Low-Power, Long-Range, Precise Localization
2 likes987 views
Presentation describes the contrast between low-power, long-range and precise (vs accurate) localization
1 of 39
Downloaded 22 times



















Recommended
The increasing need for low power, long range communication and localization ...



The increasing need for low power, long range communication and localization ...Maarten Weyn
╠²
Prof. Maarten Weyn gave a presentation on low-power communication and localization. He discussed his research in localization from opportunistic to just enough systems and low-power communication. Weyn is also the founder of one spin-off company and helped facilitate two others. He discussed low-power applications that can run for years on AA batteries or other small batteries. Weyn also covered the DASH7 protocol for low-power, mid-range wireless sensor communication and its open standard for sub-GHz ISM bands.LoRa and NB-IoT 



LoRa and NB-IoT Darshan Patil
╠²
This document provides an overview and comparison of LoRa and NB-IoT low-power wide area network (LPWA) technologies. It discusses that both technologies were developed for applications requiring long battery life and low data rates. LoRa is an unlicensed standard based on chirp spread spectrum modulation, while NB-IoT is a licensed narrowband cellular standard developed by 3GPP. Key differences are that LoRa has lower device costs and supports higher latencies, while NB-IoT can leverage existing cellular networks and has higher data rates. In conclusion, LoRa is a new dedicated technology for IoT platforms, while NB-IoT uses existing cellular infrastructure.Understand LPWA tetchnologies (Sigfox and LoRa)



Understand LPWA tetchnologies (Sigfox and LoRa)Robert V
╠²
What are LPWA networks and what are their advantages ?
What are their characateristics in comparison with other telecom technologies ?
What are the differences between LPWA technologies, especially Sigfox and LoRa ?LPWAN Technologies for Internet of Things (IoT) and M2M Scenarios



LPWAN Technologies for Internet of Things (IoT) and M2M ScenariosPeter R. Egli
╠²
Rapid technological advances in the past made possible the miniaturization of network devices to meet the cost and power consumption requirements in IoT and M2M scenarios. What is missing in this picture is a radio technology with both long range capability and a very low cost footprint. Existing radio technologies such as 3G/4G or Short Range Radio do not aptly meet the requirements of IoT scenarios because they are either too expensive or are not able to provide the required range. Other wireless technologies are geared towards high bandwidth which is in most cases not a requirement for IoT.
Emerging LPWAN technologies such as ETSI LTN or LoRAWAN are poised for filling the gap by providing long range (up to 40km) and low power connectivity. These technologies allow low cost radio devices and operation thus enabling scaling up IoT applications.Wireless communication



Wireless communicationKomal Gandhi
╠²
This document discusses the history, advantages, need, implementation, current devices and future of wireless communication. It covers the evolution of wireless technologies from early cellular phones to modern Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, explaining how wireless networks have become essential due to their convenience and mobility compared to wired connections. The future of wireless communication looks to advance connectivity through emerging technologies.Wireless communication



Wireless communicationDarshan Maru
╠²
Wireless communication allows for freedom from wires and instantaneous communication without physical connections. It provides global coverage for communication that can reach areas where wiring is infeasible or costly. Wireless communication transmits voice and data using radio waves without wires. It uses different frequency channels that can transmit information independently and in parallel. While wireless communication provides mobility and flexibility, it also faces security and physical obstruction issues compared to wired communication.
Human: Thank you for the summary. It effectively captured the key points about wireless communication in just 3 sentences as requested.Support Recovery with Sparsely Sampled Free Random Matrices for Wideband Cogn...



Support Recovery with Sparsely Sampled Free Random Matrices for Wideband Cogn...IJMTST Journal
╠²
The main objective of this project is to design an eigenvalue-based compressive SOE technique using asymptotic random matrix theory. In this project, investigating blind sparsity order estimation (SOE) techniques is an open research issue. To address this, this project presents an eigenvalue-based compressive SOE technique using asymptotic random matrix theory. Finally, this project propose a technique to estimate the sparsity order of the wideband spectrum with compressive measurements using the maximum eigenvalue of the measured signal's covariance matrix. .Hl3413921395



Hl3413921395IJERA Editor
╠²
International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) is an open access online peer reviewed international journal that publishes research and review articles in the fields of Computer Science, Neural Networks, Electrical Engineering, Software Engineering, Information Technology, Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Plastic Engineering, Food Technology, Textile Engineering, Nano Technology & science, Power Electronics, Electronics & Communication Engineering, Computational mathematics, Image processing, Civil Engineering, Structural Engineering, Environmental Engineering, VLSI Testing & Low Power VLSI Design etc.A Survey on Rendezvous Based Techniques for Power Conservation in Wireless Se...



A Survey on Rendezvous Based Techniques for Power Conservation in Wireless Se...ijceronline
╠²
International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) is dedicated to protecting personal information and will make every reasonable effort to handle collected information appropriately. All information collected, as well as related requests, will be handled as carefully and efficiently as possible in accordance with IJCER standards for integrity and objectivity.A Survey on Rendezvous Based Techniques for Power Conservation in Wireless Se...



A Survey on Rendezvous Based Techniques for Power Conservation in Wireless Se...ijceronline
╠²
International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) is dedicated to protecting personal information and will make every reasonable effort to handle collected information appropriately. All information collected, as well as related requests, will be handled as carefully and efficiently as possible in accordance with IJCER standards for integrity and objectivity.Intrusion Detection In Open Field Using Geophone (Report)



Intrusion Detection In Open Field Using Geophone (Report)Nuthan Prasad
╠²
This dissertation discusses the design of an intrusion detection system using geophones in an open field. A sensor network of geophone nodes is used to detect human intrusions by identifying footstep impulses. When intrusion is detected via kurtosis analysis, the sensor node alerts a control room which can then dispatch an unmanned ground vehicle to the location. The system aims to remotely monitor large outdoor areas with limited manpower.Localization Issues in a ZigBee based Internet of Things scenario



Localization Issues in a ZigBee based Internet of Things scenarioMassimiliano Dibitonto
╠²
Paper presented @Tyrrhenian Workshop on the Internet of Things 2009
ZigBee is probably the most popular IEEE 802.15.4 implementation used for Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN). The radio communication can also be used for localization purposes using fixed network devices as reference points. In this paper, the authors describe a procedure for automatically configuring a ZigBee-based localization appli-cation with environment-optimized parameters.Where Next



Where NextRoberto Trasarti
╠²
- The document presents a technique called WhereNext that predicts the next location of a trajectory based on analyzing patterns from previous movements without considering individual user information.
- WhereNext builds a prediction tree model from patterns of movement called T-Patterns extracted from trajectory data. It allows spatial and temporal approximation to account for noise in real trajectories.
- The method can be tuned for accuracy and prediction rate. Evaluation on a real dataset of 17,000 vehicle GPS trajectories in Milan showed it effectively predicts next locations.Hybrid Positioning



Hybrid Positioningspirentgnss
╠²
To meet the increasing demands that current and emerging location based services (LBS) are placing on location-aware technology, engineers are turning to hybrid positioning ŌĆō but what is it?
Discover:
- Why hybrid positioning is an increasingly common feature in smartphone and tablet designs
- How Wi-Fi, MEMS inertial sensors and cellular networks can all augment GNSS positioningDelivAR



