Lecture 5
- 1. THERMODYNAMICS II LECTURE 4 DUAL COMBUSTION CYCLE AND SOME SOLVED EXAMPLES 1
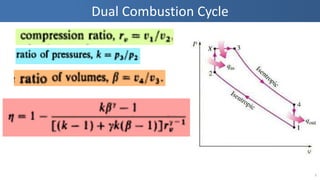
- 2. Contents ŌĆó General Discussion of dual combustion cycle ŌĆó Examples on Diesel cycle ŌĆó Home assignment 2
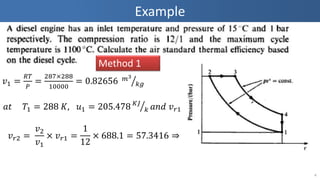
- 4. Example 4 ØæŻ1 = ØæģØæć Øæā = 287├Ś288 10000 = 0.82656 ØæÜ3 ØæśØæö ØæÄØæĪ Øæć1 = 288 ØÉŠ, Øæó1 = 205.478 ØÉŠØÉĮ Øæś ØæÄØæøØææ ØæŻ Øæ¤1 =688.1 ØæŻ Øæ¤2 = ØæŻ2 ØæŻ1 ├Ś ØæŻ Øæ¤1 = 1 12 ├Ś 688.1 = 57.3416 ŌćÆ Øæć2 = 751.37 ØæÄØæøØææ ŌäÄ2 = 768.79 Method 1
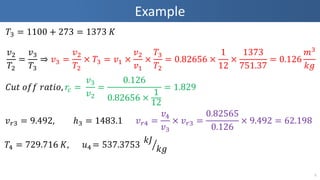
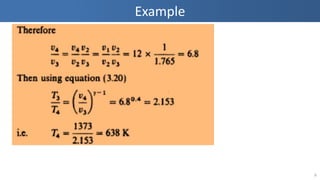
- 5. Example 5 Øæć3 = 1100 + 273 = 1373 ØÉŠ ØæŻ2 Øæć2 = ØæŻ3 Øæć3 ŌćÆ ØæŻ3 = ØæŻ2 Øæć2 ├Ś Øæć3 = ØæŻ1 ├Ś ØæŻ2 ØæŻ1 ├Ś Øæć3 Øæć2 = 0.82656 ├Ś 1 12 ├Ś 1373 751.37 = 0.126 ØæÜ3 ØæśØæö ØæŻ Øæ¤3 = 9.492, ŌäÄ3 = 1483.1 ØæŻ Øæ¤4 = ØæŻ4 ØæŻ3 ├Ś ØæŻ Øæ¤3 = 0.82565 0.126 ├Ś 9.492 = 62.198 ØÉČØæóØæĪ Øæ£ØæōØæō Øæ¤ØæÄØæĪØæ¢Øæ£, Øæ¤ØæÉ = ØæŻ3 ØæŻ2 = 0.126 0.82656 ├Ś 1 12 = 1.829 Øæć4 = 729.716 ØÉŠ, Øæó4 = 537.3753 ØæśØÉĮ ØæśØæö
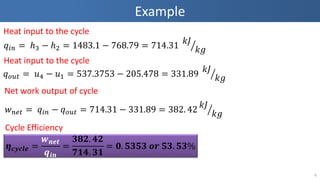
- 6. Example 6 Heat input to the cycle Øæ×Øæ¢Øæø = ŌäÄ3 ŌłÆ ŌäÄ2 = 1483.1 ŌłÆ 768.79 = 714.31 ØæśØÉĮ ØæśØæö Heat input to the cycle Øæ× Øæ£ØæóØæĪ = Øæó4 ŌłÆ Øæó1 = 537.3753 ŌłÆ 205.478 = 331.89 ØæśØÉĮ ØæśØæö Net work output of cycle Øæż ØæøØæÆØæĪ = Øæ×Øæ¢Øæø ŌłÆ Øæ× Øæ£ØæóØæĪ = 714.31 ŌłÆ 331.89 = 382. 42 ØæśØÉĮ ØæśØæö Cycle Efficiency Ø£╝ ØÆäØÆÜØÆäØÆŹØÆå = ØÆś ØÆÅØÆåØÆĢ ØÆÆØÆŖØÆÅ = ؤæؤ¢Ø¤É. ؤÆØ¤É Ø¤ĢؤÅؤÆ. ؤæؤŠ= ؤÄ. ؤōؤæؤōؤæ ØÆÉØÆō ؤōؤæ. ؤōؤæ%
- 8. Example 8
- 9. Example 9
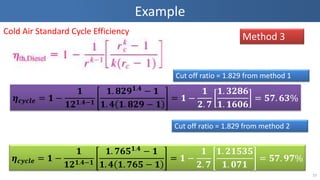
- 10. Example 10 Method 3 Cold Air Standard Cycle Efficiency Ø£╝ ØÆäØÆÜØÆäØÆŹØÆå = ؤŠŌłÆ ؤŠؤÅØ¤É Ø¤Å.ؤÆŌłÆؤŠؤÅ. ؤ¢Ø¤ÉؤŚ ؤÅ.Ø¤Æ ŌłÆ ؤŠؤÅ. Ø¤Æ Ø¤Å. ؤ¢Ø¤ÉؤŚ ŌłÆ ؤŠ= ؤŠŌłÆ ؤŠؤÉ. ؤĢ ؤÅ. ؤæؤÉؤ¢Ø¤ö ؤÅ. ؤÅؤöؤÄؤö = ؤōؤĢ. ؤöؤæ% Ø£╝ ØÆäØÆÜØÆäØÆŹØÆå = ؤŠŌłÆ ؤŠؤÅØ¤É Ø¤Å.ؤÆŌłÆؤŠؤÅ. ؤĢؤöؤō ؤÅ.Ø¤Æ ŌłÆ ؤŠؤÅ. Ø¤Æ Ø¤Å. ؤĢؤöؤō ŌłÆ ؤŠ= ؤŠŌłÆ ؤŠؤÉ. ؤĢ ؤÅ. ؤÉؤÅؤōؤæؤō ؤÅ. ؤÄؤĢؤŠ= ؤōؤĢ. ؤŚØ¤Ģ% Cut off ratio = 1.829 from method 1 Cut off ratio = 1.829 from method 2