Lecture 3 - Corporate Structure in chemical product design
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes19 views
Lecture 3 - Corporate Structure in chemical product design
1 of 13
Download to read offline












Recommended
Marketing and innovation



Marketing and innovationMaster MOI
╠²
The document discusses innovation and product failure. It suggests that new products often fail because they do not adequately fulfill the jobs customers need done in their lives. Customers are increasingly erratic and difficult to segment using traditional methods. Firms should focus on understanding the non-obvious jobs customers need fulfilled, and how new products can better address those needs through their impact on resources, processes and values within the firm.product design (managment)



product design (managment)Hafis Puzhakkal
╠²
This document discusses product design and development processes. It defines key terms like product, product development, and design process. It outlines the six phases of product development and different types of products. The document emphasizes that design is both a science and an art that maps a product's function to its form. It introduces fundamental rules of design and discusses how the design process has evolved from craftsmanship to concurrent engineering approaches using cross-functional teams.Conjoint analysis a perfect link between



Conjoint analysis a perfect link betweenprj_publication
╠²
This document discusses the gap that often exists between marketing and product design functions in new product development. It argues that conjoint analysis is an ideal tool to bridge this divide by helping develop customer-focused products. Specifically, it notes that consumer research is sometimes not fully incorporated due to perceived lack of credibility of consumer opinions or lack of help in generating innovative ideas. However, conjoint analysis can overcome these issues by systematically eliciting customer preferences and translating voice of customer information for designers.Conjoint analysis a perfect link between



Conjoint analysis a perfect link betweenprj_publication
╠²
This document discusses the gap that often exists between marketing and product design functions in new product development. It notes that while understanding customer needs is important for success, capturing the "voice of the customer" through marketing research can be challenging to incorporate into product design. The document recommends conjoint analysis as a tool that can help bridge this divide by allowing marketing information about customer preferences to be systematically incorporated into the product design process early on. This helps ensure new products are focused on consumer needs and more likely to succeed in the market.Product design and development ch4



Product design and development ch4Kavindra Singh
╠²
The document provides an overview of the product planning process outlined in Chapter 4 of the textbook "Product Design and Development" by Karl T. Ulrich and Steven D. Eppinger. It discusses identifying product development opportunities, evaluating and prioritizing projects, allocating resources and planning timing. A case study of Xerox's Lakes project to develop a digital copier platform is provided as an example. Key aspects of product planning include developing a portfolio of projects aligned with company strategy, market segmentation, technology roadmaps, and balancing fundamentally new vs. incremental projects.Product and process design



Product and process designWe Learn - A Continuous Learning Forum from Welingkar's Distance Learning Program.
╠²
In this presentation, we will discuss the concept and interrelation between product and process design and product life cycle. We will also talk about key decisions required in process design and evaluation of process design.
To know more about Welingkar SchoolŌĆÖs Distance Learning Program and courses offered, visit: http://www.welingkaronline.org/distance-learning/online-mba.html
Ch 2 product design (1)



Ch 2 product design (1)Shadina Shah
╠²
This document discusses product design and development. It outlines the key stages in product development: idea generation, feasibility study, preliminary design and testing, and final design and process. It also covers product life cycles and the importance of research and development for product design. R&D helps improve products, capture market share, and adapt to global demands. The objectives of R&D include creating new products and processes, improving quality, and gaining advantages from incentives.product Design power point.pptx



product Design power point.pptxshelememosisa
╠²
This document outlines the course objectives, outline, and content for a Product Design course taught to 5th year Mechanical Design students. The key points are:
1. The course aims to teach students about the role of market, finance, and design in new product development and give them the abilities to create a new product.
2. The course outline includes chapters on product life cycle, conceptual design, embodiment design, managing projects, and types of designs. It involves lectures, quizzes, tests, and projects.
3. The course content covers topics like product planning and specification, stimuli for new products, developing product ideas, and the product life cycle model of introduction, growth, maturity, and declineCh5ProductDesign.pdf



Ch5ProductDesign.pdfBarsena
╠²
Product design involves conceptualizing and developing physical products and services through testing and implementation. It is a multifaceted role that combines aspects of marketing, product management, industrial design, and engineering. Effective product design follows a process from identifying needs to evaluation. Related process design delineates the manufacturing steps and ensures quality production. Together, product and process design are interrelated and dynamic activities that evolve based on factors like volume, quality, and available equipment over a product's lifecycle from development to maturity and decline.New Product Development



