Lung Ultrasound Case 1
Download as pptx, pdf1 like2,051 views
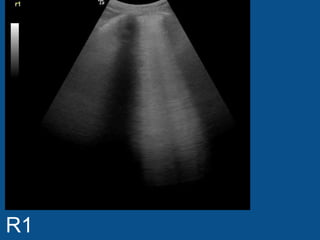
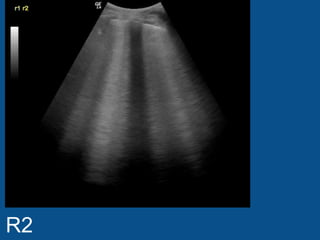
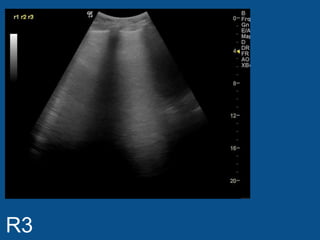
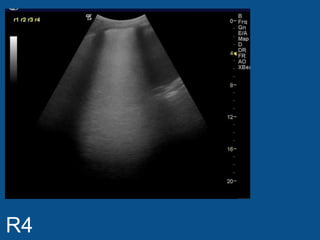
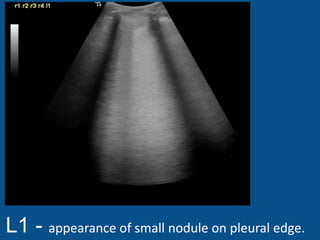
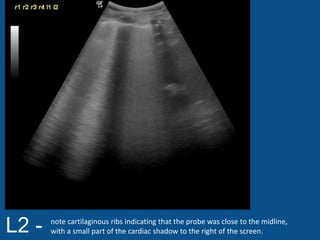
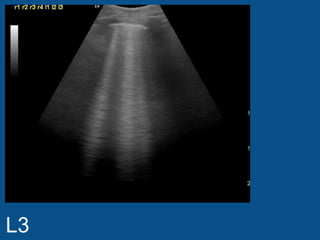
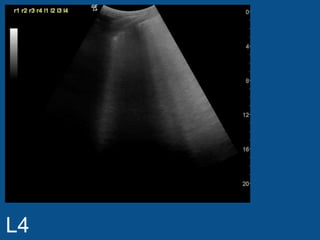
The ultrasound scan showed a small nodule on the pleural edge near the ribs and cardiac shadow, indicating the probe was close to the midline with part of the heart visible to the right. No other abnormalities were seen on the scan.
1 of 8
Downloaded 23 times
Ad
Recommended
Development of metencephalon
Development of metencephalonSidra Naeem
╠²
The document discusses the development of the metencephalon region of the brainstem. It describes how the rhombic lips form and compress to become the cerebellar plate, on which the vermis, cerebellar hemispheres, and transverse fissure develop. It also outlines the initial and developing layers of the cerebellum, including the external granular layer and migration of granule cells. Finally, it notes that some cells of the cerebellar cortex reach their definitive size after birth, while deep nuclei reach their final position before birth.Brain stem lessions in sensory symptoms
Brain stem lessions in sensory symptomsAbino David
╠²
A 62-year-old man presented with sudden onset of unsteadiness, tendency to fall to the right side, loss of sensation in the right half of the face and left side of the torso, and dysphagia. On examination, he had partial ptosis, enophthalmos, miosis of the right eye, and cerebellar signs. Localizing the lesion based on associated neurological deficits suggests a lesion in the pons, as the patient has crossed sensory loss of the face indicative of a lower motor neuron lesion of the trigeminal nerve, as well as unilateral facial numbness and potential unilateral deafness. Lesions in specific areas of the brainstem can be localized based on the cranial nervesPeripheral nerves &roots lession localisation
Peripheral nerves &roots lession localisationAbino David
╠²
The document discusses the peripheral nervous system (PNS) which is divided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The somatic system includes spinal nerves and cranial nerves which innervate skeletal muscles. The autonomic system regulates functions of internal organs. Some common neuropathies that can affect the PNS are discussed such as carpal tunnel syndrome, ulnar neuropathy, and polyneuropathies including Guillain-Barr├® syndrome. Plexopathies like brachial plexopathy and lumbosacral plexopathy are also summarized.Optic nerve
Optic nerveGreen Green
╠²
The optic nerve is the second cranial nerve that carries visual information from the retina to the brain. It passes through the optic chiasm where nerve fibers from each eye cross, then forms the optic tract through the thalamus and optic radiation to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe of the brain. The optic nerve exits the eye through the optic disk in the retina, creating the blind spot where there are no photoreceptor cells. Damage or disease of the optic nerve can cause conditions like optic atrophy, optic neuritis, and papilledema which can result in visual impairment.Eye models for review
Eye models for reviewNancyDecker
╠²
This document provides a diagram of the anatomy of the human eye, labeling the major external and internal structures including the iris, pupil, cornea, sclera, lens, vitreous body, retina, optic nerve, as well as the extraocular muscles - superior, medial, lateral, and inferior rectus muscles. It also notes the three layers of the eye - tunica fibrosa, tunica vasculosa, and tunica interna.ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 8
ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 8ICNUploads
╠²
The document notes an abnormality in the right lung, with 8cm of chest wall overlying the thoracic cage at its most shallow point, as well as minimal collapse just above the diaphragm. No abnormalities are mentioned for the left lung.Oct ultrasound case of the month
Oct ultrasound case of the month NYUMSKUS
╠²
