Karma Data Modeling
2 likes983 views
Karma data integration tool: modeling person, organizations, positions, publication data and generating RDF (N-Triples files).
1 of 16
Download to read offline















Recommended
November 19, 2014 NISO Virtual Conference: Can't We All Work Together?: Inter...



November 19, 2014 NISO Virtual Conference: Can't We All Work Together?: Inter...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Ěý
Distributed Person Data
Violeta Ilik, Digital Innovations Librarian, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Galter Health Sciences Library, ChicagoWhat do MARC, RDF, and OWL have in common?



What do MARC, RDF, and OWL have in common?Violeta Ilik
Ěý
It is understood that in the current library ecosystem, catalogers must be willing to adapt to new semantic web environment while keeping in mind the crucial library mission – providing efficient access to information. How could catalogers transform their jobs in order to enable library users to retrieve information more effectively in the age of semantic web?
Researchers have argued that catalogers have the fundamental skills to successfully work with and repurpose the metadata originally created for use in traditional library systems by utilizing various programing languages. In the new environment their jobs will require new tools and new systems but the basic skills of organization of information, knowledge of commonly used access points, and an ever growing knowledge of information technology systems will still be the same. This presentation will stress the role of catalogers in bringing the data silos down, merging, augmenting, and creating interoperable data that can be used not just in library specific systems, but in various other systems. Catalogers’ indispensable knowledge of controlled vocabularies, authority aggregators, metadata creation, metadata reuse, taxonomies, and data stores makes it all possible.
We will demonstrate how catalogers’ knowledge can be leveraged to design an institutional repository and/or a researchers profiling system, create semantic web compliant data, create ontologies, utilize unique identifiers, and (re)use data from legacy systems.Integrating with others: Stable VIVO URIs for local authority records; linkin...



Integrating with others: Stable VIVO URIs for local authority records; linkin...Violeta Ilik
Ěý
Integrating with others: Stable VIVO URIs for local authority records; linking to VIAF; ORCID organizational identifiers; W3C Dataset ontology work by Melissa Haendel & Violeta Ilik, VIVO Implementation Fest, Durham NC, March 20, 2014
Karma is a tool! Managing your Data



Karma is a tool! Managing your DataVioleta Ilik
Ěý
Managing Your Data Flows: Architecture and Data Provenance For Your Institution WorkshopManaging your DataStarting from scratch – building the perfect digital repository



Starting from scratch – building the perfect digital repositoryVioleta Ilik
Ěý
By establishing a digital repository on the Feinberg School of Medicine (FSM), Northwestern University, Chicago campus, we anticipate to gain ability to create, share, and preserve attractive, functional, and citable digital collections and exhibits. Galter Health Sciences Library did not have a repository as of November 2014. In just a few moths we formed a small team that was charged at looking to select the most suitable open source platform for our digital repository software. We followed the National Library of Medicine master evaluation criteria by looking at various factors that included: functionality, scalability, extensibility, interoperability, ease of deployment, system security, system, physical environment, platform support, demonstrated successful deployments, system support, strength of development community, stability of development organization, and strength of technology roadmap for the future. These factors are important for our case considering the desire to connect the digital repository with another platform that was an essential piece in the big FSM picture – VIVO. VIVO is a linked data platform that serves as a researchers’ hub and which provides the names of researchers from academic institutions along with their research output, affiliation, research overview, service, background, researcher’s identities, teaching, and much more.Modeling Data with Karma – Data Integration Tool



Modeling Data with Karma – Data Integration ToolVioleta Ilik
Ěý
Modeling tabular data for upload in an open source semantic web application VIVO (version 1.6 and 1.7).It Takes a Village to Grow ORCIDs on Campus: Establishing and Integrating Uni...



It Takes a Village to Grow ORCIDs on Campus: Establishing and Integrating Uni...Violeta Ilik
Ěý
This presentation describes the integration of ORCID identifiers into the open sourceĚýVireoĚýelectronic theses and dissertations (ETD) workflow, the university's digital repository, and the internally-used VIVO profile system.Ěý
Presented at Texas Conference on Digital Libraries (TCDL) 2014:
https://conferences.tdl.org/tcdl/index.php/TCDL/TCDL2014/schedConf/programThe Case for Stable VIVO URIs



The Case for Stable VIVO URIsVioleta Ilik
Ěý
The document discusses the need for stable VIVO URIs to link and disambiguate researchers across institutions and scholarly systems. It notes challenges like multiple names and institutional affiliations over time. The authors propose registering VIVO person URIs with services like OCLC to make them persistent even if local VIVO systems change. Doing so along with sameAs links between VIVO profiles and ORCID/VIAF IDs could maximize integration and discovery of scholarly contributions and expertise across different researcher profiling platforms.Visualizing data



Visualizing dataVioleta Ilik
Ěý
This document discusses using Viewshare, an open-source visualization platform, to visualize different types of data including a MODS XML file of a collection, a scientific dataset ingested as an XSL file, and data about an academic community ingested as an XSL file. It also discusses visualizing a dataset from a cross-sectional study of E. coli bacteria including visualizing the raw data, human-readable data, and a visualization of the dataset. Finally, it discusses visualizing academic communities using Texas A&M University's Computer Science and Engineering department as an example and lessons learned about better data integration through linking data.Access to Graduate Scholarship in VIVO: Establishing Connections and Tracing ...



Access to Graduate Scholarship in VIVO: Establishing Connections and Tracing ...Violeta Ilik
Ěý
This document discusses how Texas A&M University Libraries uses VIVO to connect researchers across disciplines by including graduate scholarship like theses and dissertations. It describes how theses are pushed from VIREO, the university's thesis and dissertation repository, to both VIVO and ORCID to establish academic lineages and connections. By enhancing disciplinary family trees through works and their derivatives in VIVO, researchers can better trace the impact of ideas over time.Crediting informatics and data folks in life science teams



Crediting informatics and data folks in life science teamsCarole Goble
Ěý
Science Europe LEGS Committee: Career Pathways in Multidisciplinary Research: How to Assess the Contributions of Single Authors in Large Teams, 1-2 Dec 2015, Brussels
The People Behind
Research Software
crediting from the informatics, technical point of view
NISO Webinar: Authority Control: Are You Who We Say You Are?



