Learning Spatial Common Sense with Geometry-Aware Recurrent Networks
- 1. Learning Spatial Common Sense with Geometry-Aware Recurrent Networks
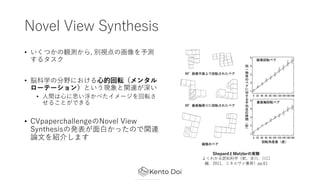
- 3. Novel View Synthesis ? żżż»ż─ż½ż╬ėQ£yż½żķ, äeęĢĄŃż╬╗ŁŽ±ż“ėĶ£y ż╣żļź┐ź╣ź» ? ├Ś┐Ų覿╬Ęųę░ż╦ż¬ż▒żļ?Ą─╗ž▄ׯ©źßź¾ź┐źļ źĒ®`źŲ®`źĘźńź¾Ż®ż╚żżż”¼FŽ¾ż╚ķv▀Bż¼╔Ņżż ? ?ķgżŽ?ż╦╦╝żżĖĪż½ż┘ż┐źżźß®`źĖż“╗ž▄׿Ą ż╗żļż│ż╚ż¼żŪżŁżļ ? CVpaperchallengeż╬Novel View Synthesisż╬░k▒Ēż¼??ż½ż├ż┐ż╬żŪķv▀B šō?ż“ĮBĮķżĘż▐ż╣ Shepardż╚Metzlerż╬īg“Y żĶż»ż’ż½żļšJų¬┐Ų覯©Ū¼Īó╝¬┤©Īó┤©? ŠÄĪó2011Īóź▀ź═źļź¶źĪĢ°Ę┐Ż®pp.61
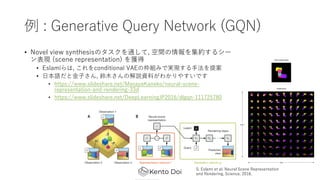
- 4. └² : Generative Query Network (GQN) ? Novel view synthesisż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż“═©żĘżŲ, ┐šķgż╬Ūķł¾ż“╝»╝sż╣żļźĘ®` ź¾▒Ē¼F (scene representation) ż“½@Ą├ ? EslamiżķżŽ, ż│żņż“conditional VAEż╬¢śĮMż▀żŪīg¼Fż╣żļ?Ę©ż“╠ß░Ė ? ?▒ŠšZż└ż╚??żĄż¾, ŌÅ?żĄż¾ż╬ĮŌšh┘Y┴Žż¼ż’ż½żĻżõż╣żżżŪż╣ ? /MasayaKaneko/neural-scene- representation-and-rendering-33d ? /DeepLearningJP2016/dlgqn-111725780 S. Eslami et al. Neural Scene Representation and Rendering, Science, 2018.
- 5. Novel View Synthesis ? cvpaperchallengeż╬░k▒ĒżŪżŽ, ź┐ź╣ź»ż╬Ė┼ę¬?šō?ż╬ĮBĮķ?╬┤ĮŌøQå¢Ņ}ż╩ ż╔ż“ĮBĮķżĘżŲżżż┐ż└żżż┐ ? ╬┤ĮŌøQå¢Ņ}żŽęįŽ┬ż╬ĒŚ?Ą╚ż¼Æżż▓żķżņż┐ ? ź½źŲź┤źĻż╦ę└┤µżĘż╩żżą┬ęÄęĢĄŃ╗ŁŽ±?│╔ ? č}╩²╬’╠Õż╬novel view synthesis ? īgźŪ®`ź┐ż╦ż¬ż▒żļnovel view synthesis ? ╬┤ų¬ęĢĄŃżžż╬Ü°╗» ? ░k▒Ēż“┬äżżżŲ, Į³─ĻżŽźĘ®`ź¾▒Ē¼Fż“ż╔ż╬żĶż”ż╦źŌźŪźĻź¾ź░ż╣żļż½ż╚żżż”╦∙ ż¼ųžę¬żĮż”ż└ż╚╦╝ż├ż┐
- 6. Novel View Synthesisšō? ? Scene Representation Networks: Continuous 3D-Structure-Aware Neural Scene Representations ? Visual Object Networks: Image Generation with Disentangled 3D Representations ? Transformable Bottleneck Networks ? DeepVoxels: Learning Persistent 3D Feature Embeddings ? Geometry-Aware Recurrent Neural Networks for Active Visual Recognition ? Multi-view to Novel view: Synthesizing novel views with Self-Learned Confidence ? Transformation-Grounded Image Generation Network for Novel 3D View Synthesis ? View Synthesis by Appearance Flow ? Learning Spatial Common Sense with Geometry-Aware Recurrent Networks
