Matrices and determinats
Download as PPT, PDF2 likes1,485 views
This document defines and describes different types of matrices including: - Upper and lower triangular matrices - Determinants which are scalars obtained from products of matrix elements according to constraints - Band matrices which are sparse matrices with nonzero elements confined to diagonals - Transpose matrices which exchange the rows and columns of a matrix - Inverse matrices which when multiplied by the original matrix produce the identity matrix
1 of 12
Downloaded 91 times



![TYPES OF MATRICES Determinant of a matrix. The determinant of a matrix A (n, n) is a scalar or polynomial, which is to obtain all possible products of a matrix according to a set of constraints, being denoted as [A]. The numerical value is also known as the matrix module. EXAMPLE:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matricesfinal-100720222116-phpapp02/85/Matrices-and-determinats-5-320.jpg)


![BASIC OPERATIONS SUM OR ADITION: Given the matrices m-by-n, A and B, their sum A + B is the matrix m-by-n calculated by adding the corresponding elements (ie (A + B) [i, j] = A [i, j] + B [i, j]). That is, adding each of the homologous elements of the matrices to add. For example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matricesfinal-100720222116-phpapp02/85/Matrices-and-determinats-9-320.jpg)
![BASIC OPERATIONS SCALAR MULTIPLICATION Given a matrix A and a scalar c, cA your product is calculated by multiplying the scalar by each element of In (ie (cA) [I j] = cA [R, j]). Ěý Example Properties Let A and B matrices and c and d scalars. Closure: If A is matrix and c is scalar, then cA is matrix. Associativity: (cd) A = c (dA) Neutral element: 1 ° A = A Distributivity: To scale: c (A + B) = cA + cB Matrix: (c + d) A = cA + dA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matricesfinal-100720222116-phpapp02/85/Matrices-and-determinats-10-320.jpg)


Recommended
matricesMrtices



matricesMrticesYourskill Tricks
Ěý
This document provides an overview of matrices including:
- Definitions of matrices, order of matrices, and compact matrix form
- Matrix multiplication and checking compatibility of matrices
- Determinants, adjoints, and inverses of matrices
- Methods for solving systems of equations using matrices including Gauss-Jordan elimination and Cramer's rule
The document also provides brief biographies of James Joseph Sylvester and Arthur Cayley, two mathematicians who made important contributions to the field of matrices.Introduction to matices



Introduction to maticesRaza Tuition center
Ěý
InshahAllah i will upload many other simple slides on various disciplines. Suggest and comment me necessary.Matrices



Matricesashishtqm
Ěý
A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers or functions. The numbers or functions are called the elements or the entries of the matrixMatrix.



Matrix.Awais Bakshy
Ěý
The document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices, including:
- Square matrices, where the number of rows equals the number of columns.
- Rectangular matrices, where the number of rows does not equal the number of columns.
- Row matrices, with only one row.
- Column matrices, with only one column.
- Null or zero matrices, with all elements equal to zero.
- Diagonal matrices, with all elements equal to zero except those on the main diagonal.
The document also discusses transpose, adjoint, and addition of matrices. presentation on matrix



presentation on matrixNikhi Jain
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices:
- Matrices are arrangements of elements in rows and columns represented by symbols.
- Types include row matrices, column matrices, square matrices, null matrices, identity matrices, diagonal matrices, scalar matrices, triangular matrices, transpose matrices, symmetric matrices, skew matrices, equal matrices, and algebraic matrices.
- Algebraic matrix operations include addition, subtraction, and multiplication where the matrices must be of the same order.Introduction of matrix



Introduction of matrixPankaj Das
Ěý
The document defines various types of matrices including row vectors, column vectors, submatrices, square matrices, triangular matrices, diagonal matrices, identity matrices, zero matrices, and diagonally dominant matrices. It provides examples of each type of matrix. It also discusses when two matrices are considered equal, which is when they have the same size and corresponding elements are equal.INTRODUCTION TO MATRICES, TYPES OF MATRICES, 



INTRODUCTION TO MATRICES, TYPES OF MATRICES, AMIR HASSAN
Ěý
INTRODUCTION TO MATRICES, TYPES OF MATRICES, FOR PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY WRITTEN BY AMIR HASSAN FROM GOVT. POST GRADUATE COLLAGE MARDAN, KPK, PAKISTAN.Matrices



Matricesashishtqm
Ěý
matrices
The beginnings of matrices goes back to the second century BC although traces can be seen back to the fourth century BC. However it was not until near the end of the 17th Century that the ideas reappeared and development really got underway.
It is not surprising that the beginnings of matrices and determinants should arise through the study of systems of linear equations. The Babylonians studied problems which lead to simultaneous linear equations and some of these are preserved in clay tablets which survive.Matrices



MatricesSachin Vyavahare
Ěý
The document provides an overview of a lecture covering matrices, matrix algebra, vectors, homogeneous coordinates, and transformations in homogeneous coordinates. Key points include: matrices are arrays of numbers; operations on matrices include addition, multiplication by a scalar, and multiplication; vectors can represent points in space as column or row matrices; homogeneous coordinates allow points to be represented by 4D vectors, enabling translations and other transformations to be described by 4x4 matrices. This provides a unified approach for combining multiple transformations.MATRICES AND ITS TYPE