NISO Webinar: Authority Control: Are You Who We Say You Are?National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Ěý
About the Webinar
In the world of authority control, it is a bit of an alphabet soup of acronyms. ORCID (Open Researcher and Contributor ID), which is a system to uniquely identify scientific and other academic authors; ISNI (International Standard Name Identifier), which identifies the public identities of contributors to media content such as books, television programs, and newspaper articles; and VIAF (Virtual International Authority File) a system that combines multiple name authority files into a single authority service, hosted by OCLC, all have their place when discussing identifiers for authority control.
Identity issues and disambiguating authors, researchers, other content creators, and their institutional affiliations are crucial as we move into a world of linked data. In this webinar, presenters will cover the implications and differences between ORCID, ISNI, and VIAF, what is the proper use of each, and some of the benefits that come with using authority files and making that information available on the Web.
Agenda
Introduction
Todd Carpenter, Executive Director, NISO
ORCID identifiers in research workflows
Simeon Warner, Director of Repository Development, Cornell University Library
ISNI: How It Works And What It Does
Laura Dawson, Product Manager, ProQuest
VIAF and its Relationships with Other Files
Thomas Hickey, Chief Scientist, OCLCScholars@Cornell: Visualizing the scholarly record



Scholars@Cornell: Visualizing the scholarly recordMuhammad Javed
Ěý
As stewards of the scholarly record, Cornell University Library is developing a data and visualization service known as Scholars@Cornell with the goal of improving the visibility of Cornell research and enabling discovery of explicit and latent patterns of scholarly collaboration. We provide aggregate views of data where dynamic visualizations become the entry points into a rich graph of knowledge that can be explored interactively to answer questions such as: Who are the experts in what areas? Which departments collaborate with each other? What are patterns of interdisciplinary research? And more. Key components of the system are Symplectic Elements to provide automated citation feeds from external sources such as Web of Science, the Scholars "Feed Machine" that performs automated data curation tasks, and the VIVO semantic linked data store. The new "VIZ-VIVO" component bridges the chasm between the back-end of semantically rich data with a front-end user experience that takes advantage of new developments in the world of dynamic web visualizations. We will demonstrate a set of D3 visualizations that leverage relationships between people (e.g., faculty), their affiliations (e.g., academic departments), and published research outputs (e.g., journal articles by subject area). We will discuss our results with two of the initial pilot partners at Cornell University, the School of Engineering and the Johnson School of Management.Agenda's for Preservation Research



Agenda's for Preservation ResearchMicah Altman
Ěý
Dr Micah Altman presented this at the Society for American Archivists 2016 Research Forum.
In this presentation I discuss some key potential topics for preservation research in the next five years. LKG Editor Dev



LKG Editor DevSimeon Warner
Ěý
A presentation of LD4P2 work on linked data editor development and lookup services in particular. Presented at US2TS, 11-13 March, 2019Linked Data Principles and RDF: University of Florida Libraries, BIBFRAME Wor...



Linked Data Principles and RDF: University of Florida Libraries, BIBFRAME Wor...Allison Jai O'Dell
Ěý
Part of a monthly series of "tech talks" given for the University of Florida Libraries, BIBFRAME Working GroupLinking Data, Linking People



Linking Data, Linking PeoplefereiraJ
Ěý
This document discusses linking data and people through ontologies and semantic web technologies. It provides examples of using RDF, FOAF, and Linked Data principles to describe people and relationships. It also showcases several applications that utilize these technologies including Vivo, a semantic publishing platform, and domain-specific knowledge environments.Asis&t webinar people directories access innovations



Asis&t webinar people directories access innovationsBert Carelli
Ěý
This document discusses using taxonomies to create people directories and author networks. It outlines Access Innovations' background in building taxonomies and their data harmony software. Taxonomies can play a role in developing better resources about people by linking entities like authors, publications, and institutions. This allows for knowledge discovery and collaboration through detailed author profiles, visualizing co-author networks, and integrating identity into publisher systems. Standards like VIAF, ORCID, and Project VIVO aim to connect names and publications across repositories through semantic linking of author data.Organizational Identifiers - Crossref LIVE Hannover



Organizational Identifiers - Crossref LIVE HannoverCrossref
Ěý
Vanessa Fairhurst talks about the Organization ID Project, now known as 'Onyar'. Presented at Crossref LIVE local Hannover, June 27th 2018. Crossref LIVE: The Benefits of Open Infrastructure (APAC time zones) - 29th O...



Crossref LIVE: The Benefits of Open Infrastructure (APAC time zones) - 29th O...Crossref
Ěý
In November 2020, Crossref formally adopted the “Principles of Open Scholarly Infrastructure” (POSI). POSI is a list of sixteen commitments that will now guide the board, staff, and Crossref’s development as an organisation into the future.
This webinar took place on the 29th October at 03:00 PM AEST (UTC+10) and covered:
- What are the Principles of Open Scholarly Infrastructure (POSI) and why are they needed?
- Why POSI is important for Crossref and how it will help realise the Research Nexus
- Open metadata and infrastructure services from Crossref
Presented in English by Cameron Neylon, Professor of Research Communications, Centre for Culture and Technology, at Curtin University, Amanda Bartell, Head of Member Experience at Crossref, and Vanessa Fairhurst, Community Engagement Manager at Crossref.
An Introduction to EZID



An Introduction to EZIDUniversity of California Curation Center
Ěý
EZID makes it simple for researchers and others to obtain and manage long-term identifiers for their digital content. The service can create and resolve identifiers, and it also allows entry and maintenance of information about the identifier (metadata). This presentation was given as part of a webinar series.Dash: data sharing made easy



