histamin (1).pptx
- 2. ’éŚ Histamine and serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) are biologically active amines that function as neurotransmitters and are found in non-neural tissues, ’éŚ have complex physiologic and pathologic effects through multiple receptor subtypes, and are often released locally. ’éŚ Together with endogenous peptides prostaglandins and leukotrienes and cytokines - called autacoids or local hormones
- 3. HISTAMINE ’éŚ important mediator of immediate allergic and inflammatory reactions, although it plays only a modest role in anaphylaxis. ’éŚ plays an important role in gastric acid secretion and ’éŚ functions as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. ’éŚ plays a role in chemotaxis of white blood cells.
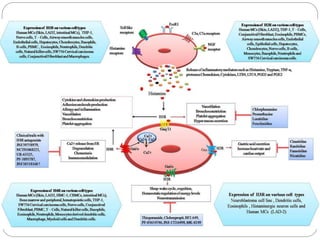
- 4. BASIC PHARMACOLOGY OF HISTAMINE ’éŚ Histamine :occurs in plants as well as in animal tissues - a component of some venoms and stinging secretions. ’éŚ formed by decarboxylation of the amino acid l- histidine, a reaction catalyzed in mammalian tissues by the enzyme histidine decarboxylase. ’éŚ histamine is either stored or rapidly inactivated. ’éŚ Very little histamine is excreted unchanged. ’éŚ The major metabolic pathways involve conversion to N- methylhistamine, methylimidazoleacetic acid, and imidazoleacetic acid (IAA).
- 5. ’éŚ Most tissue histamine is sequestered and bound in granules (vesicles) in mast cells or basophils; the histamine content of many tissues is directly related to their mast cell content. ’éŚ especially rich at sites of potential tissue injuryŌĆönose, mouth, and feet; internal body surfaces; and blood vessels, particularly at pressure points and bifurcations. ’éŚ The bound form of histamine is biologically inactive ’éŚ Non-mast cell histamine is found in several tissues, including the brain, where it functions as a neurotransmitter ’éŚ A second important nonneuronal site of histamine storage and release is the enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells of the fundus of the stomach.
- 6. Storage & Release of Histamine ’éŚ in mast cells ’éŚ can be released through several mechanisms. -IMMUNOLOGIC RELEASE -if sensitized by IgE antibodies attached to their surface membranes, degranulate explosively when exposed to the appropriate antigen -requires energy and calcium. - is a mediator in immediate (type I) allergic reactions, such as hay fever and acute urticaria IgG- or IgM-mediated immune reactions that activate the complement cascade also release histamine from mast cells and basophils -CHEMICAL AND MECHANICAL RELEASE -morphine and tubocurarine, can displace histamine from its bound form within cells
- 7. An Allergic Reaction ’éŚ Early phase reaction: occurs within minutes of exposure to an allergen and lasts for 30-90 minutes ’éŚ Late phase reaction: begins 4-8 hours later and can last for several days, often leading to chronic inflammatory disease
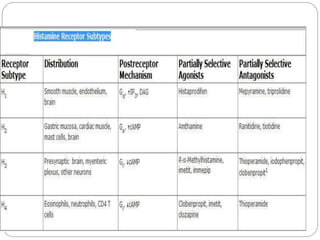
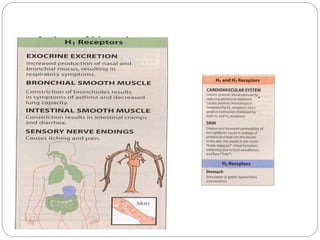
- 8. MECHANISM OF ACTION ’éŚ exerts its biologic actions by combining with specific cellular receptors on surface membrane. ’éŚ The four different histamine receptors - H1ŌĆōH4 ’éŚ H1 and H2 receptors are distributed widely in the periphery and in the CNS and their activation by histamine can exert local or widespread effects ’éŚ histamine causes itching and stimulates secretion from nasal mucosa. ’éŚ It contracts many smooth muscles, such as those of the bronchi and gut, but markedly relaxes others, including those in small blood vessels. ’éŚ Histamine also is a potent stimulus of gastric acid secretion. ’éŚ less-prominent effects include formation of edema and stimulation of sensory nerve endings. ’éŚ Bronchoconstriction and contraction of the gut are mediated by H1 receptors. ’éŚ In the CNS, H1 activation inhibits appetite and increases wakefulness. ’éŚ Gastric secretion results from the activation of H 2 receptors. ’éŚ Some responses, such as vascular dilation, are mediated by both H1and H2 receptor stimulation.