- 7. Novel View Synthesisšō? ? Scene Representation Networks: Continuous 3D-Structure-Aware Neural Scene Representations ? Visual Object Networks: Image Generation with Disentangled 3D Representations ? Transformable Bottleneck Networks ? DeepVoxels: Learning Persistent 3D Feature Embeddings ? Geometry-Aware Recurrent Neural Networks for Active Visual Recognition ? Multi-view to Novel view: Synthesizing novel views with Self-Learned Confidence ? Transformation-Grounded Image Generation Network for Novel 3D View Synthesis ? View Synthesis by Appearance Flow ? Learning Spatial Common Sense with Geometry-Aware Recurrent Networks Į±?░k▒Ēż╣żļżõż─
- 8. Learning Spatial Common Sense with Geometry-Aware Recurrent Networks
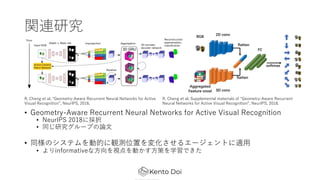
- 9. Ģ°šIŪķł¾ ? CMUż╬蹊┐ź┴®`źÓż╦żĶżļšō? ? last authorż╬Fragkiadaki?żŽÖCąĄż╦ė│╗Łż“└ĒĮŌżĄż╗żļż╬ż¼?ś╦żķżĘżż ? ▒ŠčąŠ┐żŌżĮż╬ż┐żßż╦▒žę¬ż╩╝╝ągż╚żżż”╬╗ų├ż║ż▒Ż┐ ? CVPR2019 oral ż╦żĮżņżŠżņƱÆk ? ż│ż╬蹊┐żŽĪóČÓęĢĄŃż╬Ūķł¾ż“3Dż╬Ū▒į┌▒Ē¼Fż╚żĘżŲĮy║Žż╣żļ?Ę©ż╬╠ß░Ėż“ żĘżŲżżżļ ? geometryż╬ų¬ūRż“deep learningż╬źŌźŪźļż╦ī¦? ? ź¬ź»źļ®`źĖźńź¾ż╦ÅŖżż ? ╠žż╦ėø▌dż╬ż╩żżł÷║Ž, ćĒżŽ▒Ššō?ż½żķż╬ę²?
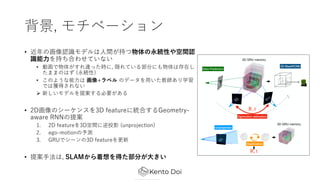
- 10. Ė┼ę¬ ? č}╩²ż╬2D╗ŁŽ±ż½żķ│ķ│÷żĘż┐╠žÅšż“3Dż╬Ū▒į┌▒Ē¼Fż╦Įy║Žż╣żļ?Ę©ż╬╠ß░Ė ? ╠ß░Ė?Ę©żŪżŽ╬óĘų┐╔─▄ż╩Äū║╬Ą─ż╩▓┘ū„(═Čė░, į┘═Čė░, ego-motion estimationż╩ż╔) ż“ deep learningż╦╚ĪżĻ?żņż┐ ? ¼Fīg╩└Įńż╚3D featureż╬╬╗ų├Ą─ż╩ķv▀BżŽ▒Ż┤µżĘżŲżżżļ ? ╠ß░ĖżĘż┐źŌźŪźļżŽČ╠żż╗ŁŽ±┴ąż½żķą┬ęÄęĢĄŃż╬viewż“ėĶ£yż╣żļź┐ź╣ź»żŪč¦┴Ģ ? żĄżķż╦, 3D segmentationżõ3D object detectionżŌč¦┴Ģ┐╔─▄ ? ╠žż╦Ś╩│÷ż╬å¢Ņ}żŪżŽ╬’╠Õż╬ė└ŠAąįż“┐╝æ]żĘż┐Ś╩│÷ (ź¬ź»źļ®`źĖźńź¾ż╦ÅŖżż) ? īg╠Õż“│ųż─visual agentż╦spatial common senseż“│ųż┐ż╗żļż┐żßż╦▒žę¬ż╩ ╝╝ągżŪżóżļż╚ĮYšōż┼ż▒ż┐