Dash: data sharing made easyUniversity of California Curation Center
Ěý
To facilitate data sharing from within the University of California system and beyond, the University of California Curation Center (UC3) is developing a new ingest and discovery layer for our data curation service, Dash. Dash uses the Merritt repository for preservation and a self-service overlay layer for submission and discovery of research datasets. The new overlay– dubbed Stash (STore And SHare)– will feature an enhanced user interface with a simple and intuitive deposit workflow, while still accommodating rich metadata. Stash will enable individual scholars to upload data through local file browse or drag-and-drop operation; describe data in terms of scientifically-meaning metadata, including methods, references, and geospatial information; identify datasets for persistent citation and retrieval; preserve and share data in an appropriate repository; and discover, retrieve, and reuse data through faceted search and browse. Stash can be implemented in conjunction with any standards-compliant repository that supports the SWORD protocol for deposit and the OAI-PMH protocol for metadata harvesting. Stash will feature native support for the DataCite or Dublin Core metadata schemas, but is designed to accommodate other schemas to support discipline-specific applications. By alleviating many of the barriers that have historically precluded wider adoption of open data principles, Stash empowers individual scholars to assert active curation control over their research outputs; encourages more widespread data preservation, publication, sharing, and reuse; and promotes open scholarly inquiry and advancement.BibBase Linked Data Triplification Challenge 2010 Presentation



BibBase Linked Data Triplification Challenge 2010 PresentationReynold Xin
Ěý
The document summarizes BibBase Triplified, a system that publishes bibliographic data from BibTeX files as structured data on the semantic web. It takes BibTeX files maintained by scientists, detects and resolves duplicates, and publishes the data as HTML pages and RDF triples. It also links entries to external datasets like DBLP and DBpedia. As of September 2010, the system had over 4,500 publications and 100 active users. Future work includes improving duplicate detection, linking to more external sources, and broadening the user base.20131029 Community Outreach Report



20131029 Community Outreach ReportORCID, Inc
Ěý
ORCID Director of Community Rebecca Bryant provides an update on ORCID Ambassadors and the Sloan-sponsored Adoption & Integration program. VictorCassen



VictorCassenVictor Cassen
Ěý
This document is a resume for Victor Cassen summarizing his technical skills and work history as a software developer. It lists his proficiency with various programming languages, frameworks and databases. It then describes his two most recent roles developing network management software and biological research tools and databases. It provides examples of projects in each role involving web services, data processing pipelines, and user-facing applications. It concludes with his educational background of a Computer Science degree from the University of Washington.LOD/LAM Presentation



LOD/LAM PresentationHafabe
Ěý
The document summarizes the origins and development of Linked Open Data for libraries, archives, and museums (LODLAM). It discusses how library standards from the 1970s did not integrate well with the wider web. It then describes the LODLAM initiative, which began in 2011 to convene leaders to publish and work with Linked Open Data from these institutions. The initiative aims to identify tools and techniques, define policies, and promote use cases to advocate for Linked Open Data in cultural heritage organizations.10. Participation Reports



10. Participation ReportsCrossref
Ěý
Crossref allows members to register and report metadata about publications including titles, authors, references, funding information, license details, and ORCID IDs. This metadata benefits both members and the public by helping members track and improve their research outputs over time, and helping the public find and assess research more easily. Crossref metadata supports linking, citing, and reusing research.ORCID & other Person iDs



ORCID & other Person iDsSimeon Warner
Ěý
Discussion of ORCID iDs in the context of other sources of authority data for persons in the library community.i5k Workspace Workshop - AGS2017



i5k Workspace Workshop - AGS2017Monica Poelchau
Ěý
Presentation used for the i5k Workspace session at the Arthropod Bioinformatics Workshop 2017 at the University of Notre DameData base in detail



Data base in detailVartika Mishra
Ěý
The document discusses biological databases, including their purpose, history, classification, features, and examples. Some key points:
- Biological databases store and organize life science data from experiments and literature for analysis and sharing.
- Major databases include GenBank, EMBL, DDBJ, Swiss-Prot, and PDB, which store nucleotide and protein sequences and structures.
- Biological databases can be classified by data type, source, maintenance status, design, organism, and access permissions.
- Primary databases directly house experimental data, while secondary databases add value through analysis and integration.
- Formats like flat files were adopted for data exchange between major nucleotide sequence databases.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Visualizing data



Visualizing dataVioleta Ilik
Ěý
This document discusses using Viewshare, an open-source visualization platform, to visualize different types of data including a MODS XML file of a collection, a scientific dataset ingested as an XSL file, and data about an academic community ingested as an XSL file. It also discusses visualizing a dataset from a cross-sectional study of E. coli bacteria including visualizing the raw data, human-readable data, and a visualization of the dataset. Finally, it discusses visualizing academic communities using Texas A&M University's Computer Science and Engineering department as an example and lessons learned about better data integration through linking data.Access to Graduate Scholarship in VIVO: Establishing Connections and Tracing ...



Access to Graduate Scholarship in VIVO: Establishing Connections and Tracing ...Violeta Ilik
Ěý
This document discusses how Texas A&M University Libraries uses VIVO to connect researchers across disciplines by including graduate scholarship like theses and dissertations. It describes how theses are pushed from VIREO, the university's thesis and dissertation repository, to both VIVO and ORCID to establish academic lineages and connections. By enhancing disciplinary family trees through works and their derivatives in VIVO, researchers can better trace the impact of ideas over time.Crediting informatics and data folks in life science teams



Crediting informatics and data folks in life science teamsCarole Goble
Ěý
Science Europe LEGS Committee: Career Pathways in Multidisciplinary Research: How to Assess the Contributions of Single Authors in Large Teams, 1-2 Dec 2015, Brussels
The People Behind
Research Software
crediting from the informatics, technical point of view
NISO Webinar: Authority Control: Are You Who We Say You Are?