MATRICES AND ITS TYPEHimanshu Negi
Ěý
The document presents information on matrices and their types. It defines a matrix as an arrangement of numbers, symbols or expressions in rows and columns. It discusses different types of matrices including row matrices, column matrices, square matrices, rectangular matrices, diagonal matrices, scalar matrices, unit/identity matrices, symmetric matrices, complex matrices, hermitian matrices, skew-hermitian matrices, orthogonal matrices, unitary matrices, and nilpotent matrices. It provides examples and definitions for hermitian matrices, orthogonal matrices, idempotent matrices, and nilpotent matrices. The presentation was given by Himanshu Negi on matrices and their types.M a t r i k s



M a t r i k sHartati Yuningsih
Ěý
1. The document discusses various types and operations of matrices including transpose, similarity, inverse, and determinant of matrices.
2. It also discusses using matrices to solve systems of linear equations by finding the inverse of the coefficient matrix or calculating the determinant.
3. The key matrix concepts covered are matrix notation, types of matrices, matrix addition/subtraction, multiplication, and using matrices to represent and solve linear systems.Matrices 1



Matrices 1Andrew Grichting
Ěý
This document provides an overview of matrices and basic matrix operations. It discusses what matrices are, how to perform operations like addition, multiplication, and taking the transpose. It also covers special types of matrices like diagonal, triangular, and identity matrices. It explains how to calculate the determinant of a 2x2 matrix and find the inverse of a 2x2 matrix using the determinant. The goal is for the reader to understand matrices, common operations, and how to calculate the determinant and inverse of a 2x2 matrix after reviewing this material.Project business maths



Project business mathsareea
Ěý
The history and development of matrix theory is summarized as follows:
1) The term "matrix" was introduced in 1850 by James Joseph Sylvester to describe rectangular arrays of numbers or expressions arranged in rows and columns.
2) The founder of modern matrix theory is considered to be Arthur Cayley, who in the 1850s introduced concepts such as inverse matrices and matrix multiplication.
3) Important developments in matrix theory continued throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, including the discovery by Arthur Cayley and William Hamilton of unique properties of matrices.Matrix and its applications by mohammad imran



Matrix and its applications by mohammad imranMohammad Imran
Ěý
This document provides an overview of matrix mathematics concepts. It discusses how matrices are useful in engineering calculations for storing values, solving systems of equations, and coordinate transformations. The outline then reviews properties of matrices and covers various matrix operations like addition, multiplication, and transposition. It also defines different types of matrices and discusses determining the rank, inverse, eigenvalues and eigenvectors of matrices. Key matrix algebra topics like solving systems of equations and putting matrices in normal form are summarized.Introduction to Matrices



Introduction to Matricesholmsted
Ěý
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. The dimensions of a matrix are written as the number of rows x the number of columns. Each individual entry in the matrix is named by its position, using the matrix name and row and column numbers. Matrices can represent systems of equations or points in a plane. Operations on matrices include addition, multiplication by scalars, and dilation of points represented by matrices.Matrix Operations



Matrix OperationsRon Eick
Ěý
A matrix is a rectangular arrangement of numbers organized in rows and columns. The order of a matrix refers to the number of rows and columns it contains. Entries are the individual numbers within the matrix. Basic matrix operations include addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and multiplication. To add or subtract matrices, they must be the same order, while scalar multiplication multiplies each entry of the matrix by the scalar.Ppt on matrices and Determinants



Ppt on matrices and DeterminantsNirmalaSolapur
Ěý
Matrices can be added, subtracted, and multiplied under certain conditions.
Addition and subtraction require matrices to be the same size.
Matrix multiplication requires the number of columns of the first matrix to equal the number of rows of the second matrix.
Matrices can also be multiplied by scalars.MATRICES



MATRICESfaijmsk
Ěý
This document provides an overview of matrices and matrix operations. It begins by stating the objectives of understanding matrix characteristics, applying basic matrix operations, knowing inverse matrices up to 3x3, and solving simultaneous linear equations up to 3 variables. It then defines what a matrix is, discusses matrix dimensions and types of matrices. The document outlines various matrix operations including addition, subtraction, multiplication and scalar multiplication. It provides examples of how to perform these operations. It also covers the transpose of a matrix and inverse matrices.Bba i-bm-u-2- matrix -



Bba i-bm-u-2- matrix -Rai University
Ěý
The document discusses various types of matrices:
- Row and column matrices are matrices with only one row or column respectively.
- A square matrix has the same number of rows and columns.
- A diagonal matrix has non-zero elements only along its main diagonal.
- An identity matrix has ones along its main diagonal and zeros elsewhere.
- A scalar matrix has all elements along its main diagonal multiplied by a scalar.
- A null matrix has all elements equal to zero.
The document also discusses properties such as the transpose of a matrix, symmetric matrices, and how to add, subtract and multiply matrices.Matrices and determinants



Matrices and determinantssom allul
Ěý
This document defines matrices and determinants, including examples and types of matrices. It describes how to add, subtract, and multiply matrices, and defines determinants and Cramer's rule. Cramer's rule is used to solve a 3x3 system of equations. The relationship between matrices and determinants is that determinants are uniquely related to square matrices but not vice versa, and determinants are used to calculate inverses.Determinants



