Introduction to hacking
- 1. Introduction to Ethical Hacking By Nitish Mehta (Illuminative works)
- 2. What we do ? 2 Illuminative works
- 3. Services we Provide ILLUMINAITVE WORKS SERVICES PHP and APPILCATION Ruby On Rails SEO Frameworks DEVELOPMENT 3 Illuminative works
- 4. Php and ItŌĆÖs Frameworks ILLUMINAITVE WORKS services PHP and Frameworks Wordpress Magento Joomla Zend 4 Illuminative works
- 5. ILLUMINAITVE WORKS SERVICES TRAINING PHP and Ruby On Rails Frameworks APPILCATION SEO ONLINE OFFLINE DEVELOPMENT
- 6. Types of training TRAINING Courses ONLINE Workshops Blogs Webcast Webinars 6 Illuminative works
- 7. Workshop and training on Application ŌĆóMobile Application development ŌĆóFacebook application development development ŌĆóTwitter application development ŌĆóEthical Hacking level -1 Ethical Hacking ŌĆóHack the Hacker (method to trackback to hacker) ŌĆóHACKERS ON CHARITY (Coming soon ) Website ŌĆóPhp ŌĆóWordpress development ŌĆóJoomla Electronics and ŌĆóElectric Circuit and PCB designing. ŌĆóAdvanced 8051 Architecture, Programming & communication Interfacing 7 Illuminative works
- 8. How can you learn from us? ’üĮ Series of Webinars. ’üĮ Watch webcast. ’üĮ Blogs ’üĮ Workshop ’üĮ Hack with hackers 8 Illuminative works
- 9. What we will discuss today ? 1. Understanding hacker objectives 2. Outlining the differences between ethical hackers and malicious hackers/crackers 3. Examining the ethical hacking processes. 4. Starting the ethical hacking process 9 Illuminative works
- 10. Who are Hackers ? ’üĮ Recently, hacker has taken on a new meaning ŌĆö ’üĮ who maliciously breaks into systems for personal gain. ’üĮ Technically, these criminals are crackers ’üĮ They modify, delete, and steal critical information, often making other people miserable ’üĮ The good-guy (white-hat) hackers donŌĆÖt like being in the same category as the bad-guy (black-hat) hackers. 10 Illuminative works
- 11. Types of Hacker ’üĮ People Categorize Hacker into many different ways ’üĮ But everyone agrees that there is 3 basic type of hacker Black Hat White Hat Grey Hat ŌĆó Individual with ŌĆó Individual ŌĆó They work for extraordinary Professional defensive and computing skills Hacker offensive at their ŌĆó Does destructive ŌĆó Used for own will work always Defensive Purpose 11 Illuminative works
- 12. Types of Ethical Hacker Former ŌĆó Reformed crackers ŌĆó First Hand Experienced Black Hats ŌĆó Less credibility ŌĆó Independent security Consultants (can White Hats be group too) ŌĆó Claim to be knowledgeable about black hat activities Consulting ŌĆó Part of ICT firms. ŌĆó Certified professionals. Firms ŌĆó Good credibility. 12 Illuminative works
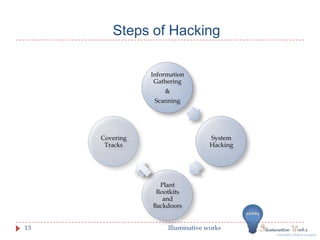
- 13. Steps of Hacking Information Gathering & Scanning Covering System Tracks Hacking Plant Rootkits and Backdoors 13 Illuminative works
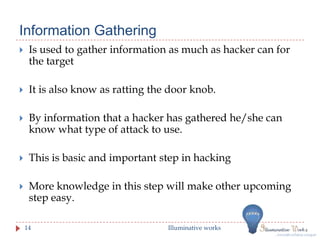
- 14. Information Gathering ’üĮ Is used to gather information as much as hacker can for the target ’üĮ It is also know as ratting the door knob. ’üĮ By information that a hacker has gathered he/she can know what type of attack to use. ’üĮ This is basic and important step in hacking ’üĮ More knowledge in this step will make other upcoming step easy. 14 Illuminative works
- 15. Scanning ’üĮ Scanning refers to pre attack phase where a hacker scan the network to find / gather information about network ’üĮ Scanning includes ’üĮ Network scan ’üĮ Port scan ’üĮ Venerability scan , ect ’üĮ A Hacker can get some high venerability which can give access easily. 15 Illuminative works
- 16. System Hacking ’üĮ Also know as gaining access ’üĮ The venerability that has been found during Information Gathering and scanning is been exploited here ’üĮ There can be many exploits with different level of threats ’üĮ Some of the threats that we are going to discuss are ’üĮ Sql Injection ’üĮ XXS cross site scripting ’üĮ LFI , RFI 16 Illuminative works