New Product Developmentabhishek.mahanty
╠²
The document discusses new product development (NPD) processes and challenges. It describes the typical 5 phase NPD process: 1) opportunity identification, 2) concept generation, 3) concept evaluation, 4) development, and 5) launch. It also discusses concurrent engineering across functions, ensuring products contribute to business goals, and managing multiple projects. Common reasons for new product failure include small markets, poor fit with company strengths, lack of benefits, and inadequate support. Not all new products come from planned processes, as some result from accidental discoveries later recognized as opportunities.Ch13 - Organisation theory design and change gareth jones



Ch13 - Organisation theory design and change gareth jonesAnkit Kesri
╠²
The document discusses how innovation, intrapreneurship, and creativity are related. It describes the different types of innovation and technological change. It also outlines the steps involved in managing the innovation process, including using cross-functional teams, quantitative modeling like PERT/CPM charts, and stage-gate development funnels. The role of information technology in fostering innovation through information efficiencies and synergies is also covered.chapter review on product and process innovation.ppt



chapter review on product and process innovation.pptTemesgenAgazhie
╠²
This document discusses different types of innovation including product and process innovation. It provides details on the steps involved in product innovation such as idea generation, concept development, marketing strategy, and commercialization. Process innovation is defined as introducing new elements to production processes. The key steps in process innovation include planning, team formation, pilot testing, training, and commercial use. Concurrent engineering is described as developing products and processes simultaneously for faster development times compared to traditional sequential approaches. Advantages include reduced time, costs and improved communication, while disadvantages can include coordination challenges.Tech clarity perspective-industrial_top_performers



Tech clarity perspective-industrial_top_performersBentley Systems
╠²
The document discusses best practices for developing industrial equipment based on a survey of 378 manufacturers. It finds that the top 17% of performers by revenue and profit growth ("Top Performers") have grown revenue 2.2 times more and profit margins 2.4 times more than average companies. Top Performers more heavily emphasize globalization, quote accuracy, and innovation. They are more likely to use advanced engineering approaches like modular design and leverage simulation, configurators, PLM, and factory simulation tools to a greater degree to support their strategies and processes.Product Design & Development - 1



Product Design & Development - 1QRCE
╠²
This document discusses key aspects of product design and development. It defines product, product development process, and design process. It outlines the six phases of product development and different types of products. The document also discusses product conceptual design, form and function, fundamental design rules, concurrent engineering approach, and composition of effective design teams.Product development process



Product development processAsif Jeelani
╠²
The document discusses product development processes. It states that product development consists of structured activities that are repeated to develop new products. The main stages of new product development are concept generation, design, development, and production. It also discusses understanding customer needs, generating product concepts, designing specifications, prototyping, testing, and commercial production. Additional concepts discussed include standardization, manufacturability, concurrent engineering, and computer-aided design in product development.Unit 1 product-design&development



Unit 1 product-design&developmentAtul Joshi
╠²
The document discusses product design and development. It describes the six phases of the product development process: product planning, concept development, system-level design, detail design, testing and refinement, and production ramp-up. Key aspects of each phase are identified. The document also discusses product verification, validation, testing, and the roles involved in product development teams. Product development involves a range of technical, marketing, and financial activities, while product design focuses specifically on meeting technical requirements. PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGN 



PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGN Alemayohu Workine
╠²
This document provides an overview of product and service design. It discusses how product and service design translates customer wants and needs into requirements. It also discusses developing new products/services, quality goals, cost targets, and prototyping. Reasons for redesign include market opportunities/threats. The document also covers value analysis, objectives of design like customer satisfaction and cost, issues like lifecycles and standardization, designing for mass customization, phases of design like idea generation and feasibility analysis, and types of processes like job shop and batch processing.How Integrated Design Solutions Are Revolutionizing Climate Systems



How Integrated Design Solutions Are Revolutionizing Climate SystemsCraft Group
╠²
Explore how Integrated Design Solutions are transforming climate systems by enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and performance. Discover innovations driving eco-friendly manufacturing and faster time-to-market for a competitive edgeConjoint analysis a perfect link between