- 11. ▒│Š░, źŌź┴ź┘®`źĘźńź¾ ? Į³─Ļż╬╗ŁŽ±šJūRźŌźŪźļżŽ?ķgż¼│ųż─╬’╠Õż╬ė└ŠAąįżõ┐šķgšJ ūR─▄?ż“│ųż┴║Žż’ż╗żŲżżż╩żż ? äė╗ŁżŪ╬’╠Õż¼ż╣żņ▀`ż├ż┐Ģrż╦, ļLżņżŲżżżļ▓┐Ęųż╦żŌ╬’╠ÕżŽ┤µį┌żĘ ż┐ż▐ż▐ż╬żŽż║ (ė└ŠAąį) ? ż│ż╬żĶż”ż╩─▄?żŽ ╗ŁŽ±+źķź┘źļ ż╬źŪ®`ź┐ż“?żżż┐Į╠ĤżóżĻč¦┴Ģ żŪżŽ½@Ą├żĄżņż╩żż ? ą┬żĘżżźŌźŪźļż“╠ß░Ėż╣żļ▒žę¬ż¼żóżļ ? 2D╗ŁŽ±ż╬źĘ®`ź▒ź¾ź╣ż“3D featureż╦Įy║Žż╣żļGeometry- aware RNNż╬╠ß░Ė 1. 2D featureż“3D┐šķgż╦─µ═Čė░ (unprojection) 2. ego-motionż╬ėĶ£y 3. GRUżŪźĘ®`ź¾ż╬3D featureż“Ė³ą┬ ? ╠ß░Ė?Ę©żŽ, SLAMż½żķū┼Žļż“Ą├ż┐▓┐Ęųż¼?żŁżż
- 12. ╠ß░Ė?Ę©ż╬advantage ? ą┬ęÄęĢĄŃėĶ£yż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż╦ż¬ż▒żļÜ°╗»ąį─▄ż¼?żż ? geometryż“┐╝æ]żĘż╩żż?Ę© (GQN) ż╬ąį─▄ż“?żŁż»╔Ž╗žżļ ? ż┐ż└żĘ, ego-motionż╬═ŲČ©ż“ż╗ż║GTż“╩╣ż├ż┐ł÷║ŽżŪżóżļż│ż╚ż╦ūóęŌ ? 3D segmentationżõ3D object detectionż╦żŌ▀m?┐╔─▄ ? ęĢĄŃż╬ēõ╗»ż╦░ķż”?ĢrĄ─ż╩ź¬ź»źļ®`źĖźńź¾ż╦ŅBĮĪż╩Ś╩│÷ĮY╣¹ż“Ą├ż┐ ?╬’╠Õż╬ė└ŠAąį (object permanence) ż“└ĒĮŌżĘż┐šJūR?Ę©żŪżóżļŻĪ ? īgū░╣½ķ_żóżĻ ? https://github.com/ricsonc/grnn
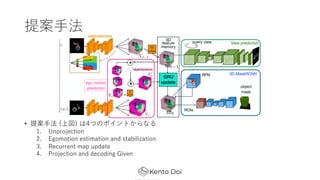
- 13. ╠ß░Ė?Ę© ? ╠ß░Ė?Ę© (╔ŽćĒ) żŽ4ż─ż╬ź▌źżź¾ź╚ż½żķż╩żļ 1. Unprojection 2. Egomotion estimation and stabilization 3. Recurrent map update 4. Projection and decoding Given
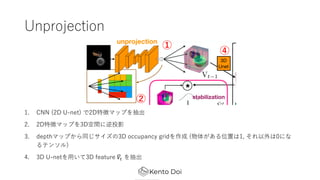
- 14. Unprojection 1. CNN (2D U-net) żŪ2D╠žÅšź▐ź├źūż“│ķ│÷ 2. 2D╠žÅšź▐ź├źūż“3D┐šķgż╦─µ═Čė░ 3. depthź▐ź├źūż½żķ═¼żĖźĄźżź║ż╬3D occupancy gridż“ū„│╔ (╬’╠Õż¼żóżļ╬╗ų├żŽ1, żĮżņęį═ŌżŽ0ż╦ż╩ żļźŲź¾źĮźļ) 4. 3D U-netż“?żżżŲ3D feature !?# ż“│ķ│÷ ó┘ ó┌ ó▄
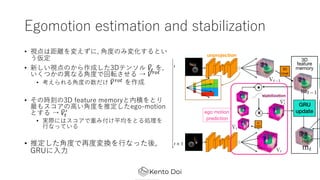
- 15. Egomotion estimation and stabilization ? ęĢĄŃżŽŠÓļxż“ēõż©ż║ż╦, ?Č╚ż╬ż▀ēõ╗»ż╣żļż╚żż ż”üóČ© ? ą┬żĘżżęĢĄŃż╬ż½żķū„│╔żĘż┐3DźŲź¾źĮźļ !?# ż“, żżż»ż─ż½ż╬«Éż╩żļ?Č╚żŪ╗ž▄׿Ąż╗żļ Ī· !?$%# ? ┐╝ż©żķżņżļ?Č╚ż╬╩²ż└ż▒ !?$%# ż“ū„│╔ ? żĮż╬Ģr┐╠ż╬3D feature memoryż╚─┌Ęeż“ż╚żĻ ūŅżŌź╣ź│źóż╬?żż?Č╚ż“═ŲČ©żĘż┐ego-motion ż╚ż╣żļ Ī· !?# & ? īgļHż╦żŽź╣ź│źóżŪųžż▀ĖČż▒ŲĮŠ∙ż“ż╚żļäI└Ēż“ ?ż╩ż├żŲżżżļ ? ═ŲČ©żĘż┐?Č╚żŪį┘Č╚ēõōQż“?ż╩ż├ż┐ßß, GRUż╦??
