Metastability
4 likes4,200 views
Metastability occurs when the inputs to a flip-flop violate the setup and hold timing requirements around the clock edge. This can cause the output to momentarily exist in an unstable intermediate state between logic 0 and 1. The likelihood of metastability increases when asynchronous inputs are sampled by a synchronous system. Well-designed synchronizers use multiple flip-flops in series to resolve metastability within the clock period and avoid failures. The mean time between synchronizer failures depends on factors like clock speed and input transition rate.
1 of 19
Downloaded 109 times

Recommended
Metastability



MetastabilityNallapati Anindra
╠²
Flip-flops can enter a metastable state where the output oscillates between 0 and 1 if setup and hold times are violated, such as with asynchronous signals, skewed clocks between domains, or changing inputs in the critical timing window. To resolve metastability, the flip-flop output will eventually settle to a stable 0 or 1 state, though the time to resolve can vary by technology. Cascading multiple flip-flops can help avoid metastable states.Synchronous and asynchronous clock



Synchronous and asynchronous clockNallapati Anindra
╠²
The document discusses synchronous and asynchronous clocks. A clock is a square wave signal generated by an oscillator that provides two levels, high and low. Clocks are used to time signals in circuits to avoid glitches, which are unpredictable outputs caused by differences in propagation delays. There are two types of clocks: synchronous clocks have the same phase but frequencies may differ, while asynchronous clocks have different phases and frequencies may also differ. Asynchronous clocks can cause glitches, so synchronization is needed to make clocks operate synchronously.Metastability,MTBF,synchronizer & synchronizer failure



Metastability,MTBF,synchronizer & synchronizer failureprashant singh
╠²
This document discusses metastability, mean time between failures (MTBF), synchronizers, and synchronizer failures. It begins with introductions to metastability and cases where it can occur. It then illustrates metastability with diagrams and graphs. It discusses how systems enter metastability and what occurs during metastability. The document derives the MTBF equation and provides an example calculation. It concludes by listing references for further information.I2C Bus (Inter-Integrated Circuit)



I2C Bus (Inter-Integrated Circuit)Varun Mahajan
╠²
The document discusses the I2C communication bus protocol. It describes the I2C bus concept of using two bi-directional lines (SDA and SCL) to allow devices with unique addresses to communicate as masters or slaves. The document outlines the I2C communication protocol including START/STOP conditions, byte format, acknowledgment, synchronization, arbitration, and 7-bit and 10-bit addressing schemes. Key aspects of the I2C bus such as typical transfer rates, hardware connections, and terminology are also summarized.Serial Communication in 8051



Serial Communication in 8051Sudhanshu Janwadkar
╠²
This presentation discusses the Serial Communication features in 8051, the support for UART. It also discusses serial vs parallel communication, simplex, duplex and full-duplex modes, MAX232, RS232 standards14 static timing_analysis_5_clock_domain_crossing



14 static timing_analysis_5_clock_domain_crossingUsha Mehta
╠²
This document discusses clock domain crossing (CDC) in integrated circuits with multiple clock domains. It defines CDC as transferring a signal between two asynchronous clock domains. Issues that can occur during CDC include metastability, data loss, and data incoherency. The document describes various synchronization techniques used to address these issues, including multi-flop synchronizers, gray coding, MUX recirculation synchronizers, and handshaking. It emphasizes that simulation and timing analysis alone are not sufficient to guarantee correct CDC behavior.Asic design flow



Asic design flowyogeshwaran k
╠²
The document describes the ASIC design flow, which consists of two main phases: logical design (frontend) and physical design (backend).
The logical design phase includes design entry, logic synthesis, system partitioning, and pre-layout simulation. This phase converts the design from HDL or schematic to a netlist.
The physical design phase includes floorplanning, placement, routing, circuit extraction, and post-layout simulation. This phase adds physical details and checks timing with parasitics. Floorplanning places blocks, placement assigns cell locations, and routing connects cells and blocks. Circuit extraction determines resistances and capacitances, and post-layout simulation verifies functionality and timing.Clock divider by 3