Conjoint analysis a perfect link betweenprjpublications
╠²
This document discusses the importance of understanding consumer needs in new product development and the gap that often exists between marketing and product design functions. It proposes that conjoint analysis is an ideal tool to bridge this divide by helping to develop customer-focused, successful products. The document provides background on new product development processes, the challenges faced by industrial designers, and the value of incorporating formal consumer research methods early in the development process. It argues that conjoint analysis can help overcome deficiencies in translating voice of the customer information for product designers to create useful, usable, and satisfying products for consumers.Conjoint analysis a perfect link between



Conjoint analysis a perfect link betweenprjpublications
╠²
The document discusses the gap that often exists between marketing and product design functions in new product development. It provides background on the importance of understanding consumer needs for developing successful new products. However, marketing research is not always effectively incorporated into product design due to perceived lack of credibility of consumer insights and inability to generate innovative ideas. The document proposes that conjoint analysis can help bridge this divide by overcoming deficiencies in translating voice of customer information for product development teams.Application of voc translationtools a case study



Application of voc translationtools a case studyiaemedu
╠²
This document provides an overview of tools that can be used to translate customer needs and preferences into product design. It discusses conjoint analysis, which measures customer preferences to help simulate customer reactions to new products. The document also mentions other voice of the customer tools like Kano analysis, Pugh matrix, quality function deployment that can be used in the new product development process to help bridge the gap between marketing and design. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer desires early in development through market research to improve the success rate of new products.Application of voc translationtools a case study



Application of voc translationtools a case studyiaemedu
╠²
The document discusses tools for translating the voice of the customer (VOC) into product design. It provides context on high new product failure rates and the importance of understanding customer needs early in the development process. The document then summarizes several VOC translation tools, including Quality Function Deployment (QFD) for translating customer wants into technical specifications, Pugh Matrix for comparing design concepts, Kano analysis for understanding customer preferences, and conjoint analysis for determining ideal product attributes based on customer tradeoffs.Class 16



Class 16Viral Kadakia
╠²
This document discusses Medtronic's shift to a platform-based approach to product development. It notes that platforms can help address problems like unexpected delays, consumer needs, or success by linking breakthrough technologies to derivative products through a common architecture. A platform strategy is designed to facilitate diffusion, commercialization, and standard-setting. The document analyzes how Medtronic's new approach encourages cumulative innovation and derivative products to leverage its technology investments across markets.Current Trends in Product Development during COVID-19



Current Trends in Product Development during COVID-19vivatechijri
╠²
This document summarizes current trends in product development during the COVID-19 pandemic. It discusses how the pandemic has accelerated existing trends like distributed product development teams collaborating online, as well as new trends like increased use of virtual prototyping and simulation to speed processes while limiting physical contact. Product development is increasingly integrating different technologies and balancing both technical and user requirements. Sustainability and the entire product lifecycle from design to end-of-life are also major considerations in current product development practices.Description of design process



Description of design processMITS Gwalior
╠²
The document describes the product design process, which includes key steps like product planning, concept development, embodiment design, and detail design. It discusses product planning in depth, including why it is important to determine the right mix of projects and provide each project with a focused mission statement. The document also covers gathering customer needs, generating concepts, and evaluating concepts to arrive at the best design.Design for Time to Market



Design for Time to MarketNosayaba Evbuomwan
╠²
This document discusses designing products for fast time to market within the context of concurrent engineering. It outlines the goals of designing for time to market as reducing cycle time and costs while improving quality. Achieving fast time to market requires top management commitment, organizational integration across functions, involving vendors early, using computer technologies, and understanding market strategies. Key factors that affect time to market include modular product design during conceptualization, overlapping activities to reduce sequencing, and integrating all product development processes.3-Process Modelling and Simulation (BCHE307L) for chemical engineering



3-Process Modelling and Simulation (BCHE307L) for chemical engineeringAABIDSHAIK3
╠²
3-Process Modelling and Simulation (BCHE307L) for chemical engineeringMore Related Content
Similar to Lecture 3 - Corporate Structure in chemical product design (20)
Ch5ProductDesign.pdf