DelivARDaniele Tatasciore
╠²
An Augmented Reality Mobile Application to Expedite the Package
Identification Process for Last-Mile Deliveries. http://lumakollektiv.com/delivar.htmlHm3114401445



Hm3114401445IJERA Editor
╠²
This document discusses the application of digital signal processing in radar signals. It provides an overview of how DSP is used extensively in modern radar systems, both at the transmitter to generate pulses and control antennas, and at the receiver to perform tasks like clutter removal and beamforming. The document also reviews some key techniques in DSP for radar signals, including constant false alarm rate processing and matched filtering for signal detection. It describes how DSP helps with tasks like tracking multiple targets, resolving measurement ambiguities, and combining information from radar and other sources.HalifaxNGGs



HalifaxNGGsNikos Kostagiolas
╠²
The document discusses N-gram graphs, which represent the proximity or co-occurrence of items in a text by modeling them as a graph. An N-gram graph is constructed by extracting n-grams from a text, determining their neighborhood based on a window size, and assigning edge weights based on co-occurrence frequencies. The document outlines the process for constructing N-gram graphs and describes their potential uses, including representing sets of items with a single graph, comparing graphs through clustering, and defining similarity measures between graphs. N-gram graphs aim to capture proximity information in a way that is domain-agnostic, allows different analysis levels, and can represent multiple texts with a single graph structure.Accurate indoor positioning system based on modify nearest point technique



Accurate indoor positioning system based on modify nearest point techniqueIJECEIAES
╠²
This document presents an accurate indoor positioning system based on a modified nearest point technique. The system uses Wi-Fi signals to estimate distances and indoor locations. It builds a fingerprint database with reference points and signal measurements collected in different environments to account for changing conditions. The case study building is divided into 7 areas to allow dynamic parameter assignment. Locations are estimated by finding the nearest reference point within a specific environment by comparing at least four nearby points. The results showed errors of less than 0.102 meters for indoor localization.Nuzzer algorithm based Human Tracking and Security System for Device-Free Pas...



Nuzzer algorithm based Human Tracking and Security System for Device-Free Pas...Eswar Publications
╠²
In recent years, majority of researches are focused on localization system for wireless environment. These researches rely on localization using devices to track the entities. In this paper, we use, a recently proposed Device-free Passive (DfP) that uses Probabilistic techniques to track locations in large-scale real environment without the need of carrying devices. The proposed system uses the Access Points (APs) and Monitoring Point (MPs) that works by monitoring and processing the changes in the received physical signals at one or more monitoring points to detect changes in the environment. The system uses continuous space estimator to return multiple location while the mortal is in motion. Our results show that the system can achieve very high probability of detection and tracking with very few false positives.REDTACTON



REDTACTONNisha Raj S N
╠²
The document discusses Red Tacton, a new human area networking technology developed in Japan. Red Tacton uses the human body as a transmission medium for data, inducing weak electric fields on the skin's surface to transmit signals up to 10 Mbps. It works by transmitting data via a tacton transmitter and receiving it using an electro-optic crystal sensor in the tacton receiver. The technology has applications for personal devices, security, and intuitive human-computer interaction through touch.J0412261066



J0412261066IOSR-JEN
╠²
This document discusses radar echo signals and multipath fading. It begins with an abstract that introduces multipath propagation as a phenomenon where radar signals take multiple paths upon reflection, in addition to the direct line of sight path. This can cause interference and fading effects. The document then provides background on radar systems and the radar range equation. It presents an approach to process received radar signals to isolate the main line of sight echo and discard weaker multipath signals. This involves analyzing signal amplitudes and retaining the highest value signal. The system components for implementing this approach include a fast microcontroller, computer, and lab link cable for programming the microcontroller using BASIC language software.Radar target detection simulation



Radar target detection simulationIJERA Editor
╠²
This document presents a computer simulation model for radar target detection. The model considers two moving targets generated using a keypad and applies nine levels of noise to simulate changing signal-to-noise ratios. As noise levels increase, the brightness of target blips on the radar display decrease by around 5% for each level. The simulation is programmed in Turbo C++ and interfaces with a computer through a parallel port to simulate a radar display and evaluate the effects of noise on target detection performance.Reactive Power Compensation in Single Phase Distribution System using SVC, ST...



Reactive Power Compensation in Single Phase Distribution System using SVC, ST...IRJET Journal
╠²
This document discusses and compares two spectrum sensing techniques for cognitive radio networks: energy detection and matched filter detection. It analyzes the performance of these techniques based on probability of detection and probability of false alarm under different signal-to-noise ratio levels and fading channel models (AWGN, flat fading, Rayleigh fading). The key findings are that matched filter detection has better performance than energy detection, but requires prior knowledge of the primary signal. Energy detection has lower complexity but performs poorly in low SNR scenarios. Overall, matched filter detection results in lower probability of false alarms compared to energy detection.Transmitter Detection Methods of Spectrum Sensing For Cognitive Radio Network...



Transmitter Detection Methods of Spectrum Sensing For Cognitive Radio Network...IRJET Journal
╠²
This document discusses and compares two spectrum sensing techniques for cognitive radio networks: energy detection and matched filter detection. It analyzes the performance of these techniques based on probability of detection and probability of false alarm under different signal-to-noise ratio levels and fading channel models (AWGN, flat fading, Rayleigh fading). The key findings are that matched filter detection has better performance than energy detection, but requires prior knowledge of the primary signal. Energy detection has lower complexity but performs poorly in low SNR scenarios. Overall, matched filter detection results in lower probability of false alarms compared to energy detection.A Cartesian Robot for RFID Signal Distribution Model Verification



A Cartesian Robot for RFID Signal Distribution Model VerificationVladimir Kulyukin
╠²
In our previous research, we addressed the problem of automating the design of passive radio-frequency (PRF)
services. An optimal PRF surface is one that offers a maximum probability of localization at a minimum instrumentation
cost, i.e., a minimum number of surface-embedded passive RFID transponders. Our previous results were based on the
assumption that the signal distribution model of an individual RFID transponder can be approximated as a circle. The
problem of automated PRF surface design was then formulated as the problem of packing a surface with circles of a
given radius. However, in practice, this approach leads to some loss of optimality: some areas of the surface may not
be covered or too many transponders may be required. More exact methods are need for verifying and constructing signal
distribution models of surface-embedded RFID transponders that can be used by surface packing algorithms to optimize the
design. In this paper, we present the design and implementation of a Cartesian robot for verifying and constructing signal
distribution models of surface-embedded RFID transponders. A model is characterized by four high-level parameters: an
RFID transponder, an RFID antenna, an RFID reader, and a surface type. The robot moves an RFID reader-antenna unit
over a PRF surface, e.g. a carpet, and systematically collects readings for various antenna positions over the surface. The
collected readings are subsequently processed to verify or construct signal distribution models. We describe experiments
with the robot to verify the localization probability of automatically designed PRF surfaces. We also present experiments
with the robot to verify and construct the signal distribution models of a specific RFID transponder.Lightweight Neighborhood Cardinality Estimation in Dynamic Wireless Networks ...