Clock divider by 3Ashok Reddy
╠²
The slide will explain how to realize circuit for clock divide by 3 with 50% duty cycle and with out 50% duty cycle.Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)



Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)Dhaval Kaneria
╠²
The SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is a synchronous serial communication protocol used for communication between devices. It uses a master-slave architecture with a single master device initiating data transfer. Key features include using separate clock and data lines, operating in full duplex mode, and allowing multiple slave devices through individual chip selects. It provides a lower pin count solution than parallel buses at the cost of slower communication speeds.VLSI Fresher Resume



VLSI Fresher Resumevikas kumar
╠²
Vikas Kumar has experience in designing and implementing various digital and analog circuits including a 32-bit RISC CPU using Verilog, an integrated round robin arbiter on an FPGA board, asynchronous and synchronous FIFOs for clock domain crossing, a two-stage op-amp using UMC 180nm technology, and a bandgap reference circuit. He has worked as an intern at KeenHeads Technologies and IISc Bangalore developing projects related to analog design, layout design, and an embedded security system. Vikas has skills in RTL coding, digital and analog design, layout design, Verilog, C/C++, MATLAB, and uses tools including Xilinx Vivado, CadVerilog Tasks & Functions



Verilog Tasks & Functionsanand hd
╠²
Tasks and functions allow designers to abstract commonly used Verilog code into reusable routines. Tasks can contain timing constructs and pass multiple values through input, output, and inout arguments. Functions must not contain timing constructs and return a single value. Tasks are similar to subroutines while functions are similar to functions in other languages like FORTRAN. Automatic tasks make tasks re-entrant to avoid issues with concurrent calls operating on shared variables.Serial Peripheral Interface



Serial Peripheral InterfaceAnurag Tomar
╠²
SPI is a serial bus standard established by Motorola and supported in silicon products from various manufacturers.
It is a synchronous serial data link that operates in full duplex (signals carrying data go in both directions simultaneously).
Devices communicate using a master/slave relationship, in which the master initiates the data frame. When the master generates a clock and selects a slave device, data may be transferred in either or both directions simultaneously.Level sensitive scan design(LSSD) and Boundry scan(BS)



Level sensitive scan design(LSSD) and Boundry scan(BS)Praveen Kumar
╠²
This presentation contains,
Introduction,design for testability, scan chain, operation, scan structure, test vectors, Boundry scan, test logic, operation, BS cell, states of TAP controller, Boundry scan instructions.
Serial Peripheral Interface



Serial Peripheral InterfaceChirag Parikh
╠²
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) allows for high-speed synchronous serial communication between microcontrollers and peripheral devices. It uses three wires (MOSI, MISO, SCK) to transmit data serially from a master to a slave device. The master device generates a clock signal on SCK to synchronize data transfer. The SS pin is used to select a specific slave device when there are multiple slaves. Common applications of SPI include in-system programming of microcontrollers and communicating with sensors, memory, and other peripherals. An example shows how to use SPI to control LEDs on a slave microcontroller from a master using button inputs.Pipelining approach



Pipelining approachGopinathD17
╠²
This document discusses pipelining as an approach to optimize sequential circuits. It describes how pipelining can be implemented using registers between logic blocks to improve resource utilization and increase throughput. This allows computations to be spread over multiple clock cycles in an assembly-line fashion. The document also discusses latch-based vs register-based pipelines and different logic styles like NORA-CMOS that can be used for pipelined structures. It covers design rules and considerations for ensuring correct pipelined operation. Finally, it briefly describes non-bistable sequential circuits like astable, monostable and Schmitt trigger circuits.Finite state machines



Finite state machinesdennis gookyi
╠²
This document discusses finite state machines (FSMs), specifically Moore and Mealy machines. It defines FSMs as circuits with a combinational block and memory block that can exist in multiple states, transitioning between states based on inputs. Moore machines output depends solely on the current state, while Mealy machines output depends on both the current state and inputs. Moore machines are safer since output only changes at clock edges, while Mealy machines are faster since output relies on inputs. Choosing between them depends on factors like whether synchronous/asynchronous operation is needed and whether speed or safety is a higher priority.Fpga