Ch5ProductDesign.pdfBarsena
╠²
Product design involves conceptualizing and developing physical products and services through testing and implementation. It is a multifaceted role that combines aspects of marketing, product management, industrial design, and engineering. Effective product design follows a process from identifying needs to evaluation. Related process design delineates the manufacturing steps and ensures quality production. Together, product and process design are interrelated and dynamic activities that evolve based on factors like volume, quality, and available equipment over a product's lifecycle from development to maturity and decline.New Product Development



New Product Developmentabhishek.mahanty
╠²
The document discusses new product development (NPD) processes and challenges. It describes the typical 5 phase NPD process: 1) opportunity identification, 2) concept generation, 3) concept evaluation, 4) development, and 5) launch. It also discusses concurrent engineering across functions, ensuring products contribute to business goals, and managing multiple projects. Common reasons for new product failure include small markets, poor fit with company strengths, lack of benefits, and inadequate support. Not all new products come from planned processes, as some result from accidental discoveries later recognized as opportunities.Ch13 - Organisation theory design and change gareth jones



Ch13 - Organisation theory design and change gareth jonesAnkit Kesri
╠²
The document discusses how innovation, intrapreneurship, and creativity are related. It describes the different types of innovation and technological change. It also outlines the steps involved in managing the innovation process, including using cross-functional teams, quantitative modeling like PERT/CPM charts, and stage-gate development funnels. The role of information technology in fostering innovation through information efficiencies and synergies is also covered.chapter review on product and process innovation.ppt



chapter review on product and process innovation.pptTemesgenAgazhie
╠²
This document discusses different types of innovation including product and process innovation. It provides details on the steps involved in product innovation such as idea generation, concept development, marketing strategy, and commercialization. Process innovation is defined as introducing new elements to production processes. The key steps in process innovation include planning, team formation, pilot testing, training, and commercial use. Concurrent engineering is described as developing products and processes simultaneously for faster development times compared to traditional sequential approaches. Advantages include reduced time, costs and improved communication, while disadvantages can include coordination challenges.Tech clarity perspective-industrial_top_performers



Tech clarity perspective-industrial_top_performersBentley Systems
╠²
The document discusses best practices for developing industrial equipment based on a survey of 378 manufacturers. It finds that the top 17% of performers by revenue and profit growth ("Top Performers") have grown revenue 2.2 times more and profit margins 2.4 times more than average companies. Top Performers more heavily emphasize globalization, quote accuracy, and innovation. They are more likely to use advanced engineering approaches like modular design and leverage simulation, configurators, PLM, and factory simulation tools to a greater degree to support their strategies and processes.Product Design & Development - 1



Product Design & Development - 1QRCE
╠²
This document discusses key aspects of product design and development. It defines product, product development process, and design process. It outlines the six phases of product development and different types of products. The document also discusses product conceptual design, form and function, fundamental design rules, concurrent engineering approach, and composition of effective design teams.Product development process



Product development processAsif Jeelani
╠²
The document discusses product development processes. It states that product development consists of structured activities that are repeated to develop new products. The main stages of new product development are concept generation, design, development, and production. It also discusses understanding customer needs, generating product concepts, designing specifications, prototyping, testing, and commercial production. Additional concepts discussed include standardization, manufacturability, concurrent engineering, and computer-aided design in product development.Unit 1 product-design&development



Unit 1 product-design&developmentAtul Joshi
╠²
The document discusses product design and development. It describes the six phases of the product development process: product planning, concept development, system-level design, detail design, testing and refinement, and production ramp-up. Key aspects of each phase are identified. The document also discusses product verification, validation, testing, and the roles involved in product development teams. Product development involves a range of technical, marketing, and financial activities, while product design focuses specifically on meeting technical requirements. PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGN 



PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGN Alemayohu Workine
╠²
This document provides an overview of product and service design. It discusses how product and service design translates customer wants and needs into requirements. It also discusses developing new products/services, quality goals, cost targets, and prototyping. Reasons for redesign include market opportunities/threats. The document also covers value analysis, objectives of design like customer satisfaction and cost, issues like lifecycles and standardization, designing for mass customization, phases of design like idea generation and feasibility analysis, and types of processes like job shop and batch processing.How Integrated Design Solutions Are Revolutionizing Climate Systems