Lightweight Neighborhood Cardinality Estimation in Dynamic Wireless Networks ...Marco Cattani
╠²
More: http://cattanimarco.com/2014/01/23/lightweight-neighborhood-cardinality-estimation-in-dynamic-wireless-networks/Automatic Target Recognition Using Recurrent Neural Networks



Automatic Target Recognition Using Recurrent Neural NetworksAbhishek Jain
╠²
Above Research Paper can be downloaded from www.zeusnumerix.com
Automatic target recognition (ATR) using recurrent neural networks (RNN) is being proposed in this work. When electromagnetic waves from radar illuminate the targets, surface currents are produced which result in scattering of incident energy. The scattered signal in the direction of radar is received as the radar signature of the target. The radar cross-section (RCS) is an important feature extracted from the radar signature that is used for target identification. The RCS values for each set of azimuth and elevation angles for a mono-static configuration serves the purpose of the dataset for the recurrent neural network (RNN)/long short-term memory (LSTM) model. The classification accuracy of 93 per cent was achieved using the RNN/LSTM model. Authors - Sumit Jana (Zeus Numerix), Prof H Shekhawat and Bharat Sehgal (IITG)Application Of Digital Signal Processing In Radar Signals



Application Of Digital Signal Processing In Radar SignalsRichard Hogue
╠²
This document discusses the application of digital signal processing techniques in radar systems. It provides an overview of how digital signal processing is used extensively in modern radar, such as at the transmitter to generate pulses and at the receiver for tasks like clutter removal and beamforming. The main tasks of a radar signal processor are discussed, including decisions about targets, maintaining constant false alarm rates, tracking targets, resolving ambiguities, and countering interference. Detection of signals is also covered, along with fast convolution filter implementations using dual and single FFT pipelines for matched filtering.The Things Conference - LPWAN Localization - Maarten Weyn



The Things Conference - LPWAN Localization - Maarten WeynMaarten Weyn
╠²
This document discusses technologies and methods for implementing location-dependent applications using localization systems. It describes various technologies that can be used for localization including global navigation satellite systems, wireless communication systems, and on-device sensors. It also summarizes different localization system architectures, location information that can be determined, and factors that affect localization accuracy such as environment, mobility, and power.Implementing a location dependent application with LPWAN



Implementing a location dependent application with LPWANMaarten Weyn
╠²
This document discusses technologies and methods for implementing location-dependent applications using localization systems. It describes various technologies that can be used for localization including global navigation satellite systems, wireless communication systems, and on-device sensors. It also summarizes different localization system architectures, location information that can be determined, and factors that affect localization accuracy such as environment, mobility, and power.More Related Content
Similar to Low-Power, Long-Range, Precise Localization (20)
A Survey on Rendezvous Based Techniques for Power Conservation in Wireless Se...



A Survey on Rendezvous Based Techniques for Power Conservation in Wireless Se...ijceronline
╠²
International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) is dedicated to protecting personal information and will make every reasonable effort to handle collected information appropriately. All information collected, as well as related requests, will be handled as carefully and efficiently as possible in accordance with IJCER standards for integrity and objectivity.A Survey on Rendezvous Based Techniques for Power Conservation in Wireless Se...



A Survey on Rendezvous Based Techniques for Power Conservation in Wireless Se...ijceronline
╠²
International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) is dedicated to protecting personal information and will make every reasonable effort to handle collected information appropriately. All information collected, as well as related requests, will be handled as carefully and efficiently as possible in accordance with IJCER standards for integrity and objectivity.Intrusion Detection In Open Field Using Geophone (Report)



Intrusion Detection In Open Field Using Geophone (Report)Nuthan Prasad
╠²
This dissertation discusses the design of an intrusion detection system using geophones in an open field. A sensor network of geophone nodes is used to detect human intrusions by identifying footstep impulses. When intrusion is detected via kurtosis analysis, the sensor node alerts a control room which can then dispatch an unmanned ground vehicle to the location. The system aims to remotely monitor large outdoor areas with limited manpower.Localization Issues in a ZigBee based Internet of Things scenario



Localization Issues in a ZigBee based Internet of Things scenarioMassimiliano Dibitonto
╠²
Paper presented @Tyrrhenian Workshop on the Internet of Things 2009
ZigBee is probably the most popular IEEE 802.15.4 implementation used for Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN). The radio communication can also be used for localization purposes using fixed network devices as reference points. In this paper, the authors describe a procedure for automatically configuring a ZigBee-based localization appli-cation with environment-optimized parameters.Where Next



Where NextRoberto Trasarti
╠²
- The document presents a technique called WhereNext that predicts the next location of a trajectory based on analyzing patterns from previous movements without considering individual user information.
- WhereNext builds a prediction tree model from patterns of movement called T-Patterns extracted from trajectory data. It allows spatial and temporal approximation to account for noise in real trajectories.
- The method can be tuned for accuracy and prediction rate. Evaluation on a real dataset of 17,000 vehicle GPS trajectories in Milan showed it effectively predicts next locations.Hybrid Positioning



Hybrid Positioningspirentgnss
╠²
To meet the increasing demands that current and emerging location based services (LBS) are placing on location-aware technology, engineers are turning to hybrid positioning ŌĆō but what is it?
Discover:
- Why hybrid positioning is an increasingly common feature in smartphone and tablet designs
- How Wi-Fi, MEMS inertial sensors and cellular networks can all augment GNSS positioningDelivAR



DelivARDaniele Tatasciore
╠²
An Augmented Reality Mobile Application to Expedite the Package
Identification Process for Last-Mile Deliveries. http://lumakollektiv.com/delivar.htmlHm3114401445



Hm3114401445IJERA Editor
╠²
This document discusses the application of digital signal processing in radar signals. It provides an overview of how DSP is used extensively in modern radar systems, both at the transmitter to generate pulses and control antennas, and at the receiver to perform tasks like clutter removal and beamforming. The document also reviews some key techniques in DSP for radar signals, including constant false alarm rate processing and matched filtering for signal detection. It describes how DSP helps with tasks like tracking multiple targets, resolving measurement ambiguities, and combining information from radar and other sources.HalifaxNGGs



HalifaxNGGsNikos Kostagiolas
╠²
The document discusses N-gram graphs, which represent the proximity or co-occurrence of items in a text by modeling them as a graph. An N-gram graph is constructed by extracting n-grams from a text, determining their neighborhood based on a window size, and assigning edge weights based on co-occurrence frequencies. The document outlines the process for constructing N-gram graphs and describes their potential uses, including representing sets of items with a single graph, comparing graphs through clustering, and defining similarity measures between graphs. N-gram graphs aim to capture proximity information in a way that is domain-agnostic, allows different analysis levels, and can represent multiple texts with a single graph structure.Accurate indoor positioning system based on modify nearest point technique



Accurate indoor positioning system based on modify nearest point techniqueIJECEIAES
╠²
This document presents an accurate indoor positioning system based on a modified nearest point technique. The system uses Wi-Fi signals to estimate distances and indoor locations. It builds a fingerprint database with reference points and signal measurements collected in different environments to account for changing conditions. The case study building is divided into 7 areas to allow dynamic parameter assignment. Locations are estimated by finding the nearest reference point within a specific environment by comparing at least four nearby points. The results showed errors of less than 0.102 meters for indoor localization.Nuzzer algorithm based Human Tracking and Security System for Device-Free Pas...



