H&L Remediation 2011
- 1. In Situ Chemical Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium in Soils and Groundwater Using Ferrous Sulfide (FeS) Nanotechnology Richard H. Christensen, PhD, LPG Indianapolis, IN ┬Ág/L Steven R. Irvin Jim V. Rouse (MWH)
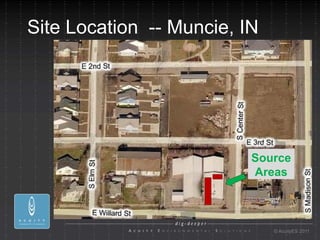
- 2. Site Location -- Muncie, IN Source Areas ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 3. Chrome Plating at its best! ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 4. Site Overview Site Conditions First investigation ÔÇô 2005 AÔÇÖ AcuityES - 2008 Status: Equipment Deconned Building Demolished FOLLOWING SLIDES - GEOLOGY - HYDROGEOLOGY - REMEDIAL APPROACH - RESULTS A ┬® AcuityES 2011
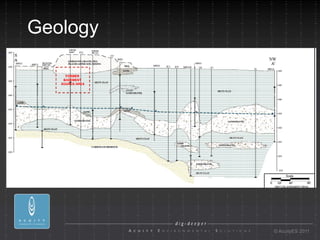
- 5. Geology FORMER BASEMENT SOURCE AREA ┬® AcuityES 2011
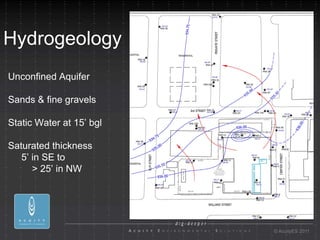
- 6. Hydrogeology Unconfined Aquifer Sands & fine gravels Static Water at 15ÔÇÖ bgl Saturated thickness 5ÔÇÖ in SE to > 25ÔÇÖ in NW ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 7. Soil Impacts Max Cr+6 concentration: 7,900,000 ┬Ág/Kg 3,600,000 ┬Ág/Kg Cr+6 at 12ÔÇÖ bgl Two Adjacent Source Areas 5,400 cubic yards of impact Perched water sand stringers ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 8. Groundwater Impacts On-Site Cr+6 800,000 ┬Ág/L 9,700,000 ┬Ág/L Groundwater CoCs 66,000 sq ft Plume Cr+6, Sb, As, and Ni Offsite Cr+6 at 58,800 ┬Ág/L ┬® AcuityES 2011
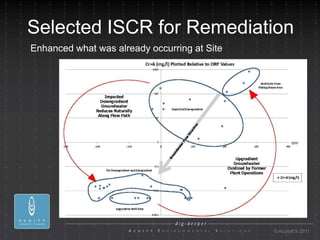
- 9. Selected ISCR for Remediation Enhanced what was already occurring at Site ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 10. Chemical Reductant ÔÇô FeS BENCH TESTED SELECTED ÔÇôFeS ÔÇóFerrous Sulfide Liquid suspension of 7% FeS ÔÇóCaSx FeS - With additional 2% free Sulfide to simulate CaSx ÔÇóSodium Thiosulfate ÔÇóSodium Metabisulfite Nanoscale: 98% crystals <5 microns ÔÇóZero Valent Iron Cation (Iron) & Anion (sulfide) Reaction ÔÇóOrganosulfates 4 H2O + Cr04 2-+ 3 Fe2- + 4 OH- ´âá 3 Fe(OH)3+ Cr(OH)3 (1) 17 H2O + 8 Cr042- + 3 HS- ´âá 3 S + 8 Cr(OH)3 + 12 OH- (2) ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 11. In-Situ Soil Blending GPS Grid Network ÔÇô 10ÔÇÖ x 10ÔÇÖ Deep to 15ÔÇÖ & Shallow to 5ÔÇÖ Dual Axis Blender ÔÇô 15ÔÇÖ Plunge Total Area ÔÇô 130ÔÇÖ x 110ÔÇÖ Computerized Dosing ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 12. In-Situ Soil Blending Dual Axis Blender FeS - 5% admix (15 gals/yd3) ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 13. In-Situ Soil Blending Thorough Mixing to 15ÔÇÖ BGL Note: Cement barrier for uncompaction ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 14. In-Situ Soil Blending Completed in 2 weeks Total FeS = 78,300 gallons Subsequent stabilization with aglime required ┬® AcuityES 2011
