Lecture_No._2_Computational_Chemistry_Tools___Application_of_computational_methods.ppt.pdf
- 1. Dr. Mazhar Amjad Gilani COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus 05-10-2020 Computational Tools and Applications of Computational methods in Different fields of Chemistry
- 2. Topics to be coveredŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. 1. Some more definitions of computational chemistry 2. Concept of Computational Models 3. Knowledge about Hardware & Software Topics to be coveredŌĆ”ŌĆ”..
- 3. Definition of Computational Chemistry ŌĆó Computational Chemistry: Use mathematical approximations and computer programs to obtain results relative to chemical problems. ŌĆó Computational Quantum Chemistry: Focuses specifically on equations and approximations derived from the postulates of quantum mechanics. Solve the Schr├Čdinger equation for molecular systems. ŌĆó Ab Initio Quantum Chemistry: Uses methods that do not include any empirical parameters or experimental data.
- 4. Computational Models/Tools ’éó A model is a system of equations, or computations used to determine the energetics of a molecule ’éó Different models use different approximations (or levels of theory) to produce results of varying levels of accuracy. ’éó There is a trade off between accuracy and computational time. ’éó There are two main types of models; those that use Schr├Čdinger's equation (or simplifications of it) and those that do not.
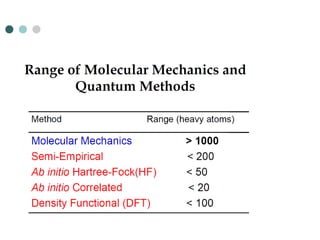
- 5. Computational Models/Tools ’éó Types of Models (Listed in order from most to least accurate) ’ü¼ Ab initio ŌĆó uses Schr├Čdinger's equation, but with approximations ’ü¼ Semi Empirical ŌĆó uses experimental parameters and extensive simplifications of Schr├Čdinger's equation ’ü¼ Molecular Mechanics ŌĆó does not use Schr├Čdinger's equation Simulated zigzag carbon nanotube
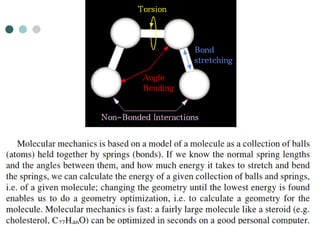
- 6. Molecular Mechanics ’éó Simplest type of calculation ’ü¼ Used when systems are very large and approaches that are more accurate become to costly (in time and memory) ’éó Does not use any quantum mechanics instead uses parameters derived from experimental or ab initio data ’ü¼ Uses information like bond stretching, bond bending, torsions, electrostatic interactions, van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding to predict the energetics of a system ’ü¼ The energy associated with a certain type of bond is applied throughout the molecule. This leads to a great simplification of the equation
- 8. To predict the energy associated with a given conformation Molecular mechanics energies have no meaning as absolute quantities Only differences in energy between two/more conformations have meaning A simple molecular mechanics energy equation is given by: Energy = Stretching Energy + Bending Energy +Torsion Energy + Non-Bonded Interaction Energy These equations together with the data (parameters) required to describe the behavior of different kinds of atoms and bonds, is called a force-field.
- 9. ŌĆó Stretching Energy The stretching energy equation is based on Hooke's law. The "kb" parameter controls the stiffness of the bond spring, while "ro" defines its equilibrium length. Unique "kb" and "ro" parameters are assigned to each pair of bonded atoms based on their types (e.g. C-C, C-H, O-C, etc.). This equation estimates the energy associated with vibration about the equilibrium bond length. This is the equation of a parabola, as can be seen in the following plot:
- 11. ŌĆó Bending Energy The bending energy equation is also based on Hooke's law. The "ktheta" parameter controls the stiffness of the angle spring, while "thetao" defines its equilibrium angle. This equation estimates the energy associated with vibration about the equilibrium bond angle:
- 12. Unique parameters for angle bending are assigned to each bonded triplet of atoms based on their types (e.g. C-C-C, C-O-C, C-C-H, etc.). The effect of the "kb" and "ktheta" parameters is to broaden or steepen the slope of the parabola. The larger the value of "k", the more energy is required to deform an angle (or bond) from its equilibrium value.
- 13. Semi Empirical ’éó Semi empirical methods use experimental data to parameterize equations ’éó Like the ab initio methods, a Hamiltonian and wave function are used ’ü¼ much of the equation is approximated or eliminated ’éó Less accurate than ab initio methods but also much faster ’éó The equations are parameterized to reproduce specific results, usually the geometry and heat of formation, but these methods can be used to find other data. Mixing of theory and experiment that makes the method semi-empirical
- 14. Ab Initio ’éó Ab initio translated from Latin means ŌĆ£from first principles.ŌĆØ This refers to the fact that no experimental data is used and computations are based on quantum mechanics. ’éó Different Levels of Ab Initio Calculations ’ü¼ Hartree-Fock (HF) ŌĆó The simplest ab initio calculation ŌĆó The major disadvantage of HF calculations is that electron correlation is not taken into consideration. ’ü¼ The M├Ėller-Plesset Perturbation Theory (MP) ’ü¼ Density Functional Theory (DFT) ’ü¼ Configuration Interaction (CI) Take into consideration electron correlation
- 17. Computational Resources Two fundamental resources are required ŌĆóHigh speed super computers (clusters) etc. ŌĆóSuitable software program
- 19. *Abbreviated Profile of Drugs (APOD) is a web-based decision and prediction program for drug discovery. Software's *ADMEWORKS DDI Simulator -- ADMEWORKS DDI Simulator is a software application for assessing the risk of potential drug-drug interactions, allowing the user to perform both quantitative simulations of Competitive and Mechanism-based inhibitions *AMBER -- Molecular Dynamics Program
- 20. *AMSOL -- Semiempirical quantum chemistry program (gas phase and solvation) *APBS: Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver -- Software for evaluating the electrostatic properties of nanoscale biomolecular systems *ArgusLab 3.0 -- Molecular Modeling Software *BioSolveIT -- Software solutions for structure and ligand-based molecular design Chemissian: quantum chemistry program for visualizing electron/spin density distribution and UV-VIS spectra, plotting molecular orbital energy level diagrams, calculating atomic orbital populations, contributions of atoms and fragments to MOs. *COSMOlogic -- Software for Life Sciences, Chemical Engineering. *GAMESS ab initio program.
- 21. *LiqCryst -- LiqCryst is a MS-Windows-based application, covers all aspects of liquid crystal research: material properties, display technology, theory, basic research and applications *MDL QSAR - Comprehensive QSAR modeling system *MOLCAS -- quantum chemistry software package *Polar -- electrochemical simulation and data analysis Q-chem -- ab initio and DFT molecular modeling package *Schrodinger, Computational Chemistry Software *Gromacs MD Software *SCIGRESS -- SCIGRESS is a unique desktop molecular modeling software package that can apply a wide range of computational models to all types of molecular systems, from small organic molecules.
- 22. References ’éó Chem Viz at http://www.shodor.org/chemviz/basis/students/introduction.html ’éó D. YOUNG, in ŌĆ£Computational Chemistry, A Practical Guide for Applying Techniques to Real World ProblemsŌĆØ (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 2001). ’éó J. SIMMONS, in An Introduction to Theoretical ChemistryŌĆØ (Cambridge Press, Cambridge, 2003). ’éó J. B. FORESMAN AND ├å. FRISCH, in ŌĆ£Exploring Chemistry with Electronic Structure Methods, 2nd EditionŌĆØ (Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, 1996).