENTATION, TYPES, DELIVERY.pptx



BREECH PRESENTATION, TYPES, DELIVERY.pptxPhilemonChizororo
╠²
This presentation was prepared by me, Dr. P. Chizororo, to help fellow professionals understand one of the most common malpresentations, Breech presentation. Visit my YouTube channel, Nexus Medical Media for all pre-clinical subjectsRecently uploaded (20)
MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
Unit 1: Introduction to Histological and Cytological techniques
’éĘ Differentiate histology and cytology
’éĘ Overview on tissue types
’éĘ Function and components of the compound light microscope
’éĘ Overview on common Histological Techniques:
o Fixation
o Grossing
o Tissue processing
o Microtomy
o Staining
o Mounting
’éĘ Application of histology and cytologyBiography of Dr. Vincenzo Giordano



Biography of Dr. Vincenzo GiordanoDr. Vincenzo Giordano
╠²
Dr. Vincenzo Giordano began his medical career 2011 at Aberdeen Royal Infirmary in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery. Here, he performed complex adult cardiothoracic surgical procedures, significantly enhancing his proficiency in patient critical care, as evidenced by his FCCS certification.Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) & Its Management Protocol



Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) & Its Management ProtocolDr Anik Roy Chowdhury
╠²
Dr. Anik Roy Chowdhury
MBBS, BCS(Health), DA, MD (Resident)
Department of Anesthesiology, ICU & Pain Medicine
Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College Hospital (ShSMCH)PARIS SYSTEM FOR URINE CYTOLOGY paris system of reporting urine slidespptx



PARIS SYSTEM FOR URINE CYTOLOGY paris system of reporting urine slidespptxDrDivitasaxena1
╠²
Paris system for reporting urine cytologyStability of Dosage Forms as per ICH Guidelines



Stability of Dosage Forms as per ICH GuidelinesKHUSHAL CHAVAN
╠²
This presentation covers the stability testing of pharmaceutical dosage forms according to ICH guidelines (Q1A-Q1F). It explains the definition of stability, various testing protocols, storage conditions, and evaluation criteria required for regulatory submissions. Key topics include stress testing, container closure systems, stability commitment, and photostability testing. The guidelines ensure that pharmaceutical products maintain their identity, purity, strength, and efficacy throughout their shelf life. This resource is valuable for pharmaceutical professionals, researchers, and regulatory experts.Asthma: Causes, Types, Symptoms & Management ŌĆō A Comprehensive Overview



Asthma: Causes, Types, Symptoms & Management ŌĆō A Comprehensive OverviewDr Aman Suresh Tharayil
╠²
This presentation provides a detailed yet concise overview of Asthma, a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. It covers the definition, etiology (causes), different types, signs & symptoms, and common triggers of asthma. The content highlights both allergic (extrinsic) and non-allergic (intrinsic) asthma, along with specific forms like exercise-induced, occupational, drug-induced, and nocturnal asthma.
Whether you are a healthcare professional, student, or someone looking to understand asthma better, this presentation offers valuable insights into the condition and its management.HUMAN SEXUALITY AND SEXUAL RESPONCE CYCLE



HUMAN SEXUALITY AND SEXUAL RESPONCE CYCLEdaminipatel37
╠²
It is all about topic of obg for new semester students Presentaci├│ "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025



Presentaci├│ "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025Badalona Serveis Assistencials
╠²
Presentaci├│ que va acompanyar la demostraci├│ pr├Āctica de metge d'Innovaci├│ Jos├® Ferrer sobre el projecte Benestar de BSA, nom d'IDIAP Pere Gol, el 5 de mar├¦ de 2025 a l'estand de XarSMART al Mobible Word Congress. Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level Curriculum



Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level CurriculumDr Ovels
╠²
Sudurpaschim province psc ( lok sewa aayog) medical officer 8th level syllabusOp-eds and commentaries 101: U-M IHPI Elevating Impact series



Op-eds and commentaries 101: U-M IHPI Elevating Impact seriesKara Gavin
╠²
A slide set about writing opinion and commentary pieces, created for the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Jan. 2025Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"



Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"Rehab Aboshama
╠²
Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"
MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
The course covers the steps undertaken from tissue collection, reception, fixation,
sectioning, tissue processing and staining. It covers all the general and special
techniques in histo/cytology laboratory. This course will provide the student with the
basic knowledge of the theory and practical aspect in the diagnosis of tumour cells
and non-malignant conditions in body tissues and for cytology focusing on
gynaecological and non-gynaecological samples.X-Ray-Generators-and-Transformers final.pdf