Fpgabharadwajareddy
╠²
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) are integrated circuits that can be configured by the customer or designer after manufacturing. FPGAs contain programmable logic components called logic blocks and a hierarchical interconnect that allows the blocks to be 'wired together' as per the design. The document discusses the basic FPGA architecture including logic blocks, interconnects and I/O blocks. It also explains the different FPGA families and programming technologies like SRAM, antifuse and EPROM/EEPROM. The Xilinx FPGA development flow and tools like ISE and its components are explained.Spyglass dft



Spyglass dftkumar gavanurmath
╠²
This document provides an overview of SpyglassDFT, a tool for comprehensive RTL design analysis. It discusses key SpyglassDFT features such as lint checking, test coverage estimation, and an integrated debug environment. Important input files for SpyglassDFT like the project file and waiver file are also outlined. The document concludes with an example flow for using SpyglassDFT to analyze clocks and resets, identify violations, and prepare the design for manufacturing test.Sequential cmos logic circuits



Sequential cmos logic circuitsSakshi Bhargava
╠²
slides gives a complete knowledge about sequential cmos logic circuits which is very useful for mtech vlsi students.Synchronous and asynchronous reset



Synchronous and asynchronous resetNallapati Anindra
╠²
This document discusses synchronous and asynchronous resets. Synchronous reset will reset a circuit at the active edge of the clock, ensuring a completely synchronous circuit. Asynchronous reset will reset a circuit without regard to the clock, making it faster but also more susceptible to glitches. The document outlines advantages and disadvantages of each type of reset.Router 1X3 ŌĆō RTL Design and Verification



Router 1X3 ŌĆō RTL Design and VerificationIJERD Editor
╠²
Routing is the process of moving a packet of data from source to destination and enables messages
to pass from one computer to another and eventually reach the target machine. A router is a networking device
that forwards data packets between computer networks. It is connected to two or more data lines from different
networks (as opposed to a network switch, which connects data lines from one single network). This paper,
mainly emphasizes upon the study of router device, itŌƤs top level architecture, and how various sub-modules of
router i.e. Register, FIFO, FSM and Synchronizer are synthesized, and simulated and finally connected to its top
module.
SPI Protocol



SPI ProtocolAnurag Tomar
╠²
The document describes the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) protocol which allows for full duplex synchronous serial communication between a master and slave device using 4 pins - MOSI, MISO, SCK, and an optional SS pin. It details the SPI registers for control, status, and data and provides examples of SPI communication with peripherals like digital pots and shift registers. Common issues like conflicts with programming interfaces and ensuring proper chip select signaling are also covered.VLSI Technology Trends



VLSI Technology TrendsUsha Mehta
╠²
This document provides an overview of VLSI technology trends over time. It discusses how Moore's Law has been sustained through transistor scaling down to the nanometer level enabled by various techniques like strained silicon, high-k dielectrics, metal gates, SOI, multi-gate transistors like FinFETs. It outlines the evolution from bipolar junction transistors to MOSFETs to integrated circuits. Short channel effects posed challenges to scaling which were addressed through new device architectures in the second generation of scaling.TMS320C6X Architecture



TMS320C6X ArchitectureShweta Tripathi
╠²
The document provides an overview of the TMS320C6x architecture. It describes the TMS320C6x as a 32-bit VLIW digital signal processor introduced by Texas Instruments. Key features include its ability to execute up to 8 instructions per cycle and support for floating point operations. The architecture includes 8 functional units, internal memory, external memory interfaces, and peripherals like EDMA controllers and timers. The TMS320C6x is well suited for applications involving real-time signal processing like image and speech processing.13 static timing_analysis_4_set_up_and_hold_time_violation_remedy