NISO Webinar: Authority Control: Are You Who We Say You Are?National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Ěý
About the Webinar
In the world of authority control, it is a bit of an alphabet soup of acronyms. ORCID (Open Researcher and Contributor ID), which is a system to uniquely identify scientific and other academic authors; ISNI (International Standard Name Identifier), which identifies the public identities of contributors to media content such as books, television programs, and newspaper articles; and VIAF (Virtual International Authority File) a system that combines multiple name authority files into a single authority service, hosted by OCLC, all have their place when discussing identifiers for authority control.
Identity issues and disambiguating authors, researchers, other content creators, and their institutional affiliations are crucial as we move into a world of linked data. In this webinar, presenters will cover the implications and differences between ORCID, ISNI, and VIAF, what is the proper use of each, and some of the benefits that come with using authority files and making that information available on the Web.
Agenda
Introduction
Todd Carpenter, Executive Director, NISO
ORCID identifiers in research workflows
Simeon Warner, Director of Repository Development, Cornell University Library
ISNI: How It Works And What It Does
Laura Dawson, Product Manager, ProQuest
VIAF and its Relationships with Other Files
Thomas Hickey, Chief Scientist, OCLCScholars@Cornell: Visualizing the scholarly record



Scholars@Cornell: Visualizing the scholarly recordMuhammad Javed
Ěý
As stewards of the scholarly record, Cornell University Library is developing a data and visualization service known as Scholars@Cornell with the goal of improving the visibility of Cornell research and enabling discovery of explicit and latent patterns of scholarly collaboration. We provide aggregate views of data where dynamic visualizations become the entry points into a rich graph of knowledge that can be explored interactively to answer questions such as: Who are the experts in what areas? Which departments collaborate with each other? What are patterns of interdisciplinary research? And more. Key components of the system are Symplectic Elements to provide automated citation feeds from external sources such as Web of Science, the Scholars "Feed Machine" that performs automated data curation tasks, and the VIVO semantic linked data store. The new "VIZ-VIVO" component bridges the chasm between the back-end of semantically rich data with a front-end user experience that takes advantage of new developments in the world of dynamic web visualizations. We will demonstrate a set of D3 visualizations that leverage relationships between people (e.g., faculty), their affiliations (e.g., academic departments), and published research outputs (e.g., journal articles by subject area). We will discuss our results with two of the initial pilot partners at Cornell University, the School of Engineering and the Johnson School of Management.Agenda's for Preservation Research



Agenda's for Preservation ResearchMicah Altman
Ěý
Dr Micah Altman presented this at the Society for American Archivists 2016 Research Forum.
In this presentation I discuss some key potential topics for preservation research in the next five years. LKG Editor Dev



LKG Editor DevSimeon Warner
Ěý
A presentation of LD4P2 work on linked data editor development and lookup services in particular. Presented at US2TS, 11-13 March, 2019Linked Data Principles and RDF: University of Florida Libraries, BIBFRAME Wor...



Linked Data Principles and RDF: University of Florida Libraries, BIBFRAME Wor...Allison Jai O'Dell
Ěý
Part of a monthly series of "tech talks" given for the University of Florida Libraries, BIBFRAME Working GroupLinking Data, Linking People



Linking Data, Linking PeoplefereiraJ
Ěý
This document discusses linking data and people through ontologies and semantic web technologies. It provides examples of using RDF, FOAF, and Linked Data principles to describe people and relationships. It also showcases several applications that utilize these technologies including Vivo, a semantic publishing platform, and domain-specific knowledge environments.Asis&t webinar people directories access innovations



Asis&t webinar people directories access innovationsBert Carelli
Ěý
This document discusses using taxonomies to create people directories and author networks. It outlines Access Innovations' background in building taxonomies and their data harmony software. Taxonomies can play a role in developing better resources about people by linking entities like authors, publications, and institutions. This allows for knowledge discovery and collaboration through detailed author profiles, visualizing co-author networks, and integrating identity into publisher systems. Standards like VIAF, ORCID, and Project VIVO aim to connect names and publications across repositories through semantic linking of author data.Organizational Identifiers - Crossref LIVE Hannover



Organizational Identifiers - Crossref LIVE HannoverCrossref
Ěý
Vanessa Fairhurst talks about the Organization ID Project, now known as 'Onyar'. Presented at Crossref LIVE local Hannover, June 27th 2018. Crossref LIVE: The Benefits of Open Infrastructure (APAC time zones) - 29th O...



Crossref LIVE: The Benefits of Open Infrastructure (APAC time zones) - 29th O...Crossref
Ěý
In November 2020, Crossref formally adopted the “Principles of Open Scholarly Infrastructure” (POSI). POSI is a list of sixteen commitments that will now guide the board, staff, and Crossref’s development as an organisation into the future.
This webinar took place on the 29th October at 03:00 PM AEST (UTC+10) and covered:
- What are the Principles of Open Scholarly Infrastructure (POSI) and why are they needed?
- Why POSI is important for Crossref and how it will help realise the Research Nexus
- Open metadata and infrastructure services from Crossref
Presented in English by Cameron Neylon, Professor of Research Communications, Centre for Culture and Technology, at Curtin University, Amanda Bartell, Head of Member Experience at Crossref, and Vanessa Fairhurst, Community Engagement Manager at Crossref.
An Introduction to EZID



An Introduction to EZIDUniversity of California Curation Center
Ěý
EZID makes it simple for researchers and others to obtain and manage long-term identifiers for their digital content. The service can create and resolve identifiers, and it also allows entry and maintenance of information about the identifier (metadata). This presentation was given as part of a webinar series.Dash: data sharing made easy



