惭补迟濒补产讲习2021
Download as pptx, pdf1 like144 views
惭础罢尝础叠の基础的な使い方について绍介するスライドです.
1 of 24
Download to read offline



![行列計算をしてみる | ベクトルと行列の定義
? MATLABは行列計算に強いので,いろいろ遊んでみよう.
1. ベクトルの計算
1. と入力すると,横ベクトル? = [1 2 3]が生成される.
2. と入力すると,縦ベクトル? =
1
2
3
が生成される.
2. 行列の定義
1. と入力すると,行列? =
1 2
3 4
が生成される.
>> A=[1 2; 3 4]
>> p=[1 2 3]
>> q=[1 2 3]’
転置を意味する
改行を意味する
6
>> q=[1; 2; 3]
TRY と入力するとどうなるだろうか.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab2021-211018032943/85/Matlab-2021-6-320.jpg)
![準備: 行列?を定義しておきます.
行列計算をしてみる | 行列の演算
1. 行列の掛け算
1. スカラーと行列の掛け算は, と書ける.
2. 行列と行列の掛け算は, と書ける.
2. 逆行列は, で簡単に求められる.
3. 固有値と固有ベクトルは, で求められる.
Vは固有ベクトルからなる正方行列で,各列が固有ベクトル.
Dは固有値を対角に持つ対角行列.
>> a*A
>> [V,D]=eig(A)
>> inv(A)
>> B = [3 4; 5 6]
>> A*B
練習問題
行列 ? =
0 1 1
?4 4 2
2 ?1 1
を対角化せよ.
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab2021-211018032943/85/Matlab-2021-7-320.jpg)
![1. スカラーとベクトルの掛け算は, と書ける.
2. ベクトルの積を計算してみよう.
1. 二つの縦ベクトル を定義する.
2. ベクトル?と?の内積は,
3. ベクトル?と?の外積は,
行列計算をしてみる | ベクトルの演算
>> a*p
>> u=[2;3;4] >> v=[5;6;7]
>> dot(u,v)
>> cross(u,v)
ベクトル?と?の内積は,? ? ? = ???で求められる.すなわち,
でも計算できる.
>> u’*v
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab2021-211018032943/85/Matlab-2021-8-320.jpg)





![構造体でプログラムをシンプルに書く
? 関数の引数が長いと書くのが大変
? 「構造体」を使ってまとめてしまえば,簡単に書き表せる
dx = F (t, x, m1, m2, J1, J2, l1, l2, d1, d2, g);
param.m1 = 1.0;
param.m2 = 1.0;
param.J1 = 1.5;
param.J2 = 1.5;
param.l1 = 1.0;
param.l2 = 1.0;
param.d1 = 0.5;
param.d2 = 0.5;
param.g = 9.8;
dx = F (t, x, param);
‘param’ という構造体の中に,
たくさんの変数が存在する
「構造体名.変数名」というフォーマット
(.の後に変数名を書く)
‘param’ だけ引いてしまえば,
中身の変数が全部ついてくる
param = [1.0 1.0 1.5 1.5 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.5 9.8]
とするよりも,各変数の意味がわかりやすい
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab2021-211018032943/85/Matlab-2021-16-320.jpg)




Ad
Recommended
Cisco Catalyst 2960-X Series Switching Architecture
Cisco Catalyst 2960-X Series Switching ArchitectureSunil Kumar Guduru
?
The document provides an overview of the Cisco Catalyst 2960-X series, highlighting its features such as FlexStack-Plus for high availability, secure network capabilities, and efficient energy use. Key specifications are compared across different models, detailing processor architecture, power options, and enhanced lifetime warranty terms. The agenda covers the product's architecture, operational ease, and advanced networking functionalities.05. DF - Latest Trends in Optical Data Center Interconnects
05. DF - Latest Trends in Optical Data Center InterconnectsDimitris Filippou
?
This document discusses the latest trends in optical data center interconnects. It notes that data center connections are moving from 10G/40G to 25G/100G, and within and between data centers. New hyperscale data center architectures are flattening traditional tiered topologies. Interconnect technologies are seeing a significant increase in 100G and 25G port densities using smaller form factors like QSFP28 and SFP28. Standards organizations are working on 50G, 200G, 400G, and next-generation 100G Ethernet to support these increases in bandwidth.Day 2 IP ROUTING
Day 2 IP ROUTINGanilinvns
?
The document provides information about IP routing, including static and dynamic routing. It discusses:
- The basics of routing including destination addresses, neighbor routers, routes, and maintaining routing information.
- The benefits and disadvantages of static routing, including less overhead but requiring manual configuration.
- Dynamic routing protocols like RIP, IGRP, and OSPF that automatically share routing information.
- Configuring and verifying static routes, as well as troubleshooting connection issues.
- Key aspects of distance vector protocols like RIP and IGRP, including updates, loops, metrics, and timers.Fundamentals of Networking
Fundamentals of Networkingjashhad
?