- 9. ’éŚ The H3 receptors are expressed mainly in the CNS, especially in the basal ganglia, hippocampus, and cortex ’éŚ Presynaptic H3 receptors function as autoreceptors on histaminergic neurons, inhibiting histamine release and modulating the release of other neurotransmitters. ’éŚ H3 receptors are also found postsynaptically, especially in the basal ganglia, but their function is still being unraveled H3 agonists promote sleep, and H3 antagonists promote wakefulness.
- 10. ’éŚ The H4 receptors primarily are found in eosinophils, dendritic cells, mast cells, monocytes, basophils, and T cells but have also been detected in the GI tract, dermal fibroblasts, CNS, and primary sensory afferent neurons ’éŚ Activation of H4 receptors has been associated with induction of cellular shape change, chemotaxis, secretion of cytokines, and upregulation of adhesion molecules, suggesting that H 4 antagonists may be useful inhibitors of allergic and inflammatory responses
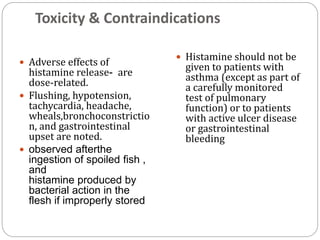
- 14. Toxicity & Contraindications ’éŚ Adverse effects of histamine release- are dose-related. ’éŚ Flushing, hypotension, tachycardia, headache, wheals,bronchoconstrictio n, and gastrointestinal upset are noted. ’éŚ observed afterthe ingestion of spoiled fish , and histamine produced by bacterial action in the flesh if improperly stored ’éŚ Histamine should not be given to patients with asthma (except as part of a carefully monitored test of pulmonary function) or to patients with active ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding
- 15. HISTAMINE ANTAGONISTS ’éŚ Physiologic antagonists, especially epinephrine, have smooth muscle actions opposite to those of histamine, but they act at different receptors. ’éŚ important clinically because injection of epinephrine can be lifesaving in systemic anaphylaxis and in other conditions in which massive release of histamineŌĆöand other mediatorsŌĆöoccurs.
- 16. ’éŚ Release inhibitors: Cromolyn and nedocromil Beta2-adrenoceptor agonist ’éŚ receptor antagonists ’éŚ H2-receptor antagonist burimamide ’éŚ H1 antagonists
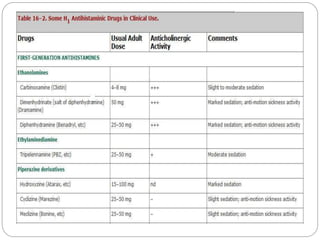
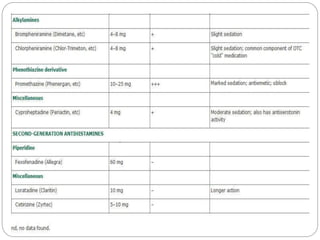
- 17. ’éŚ The H1 antagonists are conveniently divided into first-generation and second-generation agents. ’éŚ the relatively strong sedative effects of most of the first-generation drugs ’éŚ The first-generation agents are also more likely to block autonomic receptors. ’éŚ The relatively less sedating characteristic of the second-generation H1 blockers - less complete distribution into the central nervous system.