Dash: data sharing made easyUniversity of California Curation Center
Ěý
To facilitate data sharing from within the University of California system and beyond, the University of California Curation Center (UC3) is developing a new ingest and discovery layer for our data curation service, Dash. Dash uses the Merritt repository for preservation and a self-service overlay layer for submission and discovery of research datasets. The new overlay– dubbed Stash (STore And SHare)– will feature an enhanced user interface with a simple and intuitive deposit workflow, while still accommodating rich metadata. Stash will enable individual scholars to upload data through local file browse or drag-and-drop operation; describe data in terms of scientifically-meaning metadata, including methods, references, and geospatial information; identify datasets for persistent citation and retrieval; preserve and share data in an appropriate repository; and discover, retrieve, and reuse data through faceted search and browse. Stash can be implemented in conjunction with any standards-compliant repository that supports the SWORD protocol for deposit and the OAI-PMH protocol for metadata harvesting. Stash will feature native support for the DataCite or Dublin Core metadata schemas, but is designed to accommodate other schemas to support discipline-specific applications. By alleviating many of the barriers that have historically precluded wider adoption of open data principles, Stash empowers individual scholars to assert active curation control over their research outputs; encourages more widespread data preservation, publication, sharing, and reuse; and promotes open scholarly inquiry and advancement.BibBase Linked Data Triplification Challenge 2010 Presentation



BibBase Linked Data Triplification Challenge 2010 PresentationReynold Xin
Ěý
The document summarizes BibBase Triplified, a system that publishes bibliographic data from BibTeX files as structured data on the semantic web. It takes BibTeX files maintained by scientists, detects and resolves duplicates, and publishes the data as HTML pages and RDF triples. It also links entries to external datasets like DBLP and DBpedia. As of September 2010, the system had over 4,500 publications and 100 active users. Future work includes improving duplicate detection, linking to more external sources, and broadening the user base.20131029 Community Outreach Report



20131029 Community Outreach ReportORCID, Inc
Ěý
ORCID Director of Community Rebecca Bryant provides an update on ORCID Ambassadors and the Sloan-sponsored Adoption & Integration program. VictorCassen



VictorCassenVictor Cassen
Ěý
This document is a resume for Victor Cassen summarizing his technical skills and work history as a software developer. It lists his proficiency with various programming languages, frameworks and databases. It then describes his two most recent roles developing network management software and biological research tools and databases. It provides examples of projects in each role involving web services, data processing pipelines, and user-facing applications. It concludes with his educational background of a Computer Science degree from the University of Washington.LOD/LAM Presentation



LOD/LAM PresentationHafabe
Ěý
The document summarizes the origins and development of Linked Open Data for libraries, archives, and museums (LODLAM). It discusses how library standards from the 1970s did not integrate well with the wider web. It then describes the LODLAM initiative, which began in 2011 to convene leaders to publish and work with Linked Open Data from these institutions. The initiative aims to identify tools and techniques, define policies, and promote use cases to advocate for Linked Open Data in cultural heritage organizations.10. Participation Reports



10. Participation ReportsCrossref
Ěý
Crossref allows members to register and report metadata about publications including titles, authors, references, funding information, license details, and ORCID IDs. This metadata benefits both members and the public by helping members track and improve their research outputs over time, and helping the public find and assess research more easily. Crossref metadata supports linking, citing, and reusing research.ORCID & other Person iDs



ORCID & other Person iDsSimeon Warner
Ěý
Discussion of ORCID iDs in the context of other sources of authority data for persons in the library community.NISO Webinar: Authority Control: Are You Who We Say You Are?



NISO Webinar: Authority Control: Are You Who We Say You Are?National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Ěý
Linked Data Principles and RDF: University of Florida Libraries, BIBFRAME Wor...



Linked Data Principles and RDF: University of Florida Libraries, BIBFRAME Wor...Allison Jai O'Dell
Ěý
Similar to Karma Data Modeling (20)
i5k Workspace Workshop - AGS2017



i5k Workspace Workshop - AGS2017Monica Poelchau
Ěý
Presentation used for the i5k Workspace session at the Arthropod Bioinformatics Workshop 2017 at the University of Notre DameData base in detail



Data base in detailVartika Mishra
Ěý
The document discusses biological databases, including their purpose, history, classification, features, and examples. Some key points:
- Biological databases store and organize life science data from experiments and literature for analysis and sharing.
- Major databases include GenBank, EMBL, DDBJ, Swiss-Prot, and PDB, which store nucleotide and protein sequences and structures.
- Biological databases can be classified by data type, source, maintenance status, design, organism, and access permissions.
- Primary databases directly house experimental data, while secondary databases add value through analysis and integration.
- Formats like flat files were adopted for data exchange between major nucleotide sequence databases.Dataset Metadata, Tools and Approaches for Access and Preservation



Dataset Metadata, Tools and Approaches for Access and PreservationUniversity of California Curation Center
Ěý
Joan Starr's presentation at ALA Midwinter 2012 to ALCTS Intellectual Access to Preservation Metadata Interest GroupApplied semantic technology and linked data



Applied semantic technology and linked dataWilliam Smith
Ěý
Mapping a human brain generates petabytes of gene listings and the corresponding locations of these genes throughout the human brain. ĚýDue to the large dataset a prototype Semantic Web application was created with the unique ability to link new datasets from similar fields of research, and present these new models to an online community. ĚýThe resulting application presents a large set of Ěýgene to location mappings and provides new information about diseases, drugs, and side effects in relation to the genes and areas of the human brain.
In this presentation we will discuss the normalization processes and tools for adding new datasets, the user experience throughout the publishing process, the underlying technologies behind the application, and demonstrate the preliminary use cases of the project. NISO/DCMI May 22 Webinar: Semantic Mashups Across Large, Heterogeneous Insti...