13 static timing_analysis_4_set_up_and_hold_time_violation_remedyUsha Mehta
╠²
The document discusses static timing analysis concepts including set-up time, hold time, timing violations, and techniques for fixing violations. It provides examples of how delays are considered in an ideal case without set-up/hold times versus cases with set-up/hold times. Methods for calculating maximum clock frequency and identifying violations are described. Ways to address violations including adjusting buffering, cell sizing, and placement are outlined. The role of static timing analysis in ASIC design flows is also summarized.ASIC design Flow (Digital Design)



ASIC design Flow (Digital Design)Sudhanshu Janwadkar
╠²
This Presentation discusses the various terminology involved in ASIC design. Each step is described with the help of a flowchart.Combinational & Sequential ATPG.pdf



Combinational & Sequential ATPG.pdfMoinPasha12
╠²
This document summarizes topics related to test generation for combination and sequential circuits, including:
- ATPG algorithms for combinational circuits like Boolean difference, single-path sensitization, D-algorithm, and PODEM.
- Problems with testing sequential circuits and approaches like time-frame expansion, simulation-based testing, and scan-based testing.
- Key concepts for ATPG algorithms like fault cones, forward and backward implication, essential prime implicants, and singular covers.Synopsys Fusion Compiler-Comprehensive RTL-to-GDSII Implementation System



Synopsys Fusion Compiler-Comprehensive RTL-to-GDSII Implementation SystemMostafa Khamis
╠²
Fusion Compiler is the next-generation RTL-to-GDSII implementation system architected to address the complexities of advanced node designs and deliver up to 20% improved PPA while reducing Time To Results (TTR) by 2X. Perils of an Old Metric: MTBF



Perils of an Old Metric: MTBFAccendo Reliability
╠²
This document discusses the limitations of using MTBF (mean time between failures) as a reliability metric. It defines MTBF as the average operating hours divided by the number of failures. However, MTBF is misleading because it does not account for the distribution of failures over time or customer definitions of failure. The document recommends using other reliability models like Weibull or exponential distributions that better characterize failure rates over time. Overall, MTBF provides an oversimplified view of reliability and organizations should use more accurate metrics that consider failure costs, rates, and distributions.Timing issues in digital circuits



Timing issues in digital circuitsaroosa khan
╠²
The document discusses timing issues in digital circuits such as synchronization, clock skew, and clock jitter. It provides definitions and examples of these timing phenomena. Sources of skew and jitter are explained, including clock signal generation, manufacturing variations, interconnect variations, and environmental factors. The dynamic behavior of a CMOS inverter is analyzed by examining its parasitic capacitances. Solutions to timing issues include reducing clock skew through careful clock distribution, tolerating skew with circuit designs, and minimizing jitter.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)



Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)Dhaval Kaneria
╠²
The SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is a synchronous serial communication protocol used for communication between devices. It uses a master-slave architecture with a single master device initiating data transfer. Key features include using separate clock and data lines, operating in full duplex mode, and allowing multiple slave devices through individual chip selects. It provides a lower pin count solution than parallel buses at the cost of slower communication speeds.VLSI Fresher Resume



VLSI Fresher Resumevikas kumar
╠²
Vikas Kumar has experience in designing and implementing various digital and analog circuits including a 32-bit RISC CPU using Verilog, an integrated round robin arbiter on an FPGA board, asynchronous and synchronous FIFOs for clock domain crossing, a two-stage op-amp using UMC 180nm technology, and a bandgap reference circuit. He has worked as an intern at KeenHeads Technologies and IISc Bangalore developing projects related to analog design, layout design, and an embedded security system. Vikas has skills in RTL coding, digital and analog design, layout design, Verilog, C/C++, MATLAB, and uses tools including Xilinx Vivado, CadVerilog Tasks & Functions



Verilog Tasks & Functionsanand hd
╠²
Tasks and functions allow designers to abstract commonly used Verilog code into reusable routines. Tasks can contain timing constructs and pass multiple values through input, output, and inout arguments. Functions must not contain timing constructs and return a single value. Tasks are similar to subroutines while functions are similar to functions in other languages like FORTRAN. Automatic tasks make tasks re-entrant to avoid issues with concurrent calls operating on shared variables.Serial Peripheral Interface