DeterminantsSeyid Kadher
Ěý
The document discusses determinants and their properties. It defines determinants as representing single numbers obtained by multiplying and adding matrix elements in a special way. It then provides formulas for calculating determinants of matrices of order 1, 2 and 3. It also outlines several properties of determinants, such as how interchanging rows/columns, multiplying rows by constants, and adding rows affects the determinant. Finally, it discusses how determinants are used to determine whether systems of linear equations are consistent or inconsistent.Matrices And Determinants



Matrices And DeterminantsDEVIKA S INDU
Ěý
Matrices are widely used in business, economics, and other fields. They allow problems to be represented with distinct finite numbers rather than infinite gradations as in calculus. Sociologists, demographers, and economists use matrices to study groups, populations, industries, and social accounting. [/SUMMARY]WCS Specialist Maths An Introduction to Matrices PowerPoint



WCS Specialist Maths An Introduction to Matrices PowerPointKingp18
Ěý
Matrices are tables of numbers arranged in rows and columns. They can be used to store and organize data, simplify mathematical functions, and solve simultaneous equations. To multiply matrices, the numbers in corresponding positions are multiplied and summed. The determinant of a matrix is a single number that defines the matrix. Inverting a matrix allows it to be used to solve simultaneous equations in matrix form. Larger matrices use more complex rules and calculations for operations like determining the determinant and inverse.Matrices



Matricesmariacadena
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices including upper triangular, lower triangular, transpose, symmetric, and inverse matrices. It also describes common operations that can be performed on matrices such as addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and matrix multiplication. These operations have specific properties like associativity, neutral elements, and distributivity.Matrices



Matricesmanjunathindira
Ěý
This document defines and describes various types of matrices. It defines a matrix as a rectangular array of numbers or functions with m rows and n columns referred to as an m x n matrix. It then lists and defines the following types of matrices: row matrix, column matrix, null matrix, rectangular matrix, square matrix, diagonal matrix, scalar matrix, unit matrix, symmetric matrix, and skew-symmetric matrix. It provides examples of each type of matrix and their general syntax.Matrices & determinants



Matrices & determinantsindu thakur
Ěý
The document defines matrices and provides examples of different types of matrices. It discusses key concepts such as rows, columns, dimensions, entries, addition, subtraction, and multiplication of matrices. It also covers special matrices like identity matrices, inverse matrices, transpose of matrices, and using matrices to solve systems of linear equations. The document is a comprehensive overview of matrices that defines fundamental terms and concepts.Matrices



Matricesdaferro
Ěý
This document defines and explains different types of matrices:
- Upper and lower triangular matrices have zeros above or below the main diagonal of a square matrix.
- The determinant of a matrix is a scalar value obtained from the products of the matrix's elements according to certain constraints.
- A banded matrix is a sparse matrix with nonzero elements confined to a diagonal band around the main diagonal.
- The transpose of a matrix exchanges the rows and columns of the original matrix.
- For matrix multiplication to be defined, the number of columns of the left matrix must equal the number of rows of the right matrix.Basic concepts. Systems of equations



Basic concepts. Systems of equationsjorgeduardooo
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices:
- Upper and lower triangular matrices have zeros above or below the main diagonal of a square matrix.
- The determinant of a matrix is a scalar value obtained from the products of the matrix's elements according to certain constraints.
- A banded matrix is a sparse matrix with nonzero elements confined to a diagonal band around the main diagonal.
- The transpose of a matrix exchanges the rows and columns of the original matrix.
- The inverse of an invertible square matrix results in the identity matrix when multiplied by the original.Matrices and Determinants



Matrices and DeterminantsDr. Nirav Vyas
Ěý
Fundamental of Matrix and Determinants with suitable examples.. Matrix



MatrixUmar Farooq
Ěý
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. There are several types of matrices including square, rectangular, diagonal, identity, and triangular matrices. Operations that can be performed on matrices include addition, subtraction, multiplication by a scalar, and determining the transpose, determinant, and inverse of a matrix. A C program is shown that uses nested for loops to input and output the elements of a matrix.More Related Content
What's hot (18)
Matrices



MatricesSachin Vyavahare
Ěý
The document provides an overview of a lecture covering matrices, matrix algebra, vectors, homogeneous coordinates, and transformations in homogeneous coordinates. Key points include: matrices are arrays of numbers; operations on matrices include addition, multiplication by a scalar, and multiplication; vectors can represent points in space as column or row matrices; homogeneous coordinates allow points to be represented by 4D vectors, enabling translations and other transformations to be described by 4x4 matrices. This provides a unified approach for combining multiple transformations.MATRICES AND ITS TYPE



MATRICES AND ITS TYPEHimanshu Negi
Ěý
The document presents information on matrices and their types. It defines a matrix as an arrangement of numbers, symbols or expressions in rows and columns. It discusses different types of matrices including row matrices, column matrices, square matrices, rectangular matrices, diagonal matrices, scalar matrices, unit/identity matrices, symmetric matrices, complex matrices, hermitian matrices, skew-hermitian matrices, orthogonal matrices, unitary matrices, and nilpotent matrices. It provides examples and definitions for hermitian matrices, orthogonal matrices, idempotent matrices, and nilpotent matrices. The presentation was given by Himanshu Negi on matrices and their types.M a t r i k s