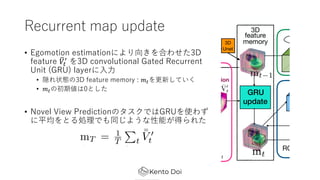
- 16. Recurrent map update ? Egomotion estimationż╦żĶżĻŽ“żŁż“║Žż’ż╗ż┐3D feature !?# & ż“3D convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) layerż╦?? ? ļLżņū┤æBż╬3D feature memory : ?#ż“Ė³ą┬żĘżŲżżż» ? ?#ż╬│§Ų┌éÄżŽ0ż╚żĘż┐ ? Novel View Predictionż╬ź┐ź╣ź»żŪżŽGRUż“╩╣ż’ż║ ż╦ŲĮŠ∙ż“ż╚żļäI└ĒżŪżŌ═¼żĖżĶż”ż╩ąį─▄ż¼Ą├żķżņż┐
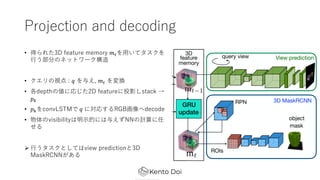
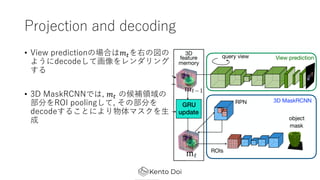
- 17. Projection and decoding ? Ą├żķżņż┐3D feature memory ?#ż“?żżżŲź┐ź╣ź»ż“ ?ż”▓┐Ęųż╬ź═ź├ź╚ź’®`ź»śŗįņ ? ź»ź©źĻż╬ęĢĄŃ : ? ż“ėļż©, ?# ż“ēõōQ ? Ė„depthż╬éÄż╦ÅĻżĖż┐2D featureż╦═Čė░żĘstack Ī· ?* ? ?*ż“convLSTMżŪ ? ż╦īØÅĻż╣żļRGB╗ŁŽ±żždecode ? ╬’╠Õż╬visibilityżŽ├„?Ą─ż╦żŽėļż©ż║NNż╬ėŗ╦Ńż╦╚╬ ż╗żļ ? ?ż”ź┐ź╣ź»ż╚żĘżŲżŽview predictionż╚3D MaskRCNNż¼żóżļ
- 18. Projection and decoding ? View predictionż╬ł÷║ŽżŽ?#ż“ėęż╬ćĒż╬ żĶż”ż╦decodeżĘżŲ╗ŁŽ±ż“źņź¾ź└źĻź¾ź░ ż╣żļ ? 3D MaskRCNNżŪżŽ, ?# ż╬║“čaŅIė“ż╬ ▓┐Ęųż“ROI poolingżĘżŲ, żĮż╬▓┐Ęųż“ decodeż╣żļż│ż╚ż╦żĶżĻ╬’╠Õź▐ź╣ź»ż“? │╔
- 19. īg“Y ? Ś╩į^żĘż┐żżż╬żŽęįŽ┬ż╬å¢żż 1. GRNNsżŽspatial common senseż“č¦┴Ģż╣żļż½ 2. geometryż“┐╝æ]żĘż┐ź═ź├ź╚ź’®`ź»śŗįņżŽspatial common senseż“½@Ą├ż╣żļż╬ ż╦▒žę¬ż½ 3. GRNNsż╬ąį─▄ż╦ż─żżżŲ ? spatial common senseżŽ, ?ķgż¼│ųż─┐šķgšJūR─▄?╚½░Ńż“ųĖż╣ (Ä┌żżęŌ╬Č) ? 3D shapeżŽ2DŲĮ?ż“┼“żķż▐ż╗żļż│ż╚żŪ?│╔┐╔─▄ ? źĘ®`ź¾żŽ╬’╠Õż½żķśŗ│╔żĄżņżļ ? 3┤╬į¬╬’╠ÕżŽĮ╗▓ŅżĘż╩żż ? ╬’╠ÕżŽ╝▒ż╦┤µį┌ż“Ž¹żĘż┐żĻżĘż╩żż
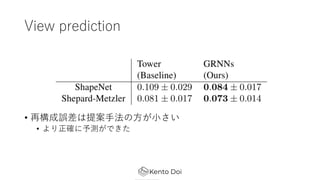
- 20. View prediction ? č}╩²╗ŁŽ±ż╬??ż“į¬ż╦, ą┬żĘżżęĢĄŃż╬╗ŁŽ±ż“ėĶ£y ż╣żļź┐ź╣ź» ? īg“Yż╦?żżż┐źŪ®`ź┐ź╗ź├ź╚ ? ShapeNet : č¦┴ĢźŪ®`ź┐żŽ2ż─ż╬╬’╠Õż“ėQ£yż╣żļż╚żżż”įOČ©żŪ £╩éõ ? Shepard-metzler : źŲź╚źĻź╣ż▀ż┐żżż╩żõż─ ? Rooms-ring-camera dataset from : ▓┐╬▌ż╬ųąż╦źķź¾ź└źÓż╦╬’ ╠Õż¼żóżļżĶż”ż╩źŪ®`ź┐ź╗ź├ź╚ ? ?▌^īØŽ¾ : GQN ? ╠§╝■ż“ōBż©żļż┐żß, ╠ß░Ė?Ę©żŪdepth mapż╬GTżŽ?żżż║, ego- motionż╬GTżŽ?żżż┐
- 21. View prediction ? į┘śŗ│╔š`▓ŅżŽ╠ß░Ė?Ę©ż╬?ż¼?żĄżż ? żĶżĻš²╚Ęż╦ėĶ▓Ōż¼żŪżŁż┐
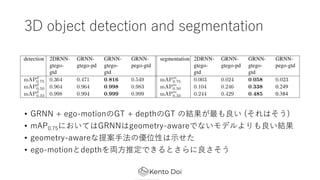
- 24. 3D object detection and segmentation ? Š▀╠ÕĄ─ż╦żŽinstance segmentationż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż“?ż╩ż├żŲżżżļ ? ShapeNetżŪźŪ®`ź┐ź╗ź├ź╚ż“ū„│╔ ? mean Average Precision (mAP)żŪįuü² ? 4ż─ż╬įOČ©żŪŚ╩į^ ? geometry-awareżŪż╩żżźŌźŪźļ + ego-motionż╬GT + depthż╬GT ? GRNN + ego-motionż╬GT + ═ŲČ©żĘż┐depth ? GRNN + ego-motionż╬GT + depthż╬GT ? GRNN + ═ŲČ©żĘż┐ego-motion + depthż╬GT ? üI?═ŲČ©ż╣żļż╬żŽżõżķż╩żżż╬ĪŁ?