The document provides an overview of network fundamentals including basic concepts in communication, network structures and topologies, transmission mediums such as twisted pair cables, coaxial cable, and optical fibers, and network protocols. It describes essential components for communication including a message, transmitter, transmission medium, receiver, and destination. Common network topologies like bus, star, ring and variations are explained. Characteristics of different cabling options are also outlined.Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) KHNOG
?
BFD is a protocol that can quickly detect failures in the forwarding path between two adjacent routers, including interfaces, data links, and forwarding planes. It operates in two modes: asynchronous mode where it periodically sends control packets, and demand mode where it only sends packets when needed. When a failure is detected, BFD triggers routing protocol actions to recalculate the routing table and reduce convergence time. It provides fast failure detection independently of media, encapsulation, topology, or routing protocol. Configuring BFD involves setting intervals at the interface level and enabling it for routing protocols.CCNP ROUTE V7 CH1
CCNP ROUTE V7 CH1Chaing Ravuth
?
This document provides an overview of basic network and routing concepts for the CCNP ROUTE certification. It discusses differentiating between dynamic routing protocols, network types including non-broadcast multi-access networks, connecting remote locations using various technologies, and understanding how different traffic types and overlay networks influence routing. The objectives cover routing protocols, branch connectivity options, and IPv6 neighbor discovery.Lan Network with Redundancy.ppt
Lan Network with Redundancy.pptSantanu Mukhopadhyay
?
This document discusses setting up a redundant LAN network. It describes what a LAN network is and the importance of network redundancy. It then provides details on various methods for implementing redundancy, including creating VPNs, using redundancy protocols like HSRP and VRRP, basic routing, MPLS routing, access lists, NAT/PAT, and configuring redundant LAN connections. The document includes configuration examples and concludes that the project was a valuable learning experience for understanding real-world networking operations.CCNA-LAB-GUIDE-V3_LAST-ADDITION (4).pdf
CCNA-LAB-GUIDE-V3_LAST-ADDITION (4).pdfpoojaswami31
?
The document provides instructions to configure basic settings on a Cisco router and switch including hostname, enable password, login banner, IP addresses, default gateway, and remote access using telnet. The configurations assign IP addresses to interfaces, set passwords to restrict access to privileged modes, and enable remote management of the devices on the network.Integrated services digital network (isdn)
Integrated services digital network (isdn)Gulu University
?
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) provides digital transmission of voice, video and data over telephone lines at high speeds. It uses dedicated digital channels that allow for faster call setup and multiple devices to share a single line. ISDN interfaces include Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI) and supports transmission speeds up to 1920 kbps, offering advantages over analog networks.40G 100G gigabit ethernet technology overview
40G 100G gigabit ethernet technology overviewMapYourTech
?
The document discusses the development of 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet standards. It notes that in 2006, the IEEE determined these faster speeds were needed - 40 Gbps for computing and 100 Gbps for network aggregation. The IEEE formed a task force in 2008 to develop these standards. Key aspects included preserving the Ethernet frame format while supporting faster speeds over fiber and copper cable. The physical coding sublayer implements a multilane distribution scheme to help meet engineering challenges, distributing data across multiple "lanes" to support various interface widths.ZTE_NR8000_Overview.pdf
ZTE_NR8000_Overview.pdfssuser3769e8
?
The document provides an overview of ZTE's NR8000 microwave solution, including:
1) The NR8000 platform can be used for access, relay, and hub stations across a wide range of frequency bands and supports technologies like header compression, adaptive coding and modulation, and physical layer aggregation.
2) The portfolio includes the NR8120, NR8250, and NR8950 products, which support capacities up to 1Gbps and integrate TDM and Ethernet traffic on a unified hybrid and packet platform.
3) The solution provides high reliability features like 1+1, 1+0 protection configurations, ring protection protocols, and SNCP/SNCP+ to double network capacity.routing
routingradhika477746
?
Routing is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic. There are several key components involved in routing, including routing algorithms, routing tables, and routing protocols. Common routing algorithms include distance vector algorithms like RIP, which use periodic updates between routers to share routing information, and link state algorithms like OSPF, which flood link state information to all routers to enable shortest path calculations. The Internet uses a hierarchical routing model with intra-domain routing protocols like OSPF and inter-domain routing with BGP.Introduction to ns2
Introduction to ns2Pradeep Kumar TS
?
This document provides an introduction to using NS2 (Network Simulator 2) for network simulation. It recommends using Linux over Windows for NS2 as support has been stopped for Windows beyond a certain version. It outlines some basic Linux commands needed for working with NS2 and describes NS2's architecture which uses C++ for implementation and OTCL for the user interface with TclCL providing the interface between them. It also gives a brief overview of NS2's capabilities for simulating protocols and networking entities and describes OTCL with examples of defining classes and objects.PON design considerations for FTTH FTTx
PON design considerations for FTTH FTTxSun Telecommunication (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
?
The document discusses considerations for designing an EPON network. It covers bandwidth requirements, splitting architecture options including 1-stage and 2-stage splitting, maximum transmission distances depending on splitting ratios, calculating the optical power budget, services that can be provided over EPON including FTTH and FTTB/C, upgrading existing networks, required network nodes and equipment, and cable types.CCNAv5 - S3: Chapter 4 Wireless Lans
CCNAv5 - S3: Chapter 4 Wireless LansVuz D? H?i
?
