Hepatotoxicity Screening Sot Poster 2008 2009
- 1. Screening for Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity: Phospholipidosis, Steatosis, Apoptosis and Inflammatory Markers K.F. Marcoe, R. Keyser, P. TB. Nguyen, Yulia Ovechkina, and C. OŌĆÖDay MDS Pharma Services ŌĆō Bothell, WA, USA Multiparametric Hepatotoxicity Screening in HepG2 Cells with Comparison in Primary Hepatocytes K.F. Marcoe, Yulia Ovechkina, R. Keyser, P. TB. Nguyen, C. OŌĆÖDay MDS Pharma Services ŌĆō Bothell, WA, USA
- 2. Drug-Induce Hepatotoxicity ’é¤ Liver major site of metabolism for most drugs ’é¤ Based on safety, hepatotoxicity recognized as a leading cause for drug withdrawal ’é¤ Toxicity of new drug candidates routinely evaluated just prior to compounds moving into clinical trial ’é¤ Late stage In vivo toxicity studies have problems ŌłÆ Costly (multiple animal species requirements) ŌłÆ Large amounts of compounds ŌłÆ Significant investment of resources tied to late findings ’é¤ In vitro early stage toxicity studies afford ŌłÆ Identification of hepatotoxic potential earlier (cost and time savings) ŌłÆ Opportunities for ranking and prioritizing or development of alternatives with lower toxicity ’é¤ Multiparameter high content cell-based screening methods in drug discovery contribute to better predictivity of human hepatotoxicity potential ’é¤ Early safety screening current priority in drug development
- 3. Early Safety Hepatotoxicity Screening Assays Development of effective in vitro cell-based screening models to assess human hepatotoxicity potential of drugs ideally requires: ’é¤ Use of high content multiplexed technologies ’é¤ Utilization of primary human cell and HepG2 cell line hepatocyte models ’é¤ Measurement of parameters ŌłÆ At the single cell level ŌłÆ Morphological and biochemical ŌłÆ Investigative of pre-lethal cytotoxic effects ŌłÆ Representative of different mechanisms of toxicity ŌłÆ Suitable for rapid throughput ŌłÆ 384 well plate format ’é¤ Minimal amount of compound for testing (1 - 2 mg)
- 4. Multiplexed High Content Screening Tools IN Cell 1000 Analyzer automated fluorescent microscopy imaging of live or fixed cells allows ’é¤ Subcellular localization AND quantitation of the cellular targets ’é¤ Multiplexing capabilities: multiple data points from a single assay well ’é¤ High sensitivity (nuclear staining allows for normalization of cellular signals against cell number) ’é¤ Measurement of individual cell responses in the heterogeneous cell populations ’é¤ Customized protocols for cell image quantitation (IN Cell Developer Software) xMAP technology using Luminex ’é¤ Flow based multiplexed microsphere assay system ’é¤ Multi-analyte protein analysis in the same well ’é¤ Nuclei staining with IN Cell imaging allows normalization of cellular signals against cell number
- 5. Multiplexed High Content Screening Hepatotoxicity Early Safety Platform HCS Hepatotoxicity Early Safety Platform Hepato-toxicity (cell proliferation, apoptosis, mitosis) Hepato-Lipid Accumulation (cell proliferation, phospholipidosis, neutral lipids) Hepato-Cytokine Secretion (cell proliferation, inflammatory markers)
- 6. Multiplexed In vitro Hepatotoxicity Assay In vitro hepatotoxicity assessment ’é¤ Cultured HepG2 cells (human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line) useful screening reagent ’é¤ Evaluation of toxicity ŌĆświndow / safety marginŌĆÖ and mechanism of death helps determine dosing and cost/benefit analysis of therapeutic agent based on prediction of in vivo toxicity potential ŌłÆ In vitro cell-based safety margin = cytotoxic concentration ŌĆō on-target potency concentration (cell-based efficacy) ŌłÆ Higher values predict higher in vivo safety margins ŌłÆ In vitro cell-base safety margins use to rank compounds based on hepatotoxicity potential in humans ŌłÆ 80% correlation between actual in vivo and in vitro cell-based toxicity results have been demonstrated (Shrivastava R, et al., OŌĆÖBrien PJ, et al., Vivek C, et al.) ŌłÆ Other factors contributing to toxicity profiles: drug properties, concentrations, protein binding and transport, pharmacokinetic characteristics ’é¤ Provides information on the relative toxicities of candidate drugs within particular compound families to aid selection of lead candidates. ’é¤ Offers insight into drug toxicity mechanism ’é¤ Provides end-point-specific drug hepatotoxicities