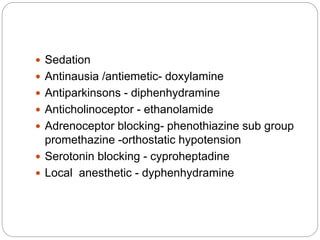
- 20. ’éŚ Sedation ’éŚ Antinausia /antiemetic- doxylamine ’éŚ Antiparkinsons - diphenhydramine ’éŚ Anticholinoceptor - ethanolamide ’éŚ Adrenoceptor blocking- phenothiazine sub group promethazine -orthostatic hypotension ’éŚ Serotonin blocking - cyproheptadine ’éŚ Local anesthetic - dyphenhydramine
- 21. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY OF H1-RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS ’éŚ Clinical Uses Allergic Reactions ’éŚ allergicrhinitis (hay fever), the H1 antagonists are second-line drugs after glucocorticoids administered by nasal spray. ’éŚ In urticaria, in which histamine is the primary mediator, the H1 antagonists arethe drugs of choice and are often quite effective if given before exposure. ’éŚ in bronchial asthma, which involves several mediators, the H1 antagonists are largely ineffective.
- 22. Motion Sickness And Vestibular Disturbances ’éŚ Scopolamine and certain first-generation H1 antagonists are the most effective agents available ’éŚ The antihistaminic drugs with the greatest effectiveness in this application are diphenhydramine and promethazine. ’éŚ The piperazines (cyclizine and meclizine) also have significant activity and are less sedating than diphenhydramine in most patients.
- 23. Nausea And Vomiting Of Pregnancy ’éŚ The piperazine derivatives were withdrawn from such use when it was demonstrated that they have teratogenic effects in rodents. ’éŚ Doxylamine, an ethanolamine H1 antagonist, was promoted for this application as a component of Bendectin, a prescription medication that also contained pyridoxine.
- 24. ’éŚ Common Cold-inhibits Rhinorrhoea ’éŚ Extrapyramidal Symptoms ’éŚ Preanesthetic Medication
- 25. Drug Interactions ’éŚ Lethal ventricular arrhythmias occurred in several patients taking either of the early second- generation agents, terfenadine or astemizole, in combination with ketoconazole, itraconazole, or macrolide antibiotics such as erythromycin- CYP3A4 ’éŚ mechanism - blockade of the HERG (IKr) potassium channels in the heart that contribute to repolarization of the action potential ’éŚ prolongation and a change in shape of the action potential, and these changes lead to arrhythmias.
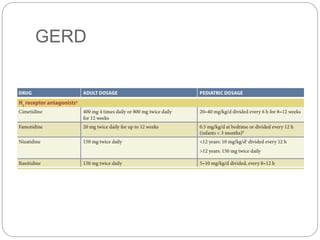
- 26. H2-RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS ’éŚ peptic ulcer disease and related gastrointestinal complaints ’éŚ cimetidine, ranitidine,famotidine, and nizatidine. ’éŚ These drugs are less potent than PPIs but still suppress 24-hour gastric acid secretion by about 70%. ’éŚ Suppression of basal and nocturnal acid secretion is about 70%
- 27. GERD
- 28. ’éŚ H3-selective ligands may be of value in sleep disorders, obesity, and cognitive and psychiatric disorders. ’éŚ Tiprolisant, an inverse H3-receptor agonist, has been shown to reduce sleep cycles in mutant mice and in humans with narcolepsy. ’éŚ H4 blockers have potential in chronic inflammatory conditions such as asthma, in which eosinophils and mast cells play a prominent role.
- 29. PHARMACOKINETICS Second generation antihistamines: ’é¦ Relatively rapid onset ’é¦ Elimination Half-Lives: ’é¦ Loratadine-up to 28 hours ’é¦ Fexofenadine-14 hours ’é¦ Cetirizine-8 hours ’é¦ Children metabolize Cetirizine faster, but rates are similar for the others
- 30. ADVERSE REACTIONS AND SIDE EFFECTS First Generation Drugs: ’é¦ Anticholinergic CNS interactions ’é¦ Gastrointestinal reactions ’é¦ Common side effects: sedation, dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision, euphoria, lack of coordination, anxiety, insomnia, tremor, nausea and vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, and dry cough Second Generation Drugs: ’é¦ Common side effects: drowsiness, fatigue, headache, nausea and dry mouth Side effects are far less common in Second Generation drugs