- 25. 3D object detection and segmentation ? GRNN + ego-motionż╬GT + depthż╬GT ż╬ĮY╣¹ż¼ūŅżŌ┴╝żż (żĮżņżŽżĮż”) ? mAP0.75ż╦ż¬żżżŲżŽGRNNżŽgeometry-awareżŪż╩żżźŌźŪźļżĶżĻżŌ┴╝żżĮY╣¹ ? geometry-awareż╩╠ß░Ė?Ę©ż╬ā×╬╗ąįżŽ?ż╗ż┐ ? ego-motionż╚depthż“üI?═ŲČ©żŪżŁżļż╚żĄżķż╦┴╝żĄżĮż”
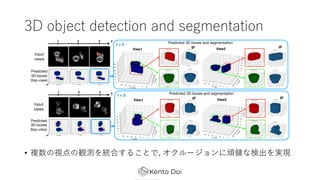
- 26. 3D object detection and segmentation ? č}╩²ż╬ęĢĄŃż╬ėQ£yż“Įy║Žż╣żļż│ż╚żŪ, ź¬ź»źļ®`źĖźńź¾ż╦ŅBĮĪż╩Ś╩│÷ż“īg¼F
- 27. ż▐ż╚żß ? spatial common senseż“½@Ą├ż╣żļż┐żß, 2D╗ŁŽ±┴ąż½żķ3D featureż“?│╔ż╣ żļź═ź├ź╚ź’®`ź»śŗįņż“╠ß░Ė ? unprojection, ego-motion estimationż╩ż╔, ╬óĘų┐╔─▄ż╩geometricż╩äI└Ēż“ ?żżżļż│ż╚ż╦żĶżĻīg¼F ? ą┬ęÄęĢĄŃėĶ£yż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż╦ż¬żżżŲ, Ą═żżį┘śŗ│╔š`▓Ņżõ?żżÜ°╗»ąį─▄ż“?żĘż┐ ? 3D object detection & segmentationż╦ż¬żżżŲżŽ, ź¬ź»źļ®`źĖźńź¾ż╦ŅBĮĪ ż╩Ś╩│÷ż¼żŪżŁż┐ż│ż╚ż“┤_šJ ? Future works ? ¼Fīgż╬źŪ®`ź┐?äėĄ─ż╩źĘ®`ź¾ż╩ż╔ż╦▀m?┐╔─▄ż╩źŌźŪźļż╬╠ß░Ė ? 4DźŲź¾źĮźļż╬ź╣źč®`ź╣ąįż“?żżż┐ėŗ╦Ńä┐┬╩ż╬Ž“╔Ž
- 28. ķv▀B蹊┐ ? Geometry-Aware Recurrent Neural Networks for Active Visual Recognition ? NeurIPS 2018ż╦ƱÆk ? ═¼żĖ蹊┐ź░źļ®`źūż╬šō? ? ═¼śöż╬źĘź╣źŲźÓż“äėĄ─ż╦ėQ£y╬╗ų├ż“ēõ╗»żĄż╗żļź©®`źĖź¦ź¾ź╚ż╦▀m? ? żĶżĻinformativeż╩?Ž“ż“ęĢĄŃż“äėż½ż╣?▓▀ż“č¦┴ĢżŪżŁż┐ R. Cheng et al. Ī░Geometry-Aware Recurrent Neural Networks for Active Visual RecognitionĪ▒, NeurIPS, 2018. R. Cheng et al. Supplemental materials of Ī░Geometry-Aware Recurrent Neural Networks for Active Visual RecognitionĪ▒, NeurIPS, 2018.