M a t r i k sHartati Yuningsih
Ěý
1. The document discusses various types and operations of matrices including transpose, similarity, inverse, and determinant of matrices.
2. It also discusses using matrices to solve systems of linear equations by finding the inverse of the coefficient matrix or calculating the determinant.
3. The key matrix concepts covered are matrix notation, types of matrices, matrix addition/subtraction, multiplication, and using matrices to represent and solve linear systems.Matrices 1



Matrices 1Andrew Grichting
Ěý
This document provides an overview of matrices and basic matrix operations. It discusses what matrices are, how to perform operations like addition, multiplication, and taking the transpose. It also covers special types of matrices like diagonal, triangular, and identity matrices. It explains how to calculate the determinant of a 2x2 matrix and find the inverse of a 2x2 matrix using the determinant. The goal is for the reader to understand matrices, common operations, and how to calculate the determinant and inverse of a 2x2 matrix after reviewing this material.Project business maths



Project business mathsareea
Ěý
The history and development of matrix theory is summarized as follows:
1) The term "matrix" was introduced in 1850 by James Joseph Sylvester to describe rectangular arrays of numbers or expressions arranged in rows and columns.
2) The founder of modern matrix theory is considered to be Arthur Cayley, who in the 1850s introduced concepts such as inverse matrices and matrix multiplication.
3) Important developments in matrix theory continued throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, including the discovery by Arthur Cayley and William Hamilton of unique properties of matrices.Matrix and its applications by mohammad imran



Matrix and its applications by mohammad imranMohammad Imran
Ěý
This document provides an overview of matrix mathematics concepts. It discusses how matrices are useful in engineering calculations for storing values, solving systems of equations, and coordinate transformations. The outline then reviews properties of matrices and covers various matrix operations like addition, multiplication, and transposition. It also defines different types of matrices and discusses determining the rank, inverse, eigenvalues and eigenvectors of matrices. Key matrix algebra topics like solving systems of equations and putting matrices in normal form are summarized.Introduction to Matrices



Introduction to Matricesholmsted
Ěý
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. The dimensions of a matrix are written as the number of rows x the number of columns. Each individual entry in the matrix is named by its position, using the matrix name and row and column numbers. Matrices can represent systems of equations or points in a plane. Operations on matrices include addition, multiplication by scalars, and dilation of points represented by matrices.Matrix Operations



Matrix OperationsRon Eick
Ěý
A matrix is a rectangular arrangement of numbers organized in rows and columns. The order of a matrix refers to the number of rows and columns it contains. Entries are the individual numbers within the matrix. Basic matrix operations include addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and multiplication. To add or subtract matrices, they must be the same order, while scalar multiplication multiplies each entry of the matrix by the scalar.Ppt on matrices and Determinants



Ppt on matrices and DeterminantsNirmalaSolapur
Ěý
Matrices can be added, subtracted, and multiplied under certain conditions.
Addition and subtraction require matrices to be the same size.
Matrix multiplication requires the number of columns of the first matrix to equal the number of rows of the second matrix.
Matrices can also be multiplied by scalars.MATRICES



MATRICESfaijmsk
Ěý
This document provides an overview of matrices and matrix operations. It begins by stating the objectives of understanding matrix characteristics, applying basic matrix operations, knowing inverse matrices up to 3x3, and solving simultaneous linear equations up to 3 variables. It then defines what a matrix is, discusses matrix dimensions and types of matrices. The document outlines various matrix operations including addition, subtraction, multiplication and scalar multiplication. It provides examples of how to perform these operations. It also covers the transpose of a matrix and inverse matrices.Bba i-bm-u-2- matrix -



Bba i-bm-u-2- matrix -Rai University
Ěý
The document discusses various types of matrices:
- Row and column matrices are matrices with only one row or column respectively.
- A square matrix has the same number of rows and columns.
- A diagonal matrix has non-zero elements only along its main diagonal.
- An identity matrix has ones along its main diagonal and zeros elsewhere.
- A scalar matrix has all elements along its main diagonal multiplied by a scalar.
- A null matrix has all elements equal to zero.
The document also discusses properties such as the transpose of a matrix, symmetric matrices, and how to add, subtract and multiply matrices.Matrices and determinants



Matrices and determinantssom allul
Ěý
This document defines matrices and determinants, including examples and types of matrices. It describes how to add, subtract, and multiply matrices, and defines determinants and Cramer's rule. Cramer's rule is used to solve a 3x3 system of equations. The relationship between matrices and determinants is that determinants are uniquely related to square matrices but not vice versa, and determinants are used to calculate inverses.Determinants



DeterminantsSeyid Kadher
Ěý
The document discusses determinants and their properties. It defines determinants as representing single numbers obtained by multiplying and adding matrix elements in a special way. It then provides formulas for calculating determinants of matrices of order 1, 2 and 3. It also outlines several properties of determinants, such as how interchanging rows/columns, multiplying rows by constants, and adding rows affects the determinant. Finally, it discusses how determinants are used to determine whether systems of linear equations are consistent or inconsistent.Matrices And Determinants



Matrices And DeterminantsDEVIKA S INDU
Ěý
Matrices are widely used in business, economics, and other fields. They allow problems to be represented with distinct finite numbers rather than infinite gradations as in calculus. Sociologists, demographers, and economists use matrices to study groups, populations, industries, and social accounting. [/SUMMARY]WCS Specialist Maths An Introduction to Matrices PowerPoint