The document outlines the concepts, operations, and security of wireless local area networks (WLANs) as per Cisco's guidelines. It covers wireless LAN technologies, configurations, channel management, and various types of threats, including rogue access points and man-in-the-middle attacks. Additionally, it highlights the importance of implementing security mechanisms such as authentication and encryption to protect WLANs.IP addressing seminar ppt
IP addressing seminar pptSmriti Rastogi
?
This document provides an overview of IP addressing, including definitions, types of IP addresses (static, dynamic, public, private), and the structure of IPv4 addresses. It also discusses the history and functioning of the TCP/IP protocol suite, including the role of subnetting and the limitations of classful addressing. Additionally, the document briefly mentions the differences between IPv4 and IPv6, highlighting the increasing prevalence of IPv4 in network usage.3GPP 5G NSA Detailed explanation 5(EN-DC Handover Call Flow)
3GPP 5G NSA Detailed explanation 5(EN-DC Handover Call Flow)Ryuichi Yasunaga
?
3GPP 5G NSA Detailed explanation (EN-DC Handover Call Flow)
?A hands-on resource for mobile engineers
※written in Japanese
Introduction to Networking Commands & Software
Introduction to Networking Commands & SoftwareMuhammadRizaHilmi
?
This document provides an overview of networking software and commands used in Windows 10. It discusses setting the IP configuration, including obtaining IP addresses dynamically from a DHCP server or manually configuring a static IP. Common networking commands and software introduced include ipconfig for viewing IP settings, ping for testing network connectivity, and Wireshark for network packet capture and analysis. The document emphasizes that networking software helps users explore, configure, troubleshoot and manage networks, while remaining transparent to end users of network services.Hamming Yapay Sinir A?? (Konu anlat?m?)
Hamming Yapay Sinir A?? (Konu anlat?m?)Murat ?zalp
?
Hamming A?lar? ve ??renmesi
Doktora YSA ders ?deviAbap tips
Abap tipsYogesh Mehra
?
This document provides a table of contents and overview of useful ABAP transactions, programs, functions, and topics for ABAP programming. It covers transactions and tools for EDI, IDoc, message control, sales, reports, object programming, file processing, and more. The document serves as a reference guide for SAP developers.Campas network design overview
Campas network design overviewAnushka Hapuhinna
?
The document provides an overview of traditional campus network designs and introduces some concepts for campus network design. It discusses traditional router and hub campus designs and moves to newer designs using virtual LAN (VLAN) technologies and multilayer switching. The key concepts covered include the access, distribution and core layers, switch blocks, core blocks, and considerations around sizing and redundancy in campus network designs.ZyXEL Next Generation GPON-FTTH solution
ZyXEL Next Generation GPON-FTTH solutionBhairave Maulekhi
?
The document discusses ZYXEL's next-generation GPON FTTH solutions, detailing the architecture and components of passive optical networks (PON) used for broadband connectivity. It outlines various applications, benefits, and cost advantages of GPON technology, emphasizing its capacity for high-speed data transmission and simplified deployment. Additionally, it provides an overview of ZYXEL's OLT product portfolio and emphasizes management tools for service providers.Bgp
BgpRaghu Kiran
?
BGP is an inter-AS routing protocol used to exchange routing and reachability information between autonomous systems on the internet. It uses path vector routing rather than distance vector, and carries richer metric information than IGPs. BGP configurations establish neighbor relationships between routers in different ASes to exchange routing updates.Optical fiber Communication
Optical fiber Communication Saurabh Kumar
?
This document provides an overview of optical fiber communication. It discusses the introduction of optical fiber, including its composition and small diameter. The history of optical fiber is summarized, from early experiments in the 1840s to widespread telecommunication use in the late 20th century. The document outlines the principle of total internal reflection that allows transmission through optical fibers and describes the main types of fibers based on mode and refractive index. Applications and advantages of optical fiber communication are also mentioned.Introduction to Bluetooth low energy
Introduction to Bluetooth low energyNEEVEE Technologies
?
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a wireless personal area network technology designed for applications in healthcare, fitness, security, and home entertainment, offering low power consumption and long battery life. It operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band with various channel and advertising mechanisms to facilitate device discovery and connections. The protocol encompasses roles for devices, security mechanisms, and profiles tailored to specific domains such as healthcare and fitness.Optical Fiber Communication
Optical Fiber Communicationibrahimnabil17
?
The document discusses different optical access network architectures including Fiber To The Building (FTTB), Fiber To The Curb (FTTC), and Fiber To The Home (FTTH). It also describes Passive Optical Networks (PON) and Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (GPON) technologies. Specifically, GPON uses wavelength division multiplexing and time division multiple access to enable bidirectional communication between an optical line terminal and multiple optical network terminals over a single fiber at data rates of 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.2 Gbps upstream.2.8 bluetooth ieee 802.15
2.8 bluetooth ieee 802.15JAIGANESH SEKAR
?