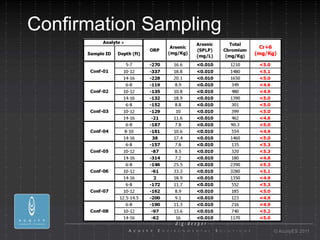
- 15. Confirmation Sampling ┬® AcuityES 2011
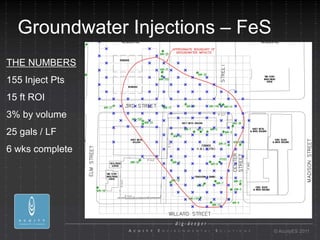
- 16. Groundwater Injections ÔÇô FeS THE NUMBERS 155 Inject Pts 15 ft ROI 3% by volume 25 gals / LF 6 wks complete ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 17. Groundwater Injections Difficult Injections Boulder Fields 6ÔÇÖ caliche Lodgement till ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 18. Groundwater Injections FeS Injection Totes 35,385 gallons injected Rotosonic Drilling Top Down Injection ÔÇô 5ft intervals ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 19. Groundwater Injections Community Sensitivity Required Residential Hours ┬® AcuityES 2011
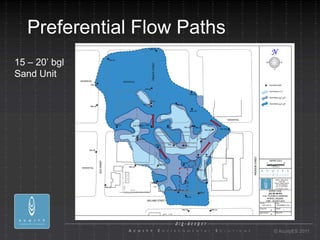
- 20. Preferential Flow Paths 15 ÔÇô 20ÔÇÖ bgl Sand Unit ┬® AcuityES 2011
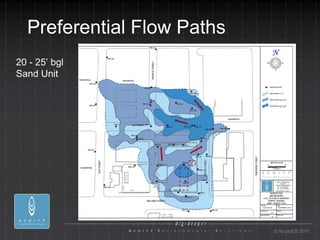
- 21. Preferential Flow Paths 20 - 25ÔÇÖ bgl Sand Unit ┬® AcuityES 2011
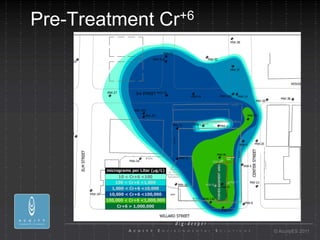
- 22. Pre-Treatment Cr +6 ┬® AcuityES 2011
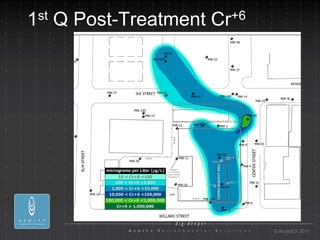
- 23. 1 st Q Post-Treatment Cr +6 ┬® AcuityES 2011
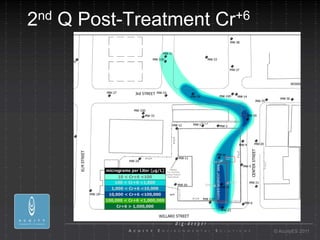
- 24. 2 nd Q Post-Treatment Cr+6 ┬® AcuityES 2011
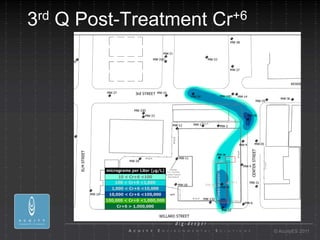
- 25. 3 rd Q Post-Treatment Cr +6 ┬® AcuityES 2011
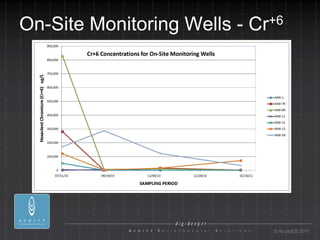
- 26. On-Site Monitoring Wells - Cr+6 ┬® AcuityES 2011
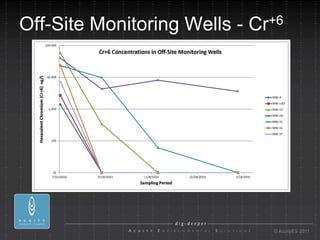
- 27. Off-Site Monitoring Wells - Cr+6 ┬® AcuityES 2011
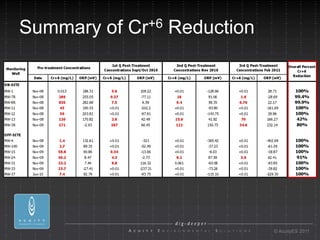
- 28. Summary of Cr+6 Reduction ┬® AcuityES 2011
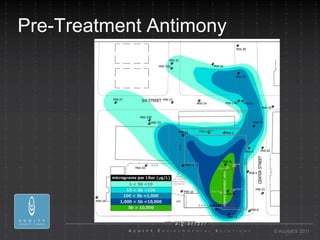
- 29. Pre-Treatment Antimony ┬® AcuityES 2011
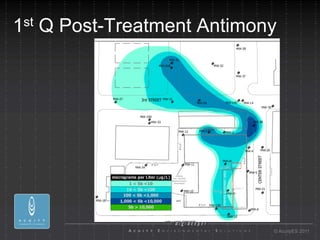
- 30. 1 st Q Post-Treatment Antimony ┬® AcuityES 2011
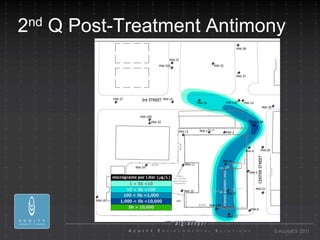
- 31. 2 nd Q Post-Treatment Antimony ┬® AcuityES 2011
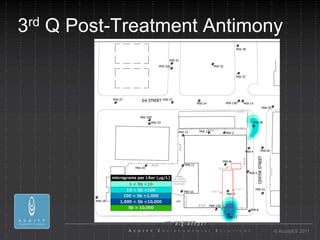
- 32. 3 rd Q Post-Treatment Antimony ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 33. Other Constituents of Concern Nickel ÔÇô off-Site up to 4,100 ┬Ág/L on-Site up to 50,000 ┬Ág/L Same footprint as Antimony Complete 100% Reduction by 1st Quarter Arsenic ÔÇô Overall reduction in pervasiveness. Occurrence generally coincides with Cr+6 ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 34. Lessons Learned 1. Forced to use Rotosonic over direct push - Budget for the unexpected 2. Chemical injection instead of GW recirculation - CanÔÇÖt wear blinders when considering delivery method options for chemicals 3. Agency onboard for the technology - Relationship, communication, education ┬® AcuityES 2011
- 35. QUESTIONS? Thank you!! ┬® AcuityES 2011