How Integrated Design Solutions Are Revolutionizing Climate SystemsCraft Group
╠²
Explore how Integrated Design Solutions are transforming climate systems by enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and performance. Discover innovations driving eco-friendly manufacturing and faster time-to-market for a competitive edgeConjoint analysis a perfect link between



Conjoint analysis a perfect link betweenprjpublications
╠²
This document discusses the importance of understanding consumer needs in new product development and the gap that often exists between marketing and product design functions. It proposes that conjoint analysis is an ideal tool to bridge this divide by helping to develop customer-focused, successful products. The document provides background on new product development processes, the challenges faced by industrial designers, and the value of incorporating formal consumer research methods early in the development process. It argues that conjoint analysis can help overcome deficiencies in translating voice of the customer information for product designers to create useful, usable, and satisfying products for consumers.Conjoint analysis a perfect link between



Conjoint analysis a perfect link betweenprjpublications
╠²
The document discusses the gap that often exists between marketing and product design functions in new product development. It provides background on the importance of understanding consumer needs for developing successful new products. However, marketing research is not always effectively incorporated into product design due to perceived lack of credibility of consumer insights and inability to generate innovative ideas. The document proposes that conjoint analysis can help bridge this divide by overcoming deficiencies in translating voice of customer information for product development teams.Application of voc translationtools a case study



Application of voc translationtools a case studyiaemedu
╠²
This document provides an overview of tools that can be used to translate customer needs and preferences into product design. It discusses conjoint analysis, which measures customer preferences to help simulate customer reactions to new products. The document also mentions other voice of the customer tools like Kano analysis, Pugh matrix, quality function deployment that can be used in the new product development process to help bridge the gap between marketing and design. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer desires early in development through market research to improve the success rate of new products.Application of voc translationtools a case study



Application of voc translationtools a case studyiaemedu
╠²
The document discusses tools for translating the voice of the customer (VOC) into product design. It provides context on high new product failure rates and the importance of understanding customer needs early in the development process. The document then summarizes several VOC translation tools, including Quality Function Deployment (QFD) for translating customer wants into technical specifications, Pugh Matrix for comparing design concepts, Kano analysis for understanding customer preferences, and conjoint analysis for determining ideal product attributes based on customer tradeoffs.Class 16



Class 16Viral Kadakia
╠²
This document discusses Medtronic's shift to a platform-based approach to product development. It notes that platforms can help address problems like unexpected delays, consumer needs, or success by linking breakthrough technologies to derivative products through a common architecture. A platform strategy is designed to facilitate diffusion, commercialization, and standard-setting. The document analyzes how Medtronic's new approach encourages cumulative innovation and derivative products to leverage its technology investments across markets.Current Trends in Product Development during COVID-19



Current Trends in Product Development during COVID-19vivatechijri
╠²
This document summarizes current trends in product development during the COVID-19 pandemic. It discusses how the pandemic has accelerated existing trends like distributed product development teams collaborating online, as well as new trends like increased use of virtual prototyping and simulation to speed processes while limiting physical contact. Product development is increasingly integrating different technologies and balancing both technical and user requirements. Sustainability and the entire product lifecycle from design to end-of-life are also major considerations in current product development practices.Description of design process



Description of design processMITS Gwalior
╠²
The document describes the product design process, which includes key steps like product planning, concept development, embodiment design, and detail design. It discusses product planning in depth, including why it is important to determine the right mix of projects and provide each project with a focused mission statement. The document also covers gathering customer needs, generating concepts, and evaluating concepts to arrive at the best design.Design for Time to Market



Design for Time to MarketNosayaba Evbuomwan
╠²
This document discusses designing products for fast time to market within the context of concurrent engineering. It outlines the goals of designing for time to market as reducing cycle time and costs while improving quality. Achieving fast time to market requires top management commitment, organizational integration across functions, involving vendors early, using computer technologies, and understanding market strategies. Key factors that affect time to market include modular product design during conceptualization, overlapping activities to reduce sequencing, and integrating all product development processes.More from AABIDSHAIK3 (6)
3-Process Modelling and Simulation (BCHE307L) for chemical engineering



3-Process Modelling and Simulation (BCHE307L) for chemical engineeringAABIDSHAIK3
╠²
3-Process Modelling and Simulation (BCHE307L) for chemical engineeringPartcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluid



Partcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluidAABIDSHAIK3
╠²
Partcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluidRecently uploaded (20)
Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdf



Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdfTotok Sulistiyanto
╠²
High Efficiency Chiller System in HVACUS Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
╠²
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads, additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1 MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the system.Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...



Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...ASHISHDESAI85
╠²
Combining 3D printing with Internet of Things (IoT) enables the creation of smart, connected, and customizable objects that can monitor, control, and optimize their performance, potentially revolutionizing various industries. oT-enabled 3D printers can use sensors to monitor the quality of prints during the printing process. If any defects or deviations from the desired specifications are detected, the printer can adjust its parameters in real time to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.Optimization of Cumulative Energy, Exergy Consumption and Environmental Life ...



Optimization of Cumulative Energy, Exergy Consumption and Environmental Life ...J. Agricultural Machinery
╠²
Optimal use of resources, including energy, is one of the most important principles in modern and sustainable agricultural systems. Exergy analysis and life cycle assessment were used to study the efficient use of inputs, energy consumption reduction, and various environmental effects in the corn production system in Lorestan province, Iran. The required data were collected from farmers in Lorestan province using random sampling. The Cobb-Douglas equation and data envelopment analysis were utilized for modeling and optimizing cumulative energy and exergy consumption (CEnC and CExC) and devising strategies to mitigate the environmental impacts of corn production. The Cobb-Douglas equation results revealed that electricity, diesel fuel, and N-fertilizer were the major contributors to CExC in the corn production system. According to the Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) results, the average efficiency of all farms in terms of CExC was 94.7% in the CCR model and 97.8% in the BCC model. Furthermore, the results indicated that there was excessive consumption of inputs, particularly potassium and phosphate fertilizers. By adopting more suitable methods based on DEA of efficient farmers, it was possible to save 6.47, 10.42, 7.40, 13.32, 31.29, 3.25, and 6.78% in the exergy consumption of diesel fuel, electricity, machinery, chemical fertilizers, biocides, seeds, and irrigation, respectively. Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
╠²
Welcome to the March 2025 issue of WIPAC Monthly the magazine brought to you by the LinkedIn Group WIPAC Monthly.
In this month's edition, on top of the month's news from the water industry we cover subjects from the intelligent use of wastewater networks, the use of machine learning in water quality as well as how, we as an industry, need to develop the skills base in developing areas such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Enjoy the latest editionEngineering at Lovely Professional University (LPU).pdf



Engineering at Lovely Professional University (LPU).pdfSona
╠²
LPUŌĆÖs engineering programs provide students with the skills and knowledge to excel in the rapidly evolving tech industry, ensuring a bright and successful future. With world-class infrastructure, top-tier placements, and global exposure, LPU stands as a premier destination for aspiring engineers.How to Make an RFID Door Lock System using Arduino



How to Make an RFID Door Lock System using ArduinoCircuitDigest
╠²
Learn how to build an RFID-based door lock system using Arduino to enhance security with contactless access control.Taykon-Kalite belgeleri



Taykon-Kalite belgeleriTAYKON
╠²
Kalite Politikam─▒z
Taykon ├ćelik i├¦in kalite, hayallerinizi bizlerle payla┼¤t─▒─¤─▒n─▒z an ba┼¤lar. Proje ├¦iziminden detaylar─▒n ├¦├Čz├╝m├╝ne, detaylar─▒n ├¦├Čz├╝m├╝nden ├╝retime, ├╝retimden montaja, montajdan teslime hayallerinizin ger├¦ekle┼¤ti─¤ini g├Črd├╝─¤├╝n├╝z ana kadar ge├¦en t├╝m a┼¤amalar─▒, ├¦al─▒┼¤anlar─▒, t├╝m teknik donan─▒m ve ├¦evreyi i├¦ine al─▒r KAL─░TE.Introduction to Safety, Health & Environment



Introduction to Safety, Health & Environmentssuserc606c7
╠²
Introduction to
Safety, Health &EnvironmentUNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptx



UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptxKesavanT10
╠²
UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptxSoil Properties and Methods of Determination