- 17. Backdoor and rootkits ’üĮ It is also called as maintaining access. ’üĮ This is done so a hacker can have all type of access for next time without bypassing or breaking the security ’üĮ For this many stuffs are used ’üĮ Trojans ’üĮ Backdoors ,rootkits ’üĮ Shells , ect 17 Illuminative works
- 18. Covering Tracks ’üĮ This is smallest and most important part in Hacking ’üĮ If this is not done then a Hacker can easily get track back. ’üĮ This is step were hacker removes all his/her identity or tracks ’üĮ History files : ’üĮ sh : .sh_history ’üĮ csh : .history ’üĮ ksh : .sh_history ’üĮ bash: .bash_history ’üĮ zsh : .history ’üĮ Backup Files : ’üĮ dead.letter, *.bak, *~ 18 Illuminative works
- 19. What does Ethical Hacker do ? ’üĮ They basically ask themselves following question ’üĮ What does a hacker/ cracker sees in the target ? ’üĮ Information gathering ’üĮ Scanning ’üĮ What can he do with that vulnerability ? ’üĮ Gaining Access ’üĮ Maintaining it ’üĮ System hacking ’üĮ Has anyone already noticed the vulnerability ? ’üĮ Maintaining Access ’üĮ Footprinting 19 Illuminative works
- 20. What is vulnerability Research ? ’üĮ Discovering and designing vulnerability in any system is called vulnerability. ’üĮ It can be classified in two ways ’üĮ Threat Level ’üĮ Low ’üĮ Medium ’üĮ High ’üĮ Exploit Range ’üĮ Local ’üĮ Remote 20 Illuminative works
- 21. Why a Ethical hacker need to have vulnerability ? ’üĮ To identify correct network vulnerability ’üĮ Protect network form being attack ’üĮ To get information that helps to prevent security problems ’üĮ To gather information about virus/ worms/ Trojan ’üĮ To find weakness in n/w and inform it to admin ’üĮ To know how to recover from such attacks 21 Illuminative works
- 22. From were you can research ? ’üĮ There are several websites from where you can stay up dated and can research ’üĮ Mine favourite are ’üĮ Packet storm : www.packetstormsecurity.com ’üĮ Security focus: www.securityfocus.com ’üĮ SANS internet storm : http://isc.sans.edu ’üĮ Security magazine : www.securitymagazine.com ’üĮ Exploit-db: www.exploit-db.com 22 Illuminative works
- 23. How can you conduct Ethical Hacking ? Talk to your client on the needs of testing Prepare NDA document and ask them to sign them Prepare a team of Ethical Hacker and create a schedule for testing Conduct the test Analyze the result and prepare the report Deliver the report to the client 23 Illuminative works
- 24. Process of Ethical Hacking Formulating the Plan specific plan Risk involve Venerability management Selecting Tools Adequate Reports on presented to managers Licensed/OS Tools documentation vulnerabilities or nontechie types Executing the plan narrow your focus Search Internet Narrow your scope Perform the attacks, with a more critical eye 24 Illuminative works
- 25. How many times we should do ? ’üĮ Make sure your systems are secure. ’üĮ New hacker exploits and security vulnerabilities are regularly uncovered ’üĮ At any time , everything can change ’üĮ Software upgrades ’üĮ Adding computer systems ’üĮ Applying patches. ’üĮ Thus regularly testing should be done. 25 Illuminative works
- 26. Future webinar dates ŌĆó Information Gathering & Scanning Methodologies- 2-2-12 NitishMehta ŌĆó Google Hacking ŌĆō Nitish Mehta 16-12-12 ŌĆó SQL injection attacks -Nitish Mehta / Naveen Badoni 6-1-13 ŌĆó Facebook and Email Hacking- Arif Ali Khan 20-1-13 ŌĆó Social Engineering-Arif Ali Khan / Nitish Mehta 2-2-13 26 Illuminative works
- 27. Q/A Round Thank You Nitish Mehta (Illuminative works ŌĆōCEO and Founder) nitish@illuminativeworks.com Facebook.com/illuminativeworks 27 Illuminative works
Editor's Notes
- #15: As name suggest that this phase is used to gather information