This document describes a case of calcific tendinitis in a 61-year-old male with shoulder pain and limited range of motion. Ultrasound images showed a hypoechoic focus with hyperechoic rim and shadow in the infraspinatus tendon, representing calcium hydroxyapatite deposition. Calcific tendinitis most commonly affects those aged 40-70 and presents as severe pain, tenderness, erythema and limited motion. It progresses through silent, mechanical, and adhesive phases. Treatment may include NSAIDs, steroids, or ultrasound-guided aspiration and lavage of the calcium deposit.Ultrasound case of the month nov 13
Ultrasound case of the month nov 13NYUMSKUS
╠²
An 81-year-old woman presented with chronic left knee pain. Ultrasound images of her left knee showed thin, hyperechoic linear foci within the hyaline cartilage of the trochlea and lateral femorotibial compartment. This is indicative of chondrocalcinosis, which is the deposition of calcium crystals within hyaline cartilage. Chondrocalcinosis can be caused by calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease or other disorders such as gout, Wilson disease, and hypothyroidism. The ultrasound findings of chondrocalcinosis include calcifications parallel to the femoral condyle that do not cause acoustic shadowing due to their small size.August 2013: NYU MSK Ultrasound case of the month
August 2013: NYU MSK Ultrasound case of the monthNYUMSKUS
╠²
An 42-year-old female presented with right anterior chest wall pain. Ultrasound images showed a cortical discontinuity along the second rib at the costochondral junction, indicating a fracture that was not visible on initial radiographs. Transverse views further depicted a small hypoechoic gap in the rib corresponding to the non-displaced fracture. Ultrasound was thus able to detect this radiographically occult rib fracture, allowing for the diagnosis of a costochondral junction fracture of the right second anterior rib.Signs in Lung Ultrasound
Signs in Lung UltrasoundICNUploads
╠²
Basic summary of the common signs in lung ultrasound - Kylie BakerSept ultrasound case of the month
Sept ultrasound case of the monthNYUMSKUS
╠²
A 53-year-old female presented with right forefoot pain and tingling in the toes. Ultrasound images showed an ovoid hypoechoic mass in the third webspace, consistent with a diagnosis of third webspace neuroma. Neuromas typically appear hypoechoic on ultrasound and may exhibit hypervascularity on power Doppler. They are located on the plantar side of the transverse metatarsal ligament and cause metatarsalgia. Treatment options include conservative measures like footwear modification and steroid injections, advanced options such as alcohol injections, radiofrequency ablation, and cryoablation, or surgical resection.The Basics of Lung Ultrasound
The Basics of Lung UltrasoundICNUploads
╠²
Ultrasound is a useful screening tool for the lungs but has limitations. An 8-view ultrasound exam of the lungs can detect extravascular lung water seen as B lines originating from the pleural line. While a normal exam has evenly spaced A lines, more than 2 B lines in any view outside the lung bases indicates abnormality. Ultrasound has good sensitivity and specificity for detecting diffuse lung abnormalities compared to chest x-ray, but can miss localized findings and has a 15% error rate in certain conditions like fibrosis or resolving illnesses.Lung Ultrasound - Case 3
Lung Ultrasound - Case 3ICNUploads
╠²
The document discusses lung scans and CT scans that were taken in different positions. Lung scans were taken erect while CT scans were supine. One scan showed strongly positive confluent B lines in the posterior lung with an indistinct edge that would not move higher when the depth was at 15cm.ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 5
ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 5ICNUploads
╠²
The document discusses a chest x-ray of a patient lying down. A small fluid buildup was detected, prompting the doctor to have the patient roll over to check the back of the lungs more closely. Upon further investigation, a small fluid buildup was again seen acting as an indicator to look more deeply.ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 10
ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 10ICNUploads
╠²
This chest x-ray report notes small abnormalities in the lungs that prompted further investigation with additional views. A small pleural effusion acted as a signal to look deeper for other issues. Two small pleural line abnormalities in the lower areas of the lungs give a high probability of a pulmonary embolism, as one wedge-shaped opacity is most typical of a small pulmonary embolism.ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 6
ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 6ICNUploads
╠²
The lung ultrasound found bright, confluent B lines and sub-pleural abnormalities in the right lung, which can indicate a more chronic condition. No significant effusion was seen. The left lung was normal with no abnormalities detected.Not all bleeding stops: acute coagulopathy of trauma by Brohi
Not all bleeding stops: acute coagulopathy of trauma by BrohiSMACC Conference
╠²
The document discusses acute traumatic coagulopathy (ATC) and its impact on mortality in trauma patients. It outlines key treatment strategies such as early hemorrhage control, permissive hypotension, and coagulopathy targeting. The document also presents statistical data on mortality rates related to different treatment protocols and the mechanisms underlying hyperfibrinolysis in ATC.Case study C A D
Case study C A Dž╣ž©ž»ž¦┘äž╣ž▓┘Ŗž▓ ž¦┘äžĘ┘ł┘Ŗž▒┘é┘Ŗ
╠²
This document summarizes the case of a 73-year-old male patient admitted to the hospital for coronary artery disease. It provides details on his medical history including diabetes, hypertension, and a history of smoking. It then discusses coronary artery disease including symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic tests, treatment options through lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery. It concludes with a nursing care plan to address ineffective airway clearance related to secretions in the bronchi.Doppler ultrasound in deep vein thrombosis
Doppler ultrasound in deep vein thrombosisSamir Haffar
╠²
Doppler ultrasound is the preferred method for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It has high specificity and sensitivity for detecting thrombi in the proximal leg veins. Isolated calf vein thrombi can be missed by Doppler in up to 30% of cases. Clinical evaluation alone is only positive for DVT in about 50% of cases. While D-dimer tests are sensitive, they are not specific for DVT. Doppler ultrasound can directly visualize thrombi as noncompressible segments within veins. Indirect signs of DVT on Doppler include loss of phasicity with respiration and loss of flow augmentation with distal compression. Contrast venography remains the gold standard but is rarely used due to risks of contrast agents and limitedDoppler ultrasound of lower limb arteries
Doppler ultrasound of lower limb arteriesSamir Haffar
╠²
This document provides information on Doppler ultrasound of lower limb arteries. It begins with the anatomy of lower limb arteries including the abdominal aorta, iliac arteries, femoral arteries, and crural arteries. It then discusses normal Doppler ultrasound findings of lower limb arteries including normal arterial diameters, waveforms, and velocities. Finally, it covers duplex ultrasound criteria for arterial evaluation and various causes of lower limb arterial diseases such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, aneurysms, and arterial occlusions.Atherosclerosis ppt
Atherosclerosis pptDr Shumayla Aslam-Faiz
╠²
Atherosclerosis is a disease where plaque builds up inside arteries. It is caused by inflammation in the arteries due to risk factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow. This can lead to complications like heart attacks or strokes if a plaque ruptures. Doctors use tests like ultrasounds and angiograms to diagnose atherosclerosis and determine if the arteries are blocked. Treatment involves lifestyle changes and medications to control risk factors and blood pressure. In severe cases, procedures like angioplasty may be needed to open blocked arteries.Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceutics
Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceuticsnishiprakashj
╠²
Its a compilation of unit 3 as per PCI syllabus of B.Pharm IV sem, Subject Physical Pharmaceutics.OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROKanhu Charan
╠²
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROSevere Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)Dr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
This slide is for educational purposes only. Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...
Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair and Presenter, Naval Daver, MD, Jessica K. Altman, MD, and Ghayas Issa, MD, Alice S. Mims, MD, MSCR, discuss acute myeloid leukemia in this CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs with Innovative Targeted Strategies.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/42f1QCa. CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 30, 2026.Protein Biochemistry (1).pptx by Professor I.H MAINA
Protein Biochemistry (1).pptx by Professor I.H MAINAlegendnasir83
╠²
A brief insight on introductory biochemistry of proteinsMore Related Content
Viewers also liked (15)
August 2013: NYU MSK Ultrasound case of the month
August 2013: NYU MSK Ultrasound case of the monthNYUMSKUS
╠²
An 42-year-old female presented with right anterior chest wall pain. Ultrasound images showed a cortical discontinuity along the second rib at the costochondral junction, indicating a fracture that was not visible on initial radiographs. Transverse views further depicted a small hypoechoic gap in the rib corresponding to the non-displaced fracture. Ultrasound was thus able to detect this radiographically occult rib fracture, allowing for the diagnosis of a costochondral junction fracture of the right second anterior rib.Signs in Lung Ultrasound
Signs in Lung UltrasoundICNUploads
╠²
Basic summary of the common signs in lung ultrasound - Kylie BakerSept ultrasound case of the month
Sept ultrasound case of the monthNYUMSKUS
╠²
A 53-year-old female presented with right forefoot pain and tingling in the toes. Ultrasound images showed an ovoid hypoechoic mass in the third webspace, consistent with a diagnosis of third webspace neuroma. Neuromas typically appear hypoechoic on ultrasound and may exhibit hypervascularity on power Doppler. They are located on the plantar side of the transverse metatarsal ligament and cause metatarsalgia. Treatment options include conservative measures like footwear modification and steroid injections, advanced options such as alcohol injections, radiofrequency ablation, and cryoablation, or surgical resection.The Basics of Lung Ultrasound
The Basics of Lung UltrasoundICNUploads
╠²
Ultrasound is a useful screening tool for the lungs but has limitations. An 8-view ultrasound exam of the lungs can detect extravascular lung water seen as B lines originating from the pleural line. While a normal exam has evenly spaced A lines, more than 2 B lines in any view outside the lung bases indicates abnormality. Ultrasound has good sensitivity and specificity for detecting diffuse lung abnormalities compared to chest x-ray, but can miss localized findings and has a 15% error rate in certain conditions like fibrosis or resolving illnesses.Lung Ultrasound - Case 3
Lung Ultrasound - Case 3ICNUploads
╠²
The document discusses lung scans and CT scans that were taken in different positions. Lung scans were taken erect while CT scans were supine. One scan showed strongly positive confluent B lines in the posterior lung with an indistinct edge that would not move higher when the depth was at 15cm.ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 5
ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 5ICNUploads
╠²
The document discusses a chest x-ray of a patient lying down. A small fluid buildup was detected, prompting the doctor to have the patient roll over to check the back of the lungs more closely. Upon further investigation, a small fluid buildup was again seen acting as an indicator to look more deeply.ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 10
ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 10ICNUploads
╠²
This chest x-ray report notes small abnormalities in the lungs that prompted further investigation with additional views. A small pleural effusion acted as a signal to look deeper for other issues. Two small pleural line abnormalities in the lower areas of the lungs give a high probability of a pulmonary embolism, as one wedge-shaped opacity is most typical of a small pulmonary embolism.ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 6
ICN Lung Ultrasound Case 6ICNUploads
╠²
The lung ultrasound found bright, confluent B lines and sub-pleural abnormalities in the right lung, which can indicate a more chronic condition. No significant effusion was seen. The left lung was normal with no abnormalities detected.Not all bleeding stops: acute coagulopathy of trauma by Brohi
Not all bleeding stops: acute coagulopathy of trauma by BrohiSMACC Conference
╠²