WCS Specialist Maths An Introduction to Matrices PowerPointKingp18
Ěý
Matrices are tables of numbers arranged in rows and columns. They can be used to store and organize data, simplify mathematical functions, and solve simultaneous equations. To multiply matrices, the numbers in corresponding positions are multiplied and summed. The determinant of a matrix is a single number that defines the matrix. Inverting a matrix allows it to be used to solve simultaneous equations in matrix form. Larger matrices use more complex rules and calculations for operations like determining the determinant and inverse.Matrices



Matricesmariacadena
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices including upper triangular, lower triangular, transpose, symmetric, and inverse matrices. It also describes common operations that can be performed on matrices such as addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and matrix multiplication. These operations have specific properties like associativity, neutral elements, and distributivity.Matrices



Matricesmanjunathindira
Ěý
This document defines and describes various types of matrices. It defines a matrix as a rectangular array of numbers or functions with m rows and n columns referred to as an m x n matrix. It then lists and defines the following types of matrices: row matrix, column matrix, null matrix, rectangular matrix, square matrix, diagonal matrix, scalar matrix, unit matrix, symmetric matrix, and skew-symmetric matrix. It provides examples of each type of matrix and their general syntax.Matrices & determinants



Matrices & determinantsindu thakur
Ěý
The document defines matrices and provides examples of different types of matrices. It discusses key concepts such as rows, columns, dimensions, entries, addition, subtraction, and multiplication of matrices. It also covers special matrices like identity matrices, inverse matrices, transpose of matrices, and using matrices to solve systems of linear equations. The document is a comprehensive overview of matrices that defines fundamental terms and concepts.Similar to Matrices and determinats (20)
Matrices



Matricesdaferro
Ěý
This document defines and explains different types of matrices:
- Upper and lower triangular matrices have zeros above or below the main diagonal of a square matrix.
- The determinant of a matrix is a scalar value obtained from the products of the matrix's elements according to certain constraints.
- A banded matrix is a sparse matrix with nonzero elements confined to a diagonal band around the main diagonal.
- The transpose of a matrix exchanges the rows and columns of the original matrix.
- For matrix multiplication to be defined, the number of columns of the left matrix must equal the number of rows of the right matrix.Basic concepts. Systems of equations



Basic concepts. Systems of equationsjorgeduardooo
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices:
- Upper and lower triangular matrices have zeros above or below the main diagonal of a square matrix.
- The determinant of a matrix is a scalar value obtained from the products of the matrix's elements according to certain constraints.
- A banded matrix is a sparse matrix with nonzero elements confined to a diagonal band around the main diagonal.
- The transpose of a matrix exchanges the rows and columns of the original matrix.
- The inverse of an invertible square matrix results in the identity matrix when multiplied by the original.Matrices and Determinants



Matrices and DeterminantsDr. Nirav Vyas
Ěý
Fundamental of Matrix and Determinants with suitable examples.. Matrix



MatrixUmar Farooq
Ěý
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. There are several types of matrices including square, rectangular, diagonal, identity, and triangular matrices. Operations that can be performed on matrices include addition, subtraction, multiplication by a scalar, and determining the transpose, determinant, and inverse of a matrix. A C program is shown that uses nested for loops to input and output the elements of a matrix.Definitions matrices y determinantes fula 2010 english subir



Definitions matrices y determinantes fula 2010 english subirHernanFula
Ěý
The document discusses the history and properties of matrices. It describes how matrices were first introduced in 1850 and how their use has expanded. It then defines key matrix terms and concepts such as order, elements, types of matrices (e.g. triangular, diagonal), operations (e.g. addition, multiplication, inverse), and properties (e.g. of symmetric, banded and transpose matrices). It also provides examples of calculating the determinant of matrices using Sarrus' rule.Presentation.pptx



Presentation.pptxAMANPATHAK87
Ěý
Matrix algebra deals with vector spaces between different dimensions. It involves operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication on matrices. A matrix is an array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. The size of a matrix is described by the number of rows and columns. Common matrix operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication, transpose, scalar multiplication, and determining if matrices are equal.Matrices



Matriceskja29
Ěý
The document provides an introduction to matrix operations including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and determinants. It defines what a matrix is and how they are represented and sized. It then explains how to perform addition and subtraction of matrices by adding or subtracting the corresponding entries. Matrix multiplication is defined as being possible only when the number of columns of the first matrix equals the rows of the second. Determinants are explained as being unique to square matrices, and formulas are given for finding the determinants of 2x2 and 3x3 matrices. Homework problems are assigned involving computing various matrix operations.Engg maths k notes(4)



Engg maths k notes(4)Ranjay Kumar
Ěý
K-Notes are concise study materials intended for quick revision near the end of preparation for exams like GATE. Each K-Note covers the concepts from a subject in 40 pages or less. They are useful for final preparation and travel. Students should use K-Notes in the last 2 months before the exam, practicing questions after reviewing each note. The document then provides a summary of key concepts in linear algebra and matrices, including matrix properties, operations, inverses, and systems of linear equations.Matrices y determinants