NISO/DCMI May 22 Webinar: Semantic Mashups Across Large, Heterogeneous Insti...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Ěý
VIVO is a semantic web application that enables discovery of research across disciplines in an institution. It allows granular editing of profiles while also ingesting data automatically from sources like HR systems. The presenter discussed VIVO's history and architecture, how it exposes linked open data through SPARQL queries and RDF views. Visualizations like co-authorship networks and implementations at various universities were also covered.NCBO Web Services: Powering Semantically Aware Applications



NCBO Web Services: Powering Semantically Aware ApplicationsTrish Whetzel
Ěý
The National Center for Biomedical Ontology provides web services and tools to enable the application of ontologies in biomedical science and clinical care. It maintains a library of biomedical ontologies and builds tools for ontology development, data annotation, and data integration. Key web services include services for ontology search, traversal, and download, as well as annotation and mapping services.Nowomics at Cambridge Open Research



Nowomics at Cambridge Open ResearchNowomics
Ěý
An introduction to Nowomics and how it helps biologists track new data and papers relevant to their research. With some background on how the site go started.Dataset Citation and Identifiers: DOIs, ARKs, and EZID



Dataset Citation and Identifiers: DOIs, ARKs, and EZIDUniversity of California Curation Center
Ěý
This document discusses persistent identifiers for datasets and describes the EZID service for assigning identifiers. It begins with an overview of data citation and identifiers, explaining what identifiers are and providing an example. It then describes how EZID can be used to create and manage persistent identifiers and associated metadata over time. The document concludes by discussing considerations for identifier selection and the role of identifiers in the life cycle of a dataset from creation through publication and archiving.Alamw15 VIVO



Alamw15 VIVOKristi Holmes
Ěý
VIVO is an open-source semantic web application and information model that enables discovery of research across disciplines at institutions. It harvests data from verified sources to create detailed profiles of faculty and researchers. The structured linked data in VIVO allows for relationships and connections between researchers, publications, grants, and more to be visualized. Libraries can play important roles in implementing and supporting VIVO through activities like outreach, training, ontology development, and technical support.Elixir at de.nbi meeting



Elixir at de.nbi meetingNiklas Blomberg
Ěý
- Data transfer
- Compute access
- Training
Data Hub:
- Secure data sharing
- Data management
- Metadata catalogues
AAI:
- Single sign-on
- User attributes
- Group management
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resources
National
resourcesNISO Webinar: Back From the Endangered List: Using Authority Data to Enhance ...



NISO Webinar: Back From the Endangered List: Using Authority Data to Enhance ...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Ěý
The document discusses the Getty Vocabularies, which are authoritative controlled vocabularies for art, architecture, and material culture. They include the Art & Architecture Thesaurus (AAT), Getty Thesaurus of Geographic Names (TGN), Union List of Artist Names (ULAN), and the developing Cultural Objects Name Authority (CONA). The vocabularies are compiled and maintained by the Getty Vocabulary Program based on contributions from users and projects. Records are merged if multiple contributors submit the same concept, person, place, or object. The vocabularies are licensed and distributed annually to institutions.Wikidata workshop for ISB Biocuration 2016



Wikidata workshop for ISB Biocuration 2016Benjamin Good
Ěý
This document discusses using Wikidata as a platform for biocuration. Wikidata is presented as a new paradigm that could reduce pain points in current biocuration practices by providing a single platform with persistent data access. It describes Wikidata's structure as a knowledge base of unique items and statements linked together to form a knowledge graph. Examples show how biomedical data like genes and proteins are represented. The document outlines Wikidata's community processes and increasing impact on applications like Wikipedia and genome browsers. It envisions the potential for researchers to contribute new biomedical knowledge through Wikidata.#LAWDI Open Context, publishing linked data in archaeology



#LAWDI Open Context, publishing linked data in archaeologyekansa
Ěý
This document discusses a publication approach to linked data in archaeology using Open Context. It began in 2007 with open access publishing of archaeology data and is now archived by the California Digital Library. Current projects study editorial and publishing workflows and are funded by various organizations. Open Context links archaeology data to data in other disciplines and uses standards like CIDOC and UBERON to annotate data. Challenges include the effort required to share usable linked data when raw data is problematic and modeling research methods.ALIAOnline Practical Linked (Open) Data for Libraries, Archives & Museums



ALIAOnline Practical Linked (Open) Data for Libraries, Archives & MuseumsJon Voss
Ěý
This document discusses practical applications of Linked Open Data (LOD) for libraries, archives, and museums. It describes how LOD allows these institutions to publish structured data on the web in ways that are interoperable and can be connected to other open datasets. Examples are given of how LOD is being used by various institutions to share metadata, images, and other cultural heritage assets on the web in open, machine-readable formats. The presenter argues that LOD represents a new paradigm that these cultural organizations should embrace to make their collections more accessible and useful on the web.Identifying The Benefit of Linked Data



Identifying The Benefit of Linked DataRichard Wallis
Ěý
The document discusses the benefits of linked data and provides instructions for creating linked data. It describes how linked data allows for connecting and sharing information on the web through the use of URIs and RDF triples. The key steps outlined for creating linked data include establishing the entities in your data, giving them URIs, describing each entity, and linking to authoritative hubs. Schema.org is presented as a vocabulary that is widely used and can be extended for specific domains.Mendeley Data: Enhancing Data Discovery, Sharing and Reuse



Mendeley Data: Enhancing Data Discovery, Sharing and ReuseAnita de Waard
Ěý
şÝşÝߣs for the NIH Workshop, 2/11/20 'The Role of Generalist and Institutional Repositories to Enhance Data Discoverability and ReuseFacilitating Open Science and Research Discovery via VIVO and the Semantic Web



Facilitating Open Science and Research Discovery via VIVO and the Semantic WebKristi Holmes
Ěý
Kristi Holmes discusses how VIVO, an open-source semantic web application, enables the discovery of research and scholarship across disciplines by creating profiles for faculty and researchers that display their publications, teaching, service, and affiliations. VIVO harvests data from internal sources like HR directories and external sources like PubMed to populate these profiles. It stores this information as linked data using semantic web standards, allowing the data to be integrated into the larger Linked Open Data cloud and consumed by other applications and systems both within and outside an institution.Martone acs presentation



Martone acs presentationNeuroscience Information Framework
Ěý
Presentation at the American Chemical Society, San Diego, March 13, 2016: Global Initiatives in Research Data Management & Discovery SymposiumCinf flash v2 final



Cinf flash v2 finalSean Ekins
Ěý
This document discusses the creation of new databases for science mobile apps, scientific databases, and scientists. It introduces the websites scimobileapps.com as a wiki to catalog science apps, scidbs.com to track the quality of scientific databases, and scientistsdb.com as a database of scientists that allows users to add their own profiles with more details than LinkedIn. The motivation is to make scientific information and tools more accessible and to get the crowd involved in maintaining these resources.20140521 sem-tech-biz-guest-lecture



20140521 sem-tech-biz-guest-lectureVladimir Alexiev, PhD, PMP
Ěý
Information School, University of Washington, 2014-05-21: INFX 598 - Introducing Linked Data: concepts, methods and tools. Guest lecture (Module 9) "Doing Business with Semantic Technologies": Introduction to Ontotext and some of its products, clients and projects.
Also see video:https://voicethread.com/myvoice/#thread/5784646/29625471/31274564Dataset Metadata, Tools and Approaches for Access and Preservation



Dataset Metadata, Tools and Approaches for Access and PreservationUniversity of California Curation Center
Ěý
NISO/DCMI May 22 Webinar: Semantic Mashups Across Large, Heterogeneous Insti...