Nuzzer algorithm based Human Tracking and Security System for Device-Free Pas...Eswar Publications
╠²
In recent years, majority of researches are focused on localization system for wireless environment. These researches rely on localization using devices to track the entities. In this paper, we use, a recently proposed Device-free Passive (DfP) that uses Probabilistic techniques to track locations in large-scale real environment without the need of carrying devices. The proposed system uses the Access Points (APs) and Monitoring Point (MPs) that works by monitoring and processing the changes in the received physical signals at one or more monitoring points to detect changes in the environment. The system uses continuous space estimator to return multiple location while the mortal is in motion. Our results show that the system can achieve very high probability of detection and tracking with very few false positives.REDTACTON



REDTACTONNisha Raj S N
╠²
The document discusses Red Tacton, a new human area networking technology developed in Japan. Red Tacton uses the human body as a transmission medium for data, inducing weak electric fields on the skin's surface to transmit signals up to 10 Mbps. It works by transmitting data via a tacton transmitter and receiving it using an electro-optic crystal sensor in the tacton receiver. The technology has applications for personal devices, security, and intuitive human-computer interaction through touch.J0412261066



J0412261066IOSR-JEN
╠²
This document discusses radar echo signals and multipath fading. It begins with an abstract that introduces multipath propagation as a phenomenon where radar signals take multiple paths upon reflection, in addition to the direct line of sight path. This can cause interference and fading effects. The document then provides background on radar systems and the radar range equation. It presents an approach to process received radar signals to isolate the main line of sight echo and discard weaker multipath signals. This involves analyzing signal amplitudes and retaining the highest value signal. The system components for implementing this approach include a fast microcontroller, computer, and lab link cable for programming the microcontroller using BASIC language software.Radar target detection simulation



Radar target detection simulationIJERA Editor
╠²
This document presents a computer simulation model for radar target detection. The model considers two moving targets generated using a keypad and applies nine levels of noise to simulate changing signal-to-noise ratios. As noise levels increase, the brightness of target blips on the radar display decrease by around 5% for each level. The simulation is programmed in Turbo C++ and interfaces with a computer through a parallel port to simulate a radar display and evaluate the effects of noise on target detection performance.Reactive Power Compensation in Single Phase Distribution System using SVC, ST...



Reactive Power Compensation in Single Phase Distribution System using SVC, ST...IRJET Journal
╠²
This document discusses and compares two spectrum sensing techniques for cognitive radio networks: energy detection and matched filter detection. It analyzes the performance of these techniques based on probability of detection and probability of false alarm under different signal-to-noise ratio levels and fading channel models (AWGN, flat fading, Rayleigh fading). The key findings are that matched filter detection has better performance than energy detection, but requires prior knowledge of the primary signal. Energy detection has lower complexity but performs poorly in low SNR scenarios. Overall, matched filter detection results in lower probability of false alarms compared to energy detection.Transmitter Detection Methods of Spectrum Sensing For Cognitive Radio Network...



Transmitter Detection Methods of Spectrum Sensing For Cognitive Radio Network...IRJET Journal
╠²
This document discusses and compares two spectrum sensing techniques for cognitive radio networks: energy detection and matched filter detection. It analyzes the performance of these techniques based on probability of detection and probability of false alarm under different signal-to-noise ratio levels and fading channel models (AWGN, flat fading, Rayleigh fading). The key findings are that matched filter detection has better performance than energy detection, but requires prior knowledge of the primary signal. Energy detection has lower complexity but performs poorly in low SNR scenarios. Overall, matched filter detection results in lower probability of false alarms compared to energy detection.A Cartesian Robot for RFID Signal Distribution Model Verification



A Cartesian Robot for RFID Signal Distribution Model VerificationVladimir Kulyukin
╠²
In our previous research, we addressed the problem of automating the design of passive radio-frequency (PRF)
services. An optimal PRF surface is one that offers a maximum probability of localization at a minimum instrumentation
cost, i.e., a minimum number of surface-embedded passive RFID transponders. Our previous results were based on the
assumption that the signal distribution model of an individual RFID transponder can be approximated as a circle. The
problem of automated PRF surface design was then formulated as the problem of packing a surface with circles of a
given radius. However, in practice, this approach leads to some loss of optimality: some areas of the surface may not
be covered or too many transponders may be required. More exact methods are need for verifying and constructing signal
distribution models of surface-embedded RFID transponders that can be used by surface packing algorithms to optimize the
design. In this paper, we present the design and implementation of a Cartesian robot for verifying and constructing signal
distribution models of surface-embedded RFID transponders. A model is characterized by four high-level parameters: an
RFID transponder, an RFID antenna, an RFID reader, and a surface type. The robot moves an RFID reader-antenna unit
over a PRF surface, e.g. a carpet, and systematically collects readings for various antenna positions over the surface. The
collected readings are subsequently processed to verify or construct signal distribution models. We describe experiments
with the robot to verify the localization probability of automatically designed PRF surfaces. We also present experiments
with the robot to verify and construct the signal distribution models of a specific RFID transponder.Lightweight Neighborhood Cardinality Estimation in Dynamic Wireless Networks ...



Lightweight Neighborhood Cardinality Estimation in Dynamic Wireless Networks ...Marco Cattani
╠²
More: http://cattanimarco.com/2014/01/23/lightweight-neighborhood-cardinality-estimation-in-dynamic-wireless-networks/Automatic Target Recognition Using Recurrent Neural Networks



Automatic Target Recognition Using Recurrent Neural NetworksAbhishek Jain
╠²
Above Research Paper can be downloaded from www.zeusnumerix.com
Automatic target recognition (ATR) using recurrent neural networks (RNN) is being proposed in this work. When electromagnetic waves from radar illuminate the targets, surface currents are produced which result in scattering of incident energy. The scattered signal in the direction of radar is received as the radar signature of the target. The radar cross-section (RCS) is an important feature extracted from the radar signature that is used for target identification. The RCS values for each set of azimuth and elevation angles for a mono-static configuration serves the purpose of the dataset for the recurrent neural network (RNN)/long short-term memory (LSTM) model. The classification accuracy of 93 per cent was achieved using the RNN/LSTM model. Authors - Sumit Jana (Zeus Numerix), Prof H Shekhawat and Bharat Sehgal (IITG)Application Of Digital Signal Processing In Radar Signals



Application Of Digital Signal Processing In Radar SignalsRichard Hogue
╠²
This document discusses the application of digital signal processing techniques in radar systems. It provides an overview of how digital signal processing is used extensively in modern radar, such as at the transmitter to generate pulses and at the receiver for tasks like clutter removal and beamforming. The main tasks of a radar signal processor are discussed, including decisions about targets, maintaining constant false alarm rates, tracking targets, resolving ambiguities, and countering interference. Detection of signals is also covered, along with fast convolution filter implementations using dual and single FFT pipelines for matched filtering.Nuzzer algorithm based Human Tracking and Security System for Device-Free Pas...