Matrices y determinantsJeannie
Ěý
This document discusses matrices and their properties. It defines a matrix as a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. It describes several types of matrices including line matrices, column matrices, square matrices, diagonal matrices, identity matrices, symmetric matrices, triangular matrices, and inverse matrices. It also explains common operations that can be performed on matrices such as addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and multiplication. Key properties of these matrix operations are provided.matrices and function ( matrix)



matrices and function ( matrix)রেজা তানজিল
Ěý
This document is an introduction to matrices presented by Reza At-Tanzil of the Department of Pharmacy at Comilla University. It defines what a matrix is, describes different types of matrices including column/row matrices, rectangular matrices, square matrices, diagonal matrices, identity matrices, null matrices, and scalar matrices. It also covers matrix operations such as matrix multiplication, transpose of a matrix, symmetric matrices, inverse of a matrix, and adjoint matrices.Matrices



MatricesDUBAN CASTRO
Ěý
This document discusses matrices and their properties. It defines what a matrix is and different types of matrices such as line matrices, column matrices, square matrices, diagonal matrices, identity matrices, symmetric matrices, triangular matrices, and inverse matrices. It also covers operations that can be performed on matrices, including addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and matrix multiplication. Properties of these operations are provided.Matrices



MatricesNORAIMA
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices including row, column, rectangular, transpose, opposite, square, symmetrical, identical, reverse, and triangular matrices. It also covers matrix operations such as addition, multiplication, and inverse matrices. Key points are that a matrix is an arrangement of numbers or other items in rows and columns, and different types of matrices are classified based on their size, elements, and properties such as symmetry.Matrices



MatricesNORAIMA
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices including row, column, rectangular, transpose, opposite, square, symmetrical, identical, reverse, and triangular matrices. It also covers matrix operations such as addition, multiplication, and inverse matrices. Key points are that a matrix is an arrangement of numbers or other items in rows and columns, and different types of matrices are classified based on their size, elements, and properties such as symmetry.Matrices



MatricesNORAIMA
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices including row, column, rectangular, transpose, opposite, square, symmetrical, identical, reverse, and triangular matrices. It also covers matrix operations such as addition, multiplication, and inverse matrices. Key points are that a matrix is an arrangement of numbers or other items in rows and columns, and different types of matrices are classified based on their size, elements, and properties such as symmetry.Matrices



MatricesNORAIMA
Ěý
This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices including row, column, rectangular, transpose, opposite, square, symmetrical, identical, reverse, and triangular matrices. It also covers matrix operations such as addition, multiplication, and inverse matrices. Key points are that a matrix is an arrangement of numbers or other items in rows and columns, and different types of matrices are classified based on their size, elements, and properties such as symmetry.Linear_Algebra_final.pdf



Linear_Algebra_final.pdfRohitAnand125
Ěý
Linear algebra concepts like vectors, matrices, and linear transformations are important for recommendation systems. Vectors represent items or users, matrices represent item-user preference data. Linear algebra allows analyzing this data to identify patterns and recommend new items. Key techniques include eigendecomposition to reduce dimensionality and identify important relationships in the data, and singular value decomposition to factor matrices for recommendations. These linear algebra concepts are essential mathematical tools for building personalized recommendation models.MATRICES.pdf



MATRICES.pdfMahatoJee
Ěý
This document defines and describes different types of matrices. It begins by defining a matrix as an arrangement of numbers, symbols or expressions in rows and columns. It then discusses the order of a matrix, elements within a matrix, and examples of 3x3 matrices. Several basic types of matrices are defined, including row matrices, column matrices, square matrices, rectangular matrices, diagonal matrices, null matrices, symmetric matrices, and skew-symmetric matrices. Related matrices such as the transpose, adjoint, and inverse of a matrix are also explained. The document concludes by defining the rank of a matrix and describing the properties of an echelon matrix.Beginning direct3d gameprogrammingmath05_matrices_20160515_jintaeks



Beginning direct3d gameprogrammingmath05_matrices_20160515_jintaeksJinTaek Seo
Ěý
This document provides an overview of linear systems and matrices. It defines key linear algebra concepts such as linear functions, linear maps, homogeneous and non-homogeneous linear systems, and plane equations. It also explains how to represent linear systems using matrices and describes common matrix operations including addition, scalar multiplication, transposition, and matrix multiplication. Finally, it discusses inverses, determinants, and using matrices to represent transformations such as rotations in 2D space.More from daferro (20)


Tratatimiento numerico de ecuaciones diferenciales (2)daferro
Ěý
1) El documento describe mĂ©todos para resolver ecuaciones elĂpticas y parabĂłlicas, incluyendo la ecuaciĂłn de Laplace y la ecuaciĂłn de conducciĂłn de calor.
2) Se explica el mĂ©todo de Crank-Nicholson para resolver numĂ©ricamente la ecuaciĂłn de conducciĂłn de calor de manera implĂcita.
3) TambiĂ©n se cubren mĂ©todos como el de Liebmann para resolver ecuaciones elĂpticas de manera iterativa.

ECUACIONES DIFERENCIALES ORDINARIASdaferro
Ěý
Este documento describe métodos numéricos para resolver ecuaciones diferenciales ordinarias, incluidos los métodos de Euler, punto medio, Heun y Runge-Kutta. Explica cómo cada método estima la pendiente para predecir valores futuros y mejorar la precisión de la solución. También proporciona ejemplos numéricos para ilustrar la aplicación de los métodos.