NISO/DCMI May 22 Webinar: Semantic Mashups Across Large, Heterogeneous Insti...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Ěý
NISO Webinar: Back From the Endangered List: Using Authority Data to Enhance ...



NISO Webinar: Back From the Endangered List: Using Authority Data to Enhance ...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Ěý
Recently uploaded (20)
How to Grant Discounts in Sale Order Lines in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Grant Discounts in Sale Order Lines in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
Ěý
Odoo offers several ways to apply the discounts on sales orders, providing flexibility for various scenarios. The discounts applied on the sales order lines are global discounts, fixed discounts, and discounts on all order lines. In this slide, we will learn how to grant discounts on the sale order line in Odoo 18. Anti-Viral Agents.pptx Medicinal Chemistry III, B Pharm SEM VI



Anti-Viral Agents.pptx Medicinal Chemistry III, B Pharm SEM VISamruddhi Khonde
Ěý
Antiviral agents are crucial in combating viral infections, causing a variety of diseases from mild to life-threatening. Developed through medicinal chemistry, these drugs target viral structures and processes while minimizing harm to host cells. Viruses are classified into DNA and RNA viruses, with each replicating through distinct mechanisms. Treatments for herpesviruses involve nucleoside analogs like acyclovir and valacyclovir, which inhibit the viral DNA polymerase. Influenza is managed with neuraminidase inhibitors like oseltamivir and zanamivir, which prevent the release of new viral particles. HIV is treated with a combination of antiretroviral drugs targeting various stages of the viral life cycle. Hepatitis B and C are treated with different strategies, with nucleoside analogs like lamivudine inhibiting viral replication and direct-acting antivirals targeting the viral RNA polymerase and other key proteins.
Antiviral agents are designed based on their mechanisms of action, with several categories including nucleoside and nucleotide analogs, protease inhibitors, neuraminidase inhibitors, reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors. The design of these agents often relies on understanding the structure-activity relationship (SAR), which involves modifying the chemical structure of compounds to enhance efficacy, selectivity, and bioavailability while reducing side effects. Despite their success, challenges such as drug resistance, viral mutation, and the need for long-term therapy remain.UTI Quinolones by Mrs. Manjushri Dabhade



UTI Quinolones by Mrs. Manjushri DabhadeDabhade madam Dabhade
Ěý
UTI quinolones by Mrs. Manjushri DabhadeURLS and routing in odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



URLS and routing in odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In Odoo 18, URLs and routing are key components of its web framework, used to handle HTTP requests. Understanding them is essential for customizing Odoo’s behavior, creating new pages, and integrating with external systems.How to Configure Outgoing and Incoming mail servers in Odoo 18



How to Configure Outgoing and Incoming mail servers in Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
Odoo 18 features a powerful email management system designed to streamline business communications directly within the platform. By setting up Outgoing Mail Servers, users can effortlessly send emails. Similarly, configuring Incoming Mail Servers enables Odoo to process incoming emails and generate records such as leads or helpdesk tickets. Design approaches and ethical challenges in Artificial Intelligence tools for...



Design approaches and ethical challenges in Artificial Intelligence tools for...Yannis
Ěý
The recent technology of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has undeniable advantages, especially with regard to improving the efficiency of all stakeholders in the education process.
At the same time, almost all responsible international organisations and experts in the field of education and educational technology point out a multitude of general ethical problems that need to be addressed. Many of these problems have already arisen in previous models of artificial intelligence or even in systems based on learning data, and several are appearing for the first time.
In this short contribution, we will briefly review some dimensions of ethical problems, both (a) the general ones related to trust, transparency, privacy, personal data security, accountability, environmental responsibility, bias, power imbalance, etc., and (b) the more directly related to teaching, learning, and education, such as students' critical thinking, the social role of education, the development of teachers' professional competences, etc.
In addition, the categorizations of possible service allocation to humans and AI tools, the human-centered approach to designing AI tools and learning data, as well as the more general design of ethics-aware applications and activities will be briefly presented. Finally, some short illustrative examples will be presented to set the basis for the debate in relation to ethical and other dilemmas.Yale VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 3-30-2025 FINAL v2...



Yale VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 3-30-2025 FINAL v2...Yale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Ěý
Measles Outbreak—Southwestern US— This briefing reviews the current situation surrounding the measles outbreaks in Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 2025 Women Leaders Program - Award Winning



2025 Women Leaders Program - Award WinningSonia McDonald
Ěý
Empower & Lead: Women in Leadership
Dive into our award-winning and dynamic programs designed to boost your confidence and equip you with bold tools and strategies. Unleash your unique leadership potential and lead with flair!
Elevate Your Game with the Women Leaders Program
Step up to the challenge with Sonia McDonald’s dynamic leadership program, perfectly blending neuroscience, personal, and professional development. With over three decades of expertise in leadership and HR, Sonia has designed a program that adapts to your busy lifestyle, offering both virtual and in-house options. Explore ten robust modules equipped with an all-encompassing toolkit, infused with cutting-edge neuroscience to enhance your understanding of leadership dynamics. Choose from engaging monthly group coaching or personalized 1:1 sessions with Sonia.
If you’re ready for a transformative journey focused on growth, neuroscience-backed courage, leadership, and freedom, this is your call to action. Join us and start leading like never before!
Transform Your Leadership.
Transform Your Life.
Women are underrepresented in key decision-making roles across almost all industries in the Australian workforce, women comprise only:
19.4% of CEOs
32.5% of key management positions
33% of board members
18% of board chairs.
IT’S TIME FOR CHANGE. JOIN THE PROGRAM TODAY.
Maximise Your Leadership Skills
Achieve the best results for yourself, your team, and for the business.
Develop & Grow Your Courage
Build courageous habits to live the life you choose.
Enhance Your Career Progression
Step in, stand up, lead and get your seat at the Table.
https://soniamcdonald.com.au/women-leaders-program/COMMON HEALTH PROBLEMS INCLUDING COMMUNICABLES AND NON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES



