Interoperability Requirements for a Sustainable Component to Support Management and Sharing of Digital Resources
- 1. EFEPLE 2011 X X X Interoperability Requirements for a Sustainable Component to Support Management and Sharing of Digital Resources Martin Memmel Knowledge Management Group DFKI GmbH martin.memmel@dfki.de
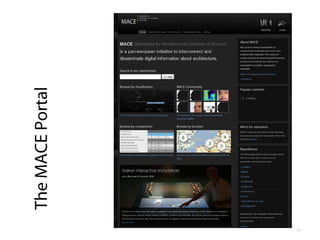
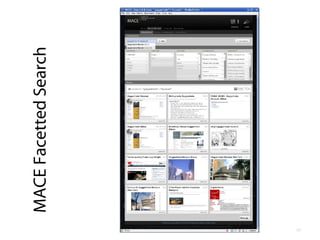
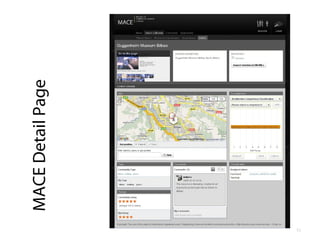
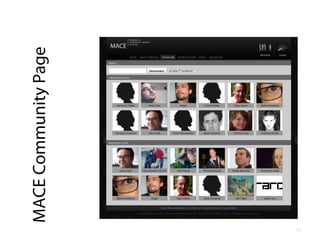
- 2. EFEPLE 2011 How we've built an open, generic and adaptable resource sharing environment that survived (implications for PLEs: up to you!) Martin Memmel Knowledge Management Group DFKI GmbH martin.memmel@dfki.de
- 3. images documents (bmp, gif, jpg, png, tif, ŌĆ”) (pdf, odt, odp, sxw, doc, ppt, ŌĆ”) videos (avi, mpeg, mov, ŌĆ”) web pages audio (aac, mp3, ŌĆ”)
- 4. Key problems ŌŚÅ Heterogeneous tools for specific resource types ŌŚÅ Limited possibilites to integrate with other tools ŌŚÅ Only basic means to organise contributions ŌŚÅ Not instantiable ŌŚÅ No means to adapt to specific scenarios ŌŚÅ Support for (future) scenarios within PLEs?
- 5. How to ensure sustainability?
- 6. A comprehensive approach is needed ŌŚÅ Contribute arbitrary resources ŌŚÅ Manage arbitrary resources ŌŚÅ Share arbitrary resources ŌŚÅ Exchange of information! ŌŚÅ Adaptable for different scenarios!
- 8. Interoperability is the ability of two or more systems or components to exchange information and to use the information that has been exchanged. [IEEE, 1991]
- 9. Where to consider interoperability? ŌŚÅ Selection of supported application scenarios ŌŚÅ Resource types to be supported ŌŚÅ Metadata to be used ŌŚÅ Interfaces offered to users and other systems
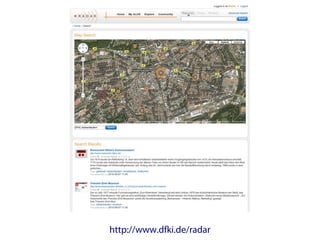
- 10. Supported Application Scenarios [http://lsdis.cs.uga.edu/projects/glycomics/report/Report2006.html]
- 11. Resources images (bmp, gif, jpg, png, tif, ŌĆ”) documents (pdf, odt, odp, sxw, doc, ppt, ŌĆ”) videos (avi, mpeg, mov, ŌĆ”) web pages audio (aac, mp3, ŌĆ”)
- 12. Incorporation of resources ŌŚÅ Contribution of new / not yet accessible resources ŌŚÅ Integration of existing resources ŌĆō Maintenance issues ŌĆō Memory requirements ŌĆō Legal concerns ŌåÆ Repository and Refactory!
- 13. Metadata
- 14. Wittgenstein ŌĆśDie Bedeutung eines Wortes ist sein Gebrauch in der SpracheŌĆÖ (ŌĆśThe meaning of a word is its use in the languageŌĆÖ) Transferred into the world of (digital) resources: ŌĆśThe meaning of a resource is its use in the communityŌĆÖ
- 15. Subjectivity and diversity ŌŚÅ No one-size-fits-all solutions ŌŚÅ Scenario-dependent metadata generation ŌŚÅ Human generated metadata ŌŚÅ Incorporation of potentially any kind of metadata
- 16. Metadata interoperability ŌŚÅ Using standards ŌŚÅ Extensibility ŌŚÅ Modularity ŌŚÅ Refinements ŌŚÅ Multilingualism ŌŚÅ Machine-processability
- 17. Interfaces
- 18. Interfaces ŌĆō Access by systems ŌŚÅ Low technical barriers for system usage ŌĆō Technical environments ŌĆō Minimal installation efforts ŌŚÅ Low conceptual barriers for system usage ŌŚÅ Access to potentially any data and functionalities ŌĆō Complex functionalities, mash-ups
- 19. User interfaces ŌŚÅ Offering access to data / functionalities in usual contexts and applications ŌĆō Services, Widgets, ŌĆ” ŌŚÅ Multilinguality ŌŚÅ Adaptability
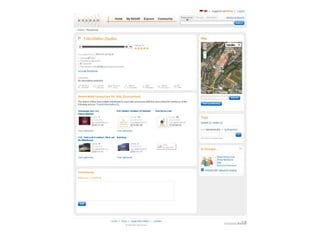
- 20. http://aloe-project.de Sample infrastructure: ALOE ...how did it change and survive?
- 21. What is ALOE? ALOE is a generic infrastructure that allows ŌŚÅ supporting access to digital resources by means of social media technologies ŌŚÅ integrating social media technologies also in existing, especially traditional environments with no or only few interaction possibilities
- 25. Information Exchange, Interfaces
- 26. Web Service API
- 27. Alternative: ALOE-XML <resource> <visibility>public</visibility> <title>Skyscrapers of glass and the curtain wall</title> <license></license> <description>Skyscrapers of glass and the curtain wall</description> <uri>http://winds-app.fit.fraunhofer.de/cgi- bin/WebObjects/windsoai.woa/wa/showContent?id=11647.lo</uri> <tags>skyscrapers curtain_wall Mies_van_der_Rohe winds mace </tags> <sharetogroups> <group>tmp</group> </sharetogroups> </resource>
- 28. Feeds
- 30. OAI Target
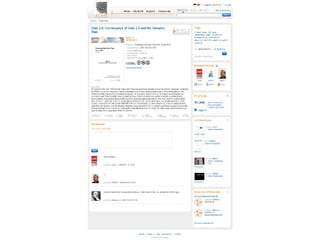
- 31. Bookmark Export
- 32. CAM Feedlet
- 34. Widgets
- 35. Mobile Frontend
- 36. ALOE Resource Metadata Individual Metadata [1..Ōł×] Classification Tag [0..Ōł×] [0..Ōł×] Basic Metadata [1] Associated Comment Metadata [0..Ōł×] [0..Ōł×] Collection Rating [0..Ōł×] [0..Ōł×] Group Usage [0..Ōł×] Metadata [1]
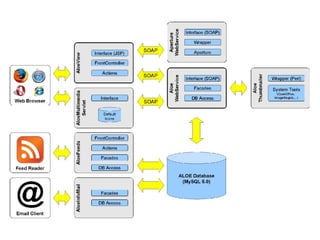
- 39. ALOE ŌĆō Used Technologies ŌŚÅ Implemented in Java (1.5), deployed in the Apache Tomcat (6.0) servlet container ŌŚÅ GUI: Realized with JSP using J2EE Design Patterns ŌŚÅ Web Service Interface: Functionalities are accessible via a SOAP/REST API realized with Apache Axis2 ŌŚÅ Storage of resources and metadata in a MySQL data base (5.0)
- 41. Evolvability for artifacts is the capacity of the systems, organizations and networks producing them to give rise to adaptive variants that flexibly meet changing requirements over the course of long-term change. [Nehaniv et al., 2006]
- 42. Requirements? Environments? ŌŚÅ What's the ecosystem? ŌŚÅ What does surviving mean? ŌĆō Active users, developers ŌŚÅ In which way are resources finite? ŌĆō Developers, time, infrastructure
- 55. Conclusions ŌŚÅ Realise a concrete solution ŌĆō but always try to be as generic as possible ŌŚÅ Try to be independent ŌŚÅ Be open, don't build another silo ŌŚÅ Think carefully about what is your core, and what are your branch-specific adaptations ŌŚÅ Build tools for setup and deployment ŌŚÅ Take your time for refactoring ŌŚÅ Don't trust your memory, write down stuff
- 56. Thanks for listening! ALOE: http://aloe-project.de MACE: http://www.mace-project.eu RADAR: http://www.dfki.de/radar mailto: memmel@dfki.de