Nuzzer algorithm based Human Tracking and Security System for Device-Free Pas...Eswar Publications
╠²
More from Maarten Weyn (10)
The Things Conference - LPWAN Localization - Maarten Weyn



The Things Conference - LPWAN Localization - Maarten WeynMaarten Weyn
╠²
This document discusses technologies and methods for implementing location-dependent applications using localization systems. It describes various technologies that can be used for localization including global navigation satellite systems, wireless communication systems, and on-device sensors. It also summarizes different localization system architectures, location information that can be determined, and factors that affect localization accuracy such as environment, mobility, and power.Implementing a location dependent application with LPWAN



Implementing a location dependent application with LPWANMaarten Weyn
╠²
This document discusses technologies and methods for implementing location-dependent applications using localization systems. It describes various technologies that can be used for localization including global navigation satellite systems, wireless communication systems, and on-device sensors. It also summarizes different localization system architectures, location information that can be determined, and factors that affect localization accuracy such as environment, mobility, and power.Trends in the IoT Landscape 2018 and how to streamline your IoT Product Deve...



Trends in the IoT Landscape 2018 and how to streamline your IoT Product Deve...Maarten Weyn
╠²
Competitors in the IoT industry will need to cooperate more in 2018 as the landscape becomes more competitive. Additionally, IoT solutions will need to offer more than just connecting devices and address specific customer problems. Various technologies like NB-IoT, LoRa, and Sigfox will continue to compete but find niche applications depending on factors like cost, bandwidth needs, battery life, and quality of service requirements. When developing an IoT product, companies should identify where they can add value through building, buying, or partnering capabilities and focus on security across device, network, and cloud layers.Dash7 alliance protocol - where rfid meets wsn



Dash7 alliance protocol - where rfid meets wsnMaarten Weyn
╠²
The document discusses the DASH7 Alliance Protocol, which originated from ISO 18000-7 and describes wireless sensor and actuator network communications. It is now an open standard for ultra-low power mid-range sensor and actuator communication across sub-GHz bands. The IDLab research group at the University of Antwerp has been actively involved in the DASH7 Alliance since 2011, developing an open source protocol stack and hardware prototypes. The protocol uses a star network topology with simple routing to extend the range of gateways while minimizing energy usage.RFID: a condensed overview



RFID: a condensed overviewMaarten Weyn
╠²
RFID is a system that uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit data between a tag and reader. It has advantages over barcodes like not needing line of sight and ability to read/write data. There are different types of tags based on power source and range. Common frequencies used are low, high and ultra-high frequency. RFID is used for applications like asset tracking, process control, data lineage tracing and automated replenishment. The Internet of Things connects physical objects through embedded technology like sensors to exchange data. Near Field Communication is a short-range wireless technology that allows data exchange when devices are 10cm apart and is used for contactless payments, ticketing and access control.DASH7 Alliance Protocol 1.0: Low-Power, Mid-Range Sensor and Actuator Communi...



DASH7 Alliance Protocol 1.0: Low-Power, Mid-Range Sensor and Actuator Communi...Maarten Weyn
╠²
This presentation presents a paper of IEEE CSCN 2015 on the DASH7 Alliance Protocol 1.0. It is an industry alliance standard for wireless sensor and actuator communication using the unlicensed sub-1 GHz bands. The paper explains its historic relation to active RFID standards ISO 18000-7 for 433 MHz communication, the basic concepts and communication paradigms of the protocol. Since the protocol is a full OSI stack specification, the paper discusses the implementation of every OSI layer.Overview of Low Power Wide Area Networks



Overview of Low Power Wide Area NetworksMaarten Weyn
╠²
Maarten Weyn gave an overview of low power wide area networks (LP-WAN) for IoT applications. He discussed various LP-WAN technologies like SigFox, LoRaWAN, LTE-M, and others. Key characteristics of these networks include long range communication, low energy consumption, low cost, very low data rates, and use of license free frequencies. Technologies differ in aspects such as data rates, range, standardization, and power consumption. SigFox uses ultra narrow band and has an uplink of 12 bytes every 12 minutes, while LoRaWAN uses spread spectrum and supports higher data payloads and bidirectional communication.DASH7: Context aware sensor and actuator data propagation system using sub-1 Ghz



DASH7: Context aware sensor and actuator data propagation system using sub-1 GhzMaarten Weyn
╠²
DASH7 is a wireless sensor network protocol that originated from ISO/IEC 18000-7 and was enhanced by the DASH7 Alliance to enable ultra low power, mid-range wireless sensor communication using sub-1GHz frequencies. It uses an asynchronous communication method involving command-response transactions and file notifications to allow for bursty, light, asynchronous, stealth, and transitional data transfer between sensors and gateways. An open source DASH7 protocol stack has been developed by CoSys-Lab and the DASH7 Alliance to support its use cases and provide a hardware-independent, full-stack solution for long range, low power, mobile wireless sensor applications.DASH7 Alliance Protocol Technical Presentation



DASH7 Alliance Protocol Technical PresentationMaarten Weyn
╠²
The Dash7 Alliance Protocol is based on ISO/IEC 18000-7, which describes parameters for active RFID communications at 433 MHz. It builds on an asynchronous wireless sensor network MAC protocol, with functionality optimized for RFID and support for fixed and mobile nodes to upload or retrieve small amounts of data. Dash7 uses GFSK modulation in the 433 MHz band and supports tag-to-tag communication through a simple routing protocol with a range that can be extended using subcontrollers.Multimodal Localization as the Key for Ambient Intelligent Applications



Multimodal Localization as the Key for Ambient Intelligent ApplicationsMaarten Weyn
╠²
What is Ambient Intelligence (AmI)
What is the function of multimodal localization for AmI
What is the related research done in CoSys-Lab (Univesity of Antwerp)
What is the focus of the research of Maarten WeynRecently uploaded (20)
[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web AppsSafe Software
╠²
Ready to simplify workflow sharing across your organization without diving into complex coding? With FME Flow Apps, you can build no-code web apps that make your data work harder for you ŌĆö fast.
In this webinar, weŌĆÖll show you how to:
Build and deploy Workspace Apps to create an intuitive user interface for self-serve data processing and validation.
Automate processes using Automation Apps. Learn to create a no-code web app to kick off workflows tailored to your needs, trigger multiple workspaces and external actions, and use conditional filtering within automations to control your workflows.
Create a centralized portal with Gallery Apps to share a collection of no-code web apps across your organization.
Through real-world examples and practical demos, youŌĆÖll learn how to transform your workflows into intuitive, self-serve solutions that empower your team and save you time. We canŌĆÖt wait to show you whatŌĆÖs possible!GDG Cloud Southlake #40: Brandon Stokes: How to Build a Great Product