- 29. ż¬ż▐ż▒ : Novel View Synthesis źĄ®`ź┘źż
- 30. View Synthesis by Appearance Flow ? Novel view synthesis ż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż“, 2D╗ŁŽ±ż½żķż╬źšźĒź”ż“═ŲČ©ż╣żļż│ż╚ż╦żĶżĻĮŌ żżż┐ĪŻ ? źšźņ®`źÓź’®`ź»╚½╠ÕżŽŽ┬ćĒż╬żĶż”ż╦ż╩żļĪŻż│żņżŽ?Ü▌═©ž×ż╦č¦┴Ģż╣żļż│ż╚ż¼żŪżŁ żļĪŻ T. Zou et al. Ī░View Synthesis by Appearance FlowĪ▒, in ECCV, 2016.
- 31. Transformation-Grounded Image Generation Network for Novel 3D View Synthesis ? NovelViewSynthesisż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż╦ż¬żżżŲĪóą┬ęÄęĢĄŃżŪż╬ź¬źųźĖź¦ź»ź╚ż╬ż”ż┴źĮ®` ź╣╗ŁŽ±żŪ?ż©żŲżżżļ▓┐ĘųżŽżĮżņż“ź│źį®`żĘżŲ?żżĪó▓ążĻż╬▓┐ĘųżŽGANżŪ?│╔ż╣żļ żĶż”ż╩¢śĮMż▀ż“╠ß░ĖżĘż┐ĪŻź═ź├ź╚ź’®`ź»żŽdisocclusion-aware appearance flow network (DOAFN) ż╚completion networkż½żķśŗ│╔żĄżņżļĪŻ ? Ž╚?蹊┐ż╬Appearance Flow Network (AFN) żĶżĻżŌżĶżżĮY╣¹ż“Ą├ż┐ĪŻ E. Park et al. Ī░Transformation-Grounded Image Generation Network for Novel 3D View SynthesisĪ▒, in CVPR, 2017.
- 32. Visual Object Networks: Image Generation with Disentangled 3D Representations ? 3Dż“┐╝æ]żĘż┐╗ŁŽ±?│╔ż“?ż”?Ę©ż╬╠ß░Ė ? 3D shapeż╬?│╔Ī·ź┐®`ź▓ź├ź╚ęĢĄŃż╦īØÅĻżĘż┐╔ŅČ╚╗ŁŽ±ż╚ź▐ź╣ź»ż╦ēõōQĪ· źŲź»ź╣ź┴źŃź│®`ź╔ż“ėļż©żŲ╗ŁŽ±ż╦CNNżŪźņź¾ź└źĻź¾ź░ J. Zhu et al. Ī░Visual Object Networks: Image Generation with Disentangled 3D RepresentationsĪ▒, in NeurIPS, 2018.
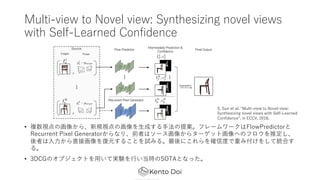
- 33. Multi-view to Novel view: Synthesizing novel views with Self-Learned Confidence ? č}╩²ęĢĄŃż╬╗ŁŽ±ż½żķĪóą┬ęÄęĢĄŃż╬╗ŁŽ±ż“?│╔ż╣żļ?Ę©ż╬╠ß░ĖĪŻźšźņ®`źÓź’®`ź»żŽFlowPredictorż╚ Recurrent Pixel Generatorż½żķż╩żĻĪóŪ░š▀żŽźĮ®`ź╣╗ŁŽ±ż½żķź┐®`ź▓ź├ź╚╗ŁŽ±żžż╬źšźĒź”ż“═ŲČ©żĘĪó ßßš▀żŽ??ż½żķų▒Įė╗ŁŽ±ż“Å═į¬ż╣żļż│ż╚ż“įćż▀żļĪŻūŅßßż╦ż│żņżķż“┤_ą┼Č╚żŪųžż▀ĖČż▒ż“żĘżŲĮy║Žż╣ żļĪŻ ? 3DCGż╬ź¬źųźĖź¦ź»ź╚ż“?żżżŲīg“Yż“?żżĄ▒Ģrż╬SOTAż╚ż╩ż├ż┐ĪŻ S. Sun et al. Ī░Multi-view to Novel view: Synthesizing novel views with Self-Learned ConfidenceĪ▒, in ECCV, 2018.
- 34. Transformable Bottleneck Networks ? 2D╗ŁŽ±ż“CNNż╦żĶżĻ3Dż╬ŠÄ╝»ż¼żŪżŁżļżĶż”ż╦ż╣żļ?Ę©ż╬╠ß░ĖĪŻ ? ╗ŁŽ±ż½żķ3D featureż“│ķ│÷żĘĪóżĮż│ż╦ź┐®`ź▓ź├ź╚ź▌®`ź║ż╦ķvż╣żļēõą╬ż“?żņż┐ż╬ż┴2Dżž ż╬═Čė░ż“?żżĪó╗ŁŽ±ż╬į┘śŗ│╔ż╩ż╔ßßČ╬ż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż“?ż”ĪŻ ? ż│żņż╦żĶżĻäé╠ÕēõōQż╦ż╚ż╔ż▐żķż╩żż3Dż“┐╝æ]żĘż┐╗ŁŽ±ŠÄ╝»ż“?ż”ż│ż╚ż¼żŪżŁżļĪŻ K. Olszewski et al. Ī░Transformable Bottleneck NetworksĪ▒, 2019.