Exposicion ecuaciones diferenciales ordinarias (edo) finaldaferro
Ěý
Este documento presenta mĂ©todos numĂ©ricos para aproximar la soluciĂłn de ecuaciones diferenciales parciales (EDP) de segundo orden. Explica el mĂ©todo de diferencias finitas para discretizar EDP y aproximar derivadas. Luego, cubre mĂ©todos explĂcitos para resolver ecuaciones parabĂłlicas de conducciĂłn de calor mediante diferencias temporales y espaciales, analizando su convergencia, estabilidad y tratamiento de condiciones de frontera. Finalmente, presenta un ejemplo numĂ©rico de aplicaciĂłn del mĂ©todo explĂcito

Example of iterative methoddaferro
Ěý
Este documento describe métodos iterativos para resolver sistemas de ecuaciones lineales, como el método de Jacobi y el método de Gauss-Seidel. Explica que los métodos iterativos calculan sucesivas aproximaciones a la solución de forma recurrente hasta converger, a diferencia de los métodos directos que obtienen la solución exacta. También discute conceptos como matriz diagonalmente dominante y cuando es más conveniente usar métodos iterativos frente a métodos directos.

Example of iterative methoddaferro
Ěý
El documento describe métodos iterativos para resolver sistemas de ecuaciones lineales, como el método de Jacobi y Gauss-Seidel. El método de Jacobi involucra iterar una ecuación de recurrencia para mejorar sucesivamente las aproximaciones a la solución, mientras que Gauss-Seidel mejora sobre Jacobi actualizando las variables una por una en cada iteración en lugar de todas juntas.![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727210010-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727210010-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Factorizacion lu[1]daferro
Ěý
Este documento presenta la factorización LU de una matriz como el producto de una matriz triangular inferior y una superior. Explica el proceso de descomposición de una matriz A en las matrices L y U, y cómo usar esta descomposición para resolver sistemas de ecuaciones lineales de la forma Ax=b de manera más eficiente que otros métodos. Incluye ejemplos numéricos para ilustrar los pasos de la factorización LU y su aplicación para resolver sistemas de ecuaciones.![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727204723-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727204723-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Factorizacion lu[1]daferro
Ěý
Este documento describe la factorización LU de una matriz. Explica que la factorización LU descompone una matriz A en el producto de una matriz triangular inferior L y una matriz triangular superior U. Esto permite resolver sistemas de ecuaciones lineales de forma más eficiente mediante sustitución hacia adelante y hacia atrás. Incluye ejemplos numéricos para ilustrar cómo aplicar la factorización LU para resolver sistemas de ecuaciones.![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727185409-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727185409-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Factorizacion lu[1]daferro
Ěý
La factorización LU descompone una matriz A en el producto de una matriz triangular inferior L y una matriz triangular superior U. Esto permite resolver sistemas de ecuaciones lineales de forma más eficiente mediante sustitución hacia adelante y hacia atrás. El documento explica el proceso de obtener las matrices L y U y usarlas para resolver un sistema de ecuaciones dado como ejemplo.Roots of polynomials



Roots of polynomialsdaferro
Ěý
The Bairstow method and Muller method are techniques for calculating the roots of polynomials.
The Bairstow method uses synthetic division to iteratively calculate the roots of a polynomial by dividing it by quadratic factors (x^2 - rx - s) until the remainder is zero. It obtains better approximations of r and s at each iteration to isolate the roots.
The Muller method fits a parabola through three initial guesses to obtain the coefficients a, b, c of the quadratic formula. It then uses the quadratic formula to find the root, and iterates with new guesses to converge on more accurate roots.
Both methods use iterative techniques to gradually converge on the real and complex roots of polynomials withoutRoots of polynomials



Roots of polynomialsdaferro
Ěý
The Bairstow method and Muller method are techniques for calculating the roots of polynomials.
The Bairstow method uses synthetic division to iteratively calculate the roots of a polynomial by dividing it by quadratic factors (x^2 - rx - s) until the remainder is zero. It obtains better approximations of r and s at each iteration to isolate the roots.
The Muller method fits a parabola through three initial guesses to obtain coefficients a, b, c. It then uses the quadratic formula on the parabola to find the root, and iterates with new guesses until converging on a solution.
Both methods use iterative techniques to refine initial guesses and isolate the roots of polynomials without usingMet.biseccion



Met.bisecciondaferro
Ěý
This document describes the bisection method for finding the root of a function. It shows an example of applying the bisection method to find a root between 0.5 and 0.6 over 15 iterations. At each iteration, it calculates the function values at the lower and upper bounds and their product to determine if a sign change has occurred, identifying a root within the bounds. The root converges to 0.57 and the error decreases with each iteration.Roots of polynomials



Roots of polynomialsdaferro
Ěý
The Bairstow method is an iterative technique for finding the roots of polynomials by calculating the coefficients of a quadratic factor. It works by taking an initial approximation of the quadratic factor and generating better approximations using partial derivatives until the remainder of dividing the polynomial by the quadratic factor is zero, giving the roots. The method calculates the partial derivatives to update the approximations in a way that avoids having to perform calculations with complex numbers directly. When applied repeatedly, it can find all roots of polynomials of third order or higher.Gauss



Gaussdaferro
Ěý
Gaussian Elimination is a variation of the Gauss elimination method that can solve up to 15-20 simultaneous equations with 8-10 significant digits of precision on a computer. It differs from Gaussian elimination by normalizing all rows when using them as the pivot equation, resulting in an identity matrix rather than a triangular matrix. This avoids needing to perform back substitution. The method is demonstrated through solving a system of 3 equations with 3 unknowns via Gaussian elimination, resulting in values for the 3 unknowns. Advantages of the Gaussian-Jordan method include requiring approximately 50% fewer operations than Gaussian elimination and providing a direct method for obtaining the inverse matrix.![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100720224521-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100720224521-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Factorizacion lu[1]daferro
Ěý
Este documento describe la factorización LU de una matriz. Explica que la factorización LU descompone una matriz A en el producto de una matriz triangular inferior L y una matriz triangular superior U. Esto permite resolver sistemas de ecuaciones lineales de forma más eficiente mediante sustitución hacia adelante y hacia atrás. El documento también incluye ejemplos numéricos para ilustrar los pasos del proceso de factorización LU.