GDG Cloud Southlake #40: Brandon Stokes: How to Build a Great ProductJames Anderson
╠²
How to Build a Great Product
Being a tech entrepreneur is about providing a remarkable product or service that serves the needs of its customers better, faster, and cheaper than anything else. The goal is to "make something people want" which we call, product market fit.
But how do we get there? We'll explore the process of taking an idea to product market fit (PMF), how you know you have true PMF, and how your product strategies differ pre-PMF from post-PMF.
Brandon is a 3x founder, 1x exit, ex-banker & corporate strategist, car dealership owner, and alumnus of Techstars & Y Combinator. He enjoys building products and services that impact people for the better.
Brandon has had 3 different careers (banking, corporate finance & strategy, technology) in 7 different industries; Investment Banking, CPG, Media & Entertainment, Telecommunications, Consumer application, Automotive, & Fintech/Insuretech.
He's an idea to revenue leader and entrepreneur that helps organizations build products and processes, hire talent, test & iterate quickly, collect feedback, and grow in unregulated and heavily regulated industries.THE BIG TEN BIOPHARMACEUTICAL MNCs: GLOBAL CAPABILITY CENTERS IN INDIA



THE BIG TEN BIOPHARMACEUTICAL MNCs: GLOBAL CAPABILITY CENTERS IN INDIASrivaanchi Nathan
╠²
This business intelligence report, "The Big Ten Biopharmaceutical MNCs: Global Capability Centers in India", provides an in-depth analysis of the operations and contributions of the Global Capability Centers (GCCs) of ten leading biopharmaceutical multinational corporations in India. The report covers AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Novartis, Sanofi, Roche, Pfizer, Novo Nordisk, and Eli Lilly. In this report each company's GCC is profiled with details on location, workforce size, investment, and the strategic roles these centers play in global business operations, research and development, and information technology and digital innovation.UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 2



UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 2DianaGray10
╠²
In session 2, we will introduce you to Data manipulation in UiPath Studio.
Topics covered:
Data Manipulation
What is Data Manipulation
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
RegEx Builder
Date and Time
Required Self-Paced Learning for this session:
Data Manipulation with Strings in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h 30m - https://academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-strings-in-studio
Data Manipulation with Lists and Dictionaries in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h - https:/academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-lists-and-dictionaries-in-studio
Data Manipulation with Data Tables in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h 30m - https:/academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-data-tables-in-studio
Ōüē’ĖÅ For any questions you may have, please use the dedicated Forum thread. You can tag the hosts and mentors directly and they will reply as soon as possible. Transcript: AI in publishing: Your questions answered - Tech Forum 2025



Transcript: AI in publishing: Your questions answered - Tech Forum 2025BookNet Canada
╠²
George Walkley, a publishing veteran and leading authority on AI applications, joins us for a follow-up to his presentation "Applying AI to publishing: A balanced and ethical approach". George gives a brief overview of developments since that presentation and answers attendees' pressing questions about AIŌĆÖs impact and potential applications in the book industry.
Link to recording and presentation slides: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/ai-in-publishing-your-questions-answered/
Presented by BookNet Canada on February 20, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.Dev Dives: Unlock the future of automation with UiPath Agent Builder



Dev Dives: Unlock the future of automation with UiPath Agent BuilderUiPathCommunity
╠²
This webinar will offer you a first look at the powerful capabilities of UiPath Agent Builder, designed to streamline your automation processes and enhance your workflow efficiency.
¤ōĢ During the session, you will:
- Discover how to build agents with low-code experience, making it accessible for both developers and business users.
- Learn how to leverage automations and activities as tools within your agents, enabling them to handle complex and dynamic workflows.
- Gain insights into the AI Trust Layer, which provides robust management and monitoring capabilities, ensuring trust and transparency in your automation processes.
- See how agents can be deployed and integrated with your existing UiPath cloud and Studio environments.
¤æ©ŌĆŹ¤Å½ Speaker:
Zach Eslami, Sr. Manager, Product Management Director, UiPath
ŌÅ® Register for our upcoming Dev Dives March session:
Unleash the power of macOS Automation with UiPath
¤æē AMER: https://bit.ly/Dev_Dives_AMER_March
¤æē EMEA & APJ:https://bit.ly/Dev_Dives_EMEA_APJ_March
This session was streamed live on February 27, 2025, 15:00 GMT.
Check out future Dev Dives 2025 sessions at:
¤Ü® https://bit.ly/Dev_Dives_2025
Caching for Performance Masterclass: Caching Strategies



Caching for Performance Masterclass: Caching StrategiesScyllaDB
╠²
Exploring the tradeoffs of common caching strategies ŌĆō and a look at the architectural differences.
- Which strategies exist
- When to apply different strategies
- ScyllaDB cache designAgentic AI: The 2025 Next-Gen Automation Guide



Agentic AI: The 2025 Next-Gen Automation GuideThoughtminds
╠²
Introduction to Agentic AI: Explains how it differs from traditional automation and its ability to make independent decisions.
Comparison with Generative AI: A structured comparison between Generative AI (content creation) and Agentic AI (autonomous action-taking).
Technical Breakdown: Covers core components such as LLMs, reinforcement learning, and cloud infrastructure that power Agentic AI.
Real-World Use Cases (2025 & Beyond): Examines how Agentic AI is transforming industries like insurance, healthcare, retail, finance, and cybersecurity.
Business Impact & ROI: Discusses case studies from Unilever, FedEx, and more, showcasing cost savings and operational efficiency improvements.
Challenges & Risks: Highlights bias, security threats, regulatory compliance, and workforce reskilling as critical challenges in AI adoption.
5-Step Implementation Strategy: A practical roadmap to help organizations integrate Agentic AI seamlessly.
Future Predictions (2025-2030): Forecasts on AI-driven workforce evolution, industry disruptions, and the rise of Quantum AI.UiPath Document Understanding - Generative AI and Active learning capabilities



UiPath Document Understanding - Generative AI and Active learning capabilitiesDianaGray10
╠²
This session focus on Generative AI features and Active learning modern experience with Document understanding.
Topics Covered:
Overview of Document Understanding
How Generative Annotation works?
What is Generative Classification?
How to use Generative Extraction activities?
What is Generative Validation?
How Active learning modern experience accelerate model training?
Q/A
ŌØō If you have any questions or feedback, please refer to the "Women in Automation 2025" dedicated Forum thread. You can find there extra details and updates. SECURE BLOCKCHAIN FOR ADMISSION PROCESSING IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS.pdf



SECURE BLOCKCHAIN FOR ADMISSION PROCESSING IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS.pdfspub1985
╠²
SECURE BLOCKCHAIN FOR ADMISSION PROCESSING IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS.pdfUnderstanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptx



Understanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptxshyamraj55
╠²
Understanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptx | ### ║▌║▌▀Ż Deck Description:
This presentation features Atul, a Senior Solution Architect at NTT DATA, sharing his journey into traditional AI using Azure's Custom Vision tool. He discusses how AI mimics human thinking and reasoning, differentiates between predictive and generative AI, and demonstrates a real-world use case. The session covers the step-by-step process of creating and training an AI model for image classification and object detectionŌĆöspecifically, an ad display that adapts based on the viewer's gender. Atulavan highlights the ease of implementation without deep software or programming expertise. The presentation concludes with a Q&A session addressing technical and privacy concerns.2025-02-27 Tech & Play_ Fun, UX, and Community.pdf