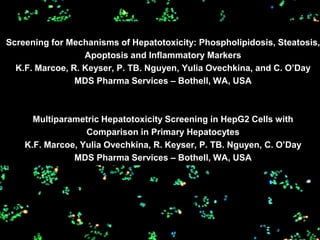
- 7. Multiplexed In vitro Hepatotoxicity Assay Multiplexed Hepatotoxicity Assay ’é¤ HepG2 cells seeded in 384-well Collagen I coated optical plates, incubated 24 hrs ’é¤ Cells incubated 72 hrs with test compounds serially diluted ┬Į log over 10 concentrations ’é¤ Post 72 hrs incubation cells fixed and immunolabeled with: ŌłÆ Anti-active Caspase-3 for detection of apoptosis ŌłÆ Anti-phospho-Histone-3 for detection of cell cycle ŌłÆ Stained with a nuclear dye for cell proliferation quantification ’é¤ Automated fluorescence microscopy carried out using a GE Healthcare IN Cell Analyzer 1000 ’é¤ Images collected with a 4X objective
- 8. Multiplexed In vitro Hepatotoxicity Assay Vehicle Vinblastine Labels: Nuclei - green; Apoptotic cells - blue; Mitotic cells - red Cell Proliferation Apoptosis Induction Cell Cycle Block Percent of Control over Background over Background Fold Induction 160 100 6 Fold Induction 140 80 120 100 60 4 80 60 40 2 40 20 20 0 0 -13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 0 -13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 [Vinblastine], M [Vinblastine], M [Vinblastine], M HepG2, 72 hr assay
- 9. Primary human hepatotoxicity assay: MTS and HCS comparison Amiodarone Valproic acid Amitriplyline 100 160 120 140 100 80 120 MTS 80 100 POC POC POC 60 80 60 40 60 40 40 20 20 20 0 0 0 0.01 1 100 0.01 1 100 0.0 1 100 Concentration microM Concentration microM 1 Concentration microM HCS 24 hour compound treatment of human primary hepatocytes; High Content Screening approach (HCS)
- 10. Primary human hepatotoxicity assay: MTS and HCS comparison HCS % of attached MTS Viability IC50 Compound live cells IC50 (microM) (microM) Tamoxifen 36.7 ┬▒ 5.6 19.8 ┬▒ 0.7 Chlorpramazine 28.0 ┬▒ 6.9 26.4 ┬▒ 1.8 Amitriplyline 49.39 ┬▒ 4.06 62.3 ┬▒ 4.2 Amiodarone 125 ┬▒ 10 146 ┬▒ 22 Valproic acid >500 >500 Astemizole 6.39 ┬▒ 2.38 12.2 ┬▒ 2.1 Rosiglitazone 354 ┬▒ 133 413 ┬▒ 80 Troglitzqone 157 ┬▒ 6 122 ┬▒ 42 24 hour compound treatment of human primary hepatocytes; High Content Screening approach (HCS)
- 11. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Lipid Accumulation Assay ’é¤ In vitro hepato-lipid accumulation assessment ŌłÆ Cultured HepG2 cells (human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line) ’é¤ Phospholipidosis accumulation of excess phospholipids in cells ŌłÆ Cationic amphiphilic drugs often induce phospholipidosis in vivo ŌłÆ Toxic effect due to drug or metabolite accumulation in affected tissue, leads to acute and chronic disease ŌłÆ Liver and lung common targets ’é¤ Neutral lipid accumulation ŌłÆ Steatosis accumulation of fatty acids ŌłÆ Other mechanisms of lipid accumulation ŌłÆ Can cause enlargement of the liver and irreversible cell damage ’é¤ Flags drug candidate hepatotoxicity potential in the lead optimization stage of drug discovery ’é¤ End-point-specific drug-induced mechanism of hepatotoxicity
- 12. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Lipid Accumulation Assay Multiplexed Hepato-Lipid Accumulation Assay ’é¤ HepG2 cells seeded in 384-well Collagen I coated optical plates, incubated 24 hrs ’é¤ Cells incubated for 48 hrs with ŌłÆ Fluorescently-labeled phospholipid (Invitrogen, H34350) for phospholipid accumulation detection ŌłÆ Test compounds serially diluted ┬Į log over 10 concentrations ’é¤ Post 48 hrs incubation cells fixed and stained with ŌłÆ Neutral lipid dye (Invitrogen, H34476) for neutral lipid detection ŌłÆ Nuclear dye for cell proliferation quantification ’é¤ Automated fluorescence microscopy carried out using a GE Healthcare INCell Analyzer 1000 ’é¤ Images were collected with a 4X objective.