Soil Properties and Methods of DeterminationRajani Vyawahare
╠²
This PPT covers the index and engineering properties of soil. It includes details on index properties, along with their methods of determination. Various important terms related to soil behavior are explained in detail. The presentation also outlines the experimental procedures for determining soil properties such as water content, specific gravity, plastic limit, and liquid limit, along with the necessary calculations and graph plotting. Additionally, it provides insights to understand the importance of these properties in geotechnical engineering applications.Mathematics behind machine learning INT255 INT255__Unit 3__PPT-1.pptx



Mathematics behind machine learning INT255 INT255__Unit 3__PPT-1.pptxppkmurthy2006
╠²
Mathematics behind machine learning INT255 How to Build a Maze Solving Robot Using Arduino



How to Build a Maze Solving Robot Using ArduinoCircuitDigest
╠²
Learn how to make an Arduino-powered robot that can navigate mazes on its own using IR sensors and "Hand on the wall" algorithm.
This step-by-step guide will show you how to build your own maze-solving robot using Arduino UNO, three IR sensors, and basic components that you can easily find in your local electronics shop.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
╠²
Optimization of Cumulative Energy, Exergy Consumption and Environmental Life ...



Optimization of Cumulative Energy, Exergy Consumption and Environmental Life ...J. Agricultural Machinery
╠²
Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
╠²
Lecture 3 - Corporate Structure in chemical product design
- 1. Gani, Comp. Chem. Engg., 28 (2004), p. 2441 ŌĆō 2457.
- 2. A Typical FMCG Company Villadsen, Chem. Eng. Sci., 52(17), 2857 ŌĆō 2864 (1997).
- 3. Changes in the Chemical Industries ’ü« Commodity manufacturers are facing a crisis: ’ü« Optimization and restructuring (downsizing) are not working. ’ü« Ruthless minimization of research and concentration on in-house efficiency ’ü« Many firms are leaving the chemical business ’ü« Some are turning to specialty products.
- 4. Changes in the Chemical Industries
- 5. Changes in the Chemical Industries
- 6. Changes in Corporate Culture ’ü« Corporations organize product development in two ways: ’ü« Organization by function ’ü« Organization by project ’ü« Both can be effective ’ü« Functional organization is like a chemical reaction in series. ’ü« Project organization is like a chemical reaction in parallel.
- 8. Corporate Strategy: ŌĆ£Market pullŌĆØ vs. ŌĆ£Technology pushŌĆØ ’ü« ŌĆ£Necessity is the mother of inventionŌĆØ ’ü« Market pull: there is a market looking for a technology, e.g., Freon. ’ü« Technology push: there is a technology looking for a market, e.g., Botox. ’ü« A ŌĆ£platform technologyŌĆØ is a technology successful in one or more markets and has potential applications in many more markets.
- 9. Market Pull vs. Technology Push
- 10. The Product Design Procedure ’ü« Product design depends on four steps: ’ü« Needs. What needs should the product fulfill? ’ü« Ideas. What different products could satisfy these needs? ’ü« Selection. Which ideas are the most promising? ’ü« Manufacture. How can we make the product in commercial quantities? ’ü« Application of this template leads to new features of the design process. ’ü« The entire course is organized around this procedure.
- 11. Criticisms of this procedure ’ü« Not general (yes, the steps will usually have to be iteratively sequenced). ’ü« Management, not technology, is the key (no, can management circumvent the second law of thermodynamics?). ’ü« Product design is a part of process design (no, we must go beyond process design, as shown next).
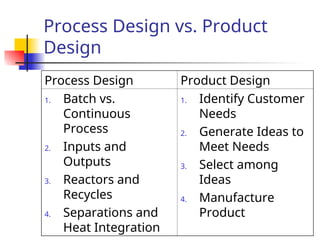
- 12. Process Design vs. Product Design ’ü« Product design emphasizes decisions made before those of process design. ’ü« In process design we know what the product is; not so in product design. ’ü« Commodity chemical manufacture best served by process design (no product differentiation). ’ü« Specialty product development best served by product design (product is differentiated). ’ü« Focus of process design is efficient manufacture (recycle, heat integration, optimization, etc.) ; focus of product design is speed to reach the market place.
- 13. Process Design vs. Product Design Process Design Product Design 1. Batch vs. Continuous Process 2. Inputs and Outputs 3. Reactors and Recycles 4. Separations and Heat Integration 1. Identify Customer Needs 2. Generate Ideas to Meet Needs 3. Select among Ideas 4. Manufacture Product