2025-02-27 Tech & Play_ Fun, UX, and Community.pdfkatalinjordans1
╠²
2025-02-27 Tech & Play_ Fun, UX, and Community.pdfUiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 1



UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 1DianaGray10
╠²
Welcome to UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 1.
In this session, we will cover the following topics:
Introduction to RPA & UiPath Studio
Overview of RPA and its applications
Introduction to UiPath Studio
Variables & Data Types
Control Flows
You are requested to finish the following self-paced training for this session:
Variables, Constants and Arguments in Studio 2 modules - 1h 30m - https://academy.uipath.com/courses/variables-constants-and-arguments-in-studio
Control Flow in Studio 2 modules - 2h 15m - https:/academy.uipath.com/courses/control-flow-in-studio
Ōüē’ĖÅ For any questions you may have, please use the dedicated Forum thread. You can tag the hosts and mentors directly and they will reply as soon as possible. 10 FinTech Solutions Every Business Should Know!.pdf



10 FinTech Solutions Every Business Should Know!.pdf Yodaplus Technologies Private Limited
╠²
FinTech is reshaping the way businesses handle payments, risk management, and financial operations. From AI-driven fraud detection to blockchain-powered security, the right FinTech solutions can streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve decision-making. This guide explores 10 essential FinTech tools that help businesses stay ahead in an increasingly digital economy.
Discover how digital payments, credit risk management, treasury solutions, AI, blockchain, and RegTech can enhance efficiency, security, and profitability.
Read now to learn how businesses are leveraging FinTech for smarter financial management!Predictive vs. Preventive Maintenance ŌĆö Which One is Right for Your Factory



Predictive vs. Preventive Maintenance ŌĆö Which One is Right for Your FactoryDiagsense ltd
╠²
Efficient maintenance is the backbone of any manufacturing operation. It ensures that machinery runs smoothly, minimizes downtime and optimizes overall productivity. Earlier, factories have relied on preventive maintenance but with advancements in technology, Manufacturing PdM Solutions is gaining traction. The question isŌĆöwhich one is the right fit for your factory? LetŌĆÖs break it down.Caching for Performance Masterclass: Caching at Scale



Caching for Performance Masterclass: Caching at ScaleScyllaDB
╠²
Weighing caching considerations for use cases with different technical requirements and growth expectations.
- Request coalescing
- Negative sharding
- Rate limiting
- Sharding and scalingUiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 1



UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 1DianaGray10
╠²
Welcome to UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 1.
In this session, we will cover the following topics:
Introduction to RPA & UiPath Studio
Overview of RPA and its applications
Introduction to UiPath Studio
Variables & Data Types
Control Flows
You are requested to finish the following self-paced training for this session:
Variables, Constants and Arguments in Studio 2 modules - 1h 30m - https://academy.uipath.com/courses/variables-constants-and-arguments-in-studio
Control Flow in Studio 2 modules - 2h 15m - https:/academy.uipath.com/courses/control-flow-in-studio
Ōüē’ĖÅ For any questions you may have, please use the dedicated Forum thread. You can tag the hosts and mentors directly and they will reply as soon as possible. 5 Must-Use AI Tools to Supercharge Your Productivity



5 Must-Use AI Tools to Supercharge Your Productivitycryptouniversityoffi
╠²
5 Must-Use AI Tools to Supercharge Your Productivity!
AI is changing the game! ¤ÜĆ From research to creativity and coding, here are 5 powerful AI tools you should try.
NotebookLM
¤ōÜ NotebookLM ŌĆō Your AI Research Assistant
Ō£ģ Organizes & summarizes notes
Ō£ģ Generates insights from multiple sources
Ō£ģ Ideal for students, researchers & writers
¤ōØ Boost your productivity with smarter note-taking!
Napkin.ai
¤Ä© Napkin.ai ŌĆō The Creativity Booster
Ō£ģ Connects and organizes ideas
Ō£ģ Perfect for writers, designers & entrepreneurs
Ō£ģ Acts as your AI-powered brainstorming partner
¤ÆĪ Unleash your creativity effortlessly!
DeepSeek
¤öŹ DeepSeek ŌĆō Smarter AI Search
Ō£ģ Delivers deeper & more precise search results
Ō£ģ Analyzes large datasets for better insights
Ō£ģ Ideal for professionals & researchers
¤öÄ Find what you needŌĆöfaster & smarter!
ChatGPT
¤Æ¼ ChatGPT ŌĆō Your AI Chat Assistant
Ō£ģ Answers questions, writes content & assists in coding
Ō£ģ Helps businesses with customer support
Ō£ģ Boosts learning & productivity
¤ż¢ From content to codingŌĆöChatGPT does it all!
Devin AI
¤Æ╗ Devin AI ŌĆō AI for Coders
Ō£ģ Writes, debugs & optimizes code
Ō£ģ Assists developers at all skill levels
Ō£ģ Makes coding faster & more efficient
¤æ©ŌĆŹ¤Æ╗ Let AI be your coding partner!
¤ÜĆ AI is transforming the way we work!L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardness



L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardnessRostislavDaniel
╠²
Introduction to NanoindentationLow-Power, Long-Range, Precise Localization
- 1. Low-Power, Long-Range, Precise Localization Nextech 2014, Rome - 28 August 2014 Prof. Maarten Weyn maarten.weyn@uantwerpen.be
- 2. Research: Maarten Weyn I Localization: from Opportunistic to Just Enough I Low-power communication I Low-power
- 3. rmware development I Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Courses: I Mobile Communication I Digital Communication I Real-Time Localization Systems (Eng) I Ambient Intelligence (Eng): interaction between low-power communication, sensors, actuators, low-power hardware and algorithms 2
- 4. What I'm not going to do... I No sales talk I No academic formula's and equations I No futuristic foresights I No "You should's" 3
- 5. Low-Power, Long-Range, Precise Localization 4
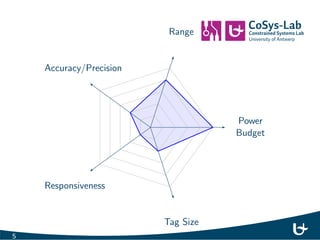
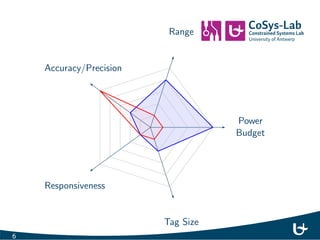
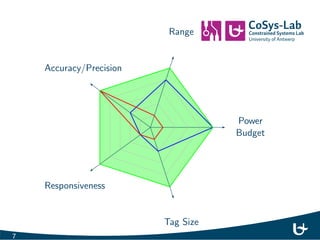
- 6. Power Budget Range Accuracy/Precision Responsiveness Tag Size 5
- 7. Power Budget Range Accuracy/Precision Responsiveness Tag Size 6
- 8. Power Budget Range Accuracy/Precision Responsiveness Tag Size 7
- 9. Power Budget Low Power?: I LG Nexus 5: 2300 mAh / day ?!!! I Raspberry pi: 500 mAh I TelosB 8
- 10. Power Budget Low Power?: I LG Nexus 5: 2300 mAh / day ?!!! I Raspberry pi: 500 mAh I TelosB Application Driven: I e.g.: 1 year on coin cell (220 mAh) I e.g.: "the lifetime of the bird and weight 1 gram I e.g.: 2 year on 1/2 AA 3.6V battery (1100 mAh) ! 62Ah=day 8
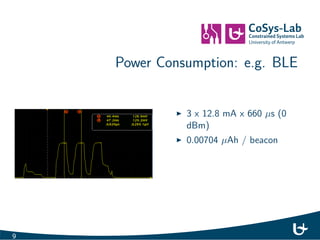
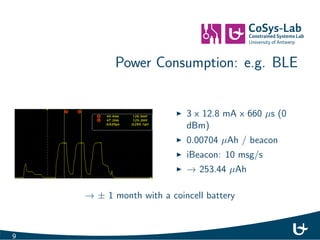
- 11. Power Consumption: e.g. BLE I 3 x 12.8 mA x 660 s (0 dBm) I 0.00704 Ah / beacon 9
- 12. Power Consumption: e.g. BLE I 3 x 12.8 mA x 660 s (0 dBm) I 0.00704 Ah / beacon I iBeacon: 10 msg/s I ! 253.44 Ah ! 1 month with a coincell battery 9
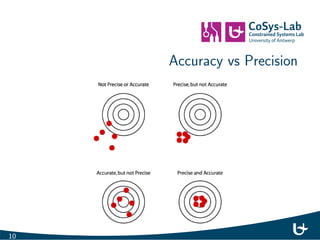
- 13. Accuracy vs Precision 10
- 14. Accuracy vs Precision Source: Versus Technology, Inc. 11
- 15. Range 12
- 16. Range 13
- 17. Range 14
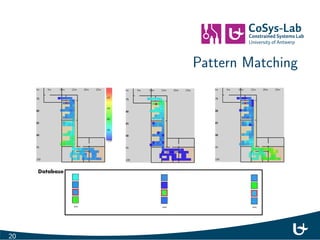
- 18. Techniques I Signal Strength: I Attenuation I Pattern Matching (Fingerprinting) I Presence / Proximity I Time (Ranging): I Time of Flight - Time Dierence of Arrival I Round Trip Time I Direction Finding / Angle of Arrival 15
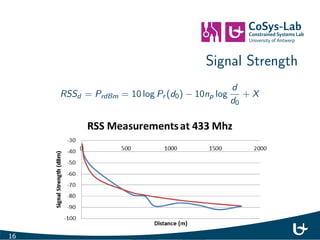
- 19. Signal Strength RSSd = PrdBm = 10 log Pr (d0) 10np log d d0 + X 16
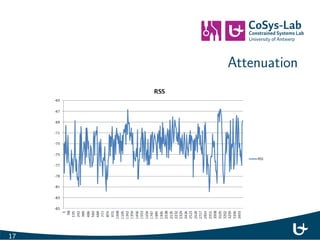
- 20. Attenuation 17
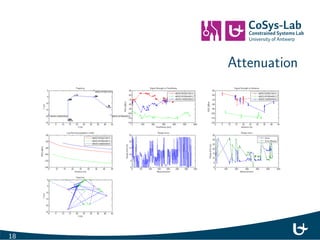
- 21. Attenuation 18
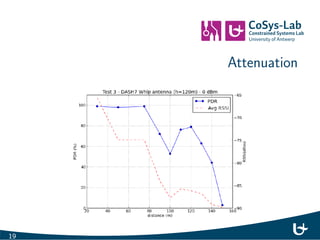
- 22. Attenuation 19
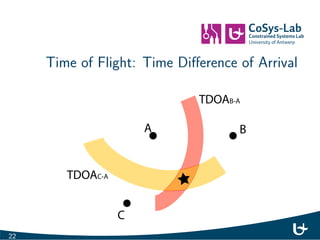
- 25. Time of Flight: Time Dierence of Arrival TDOAB-A TDOAC-A A B C 22
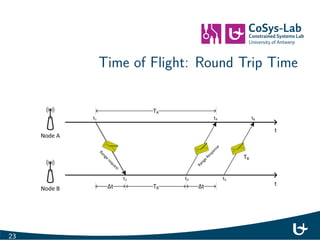
- 26. Time of Flight: Round Trip Time 23
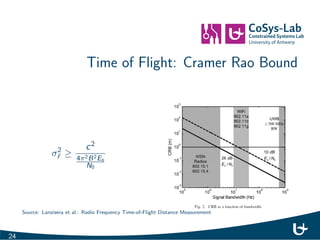
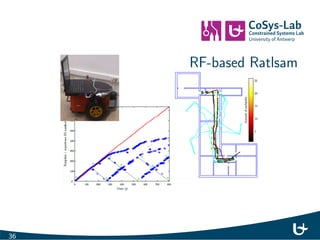
- 27. Time of Flight: Cramer Rao Bound 2 ^r c2 42B2Es N0 Source: Lanzisera et al.: Radio Frequency Time-of-Flight Distance Measurement 24
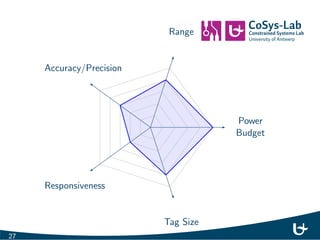
- 30. Power Budget Range Accuracy/Precision Responsiveness Tag Size 27
- 31. 28
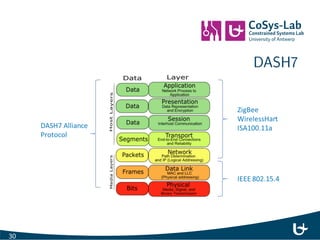
- 32. DASH7 Active RFID Standard for 433 MHz. I Build on top of asynchronous WSN MAC. I High level functionality optimized for RFID. I De
- 33. nes full functional RFID tag. I Can be extended to non RFID applications. Supports Tag to Tag communication. DASH7 Alliance Protocol is designed to support
- 34. xed and mobile nodes that need to upload or retrieve small chunks of information 29
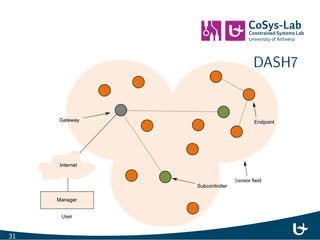
- 35. DASH7 30
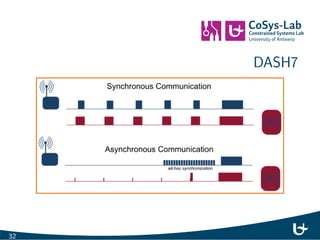
- 36. DASH7 31
- 37. DASH7 32
- 38. Open Source Stack for DASH7 http://oss-7.cosys.be LGPL v2.1 33
- 39. Open Source Stack for DASH7 34

