Industrial fire , safety and prevention MME 2021.pptx
- 1. INDUSTRIAL FIRE , SAFETY AND PREVENTION ENGR. OCHERI C. TRAINING/ WORKSHOP Dept. of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Date : 19 -23 APRIL 2021 Venue : Nigerian Liquefied Natural Gas ( NLNG) Laboratory
- 3. WHY FIRE TRAINING ïµ Because management care about your safety ïµ Because many people are unnecessarily injured by fire at work each year ïµ Because Fire Risk assessment flagged a need to train staff in Fire Safety
- 4. WHAT IS FIRE? ⢠Fire is a SPECTACULAR example of a FAST chemical reaction between a combustible substance and oxygen accompanied by the evolution of heat
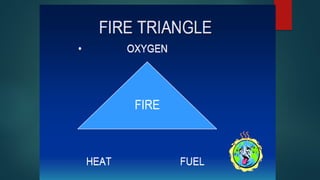
- 5. 3 FIRE REQUIRMENT . ⢠1. Oxygen ⢠2. Fuel ⢠3. A source of energy i.e. HEAT ïµ FIRE TRIANGLE: (HEAT + O2 + IGNITION)
- 7. CAUSES OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠SMOKING: ïµ Litters in factories provides essential fuels in fire accident . Smoking near fuel depot and jerry cans used to transport and store petrol during fuel crises also contribute to INDUSTRIAL FIRE. ïµ CHEMICALS ïµ Lack of adherence to chemical safety ïµ requirements and improper storage
- 8. CAUSES OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠DIRT AND UNTIDINESS ïµ Refuse and process waste are good ïµ kindling for a fire to start or help a fire to expand. ⢠CONTRACTORSâ OPERATIONS ïµ Building and maintenance contractors often use a variety of Equipment, which can produce a great deal of heat ïµ (blowlamps, welding and simple drilling.)
- 9. CAUSES OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠PROCESS HAZARD ïµ A: Faults in process plants leads to: ïµ 1.Overheated machinery bearings and frictional sparks. ïµ 2. Tremendous amount of HEAT. ïµ B: Sparks from cutting and welding tools ïµ C: Lack of regular maintenance
- 10. CAUSES OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS ⢠Flammable solvents of all kinds are both necessary and dangerous in many industrial processes. ⢠With Nigeriaâs peculiar problem of petrol shortages, experience has shown that often this most dangerous of all substances is badly transported and stored.
- 11. CAUSES OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠POOR HOUSE KEEPING ⢠Warehousing inadequate standards . ⢠Improperly stacked goods allow a fire to start unnoticed and also impede fire-fighting operations when eventually detected. ⢠Office waste must be regularly removed. ïµ Cleanliness is particularly essential in an office to avoid simmering files, which can spread undetected
- 12. CAUSES OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠ARSON ⢠This subject has already received substantial publicity in the national press and other media. ⢠Damage by riot is another danger, which can be included in this category. ⢠Bomb Blast/Terrorist Activities
- 13. PHCN: Major cause of FIRE DISASTER in NIGERIA ⢠ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT AND WIRING. ⢠Short circuits, and faults resulting in excess current flow generating heat, which ignites insulation and flammable materials lying nearby. ⢠Broken Strands, loosely fitted plugs, overloaded sockets; improperly secured terminals can cause arcing and sparking. ⢠Deterioration of insulation and wiring leads to ageing, mechanical damage and excessive heat because of overloading. ⢠Unprofessional Alteration and addition to existing installation. ⢠Wiring installed by incompetent persons and not reaching ïµ acceptable standards. ⢠Inferior materials.
- 14. EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠Direct EFFECT: ⢠(a) âno effectâ or near misses ⢠(b) minor injury ⢠(C) major injury ⢠(d) property damage ⢠(e) Business closure
- 15. EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠INDIRECT EFFECTS: refers to the consequence flowing from the direct effect of fire. ⢠(a) for the injured person ⢠* loss of earning or earning capacity ⢠*disrupted family life. ⢠*disrupted personal life, and ⢠*other consequences e.g. pain & suffering
- 16. EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠(b) for the company: ⢠* injury costs ⢠* production loss costs. ⢠* property damage costs. ⢠* reduction in employee morale. ⢠* poor reputation as a result of adverse media ïµ publicity. ïµ â¢ * poor customer relations following adverse media publicity.
- 17. EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠* lost time â supervisors, workers and others. ⢠* product damage cost. ⢠* first aid and medical cost. ⢠* increased employerâs liability premium. ⢠* legal cost, e.g. fines imposed by court, legal representation fees ⢠* cost of changes in practice arising from prosecution or as a result of enforcement action, e.g. prohibition or improvement notice. ⢠* training cost e.g. retraining of injured employee or
- 18. PREVENTION OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠FIRE RISK ASSESMENT ⢠Identify the FIRE HAZARD in our offices. ⢠Identify the PEOPLE who could be at RISK. ⢠ELIMINATE, CONTROL or AVOID the fire hazard. ⢠Ensure that the existing FIRE ïµ SAFETY PROVISION meet up to standard. ⢠Record FINDINGS. ⢠Prepare EMERGENCY PLAN. ⢠REVIEW FRA Periodically.