The document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology, detailing its architecture including piconets and scatternets, as well as the various layers such as radio, baseband, and L2CAP. It describes the frame formats and types used in Bluetooth communication, highlighting the role of each layer and the mechanisms for data transmission. Additionally, it cites references for further reading on data communication and networking.RSTP (rapid spanning tree protocol)
RSTP (rapid spanning tree protocol)Netwax Lab
?
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), introduced as IEEE 802.1w in 2001, significantly improves the convergence time after topology changes when compared to the original Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), allowing response times within milliseconds. RSTP features three port states (discarding, learning, forwarding) and five port roles (root, designated, alternate, backup, disabled) to enhance efficiency and compatibility with STP. The protocol operates with advanced mechanisms like the proposal/agreement process for rapid transitions and integrates well within networks using both RSTP and STP protocols.【SIROK技術勉強会 #4】機械学習と線形代数の基礎
【SIROK技術勉強会 #4】機械学習と線形代数の基礎Shuntaro Tamura
?
【30席増席!】SED ?SIROK技術勉強会 #4「機械学習と線形代数の基礎」?
https://atnd.org/events/68945
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
日時:2015/08/18 (火) 19:30 to 21:00
場所:渋谷プライムプラザ4F セミナルーム
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Integrated services digital network (isdn)
Integrated services digital network (isdn)Gulu University
?
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) provides digital transmission of voice, video and data over telephone lines at high speeds. It uses dedicated digital channels that allow for faster call setup and multiple devices to share a single line. ISDN interfaces include Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI) and supports transmission speeds up to 1920 kbps, offering advantages over analog networks.40G 100G gigabit ethernet technology overview
40G 100G gigabit ethernet technology overviewMapYourTech
?
The document discusses the development of 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet standards. It notes that in 2006, the IEEE determined these faster speeds were needed - 40 Gbps for computing and 100 Gbps for network aggregation. The IEEE formed a task force in 2008 to develop these standards. Key aspects included preserving the Ethernet frame format while supporting faster speeds over fiber and copper cable. The physical coding sublayer implements a multilane distribution scheme to help meet engineering challenges, distributing data across multiple "lanes" to support various interface widths.ZTE_NR8000_Overview.pdf
ZTE_NR8000_Overview.pdfssuser3769e8
?
The document provides an overview of ZTE's NR8000 microwave solution, including:
1) The NR8000 platform can be used for access, relay, and hub stations across a wide range of frequency bands and supports technologies like header compression, adaptive coding and modulation, and physical layer aggregation.
2) The portfolio includes the NR8120, NR8250, and NR8950 products, which support capacities up to 1Gbps and integrate TDM and Ethernet traffic on a unified hybrid and packet platform.
3) The solution provides high reliability features like 1+1, 1+0 protection configurations, ring protection protocols, and SNCP/SNCP+ to double network capacity.routing
routingradhika477746
?
Routing is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic. There are several key components involved in routing, including routing algorithms, routing tables, and routing protocols. Common routing algorithms include distance vector algorithms like RIP, which use periodic updates between routers to share routing information, and link state algorithms like OSPF, which flood link state information to all routers to enable shortest path calculations. The Internet uses a hierarchical routing model with intra-domain routing protocols like OSPF and inter-domain routing with BGP.Introduction to ns2
Introduction to ns2Pradeep Kumar TS
?
This document provides an introduction to using NS2 (Network Simulator 2) for network simulation. It recommends using Linux over Windows for NS2 as support has been stopped for Windows beyond a certain version. It outlines some basic Linux commands needed for working with NS2 and describes NS2's architecture which uses C++ for implementation and OTCL for the user interface with TclCL providing the interface between them. It also gives a brief overview of NS2's capabilities for simulating protocols and networking entities and describes OTCL with examples of defining classes and objects.PON design considerations for FTTH FTTx
PON design considerations for FTTH FTTxSun Telecommunication (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
?
The document discusses considerations for designing an EPON network. It covers bandwidth requirements, splitting architecture options including 1-stage and 2-stage splitting, maximum transmission distances depending on splitting ratios, calculating the optical power budget, services that can be provided over EPON including FTTH and FTTB/C, upgrading existing networks, required network nodes and equipment, and cable types.CCNAv5 - S3: Chapter 4 Wireless Lans
CCNAv5 - S3: Chapter 4 Wireless LansVuz D? H?i
?
The document outlines the concepts, operations, and security of wireless local area networks (WLANs) as per Cisco's guidelines. It covers wireless LAN technologies, configurations, channel management, and various types of threats, including rogue access points and man-in-the-middle attacks. Additionally, it highlights the importance of implementing security mechanisms such as authentication and encryption to protect WLANs.IP addressing seminar ppt
IP addressing seminar pptSmriti Rastogi
?
This document provides an overview of IP addressing, including definitions, types of IP addresses (static, dynamic, public, private), and the structure of IPv4 addresses. It also discusses the history and functioning of the TCP/IP protocol suite, including the role of subnetting and the limitations of classful addressing. Additionally, the document briefly mentions the differences between IPv4 and IPv6, highlighting the increasing prevalence of IPv4 in network usage.3GPP 5G NSA Detailed explanation 5(EN-DC Handover Call Flow)
3GPP 5G NSA Detailed explanation 5(EN-DC Handover Call Flow)Ryuichi Yasunaga
?