COMMON HEALTH PROBLEMS INCLUDING COMMUNICABLES AND NON COMMUNICABLE DISEASESSonaliGupta630281
Ěý
COMMUNICABLE AND NON COMMUNICABLE DISEASESBerry_Kanisha_BAS_PB1_202503 (2) (2).pdf



Berry_Kanisha_BAS_PB1_202503 (2) (2).pdfKanishaBerry
Ěý
Kanisha Berry's Full Sail University Personal Branding Exploration Assignment Personal Brand exploration powerpoint pp1



Personal Brand exploration powerpoint pp1rayvoisine3
Ěý
This is a powerpoint about what I want to do in my future. if you would like to know more about me please check it out. Unit 3: Combustion in Spark Ignition Engines



Unit 3: Combustion in Spark Ignition EnginesNileshKumbhar21
Ěý
Stages of combustion, Ignition lag, Flame propagation, Factors affecting flame
speed, Abnormal combustion, Influence of engine design and operating
variables on detonation, Fuel rating, Octane number, Fuel additives, HUCR,
Requirements of combustion chambers of S.I. Engines and its types.Role of Teacher in the era of Generative AI



Role of Teacher in the era of Generative AIProf. Neeta Awasthy
Ěý
We need to layer the technology onto existing workflows
Follow the teachers who inspire you because that instills passion Curiosity & Lifelong Learning.
You can benefit from generative AI even when its intelligence is worse-because of the potential for cost and time savings in low-cost-of-error environments.
Bot tutors are already yielding effective results on learning and mastery.
GenAI may increase the digital divide- its gains may accrue disproportionately to those who already have domain expertise.
GenAI can be used for Coding
Complex structures
Make the content
Manage the content
Solutions to complex numerical problems
Lesson plan
Assignment
Quiz
Question bank
Report & summary of content
Creating videos
Title of abstract & summaries and much more like...
Improving Grant Writing
Learning by Teaching Chatbots
GenAI as peer Learner
Data Analysis for Non-Coders
Student Course Preparation
To reduce Plagiarism
Legal Problems for classes
Understanding Student Learning in Real Time
Simulate a poor
Faculty co-pilot chatbot
Generate fresh Assessments
Data Analysis Partner
Summarize student questions in real-time
Assess depth of students' understanding
The skills to foster are Listening
Communicating
Approaching the problem & solving
Making Real Time Decisions
Logic
Refining Memories
Learning Cultures & Syntax (Foreign Language)
Chatbots & Agentic AI can never so what a professor can do.
The need of the hour is to teach Creativity
Emotions
Judgement
Psychology
Communication
Human Emotions
…………Through various content!
Unit1 Inroduction to Internal Combustion Engines



Unit1 Inroduction to Internal Combustion EnginesNileshKumbhar21
Ěý
Introduction of I. C. Engines, Types of engine, working of engine, Nomenclature of engine, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle Fuel air cycles Characteristics of fuel - air mixtures Actual cycles, Valve timing diagram for high and low speed engine, Port timing diagramYale VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 3-30-2025 FINAL v2...



Yale VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 3-30-2025 FINAL v2...Yale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Ěý
Karma Data Modeling
- 1. #VIVOifest15 Karma data integration: creating semantic web compliant VIVO data Violeta Ilik @violetailik Galter Health Sciences Library Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute (NUCATS), Chicago, IL https://galter.northwestern.edu/staff/Violeta-Ilik http://vivo.vivoweb.org/display/n10603
- 2. #VIVOifest15 Outline: •  Examine your data •  Clean your data •  Create local ontology extensions (optional) •  Model your data •  Load your data Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 3. #VIVOifest15 Examine your data Accommodate within existing ontologies most of your data Opt for local extensions if necessary •  Local unique identifiers (people & organizations) •  Specific needs (publication types; non-traditional scholarly outputs …) Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 4. #VIVOifest15 Clean your data •  Utilizing local resources and skills – polyglot programing skills (Python, Perl, XSLT, SAS, R, OpenRefine) Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 5. #VIVOifest15 Ontology: VIVO core Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 6. #VIVOifest15 VIVO local ontology extensions Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 7. #VIVOifest15 Modeling organizations/units data Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 8. #VIVOifest15 Modeling organizations/units data Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 9. #VIVOifest15 Modeling person data Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 10. #VIVOifest15 Modeling person data Violeta Ilik @violetailik
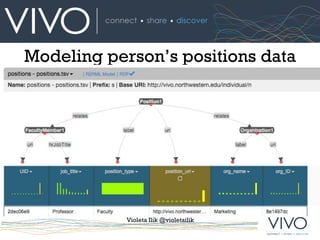
- 11. #VIVOifest15 Modeling person’s positions data Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 12. #VIVOifest15 Modeling person’s positions data Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 13. #VIVOifest15 Modeling publications data – academic articles Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 14. #VIVOifest15 Modeling publications data – comparative study Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 15. #VIVOifest15 References: •  https://github.com/vioil/ontology_extensions •  https://github.com/vioil/R2RML-Karma • https://www.youtube.com/channel/ UCb9vsw2XvZDzZtEwe0aH9eA •  http://www.isi.edu/integration/karma/ Violeta Ilik @violetailik
- 16. #VIVOifest15 Discussion Thank you Violeta Ilik Violeta Ilik @violetailik