Serial Peripheral InterfaceAnurag Tomar
╠²
SPI is a serial bus standard established by Motorola and supported in silicon products from various manufacturers.
It is a synchronous serial data link that operates in full duplex (signals carrying data go in both directions simultaneously).
Devices communicate using a master/slave relationship, in which the master initiates the data frame. When the master generates a clock and selects a slave device, data may be transferred in either or both directions simultaneously.Level sensitive scan design(LSSD) and Boundry scan(BS)



Level sensitive scan design(LSSD) and Boundry scan(BS)Praveen Kumar
╠²
This presentation contains,
Introduction,design for testability, scan chain, operation, scan structure, test vectors, Boundry scan, test logic, operation, BS cell, states of TAP controller, Boundry scan instructions.
Serial Peripheral Interface



Serial Peripheral InterfaceChirag Parikh
╠²
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) allows for high-speed synchronous serial communication between microcontrollers and peripheral devices. It uses three wires (MOSI, MISO, SCK) to transmit data serially from a master to a slave device. The master device generates a clock signal on SCK to synchronize data transfer. The SS pin is used to select a specific slave device when there are multiple slaves. Common applications of SPI include in-system programming of microcontrollers and communicating with sensors, memory, and other peripherals. An example shows how to use SPI to control LEDs on a slave microcontroller from a master using button inputs.Pipelining approach



Pipelining approachGopinathD17
╠²
This document discusses pipelining as an approach to optimize sequential circuits. It describes how pipelining can be implemented using registers between logic blocks to improve resource utilization and increase throughput. This allows computations to be spread over multiple clock cycles in an assembly-line fashion. The document also discusses latch-based vs register-based pipelines and different logic styles like NORA-CMOS that can be used for pipelined structures. It covers design rules and considerations for ensuring correct pipelined operation. Finally, it briefly describes non-bistable sequential circuits like astable, monostable and Schmitt trigger circuits.Finite state machines



Finite state machinesdennis gookyi
╠²
This document discusses finite state machines (FSMs), specifically Moore and Mealy machines. It defines FSMs as circuits with a combinational block and memory block that can exist in multiple states, transitioning between states based on inputs. Moore machines output depends solely on the current state, while Mealy machines output depends on both the current state and inputs. Moore machines are safer since output only changes at clock edges, while Mealy machines are faster since output relies on inputs. Choosing between them depends on factors like whether synchronous/asynchronous operation is needed and whether speed or safety is a higher priority.Fpga



Fpgabharadwajareddy
╠²
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) are integrated circuits that can be configured by the customer or designer after manufacturing. FPGAs contain programmable logic components called logic blocks and a hierarchical interconnect that allows the blocks to be 'wired together' as per the design. The document discusses the basic FPGA architecture including logic blocks, interconnects and I/O blocks. It also explains the different FPGA families and programming technologies like SRAM, antifuse and EPROM/EEPROM. The Xilinx FPGA development flow and tools like ISE and its components are explained.Spyglass dft



Spyglass dftkumar gavanurmath
╠²
This document provides an overview of SpyglassDFT, a tool for comprehensive RTL design analysis. It discusses key SpyglassDFT features such as lint checking, test coverage estimation, and an integrated debug environment. Important input files for SpyglassDFT like the project file and waiver file are also outlined. The document concludes with an example flow for using SpyglassDFT to analyze clocks and resets, identify violations, and prepare the design for manufacturing test.Sequential cmos logic circuits



Sequential cmos logic circuitsSakshi Bhargava
╠²
slides gives a complete knowledge about sequential cmos logic circuits which is very useful for mtech vlsi students.Synchronous and asynchronous reset



Synchronous and asynchronous resetNallapati Anindra
╠²
This document discusses synchronous and asynchronous resets. Synchronous reset will reset a circuit at the active edge of the clock, ensuring a completely synchronous circuit. Asynchronous reset will reset a circuit without regard to the clock, making it faster but also more susceptible to glitches. The document outlines advantages and disadvantages of each type of reset.Router 1X3 ŌĆō RTL Design and Verification