3GPP 5G NSA Detailed explanation (EN-DC Handover Call Flow)
?A hands-on resource for mobile engineers
※written in Japanese
Introduction to Networking Commands & Software
Introduction to Networking Commands & SoftwareMuhammadRizaHilmi
?
This document provides an overview of networking software and commands used in Windows 10. It discusses setting the IP configuration, including obtaining IP addresses dynamically from a DHCP server or manually configuring a static IP. Common networking commands and software introduced include ipconfig for viewing IP settings, ping for testing network connectivity, and Wireshark for network packet capture and analysis. The document emphasizes that networking software helps users explore, configure, troubleshoot and manage networks, while remaining transparent to end users of network services.Hamming Yapay Sinir A?? (Konu anlat?m?)
Hamming Yapay Sinir A?? (Konu anlat?m?)Murat ?zalp
?
Hamming A?lar? ve ??renmesi
Doktora YSA ders ?deviAbap tips
Abap tipsYogesh Mehra
?
This document provides a table of contents and overview of useful ABAP transactions, programs, functions, and topics for ABAP programming. It covers transactions and tools for EDI, IDoc, message control, sales, reports, object programming, file processing, and more. The document serves as a reference guide for SAP developers.Campas network design overview
Campas network design overviewAnushka Hapuhinna
?
The document provides an overview of traditional campus network designs and introduces some concepts for campus network design. It discusses traditional router and hub campus designs and moves to newer designs using virtual LAN (VLAN) technologies and multilayer switching. The key concepts covered include the access, distribution and core layers, switch blocks, core blocks, and considerations around sizing and redundancy in campus network designs.ZyXEL Next Generation GPON-FTTH solution
ZyXEL Next Generation GPON-FTTH solutionBhairave Maulekhi
?
The document discusses ZYXEL's next-generation GPON FTTH solutions, detailing the architecture and components of passive optical networks (PON) used for broadband connectivity. It outlines various applications, benefits, and cost advantages of GPON technology, emphasizing its capacity for high-speed data transmission and simplified deployment. Additionally, it provides an overview of ZYXEL's OLT product portfolio and emphasizes management tools for service providers.Bgp
BgpRaghu Kiran
?
BGP is an inter-AS routing protocol used to exchange routing and reachability information between autonomous systems on the internet. It uses path vector routing rather than distance vector, and carries richer metric information than IGPs. BGP configurations establish neighbor relationships between routers in different ASes to exchange routing updates.Optical fiber Communication
Optical fiber Communication Saurabh Kumar
?
This document provides an overview of optical fiber communication. It discusses the introduction of optical fiber, including its composition and small diameter. The history of optical fiber is summarized, from early experiments in the 1840s to widespread telecommunication use in the late 20th century. The document outlines the principle of total internal reflection that allows transmission through optical fibers and describes the main types of fibers based on mode and refractive index. Applications and advantages of optical fiber communication are also mentioned.Introduction to Bluetooth low energy
Introduction to Bluetooth low energyNEEVEE Technologies
?
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a wireless personal area network technology designed for applications in healthcare, fitness, security, and home entertainment, offering low power consumption and long battery life. It operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band with various channel and advertising mechanisms to facilitate device discovery and connections. The protocol encompasses roles for devices, security mechanisms, and profiles tailored to specific domains such as healthcare and fitness.Optical Fiber Communication
Optical Fiber Communicationibrahimnabil17
?
The document discusses different optical access network architectures including Fiber To The Building (FTTB), Fiber To The Curb (FTTC), and Fiber To The Home (FTTH). It also describes Passive Optical Networks (PON) and Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (GPON) technologies. Specifically, GPON uses wavelength division multiplexing and time division multiple access to enable bidirectional communication between an optical line terminal and multiple optical network terminals over a single fiber at data rates of 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.2 Gbps upstream.2.8 bluetooth ieee 802.15
2.8 bluetooth ieee 802.15JAIGANESH SEKAR
?
The document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology, detailing its architecture including piconets and scatternets, as well as the various layers such as radio, baseband, and L2CAP. It describes the frame formats and types used in Bluetooth communication, highlighting the role of each layer and the mechanisms for data transmission. Additionally, it cites references for further reading on data communication and networking.RSTP (rapid spanning tree protocol)
RSTP (rapid spanning tree protocol)Netwax Lab
?
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), introduced as IEEE 802.1w in 2001, significantly improves the convergence time after topology changes when compared to the original Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), allowing response times within milliseconds. RSTP features three port states (discarding, learning, forwarding) and five port roles (root, designated, alternate, backup, disabled) to enhance efficiency and compatibility with STP. The protocol operates with advanced mechanisms like the proposal/agreement process for rapid transitions and integrates well within networks using both RSTP and STP protocols.Similar to 惭补迟濒补产讲习2021 (20)
【SIROK技術勉強会 #4】機械学習と線形代数の基礎
【SIROK技術勉強会 #4】機械学習と線形代数の基礎Shuntaro Tamura
?