The document discusses acute traumatic coagulopathy (ATC) and its impact on mortality in trauma patients. It outlines key treatment strategies such as early hemorrhage control, permissive hypotension, and coagulopathy targeting. The document also presents statistical data on mortality rates related to different treatment protocols and the mechanisms underlying hyperfibrinolysis in ATC.Case study C A D
Case study C A Dž╣ž©ž»ž¦┘äž╣ž▓┘Ŗž▓ ž¦┘äžĘ┘ł┘Ŗž▒┘é┘Ŗ
╠²
This document summarizes the case of a 73-year-old male patient admitted to the hospital for coronary artery disease. It provides details on his medical history including diabetes, hypertension, and a history of smoking. It then discusses coronary artery disease including symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic tests, treatment options through lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery. It concludes with a nursing care plan to address ineffective airway clearance related to secretions in the bronchi.Doppler ultrasound in deep vein thrombosis
Doppler ultrasound in deep vein thrombosisSamir Haffar
╠²
Doppler ultrasound is the preferred method for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It has high specificity and sensitivity for detecting thrombi in the proximal leg veins. Isolated calf vein thrombi can be missed by Doppler in up to 30% of cases. Clinical evaluation alone is only positive for DVT in about 50% of cases. While D-dimer tests are sensitive, they are not specific for DVT. Doppler ultrasound can directly visualize thrombi as noncompressible segments within veins. Indirect signs of DVT on Doppler include loss of phasicity with respiration and loss of flow augmentation with distal compression. Contrast venography remains the gold standard but is rarely used due to risks of contrast agents and limitedDoppler ultrasound of lower limb arteries
Doppler ultrasound of lower limb arteriesSamir Haffar
╠²
This document provides information on Doppler ultrasound of lower limb arteries. It begins with the anatomy of lower limb arteries including the abdominal aorta, iliac arteries, femoral arteries, and crural arteries. It then discusses normal Doppler ultrasound findings of lower limb arteries including normal arterial diameters, waveforms, and velocities. Finally, it covers duplex ultrasound criteria for arterial evaluation and various causes of lower limb arterial diseases such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, aneurysms, and arterial occlusions.Atherosclerosis ppt
Atherosclerosis pptDr Shumayla Aslam-Faiz
╠²
Atherosclerosis is a disease where plaque builds up inside arteries. It is caused by inflammation in the arteries due to risk factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow. This can lead to complications like heart attacks or strokes if a plaque ruptures. Doctors use tests like ultrasounds and angiograms to diagnose atherosclerosis and determine if the arteries are blocked. Treatment involves lifestyle changes and medications to control risk factors and blood pressure. In severe cases, procedures like angioplasty may be needed to open blocked arteries.Recently uploaded (20)
Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceutics
Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceuticsnishiprakashj
╠²
Its a compilation of unit 3 as per PCI syllabus of B.Pharm IV sem, Subject Physical Pharmaceutics.OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROKanhu Charan
╠²
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROSevere Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)Dr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
This slide is for educational purposes only. Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...
Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair and Presenter, Naval Daver, MD, Jessica K. Altman, MD, and Ghayas Issa, MD, Alice S. Mims, MD, MSCR, discuss acute myeloid leukemia in this CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs with Innovative Targeted Strategies.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/42f1QCa. CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 30, 2026.Protein Biochemistry (1).pptx by Professor I.H MAINA
Protein Biochemistry (1).pptx by Professor I.H MAINAlegendnasir83
╠²
A brief insight on introductory biochemistry of proteinsTuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptx
Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
The presentation contains preventive therapy, the DOTS program, and the national program of Nepal. This material is intended for educational purposes only.ELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.GOKULAKRISHNAN JANARTHANAN
╠²
Electromyography is basically the study of motor unit activity.