- 19. PREVENTION OF INDUSTRIAL FIRE ⢠Provision of Fire Extinguishers. ⢠Provision of Information / Training. ⢠Provision of Fire Alarm. ⢠Provision of Fire Escape Route. ⢠Provision of Fire Risk Assessment. ïµ (Yearly)
- 20. CLASSIFICATION OF FIRE ⢠A: Solid material of Organic nature: wood paper & Fabric ⢠B: Flammable liquids: Petrol, diesel etc ⢠C: Gases: Acetylene Butane ⢠D: Metals: Magnesium, Sodium, Aluminum
- 21. CLASSES OF FIRE ïµ EXTINGUISHERS ⢠CO2 CARBON DIOXIDE ⢠COLOUR: BLACK or RED ⢠FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS (faster than foam) ⢠AVAILABLE IN 1KG,3KG, 5KG, 20KG. ⢠RANGE: 2-3MTRS ⢠DISCHARGE TIME: 6â23S
- 22. CLASSES OF FIRE ïµEXTINGUISHERS ïµâ¢ DCP (DRY CHEMICAL POWDER) ïµâ¢ COLOUR: FRENCH BLUE or RED ïµâ¢ LIVE ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT ïµâ¢ AVAILABLE IN 1,2,3,4,6,9, 12, 50, 75KG ïµâ¢ RANGE: 2-8MTS ïµâ¢ DISCHARGE TIME: 6-23S
- 23. CLASSES OF FIRE ïµ EXTINGUISHERS ïµ â¢ H2O (WATER) ïµ â¢ COLOUR: RED ïµ â¢ ORDINARY ïµ COMBUSTIBLE ïµ MATERIAL (wood, ïµ paper & paper) ïµ â¢ 9ltrs=10kg ïµ â¢ RANGE:9LTRS
- 24. CLASSES OF FIRE ïµ EXTINGUISHERS ïµ â¢ FOAM FIRE ïµ EXTINGUISHERS. ïµ â¢ COLOUR: PALE CREAM ïµ â¢ USED FOR EXTINGUISHING ïµ FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS. ïµ â¢ AVAILABLE IN 4.5L & 9L. ïµ â¢ WEIGHS 10-15KG ïµ â¢ RANGE:7-10m
- 25. Fire Extinguishers - Blanket ïµ â¢ Any colour body or label but they are usually red or white ïµ â¢ For use on any type of fire but best on small contained class B fires and people on fire. ïµ â¢ Extinguishes by asphyxiating
- 26. Fire Safety At Home ïµ â¢ Fire works ïµ â¢ Candles, lamps ïµ â¢ Cooking gas/ kerosene stove ïµ â¢ Smoking in bed ïµ â¢ Electrical equipment ïµ â¢ Children playing with matches
- 28. GOOD HOUSEKEEPING ïµ â¢ Good house keeping is essential part of sound management practice. ïµ It benefits efficiency, aids production and it is also good for fire protection. ïµ Well organized and carefully maintained premises are safer from fire.
- 29. GOOD HOUSEKEEPING ïµ The chance of fire breaking out is reduced; should fire occur, it could be more readily controlled. Below is a list of duties, which will serve as a safety aide-memoir to management. ïµ â¢ Cleanliness and tidiness. ïµ â¢ Staff should tidy their personal workplace. ïµ â¢ Combustible materials waste and process should be kept clear of the premises.
- 30. GOOD HOUSE-KEEPING ïµ â¢ Waste with special hazards should be labeled, flammable liquid, paint rags, oily rags. ïµ â¢ Waste containers should be removed from building at the end of each day, or more frequently if necessary. ïµ â¢ Waste awaiting disposal should not be accessible to public. ïµ â¢ Waste burning on site must be controlled and supervised. ïµ â¢ Pipes, beams, trusses, ledges deducting and electric fittings should be regularly cleaned. ïµ â¢ Areas in the building and around must be kept free of accumulated packaging materials and cleaned.