【30席増席!】SED ?SIROK技術勉強会 #4「機械学習と線形代数の基礎」?
https://atnd.org/events/68945
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
日時:2015/08/18 (火) 19:30 to 21:00
場所:渋谷プライムプラザ4F セミナルーム
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーStatGenSummerSchool2023_Rsoftware.pdf
StatGenSummerSchool2023_Rsoftware.pdfThe University of Tokyo, Osaka University, RIKEN IMS
?
Statstical Genetics Summer School 2023
http://www.sg.med.osaka-u.ac.jp/school_2023.html
Aug 25-27th 2023, Osaka University, The University of Tokyo, RIKENm, Japan
マイクロマウスのための MATLAB/Simulink 講座 第1回 - MATLAB入門
マイクロマウスのための MATLAB/Simulink 講座 第1回 - MATLAB入門Teng Tokoro
?
2019/1/19に开催したマイクロマウスのための惭础罢尝础叠/厂颈尘耻濒颈苍办讲座の第1回资料です.惭础罢尝础叠の基本操作と,ログデータ可视化のためのプロットを主に扱っています.Pythonとdeep learningで手書き文字認識
Pythonとdeep learningで手書き文字認識Ken Morishita
?
この続きで罢丑别补苍辞の使い方について简単に书きました:丑迟迟辫://辩颈颈迟补.肠辞尘/颈迟别尘蝉/3蹿产蹿6补蹿714肠1蹿66蹿99别9Pythonによる機械学習入門?基礎からDeep Learningまで?
Pythonによる機械学習入門?基礎からDeep Learningまで?Yasutomo Kawanishi
?
電子情報通信学会総合大会2016
企画セッション
「パターン認識?メディア理解」必須ソフトウェアライブラリ
手とり足とりガイド【Deep Learning (MIT Press)】線形代数 2.1~2.7
【Deep Learning (MIT Press)】線形代数 2.1~2.7京都大学人工知能研究会 KaiRA
?
京都大学人工知能研究会 KaiRA( https://kyoto-kaira.github.io/ )の輪読資料ですGood coding for research
Good coding for researchKeiji Harada
?
MATLABにおけるscriptの書き方についてのセミナー資料。Readable Codeの考え方に基づいています。我ながらニッチだなーwAd
Recently uploaded (8)
PGConf.dev 2025 参加レポート (JPUG総会併設セミナー2025 発表資料)
PGConf.dev 2025 参加レポート (JPUG総会併設セミナー2025 発表資料)NTT DATA Technology & Innovation
?
PGConf.dev 2025 参加レポート
(JPUG総会併設セミナー2025 発表資料)
2025年6月14日(土)
NTTデータ
OSSビジネス推進室
貞弘 泰輔、池田 凛太郎Protect Your IoT Data with UbiBot's Private Platform.pptx
Protect Your IoT Data with UbiBot's Private Platform.pptxユビボット 株式会社
?
Our on-premise IoT platform offers a secure and scalable solution for businesses, with features such as real-time monitoring, customizable alerts and open API support, and can be deployed on your own servers to ensure complete data privacy and control.Ad
惭补迟濒补产讲习2021
- 2. はじめに 2 MATLABは,科学計算に特化した数値解析ソフトウェア. ? 数値解析(シミュレーション) ? 信号処理 ? データ解析 ? 機械学習 様々な計算に対応する 多用なツールボックスを備えている. 最近では,ロボティクスの需要に応えるため, Robotics toolboxや,ROS (Robot OS)との連携もできるようにアップデートされた. ? データの扱いが簡単 変数の型を指定する必要がない ? プログラミングが簡単 Pythonのように,シンプルなコードで書ける ? 描画が得意 きれいなプロットを簡単に作成可能
- 3. もくじ 1. 基本的な使い方 2. プログラムを作る 3. 可視化する 4. 構造体とオブジェクト指向プログラミング 5. 付録 3
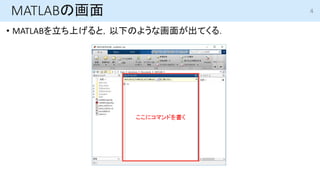
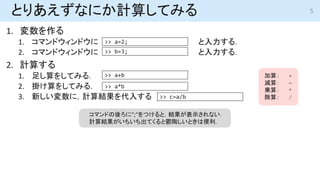
- 5. とりあえずなにか計算してみる 1. 変数を作る 1. コマンドウィンドウに と入力する. 2. コマンドウィンドウに と入力する. 2. 計算する 1. 足し算をしてみる. 2. 掛け算をしてみる. 3. 新しい変数に,計算結果を代入する >> a=2; >> b=3; >> a+b >> a*b コマンドの後ろに”;”をつけると,結果が表示されない. 計算結果がいちいち出てくると鬱陶しいときは便利. >> c=a/b 加算: + 減算: - 乗算: * 除算: / 5
- 6. 行列計算をしてみる | ベクトルと行列の定義 ? MATLABは行列計算に強いので,いろいろ遊んでみよう. 1. ベクトルの計算 1. と入力すると,横ベクトル? = [1 2 3]が生成される. 2. と入力すると,縦ベクトル? = 1 2 3 が生成される. 2. 行列の定義 1. と入力すると,行列? = 1 2 3 4 が生成される. >> A=[1 2; 3 4] >> p=[1 2 3] >> q=[1 2 3]’ 転置を意味する 改行を意味する 6 >> q=[1; 2; 3] TRY と入力するとどうなるだろうか.