Router 1X3 ŌĆō RTL Design and VerificationIJERD Editor
╠²
Routing is the process of moving a packet of data from source to destination and enables messages
to pass from one computer to another and eventually reach the target machine. A router is a networking device
that forwards data packets between computer networks. It is connected to two or more data lines from different
networks (as opposed to a network switch, which connects data lines from one single network). This paper,
mainly emphasizes upon the study of router device, itŌƤs top level architecture, and how various sub-modules of
router i.e. Register, FIFO, FSM and Synchronizer are synthesized, and simulated and finally connected to its top
module.
SPI Protocol



SPI ProtocolAnurag Tomar
╠²
The document describes the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) protocol which allows for full duplex synchronous serial communication between a master and slave device using 4 pins - MOSI, MISO, SCK, and an optional SS pin. It details the SPI registers for control, status, and data and provides examples of SPI communication with peripherals like digital pots and shift registers. Common issues like conflicts with programming interfaces and ensuring proper chip select signaling are also covered.VLSI Technology Trends



VLSI Technology TrendsUsha Mehta
╠²
This document provides an overview of VLSI technology trends over time. It discusses how Moore's Law has been sustained through transistor scaling down to the nanometer level enabled by various techniques like strained silicon, high-k dielectrics, metal gates, SOI, multi-gate transistors like FinFETs. It outlines the evolution from bipolar junction transistors to MOSFETs to integrated circuits. Short channel effects posed challenges to scaling which were addressed through new device architectures in the second generation of scaling.TMS320C6X Architecture



TMS320C6X ArchitectureShweta Tripathi
╠²
The document provides an overview of the TMS320C6x architecture. It describes the TMS320C6x as a 32-bit VLIW digital signal processor introduced by Texas Instruments. Key features include its ability to execute up to 8 instructions per cycle and support for floating point operations. The architecture includes 8 functional units, internal memory, external memory interfaces, and peripherals like EDMA controllers and timers. The TMS320C6x is well suited for applications involving real-time signal processing like image and speech processing.13 static timing_analysis_4_set_up_and_hold_time_violation_remedy



13 static timing_analysis_4_set_up_and_hold_time_violation_remedyUsha Mehta
╠²
The document discusses static timing analysis concepts including set-up time, hold time, timing violations, and techniques for fixing violations. It provides examples of how delays are considered in an ideal case without set-up/hold times versus cases with set-up/hold times. Methods for calculating maximum clock frequency and identifying violations are described. Ways to address violations including adjusting buffering, cell sizing, and placement are outlined. The role of static timing analysis in ASIC design flows is also summarized.ASIC design Flow (Digital Design)



ASIC design Flow (Digital Design)Sudhanshu Janwadkar
╠²
This Presentation discusses the various terminology involved in ASIC design. Each step is described with the help of a flowchart.Combinational & Sequential ATPG.pdf



Combinational & Sequential ATPG.pdfMoinPasha12
╠²
This document summarizes topics related to test generation for combination and sequential circuits, including:
- ATPG algorithms for combinational circuits like Boolean difference, single-path sensitization, D-algorithm, and PODEM.
- Problems with testing sequential circuits and approaches like time-frame expansion, simulation-based testing, and scan-based testing.
- Key concepts for ATPG algorithms like fault cones, forward and backward implication, essential prime implicants, and singular covers.Synopsys Fusion Compiler-Comprehensive RTL-to-GDSII Implementation System



Synopsys Fusion Compiler-Comprehensive RTL-to-GDSII Implementation SystemMostafa Khamis
╠²
Fusion Compiler is the next-generation RTL-to-GDSII implementation system architected to address the complexities of advanced node designs and deliver up to 20% improved PPA while reducing Time To Results (TTR) by 2X. Viewers also liked (10)
Perils of an Old Metric: MTBF