![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727210010-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727210010-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727204723-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727204723-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727185409-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100727185409-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100720224521-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Factorizacion lu[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/factorizacionlu1-100720224521-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Matrices and determinats
- 1. DANIEL FERNANDO RODRIGUEZ COD: 2073410 PETROLEUM ENGINEERING Bucaramanga, Julio 2010 METODOS NUMERICOS MATRICES AND DETERMINATS MATRICES AND DETERMINATS MATRICES AND DETERMINATS
- 2. Definition A matrix is a rectangular arrangement of numbers. For example, An alternative notation uses large parentheses instead of box brackets:
- 3. The horizontal and vertical lines in a matrix are called rows and columns , respectively. The numbers in the matrix are called its entries or its elements . To specify a matrix's size, a matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m -by- n matrix or m ĚýĂ—Ěý n matrix, while m and n are called its dimensions . The above is a 4-by-3 matrix.
- 4. TYPES OF MATRICES Upper triangular matrix If a square matrix in which all the elements that are below the main diagonal are zeros. the matrix must be square. Lower triangular matrix If a matrix in which all the elements that are above the main diagonal are zeros. the matrix must be square.
- 5. TYPES OF MATRICES Determinant of a matrix. The determinant of a matrix A (n, n) is a scalar or polynomial, which is to obtain all possible products of a matrix according to a set of constraints, being denoted as [A]. The numerical value is also known as the matrix module. EXAMPLE:
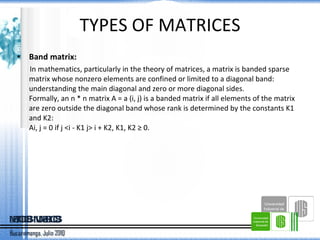
- 6. TYPES OF MATRICES Band matrix: In mathematics, particularly in the theory of matrices, a matrix is banded sparse matrix whose nonzero elements are confined or limited to a diagonal band: understanding the main diagonal and zero or more diagonal sides. Formally, an n * n matrix A = a (i, j) is a banded matrix if all elements of the matrix are zero outside the diagonal band whose rank is determined by the constants K1 and K2: Ai, j = 0 if j <i - K1 j> i + K2, K1, K2 ≥ 0.
- 7. TYPES OF MATRICES Transpose Matrix If we have a matrix (A) any order mxn, then its transpose is another array (A) of order nxm where they exchange the rows and columns of the matrix (A). The transpose of a matrix is denoted by the symbol "T" and is, therefore, that the transpose of the matrix A is represented by AT. Clearly, if A is an array of size mxn, At its transpose will nxm size as the number of columns becomes row and vice versa.If the matrix A is square, its transpose is the same size. EXAMPLE:
- 8. TYPES OF MATRICES Two matrices of order n are reversed if your product is the unit matrix of order n. A matrix has inverse is said to be invertible or scheduled, otherwise called singular. Properties (A ° B) -1 = B-1 to-1 (A-1) -1 = A (K • A) -1 = k-1 to-1 (A t) -1 = (A -1) t Inverse matrix calculation by determining =Matrix Inverse = Determinant of the matrix = Matrix attached = Matrix transpose of the enclosed
- 9. BASIC OPERATIONS SUM OR ADITION: Given the matrices m-by-n, A and B, their sum A + B is the matrix m-by-n calculated by adding the corresponding elements (ie (A + B) [i, j] = A [i, j] + B [i, j]). That is, adding each of the homologous elements of the matrices to add. For example:
- 10. BASIC OPERATIONS SCALAR MULTIPLICATION Given a matrix A and a scalar c, cA your product is calculated by multiplying the scalar by each element of In (ie (cA) [I j] = cA [R, j]). Ěý Example Properties Let A and B matrices and c and d scalars. Closure: If A is matrix and c is scalar, then cA is matrix. Associativity: (cd) A = c (dA) Neutral element: 1 ° A = A Distributivity: To scale: c (A + B) = cA + cB Matrix: (c + d) A = cA + dA
- 11. BASIC OPERATIONS The product of two matrices can be defined only if the number of columns in the left matrix is the same as the number of rows in the matrix right. If A is an m Ă— n matrix B is a matrix n Ă— p, then their matrix product AB is m Ă— p matrix (m rows, p columns) given by: for each pair i and j. For example:
- 12. BIBLIOGRAPHY http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matriz_(matem%C3%A1tica) http://www.fagro.edu.uy/~biometria/Estadistica%202/MATRICES%201.pdf http://descartes.cnice.mec.es/materiales_didacticos/matrices/matrices_operaciones_II.htm http://docencia.udea.edu.co/GeometriaVectorial/uni2/seccion21.html