In electromyography, the study of the electrical activity of contracting muscle provides information concerning the structure and function of the motor units.
RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care
RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient CarePVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, FASCO, David F. McDermott, MD, and Tian Zhang, MD, MHS, prepared useful Practice Aids pertaining to renal cell carcinoma for this CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4brGF4h. CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 30, 2026.Design of cosmeceuticals products;sunprotection,sunscreens
Design of cosmeceuticals products;sunprotection,sunscreensSwami ramanand teerth marathwada university
╠²
Design of cosmeceuticals products and improving the skin to protection sun burning, used sunscreens, sunprotections AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontie...
AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontie...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Co-Chairs, Gloria Chiang, MD, and Ana M. Franceschi, MD, PhD, discuss AlzheimerŌĆÖs disease in this CME/AAPA activity titled ŌĆ£AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontier in Diagnosis and Treatment.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/AAPA information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/43CE1XA. CME/AAPA credit will be available until July 3, 2026.Bias, Cofounding Bias, Matching , Blinding
Bias, Cofounding Bias, Matching , BlindingDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
The slide contains small sippets about the bias, confounding bias, and the ways by which we can remove them. Like by using the methods such as matching and blinding. This slide can be useful as a reference for students in MBBS. COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTION.pptx
COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTION.pptxPackialakshmiP
╠²
COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTIONPatient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on...
Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Co-Chairs, Prof. Dr. Patrick Sch├Čffski, MPH, and Breelyn A. Wilky, MD, discuss desmoid tumors in this CME activity titled ŌĆ£Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on Gamma Secretase Inhibitors for Progressive Disease.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4iDPUQY. CME credit will be available until June 29, 2026.Yoga Postures to Practice
for Holistic (Physical, Mental, and Cognitive) Well...
Yoga Postures to Practice
for Holistic (Physical, Mental, and Cognitive) Well...Bhoj Raj Singh
╠²
An ancient System for holistic health (mental and physical) and wellbeing, is a scientific art of living with harmony (connecting) of mind and body. Although much more ancient than Patanjali, who documented yoga systematically about 2000 years ago, Patanjali is often referred to as the "father of modern yoga."
Yoga postures are commonly depicted in ancient paintings, carvings, and sculptures in almost all civilizations and religions, thus Yoga canŌĆÖt be described as an act of Hinduism. It originated long before any religion on Earth, with the emergence of life on the Planet. All yoga poses are natural, and what is not natural is not yoga; it is╠²Viyoga.
Besides Vedic Yoga, Hatha, Vinyasa, Ashtanga, Iyengar, Yin, Restorative, Kundalini, Bikram, Sahaj, and Power yoga are some popular types.
Vinyasa╠²Yoga is the closest form to Vedic Yoga; it is known for its flowing movements, not very rigorous, not too much straining, actions flow with the breath.
Though all yoga may lead to meditation (Dhyan) for your inner upliftment, it is not the same as described in Hinduism for self-liberation.
In Hinduism, different paths of life looking distinct but can be practiced all together, they are: Karma Yoga (selfless action and service), Bhakti Yoga (devotion and love for God or Godly power), Jnana (Gyan) Yoga (gaining knowledge for self-realization through wisdom), Dhyan Yoga (meditation) and Kriya Yoga (optimum utilization of your vital and muscular energy).╠²
Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docx
Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docxkopalsharma85
╠²
pharmacy exercise on aspirin powderComputer aided formulation development optimization
Computer aided formulation development optimizationSwami ramanand teerth marathwada university
╠²
Concept of optimization, optimization parameters, factorial design, optimization technology & screening design. Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...
Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care
RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient CarePVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Design of cosmeceuticals products;sunprotection,sunscreens
Design of cosmeceuticals products;sunprotection,sunscreensSwami ramanand teerth marathwada university
╠²
AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontie...
AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontie...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on...
Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Ad