X-Ray-Generators-and-Transformers final.pdfMohd Faraz
╠²
An X-ray generator is a crucial device used in medical imaging, industry, and research to produce X-rays. It operates by accelerating electrons toward a metal target, generating X-ray radiation. Key components include the X-ray tube, transformer assembly, rectifier system, and high-tension circuits. Various types, such as single-phase, three-phase, constant potential, and high-frequency generators, offer different efficiency levels. High-frequency generators are the most advanced, providing stable, high-quality imaging with minimal radiation exposure. X-ray generators play a vital role in diagnostics, security screening, and industrial testing while requiring strict radiation safety measures.Flag Screening in Physiotherapy Examination.pptx



Flag Screening in Physiotherapy Examination.pptxBALAJI SOMA
╠²
Flag screening is a crucial part of physiotherapy assessment that helps in identifying medical, psychological, occupational, and social barriers to recovery. Recognizing these flags ensures that physiotherapists make informed decisions, provide holistic care, and refer patients appropriately when necessary. By integrating flag screening into practice, physiotherapists can optimize patient outcomes and prevent chronicity of conditions.Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for Neurosurgeons



Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for NeurosurgeonsDhaval Shukla
╠²
This presentation delves into the latest advancements in non-invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring techniques, specifically tailored for neurosurgeons. It covers the importance of ICP monitoring in clinical practice, explores various non-invasive methods, and discusses their accuracy, reliability, and clinical applications. Attendees will gain insights into the benefits of non-invasive approaches over traditional invasive methods, including reduced risk of complications and improved patient outcomes. This comprehensive overview is designed to enhance the knowledge and skills of neurosurgeons in managing patients with neurological conditions.
Invasive systems are commonly used for monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) in traumatic brain injury (TBI) and are considered the gold standard. The availability of invasive ICP monitoring is heterogeneous, and in low- and middle-income settings, these systems are not routinely employed due to high cost or limited accessibility. The aim of this presentation is to develop recommendations to guide monitoring and ICP-driven therapies in TBI using non-invasive ICP (nICP) systems.
MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
HEMORRHOIDS- anatomy, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnosis and management.pptx
- 1. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES ŌĆó Anatomy ŌĆó Types ŌĆó Classification ŌĆó Etiology ŌĆó Investigations ŌĆó Complications ŌĆó Treatment Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 2. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES ’é¦ The word ŌĆśHemorrhoidŌĆÖ is derived from Greek words Haima (bleed) + Rhoos (flowing), mean bleeding. ’é¦ The word pile is derived from the Latin word ŌĆśPilaŌĆÖ means ball or a mass. ’é¦ Anal cushions are aggregations of blood vessels (Arterioles, venules), smooth muscles and elastic connective tissue in the submucosa that normally reside in left lateral, right posterolateral and right anterolateral anal canal. ’é¦ These positions can be found at 3, 7 and 11 oŌĆÖclock. ’é¦ The anal canal is lined by the anal cushions Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 3. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES Hemorrhoids consist of dilated venous plexus, a small artery and areolar tissue. ŌĆó Piles can be mucosal or vascular. ’é¦ Vascular type is seen in young. ’é¦ Mucosal is seen in old. ŌĆó Present concept is weakening of ParkŌĆÖs ligament TYPES ŌĆó Hemorrhoids can either be: Ō×ó Internal- above the dentate (pectineal) line, covered with mucous membrane Ō×ó External- below the dentate (pectineal) line, covered with skin Ō×ó Interno-external- together occur. Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 4. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES CLASSIFICATION Hemorrhoids can be classified according: Ō×ó Location Ō×ó Severity ACCORDING TO LOCATION Primary hemorrhoids: ŌĆó Located at 3, 7, 11 oŌĆÖclock positions related to the branches of the superior hemorrhoidal vessels which divides on the right side into 2, and on the left side it continues as 1 Secondary hemorrhoids: One which occur between the primary sites. Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 5. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES ACCORDING TO SEVERTIY First degree: piles within that may bleed but does not come out Second degree: piles that prolapse during defecation but returns back spontaneously Third degree: piles prolapsed during defecation, can be replaced back only by manual help Fourth degree: pile that are permanently prolapsed.