![Interoperability is the ability of two or more
systems or components to exchange
information and to use the information
that has been exchanged.
[IEEE, 1991]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110330efeple-110402063527-phpapp02/85/Interoperability-Requirements-for-a-Sustainable-Component-to-Support-Management-and-Sharing-of-Digital-Resources-8-320.jpg)

![Supported Application Scenarios
[http://lsdis.cs.uga.edu/projects/glycomics/report/Report2006.html]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110330efeple-110402063527-phpapp02/85/Interoperability-Requirements-for-a-Sustainable-Component-to-Support-Management-and-Sharing-of-Digital-Resources-10-320.jpg)


















![ALOE Resource Metadata
Individual
Metadata [1..Ōł×]
Classification Tag
[0..Ōł×] [0..Ōł×]
Basic Metadata [1]
Associated Comment
Metadata [0..Ōł×] [0..Ōł×]
Collection Rating
[0..Ōł×] [0..Ōł×]
Group Usage
[0..Ōł×] Metadata [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110330efeple-110402063527-phpapp02/85/Interoperability-Requirements-for-a-Sustainable-Component-to-Support-Management-and-Sharing-of-Digital-Resources-36-320.jpg)



![Evolvability for artifacts is the capacity of
the systems, organizations and networks
producing them to give rise to adaptive
variants that flexibly meet changing
requirements over the course of long-term
change.
[Nehaniv et al., 2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110330efeple-110402063527-phpapp02/85/Interoperability-Requirements-for-a-Sustainable-Component-to-Support-Management-and-Sharing-of-Digital-Resources-41-320.jpg)