- 7. 準備: 行列?を定義しておきます. 行列計算をしてみる | 行列の演算 1. 行列の掛け算 1. スカラーと行列の掛け算は, と書ける. 2. 行列と行列の掛け算は, と書ける. 2. 逆行列は, で簡単に求められる. 3. 固有値と固有ベクトルは, で求められる. Vは固有ベクトルからなる正方行列で,各列が固有ベクトル. Dは固有値を対角に持つ対角行列. >> a*A >> [V,D]=eig(A) >> inv(A) >> B = [3 4; 5 6] >> A*B 練習問題 行列 ? = 0 1 1 ?4 4 2 2 ?1 1 を対角化せよ. 7
- 8. 1. スカラーとベクトルの掛け算は, と書ける. 2. ベクトルの積を計算してみよう. 1. 二つの縦ベクトル を定義する. 2. ベクトル?と?の内積は, 3. ベクトル?と?の外積は, 行列計算をしてみる | ベクトルの演算 >> a*p >> u=[2;3;4] >> v=[5;6;7] >> dot(u,v) >> cross(u,v) ベクトル?と?の内積は,? ? ? = ???で求められる.すなわち, でも計算できる. >> u’*v 8
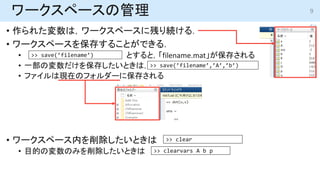
- 9. ワークスペースの管理 ? 作られた変数は,ワークスペースに残り続ける. ? ワークスペースを保存することができる. ? とすると,「filename.mat」が保存される ? 一部の変数だけを保存したいときは, とする ? ファイルは現在のフォルダーに保存される ? ワークスペース内を削除したいときは ? 目的の変数のみを削除したいときは >> clear >> clearvars A b p >> save(’filename’) >> save(’filename’,’A’,’b’) 9
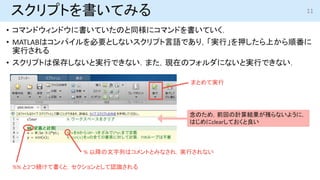
- 11. スクリプトを書いてみる ? コマンドウィンドウに書いていたのと同様にコマンドを書いていく. ? MATLABはコンパイルを必要としないスクリプト言語であり,「実行」を押したら上から順番に 実行される ? スクリプトは保存しないと実行できない.また,現在のフォルダにないと実行できない. まとめて実行 % 以降の文字列はコメントとみなされ,実行されない %% と2つ続けて書くと,セクションとして認識される 念のため,前回の計算結果が残らないように, はじめにclearしておくと良い 11
- 12. sin関数のプロット ? MATLABは描画機能も充実しており,2次元プロットも3次元プロットもできる. figure プロットするウィンドウを生成 plot(x,y) xに対するyを2次元にプロット.ベクトルxとyは同じサイズでないといけない. xlabel 軸の説明を追加.TeX形式を使ってきれいに書くことができる 12 Commands
- 13. 関数を作る ? MATLABには,sin関数のように予め定義された変数がたくさんある. ? それに加えて,自分で関数を作ることもできる. 13 スクリプトで function と書くと,引数と返り値をもつ関数が定義できる. 関数内で中間変数を定義できる. これはワークスペースに残らない 練習問題 4次のルンゲクッタ法で微分方程式を解いてみよう ? + 2? + 3? = ??2?