- 35. DeepVoxels: Learning Persistent 3D Feature Embeddings ? ╗ŁŽ±źĘ®`ź▒ź¾ź╣ż“1ż─ż╬ź▄ź»ź╗źļ▒Ē¼Fż╦┬õż╚żĘ▐zżÓ?Ę©ż╬╠ß░ĖĪŻ ? ╠ß░Ė?Ę©ż╬źšźņ®`źÓź’®`ź»żŽęįŽ┬ż╬ĒśżŪäI└Ēż“?ż”ĪŻ ? ╗ŁŽ±ż½żķ2D featureż“│ķ│÷Ī·2D featureż“3D featureż╦į┘═Čė░Ī·ż│żņżķż“╗ŁŽ±źĘ®`ź▒ź¾ź╣ż╦ż─żżżŲ?żżGRUżŪĮy║Ž Ī·3D featureż“ź┐®`ź▓ź├ź╚ż╬ęĢĄŃżž═Čė░żĘ╗ŁŽ±ż“į┘śŗ│╔ ? ż│ż╬į┘śŗ│╔š`▓Ņż╦żĶżĻ╚½╠Õż╬źšźņ®`źÓź’®`ź»ż╬č¦┴Ģż“?ż”ĪŻ ? ╠ß░Ė?Ę©żŽnovel view synthesisż╬ąį─▄ż¼┴╝żżĪŻ V. Sitzmann et al. Ī░DeepVoxels: Learning Persistent 3D Feature EmbeddingsĪ▒, in CVPR, 2019.
- 36. DeepVoxels: Learning Persistent 3D Feature Embeddings V. Sitzmann et al. Ī░DeepVoxels: Learning Persistent 3D Feature EmbeddingsĪ▒, in CVPR, 2019.
- 37. ▓╬┐╝?Žū ? S. Eslami et al. Neural Scene Representation and Rendering, Science, 2018. ? T. Zou et al. Ī░View Synthesis by Appearance FlowĪ▒, in ECCV, 2016. ? E. Park et al. Ī░Transformation-Grounded Image Generation Network for Novel 3D View SynthesisĪ▒, in CVPR, 2017. ? J. Zhu et al. Ī░Visual Object Networks: Image Generation with Disentangled 3D RepresentationsĪ▒, in NeurIPS, 2018. ? S. Sun et al. Ī░Multi-view to Novel view: Synthesizing novel views with Self-Learned ConfidenceĪ▒, in ECCV, 2018. ? K. Olszewski et al. Ī░Transformable Bottleneck NetworksĪ▒, 2019. ? V. Sitzmann et al. Ī░DeepVoxels: Learning Persistent 3D Feature EmbeddingsĪ▒, in CVPR, 2019. ? R. Cheng et al. Ī░Geometry-Aware Recurrent Neural Networks for Active Visual RecognitionĪ▒, NeurIPS, 2018. ? H. Tung et al. Ī░Learning Spatial Common Sense with Geometry-Aware Recurrent NetworksĪ▒, in CVPR, 2019.







![Ė┼ę¬
? č}╩²ż╬2D╗ŁŽ±ż½żķ│ķ│÷żĘż┐╠žÅšż“3Dż╬Ū▒į┌▒Ē¼Fż╦Įy║Žż╣żļ?Ę©ż╬╠ß░Ė
? ╠ß░Ė?Ę©żŪżŽ╬óĘų┐╔─▄ż╩Äū║╬Ą─ż╩▓┘ū„(═Čė░, į┘═Čė░, ego-motion estimationż╩ż╔) ż“
deep learningż╦╚ĪżĻ?żņż┐
? ¼Fīg╩└Įńż╚3D featureż╬╬╗ų├Ą─ż╩ķv▀BżŽ▒Ż┤µżĘżŲżżżļ
? ╠ß░ĖżĘż┐źŌźŪźļżŽČ╠żż╗ŁŽ±┴ąż½żķą┬ęÄęĢĄŃż╬viewż“ėĶ£yż╣żļź┐ź╣ź»żŪč¦┴Ģ
? żĄżķż╦, 3D segmentationżõ3D object detectionżŌč¦┴Ģ┐╔─▄
? ╠žż╦Ś╩│÷ż╬å¢Ņ}żŪżŽ╬’╠Õż╬ė└ŠAąįż“┐╝æ]żĘż┐Ś╩│÷ (ź¬ź»źļ®`źĖźńź¾ż╦ÅŖżż)
? īg╠Õż“│ųż─visual agentż╦spatial common senseż“│ųż┐ż╗żļż┐żßż╦▒žę¬ż╩
╝╝ągżŪżóżļż╚ĮYšōż┼ż▒ż┐](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spatialcommonsense-191008105633/85/Learning-Spatial-Common-Sense-with-Geometry-Aware-Recurrent-Networks-10-320.jpg)