- 6. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES ETIOLOGY ’é¦ Hereditary ’é¦ Idiopathic ’é¦ Morphologic: weight of the blood column without valves causes high pressure. ŌĆó Veins in the lower rectum are in loose submucosal plane but the veins above enter the muscular layer, which on contraction increases the venous congestion below (more prevalent in patients with constipation). ŌĆó Superior rectal veins have no valves (as they are tributaries of portal vein) and so more congestion. Other causes: Ō×ó Straining, diarrhea, constipation, hard stool, low fiber diet, over-purgation Ō×ó Carcinoma rectum, portal hypertension (rare cause) Ō×ó Pregnancy: during pregnancy raised progesterone relaxes the venous wall and reduces its tone, enlarged uterus compresses the pelvic vein and constipation is a common problem. Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 7. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES CLINICAL FEATURES ŌĆó It occurs at any age but mostly between 30 to 65 years. ŌĆó Incidence is equal in both sexes. ŌĆó Painless Bleeding- 1st symptom- ŌĆśsplash in the panŌĆÖ- ŌĆśbright red and freshŌĆÖ- occurs during defecation ŌĆó Mass per anum. ŌĆó Pain- may be due to prolapse, infection or spasm ŌĆó Prolapse of internal hemorrhoids may produce moisture in the anal region or mucus discharge that causing itching. ŌĆó Anemia- secondary Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 8. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES EXAMINATION ’é¦ On inspection, prolapsed piles will be visualized ’é¦ On P/R examination, only thrombosed piles can be felt. INVESTIGATIONS ’é¦ Proctoscopy: note number, degree, size, surface and appearance of piles as well as features of chronicity of the prolapse. ’é¦ Sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy: malignancy ’é¦ Endoscopy to rule out other sources of rectal bleeding e.g. cancer and inflammatory bowel disease. ’é¦ Full blood count-check for anemia (hematocrit) and platelet count Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 9. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES COMPLICATIONS ŌĆó Profuse hemorrhage which may require blood transfusion ŌĆó Strangulation- by anal sphincter ŌĆó Thrombosis- piles appear dark purple/black, feels solid and tender ŌĆó Ulceration ŌĆó Gangrene ŌĆó Fibrosis ŌĆó Stenosis ŌĆó Suppuration leads to perianal or submucosal abscess ŌĆó Pylephlebitis (portal pyaemia) is rare but can occur in 3rd degree piles after surgery. Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 10. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES TREATMENT Medical ’āś Sitz bath- immersing anal region for 15-20 minutes, 2-3 times a day. ŌĆó To reduce edema, pain and promote healing ’āś Analgesics, local anesthetic cream ’āś Antihistamines ’āś Antibiotics ’āś Laxatives ’āś Local anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs e.g. annomax Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
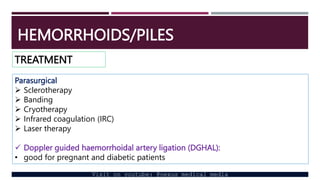
- 11. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES TREATMENT Parasurgical ’āś Sclerotherapy ’āś Banding ’āś Cryotherapy ’āś Infrared coagulation (IRC) ’āś Laser therapy ’ā╝ Doppler guided haemorrhoidal artery ligation (DGHAL): ŌĆó good for pregnant and diabetic patients Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 12. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES TREATMENT Surgical ’āś Open haemorrhoidectomy (Milligan-Morgan)-Britain ’āś Closed haemorrhoidectomy (Hill-Fergusson)- USA ’āś Stapled haemorrhoidopexy (Antonio Longo) ’āś Anal stretching Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 13. HEMORRHOIDS/PILES SEVERITY MEDICAL PARASURGICAL SURGICAL 1st degree Medical interventions usually enough ŌĆó Sclerotherapy can be done ŌĆó DGHAL can be done 2nd degree Medical interventions usually enough ŌĆó Sclerotherapy can be done ŌĆó BarronŌĆÖs banding is done ŌĆó DGHAL can be done 3rd degree Medical interventions can help patients especially before surgery ŌĆó Laser therapy can be done ŌĆó DGHAL can be done Hemorrhoidectomy is gold standard 4th degree Medical interventions can help patients especially before DGHAL can be done Hemorrhoidectomy is gold standard Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media
- 14. HEMORRHOIDECTOMY Visit on youtube: @nexus medical media