- 14. ライブスクリプトを活用する ? ライブスクリプトを使用すると,充実したノート機能を使用できる. ? 詳しい説明や,数式を記入することができて便利! ? 計算結果も一緒に表示してくれるので,ひと目で計算が把握できる. 14 ノートはフォーマットを決めて,タイトルを付けたりできる 「挿入」タブから数式の入力が可能 MATLABコードとノートを任意に切替可能 計算結果や図はノートの右スペースに表示される
- 15. 練習問題 1. 行列 ? = 0 1 1 ?4 4 2 2 ?1 1 を対角化しよう 2. 4次のルンゲクッタ法アルゴリズムを組み,微分方程式を解いてみよう 可能なら,解析解を求め,数値計算の結果と並べてプロットしてみよう (数値計算は十分な精度で計算できているか?) 15 (2) ? + 2? + 3? = ??2? 初期値は? ? = 1, ? ? = 0 (1) ? ? 2? = ?? 初期値は? ? = 0
- 16. 構造体でプログラムをシンプルに書く ? 関数の引数が長いと書くのが大変 ? 「構造体」を使ってまとめてしまえば,簡単に書き表せる dx = F (t, x, m1, m2, J1, J2, l1, l2, d1, d2, g); param.m1 = 1.0; param.m2 = 1.0; param.J1 = 1.5; param.J2 = 1.5; param.l1 = 1.0; param.l2 = 1.0; param.d1 = 0.5; param.d2 = 0.5; param.g = 9.8; dx = F (t, x, param); ‘param’ という構造体の中に, たくさんの変数が存在する 「構造体名.変数名」というフォーマット (.の後に変数名を書く) ‘param’ だけ引いてしまえば, 中身の変数が全部ついてくる param = [1.0 1.0 1.5 1.5 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.5 9.8] とするよりも,各変数の意味がわかりやすい 16
- 17. オブジェクト指向プログラミングへの発展 ? 「オブジェクト」はデータ(メンバ変数)と命令(メソッド)が一体になっている ? 構造体のように多くの変数をまとめて管理できる ? メソッドとして,関数を内部に持つことができる 17 戦隊物クラス ? 色 ? 得意技 ? 変身(色,得意技) ? 得意技で戦う メンバ変数 メソッド 実体化 色:赤 得意技:仁王立ち 例 「クラス」はオブジェクトの 設計図 クラスから実際にオブジェクトを生成することを実体化という 生成したオブジェクトを「インスタンス」とも呼ぶ
- 18. クラスとインスタンス ? 同じ設計図(クラス)から,様々なインスタンスを作れる ? 「戦隊物クラス」からたくさんのヒーローが作れる ? この場合,「色」と「得意技」は実体化の瞬間に代入しておいたほうがいい ? 実体化した瞬間に実行されるメソッドを作れる.これをコンストラクタという 18 戦隊物クラス ? 色 ? 得意技 ? 変身(色,得意技) ? 得意技で戦う メンバ変数 メソッド 実体化 色:赤 得意技:仁王立ち 実体化 色:青 得意技:手刀 実体化 色:ピンク 得意技:踊る 例 コンストラクタにしておくのがよい
- 19. MATLABプログラムにするとこんな感じ 戦隊物クラス ? 色 ? 得意技 ? 変身(色,得意技) ? 得意技で戦う メンバ変数 メソッド 例 コンストラクタ classdef ranger properties % メンバ変数 color; skill; end methods function ranger(self, color_, skill_) self.color = color_; self.skill = skill_; end function fight(self) ~~~ end end end clear % 赤レンジャーの実体化 akaRanger = ranger(‘red‘,‘Kamehameha‘); % 赤レンジャーに戦わせる(引数不要) akaRanger.fight; % 青レンジャーになってもらう akaRanger.color = ‘blue‘; ranger.m main.m コンストラクタはクラス名と同じメソッド 19
- 20. 付録 | 見やすいフォントに変更しよう ? 1とl,0とOなど,見分けにくい文字が多いと大変! ? MATLABの表示フォントを変更してみよう 見やすいフォントの例 ? consolas ? メイリオ ? Osaka-等幅 など 20
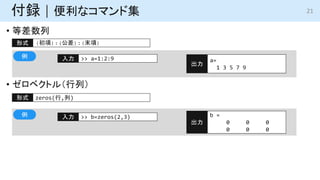
- 21. ? 等差数列 ? ゼロベクトル(行列) 付録 | 便利なコマンド集 >> a=1:2:9 入力 a= 1 3 5 7 9 出力 (初項):(公差):(末項) 形式 例 zeros(行,列) 形式 >> b=zeros(2,3) 入力 b = 0 0 0 0 0 0 出力 例 21
- 22. 付録 | 基本構造① ? 条件分岐(IF) ? 繰り返し(FOR) 22 disp(’Please input 1’) x = input(prompt) if x == 1 disp(’Thanks’) else disp(’Nooo! ’) end if 条件A (条件Aに合致したときの処理) else if 条件B (条件Bに合致したときの処理) else (条件AにもBにも合致しないときの処理) end 形式 例 for (変数)=(初項):(公差):(末項) (繰り返す処理) end 形式 NUM = 100; x = zeros(NUM); x(1) = 1; x(2) = 1; for i = 3:NUM x(i) = x(i-1)+x(i-2); end 例 公差は省略可能. 省略した場合,公差は自動的に1になる.
- 23. 付録 | 基本構造② ? 条件分岐(SWITCH) ? 繰り返し(WHILE) 23 disp(’Input 1,2,3,or 4’) x = input(prompt) switch x case 1 disp(’You Win!’); otherwise disp(’You Lose... ’) end switch (変数) case (値1) (変数==値1のときの処理) case (値2) (変数==値2のときの処理) otherwise (どれにも当てはまらないときの処理) end 形式 例 while (条件) (条件を満たす間,繰り返す処理) end 形式 x = 0; while x < 100 x = x + 1; end 例
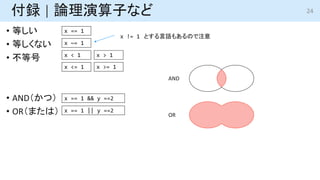
- 24. 付録 | 論理演算子など ? 等しい ? 等しくない ? 不等号 ? AND(かつ) ? OR(または) 24 x == 1 x ~= 1 x < 1 x > 1 x <= 1 x >= 1 x == 1 && y ==2 x == 1 || y ==2 AND OR x != 1 とする言語もあるので注意