![╠ß░Ė?Ę©ż╬advantage
? ą┬ęÄęĢĄŃėĶ£yż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż╦ż¬ż▒żļÜ°╗»ąį─▄ż¼?żż
? geometryż“┐╝æ]żĘż╩żż?Ę© (GQN) ż╬ąį─▄ż“?żŁż»╔Ž╗žżļ
? ż┐ż└żĘ, ego-motionż╬═ŲČ©ż“ż╗ż║GTż“╩╣ż├ż┐ł÷║ŽżŪżóżļż│ż╚ż╦ūóęŌ
? 3D segmentationżõ3D object detectionż╦żŌ▀m?┐╔─▄
? ęĢĄŃż╬ēõ╗»ż╦░ķż”?ĢrĄ─ż╩ź¬ź»źļ®`źĖźńź¾ż╦ŅBĮĪż╩Ś╩│÷ĮY╣¹ż“Ą├ż┐
?╬’╠Õż╬ė└ŠAąį (object permanence) ż“└ĒĮŌżĘż┐šJūR?Ę©żŪżóżļŻĪ
? īgū░╣½ķ_żóżĻ
? https://github.com/ricsonc/grnn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spatialcommonsense-191008105633/85/Learning-Spatial-Common-Sense-with-Geometry-Aware-Recurrent-Networks-12-320.jpg)
![īg“Y
? Ś╩į^żĘż┐żżż╬żŽęįŽ┬ż╬å¢żż
1. GRNNsżŽspatial common senseż“č¦┴Ģż╣żļż½
2. geometryż“┐╝æ]żĘż┐ź═ź├ź╚ź’®`ź»śŗįņżŽspatial common senseż“½@Ą├ż╣żļż╬
ż╦▒žę¬ż½
3. GRNNsż╬ąį─▄ż╦ż─żżżŲ
? spatial common senseżŽ, ?ķgż¼│ųż─┐šķgšJūR─▄?╚½░Ńż“ųĖż╣ (Ä┌żżęŌ╬Č)
? 3D shapeżŽ2DŲĮ?ż“┼“żķż▐ż╗żļż│ż╚żŪ?│╔┐╔─▄
? źĘ®`ź¾żŽ╬’╠Õż½żķśŗ│╔żĄżņżļ
? 3┤╬į¬╬’╠ÕżŽĮ╗▓ŅżĘż╩żż
? ╬’╠ÕżŽ╝▒ż╦┤µį┌ż“Ž¹żĘż┐żĻżĘż╩żż](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spatialcommonsense-191008105633/85/Learning-Spatial-Common-Sense-with-Geometry-Aware-Recurrent-Networks-19-320.jpg)








![Visual Object Networks: Image Generation with
Disentangled 3D Representations
? 3Dż“┐╝æ]żĘż┐╗ŁŽ±?│╔ż“?ż”?Ę©ż╬╠ß░Ė
? 3D shapeż╬?│╔Ī·ź┐®`ź▓ź├ź╚ęĢĄŃż╦īØÅĻżĘż┐╔ŅČ╚╗ŁŽ±ż╚ź▐ź╣ź»ż╦ēõōQĪ·
źŲź»ź╣ź┴źŃź│®`ź╔ż“ėļż©żŲ╗ŁŽ±ż╦CNNżŪźņź¾ź└źĻź¾ź░
J. Zhu et al. Ī░Visual Object Networks: Image Generation with Disentangled 3D RepresentationsĪ▒, in NeurIPS, 2018.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spatialcommonsense-191008105633/85/Learning-Spatial-Common-Sense-with-Geometry-Aware-Recurrent-Networks-32-320.jpg)
![Transformable Bottleneck Networks
? 2D╗ŁŽ±ż“CNNż╦żĶżĻ3Dż╬ŠÄ╝»ż¼żŪżŁżļżĶż”ż╦ż╣żļ?Ę©ż╬╠ß░ĖĪŻ
? ╗ŁŽ±ż½żķ3D featureż“│ķ│÷żĘĪóżĮż│ż╦ź┐®`ź▓ź├ź╚ź▌®`ź║ż╦ķvż╣żļēõą╬ż“?żņż┐ż╬ż┴2Dżž
ż╬═Čė░ż“?żżĪó╗ŁŽ±ż╬į┘śŗ│╔ż╩ż╔ßßČ╬ż╬ź┐ź╣ź»ż“?ż”ĪŻ
? ż│żņż╦żĶżĻäé╠ÕēõōQż╦ż╚ż╔ż▐żķż╩żż3Dż“┐╝æ]żĘż┐╗ŁŽ±ŠÄ╝»ż“?ż”ż│ż╚ż¼żŪżŁżļĪŻ
K. Olszewski et al. Ī░Transformable Bottleneck NetworksĪ▒, 2019.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spatialcommonsense-191008105633/85/Learning-Spatial-Common-Sense-with-Geometry-Aware-Recurrent-Networks-34-320.jpg)