- 31. ACTION: IN CASE OF FIRE ïµ â¢ RAISE THE ALARM ïµ â¢ CALL SECURITY ON EXT. 2727 or 2999 ïµ â¢ ATTACK THE FIRE (EXTINGUISHERS) ïµ â¢ EVACUATE THE BUILDING
- 32. P.A.S.S. PRINCIPLE (How to use an extinguisher) ïµ â¢ P= PULL THE PIN ïµ â¢ A= AIM AT BASE OF FIRE. ïµ â¢ S= SQUEEZE THE LEVER. ïµ â¢ S= SWEEP THE AFFECTED ïµ AREA FROM SIDE TO SIDE
- 33. ïµ GENERAL RULE FOR FIGHTING FIRE ïµ â¢ SOUND THE ALARM. ïµ â¢ CALL SECURITY- ?????????( What is the Security Number???) ïµ â¢ ENSURE YOU SELECT THE RIGHT EXTINGUISHER. ïµ â¢ RE-ASSESS THE FIRE. (gas cylinders, chemicals, fuel) ïµ â¢ KEEP ESCAPE ROUTE BEHIND YOU (tackle the fire from furthest distance possible.) ïµ â¢ NEVER LET FIRE GET BETWEEN YOU AND YOUR EXIT. ïµ â¢ CONSIDER THE EFFECT OF SMOKE. ïµ â¢ IF YOU ARE IN DOUBT STOP, CLOSE DOOR AND GET
- 35. ïµINTRODUCTION ⢠Industrial Fire Safety is the set of practices intended to reduce the destruction caused by fire. ⢠Industrial Fire Safety measures include those that are intended to prevent ignition of an
- 36. What is Industrial Fire Safety? ïµ Industrial fire safety is primarily a management activity which is concerned with ïµ Reducing ïµ Controlling & ïµ Eliminating fire accident from ïµ the industries or industrial units.
- 37. Causes of Industrial Fire Accidents ⢠Unsafe conditions ïµ The job itself ïµ Psychological conditions ïµ Machinery & Equipment ⢠Unsafe Acts ⢠Miscellaneous Causes
- 38. Common Causes For Fire Hazards In Industries ⢠Electrical systems that are overloaded, resulting in hot wiring or connections, or failed components ⢠Combustible storage areas with insufficient protection ⢠Combustibles near equipment that generates heat, flame, or sparks ⢠Candles and other open flames ⢠Smoking (Cigarettes, cigars, pipes, lighters, etc.) ⢠Equipment that generates heat and utilizes combustible materials
- 39. Flammable liquids and aerosols ⢠Flammable solvents (and rags soaked with solvent) placed in enclosed trash cans ⢠Fireplace chimneys not properly or regularly cleaned ⢠Electrical wiring in poor condition ⢠Leaking Batteries ⢠Personal ignition sources - matches, lighters ⢠Electronic and electrical equipment
- 40. Significance of Industrial Fire Safety ïµ Industrial fire hazards causes a great loss to both the ïµ Employer & Employee, thatâs it is having importance ïµ Cost of compensation ïµ Cost of medical-aid ïµ Cost of training a new worker ïµ Cost of the lost time ïµ Cost of investigation ïµ Cost of supervision & inspections ïµ Cost to the Govt. in terms of factory inspectors, &
- 41. ïµ Cost of spoilage of materials ïµ Cost of the damage of machinery ïµ Cost of cost of wages payable during injury ïµ Cost of loss of confidence ïµ Cost of loss to the worker and his family
- 42. Objectives of Industrial Fire Safety ïµ ï¨ To prevent fire accidents in the plant by reducing the fire hazard to minimum. ïµ To eliminate fire accident caused work stoppage and lost production. ïµ To achieve lower workmenâs compensation, insurance rates and reduce all other direct and indirect costs of fire accidents. ïµ To prevent loss of life, permanent disability and the loss of income of worker by eliminating causes of fire accidents. ïµ To evaluate employeeâs confidence by promoting safe work place and good working condition ïµ To educate all members of the organization in continuous state of safety mindless and to make supervision competent and intensely safety minded.
- 43. Measures To Ensure Industrial Fire Safety ⢠Fire Safety Policy ⢠Fire Safety Committee ⢠Fire Safety Engineering ⢠Fire Safety Education & Training
- 44. Four E's of Fire Safety ⢠Engineering: i.e. safety at the design, equipment installation stage. ⢠Education: i.e. education of employees in fire safety practices. ⢠Enlistment: i.e. it concerns the attitude of the employees ïµ and management towards the programmed and its purpose. This necessary arose the interest of employees in fire accident prevention and safety consciousness.
- 45. Safety Inspection Procedures ïµ ï Safety audit â A safety audit subjects each area of a companyâs activity to a systematic critical examination with the object of minimizing loss. ïµ ï Safety survey- A safety survey is a detailed examination in depth of a narrower field of activity. ïµ ï Safety inspection- ï§ A routine scheduled inspection of a unit or department, which may be ï§ carried out by someone ( may be a fire safety representative ) from within the unit, possibly
- 49. Conclusion ⢠Over time, an increased understanding of the many factors that contribute to the risk of fire has led to positive developments in the fire protection of industrial structures. Improvements in public fire protection systems and services, as well as increased use of private active or passive systems through fire- protection and loss-control engineering, has meant an overall decrease in the cost of industrial fire hazards. ïµ A discussion of the factors affecting insurance premium
- 50. ïµThank you for attending and listening