- 13. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Lipid Accumulation Assay (HepG2) HepG2, 48 hr assay
- 14. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Lipid Accumulation Assay (HepG2) Hepato-Neutral Lipid Accumulation Assay Labels: Nuclei - green; Neutral lipids - red HepG2, 48 hr assay
- 15. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Lipid Accumulation Assay (HepG2) HepG2, 48 hr assay
- 16. In vitro Hepato-Lipid Accumulation Assay using primary human hepatocytes in 384 WP
- 17. In vitro Hepato-Lipid Accumulation Assay using primary human hepatocytes in 384 WP Amiodarone Amitriplyline
- 18. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Cytokine Secretion Assay Multiplexed Hepato-Cytokine Secretion Assay IN Cell xMAPŌäó Automated technology fluorescent using microscopy Luminex ’āĀ imaging ’āĀ Markers of cell count inflammation normalization
- 19. xMAP technology-Multiple Analytes /Well ’é¤ Multiplexing: Up to 100 analytes/well ’é¤ Analytes cytokines or other inflammatory markers ’é¤ Flow based assay system. Uses beads loaded with different concentrations of 2 dyes. ’é¤ Each bead has itŌĆÖs own unique spectral signature (100 possible), antibodies are derivitized to unique bead ’é¤ Beads are incubated with test sample ’é¤ Sandwich assay performed with a biotinylated second antibody (mouse) ’é¤ Streptavidin labeled with phycoerythrin (PE) used for detection ’é¤ Beads are run individually (Flow) through a laser which detects the exact bead and then determines whether PE is associated
- 20. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Cytokine Secretion Assay (HepG2) Multiplexed Hepato-Cytokine Secretion Assay ’é¤ Biomarker secretion, as markers of inflammation ’é¤ Nuclear count, analyte normalization to cell number ’é¤ HepG2 cells seeded into 96-well Collagen I coated optical plates incubated 24 hrs ’é¤ Cells treated with LPS, TNF╬▒, IL-1╬▓ and acetaminophen serially diluted ┬Į log over 8 concentrations incubated 48 hrs ’é¤ Post 48 hrs incubation supernatants collected, cytokine detection was carried out using Luminex xMAPŌäó technology ’é¤ To quantify cell proliferation the monolayer of HepG2 cells remaining in each plate was immediately stained with nuclear dye for normalization ’é¤ Images were collected using a GE Healthcare INCell Analyzer 1000
- 21. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Cytokine Secretion Assay ’é¤ HepG2 cells treated with LPS, TNF╬▒, IL-1╬▓ and acetaminophen HepG2 cells ’é¤ Screened for the secretory presence of 30 human inflammatory markers: LPS, TNF╬▒, IL-1╬▓ and acetaminophen IL-1╬▒, IL-1╬▓, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p40, IL- 12-70, IL-13, INF╬│, INF╬▒2a, Fibrinogen, Apo AI, Apo AII, Apo B, IP-10, GM-CSF, G-CSF, CRP, Haptoglobin, Apo CII, Apo CIII and MCP-1, MIP-1╬▒, MIP-1╬▓, SAA Apo E TNF╬▒, IL-1 receptor antagonist
- 22. Multiplexed In vitro Hepato-Cytokine Secretion Assay (HepG2)
- 23. Early Safety Screening for Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity Conclusion: ’é¤ We have developed a robust and rapid throughput screening system using HepG2 cells that allows early assessment of acute and chronic mechanisms of hepatotoxicity ’é¤ Compounds with known hepatotoxicities tested in validating the capabilities of this multiparametric HCS system in identifying and quantifying toxicities relevant to cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, steatosis/cholestasis and phospholipidosis demonstrated high concordance with reported hepatotoxic profile for each compound tested ’é¤ Evaluation of cytokine secretion in HepG2 cells to identify measurable biomarkers of inflammation demonstrated significant secretion levels for 6 of the cytokines tested thus validating this multiplexed approach for quantifying indications of hepatic inflammation ’é¤ These hepatotoxicity screening assays are sensitive and reproducible and provide results that previously only have been attainable in more complex in vivo models ’é¤ Our cost-effective in vitro multiplexed HCS platform offers comprehensive predictive information allowing pre-selection of drug scaffold designs with long-term hepatotoxicity considerations and may even have more relevance when performed in normal primary hepatocytes






![Multiplexed In vitro Hepatotoxicity Assay
Vehicle Vinblastine
Labels: Nuclei - green; Apoptotic cells - blue; Mitotic cells - red
Cell Proliferation Apoptosis Induction Cell Cycle Block
Percent of Control
over Background
over Background
Fold Induction
160 100 6
Fold Induction
140
80
120
100 60 4
80
60 40
2
40 20
20
0 0
-13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 0
-13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6
[Vinblastine], M [Vinblastine], M
[Vinblastine], M
HepG2, 72 hr assay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepatotoxicityscreeningsotposter20082009-13279898294533-phpapp01-120131000612-phpapp01/85/Hepatotoxicity-Screening-Sot-Poster-2008-2009-8-320.jpg)