Perils of an Old Metric: MTBFAccendo Reliability
╠²
This document discusses the limitations of using MTBF (mean time between failures) as a reliability metric. It defines MTBF as the average operating hours divided by the number of failures. However, MTBF is misleading because it does not account for the distribution of failures over time or customer definitions of failure. The document recommends using other reliability models like Weibull or exponential distributions that better characterize failure rates over time. Overall, MTBF provides an oversimplified view of reliability and organizations should use more accurate metrics that consider failure costs, rates, and distributions.Timing issues in digital circuits



Timing issues in digital circuitsaroosa khan
╠²
The document discusses timing issues in digital circuits such as synchronization, clock skew, and clock jitter. It provides definitions and examples of these timing phenomena. Sources of skew and jitter are explained, including clock signal generation, manufacturing variations, interconnect variations, and environmental factors. The dynamic behavior of a CMOS inverter is analyzed by examining its parasitic capacitances. Solutions to timing issues include reducing clock skew through careful clock distribution, tolerating skew with circuit designs, and minimizing jitter.Overview and Basic Maintenance



Overview and Basic MaintenanceFuangwith Sopharath
╠²
The document outlines an agenda for a presentation on IBM DB2 9.1 fundamentals and basic maintenance. The presentation covers an overview of DB2, its structure, labs on introduction to the command line processor, creating a new database, backup and restore, and import/export. It also previews topics to be covered the following day, including SQL, system catalogs, tablespaces, tables, procedures, functions, views, and triggers.Basics in Maintenance



Basics in Maintenanceraghuttam
╠²
This document discusses maintenance and methods for tracking losses and overcoming losses through proper maintenance activities. It defines maintenance as actions to retain or restore equipment to its maximum useful life. The three main types of maintenance are preventive, breakdown, and corrective. Preventive maintenance includes periodic and predictive maintenance. Periodic maintenance involves spare part replacement on a predefined schedule, while predictive maintenance uses equipment like bearing meters to determine condition-based maintenance. Metrics like mean time between failure (MTBF) and mean time to repair (MTTR) are discussed to measure equipment reliability and maintainability. Uptime is also defined as a percentage measure of up-time without downtime.

Cuadros de mantenimiento de maquinariasAnibal Cruz
╠²
Este documento presenta el programa de mantenimiento preventivo y correctivo de maquinaria y equipos de la empresa CONFASE S.A. para un proyecto de construcci├│n. Describe los procedimientos para el ingreso, inspecci├│n y mantenimiento de maquinaria, incluyendo responsabilidades del personal. Tambi├®n presenta un cuadro con las principales tareas de mantenimiento preventivo y correctivo a realizar.Maintenance



MaintenanceKulbhushan Sharma
╠²
The document discusses plant maintenance procedures. It defines maintenance as finding faults in equipment before or after breakdown to maintain operational efficiency. The objectives of maintenance are to increase reliability, maximize equipment life, maximize production capacity, and minimize costs and interruptions. Maintenance types include planned (preventive, corrective, predictive), and unplanned. Key steps in preventive maintenance procedures are identifying equipment, creating schedules, history cards, job specifications, programming, inspections, and applying feedback.

6 formato mantenimientos y cronogramaPaola Rincon
╠²
Este documento contiene formatos y cronogramas de mantenimiento preventivo para varios equipos de laboratorio, incluyendo un piano de c├®lulas, un agitador, una microcentr├Łfuga y una centr├Łfuga para seis tubos. Describe los procedimientos de limpieza diaria, control mensual y calibraci├│n semestral requeridos para garantizar el correcto funcionamiento de cada equipo.

Formatos basicos de mantenimientolinamartinfer
╠²
El documento presenta una serie de formatos b├Īsicos para el sistema de gesti├│n de la calidad del departamento de mantenimiento de la facultad de ingenier├Ła mec├Īnica, incluyendo hojas de vida, fichas t├®cnicas, planos, listados de partes, planes de mantenimiento preventivo, mapas de seguridad, procedimientos para reparaci├│n y cambio de partes, hojas de rutina de limpieza y lubricaci├│n, asistencia t├®cnica y solicitud de quejas.Types of maintenance



Types of maintenanceAbhik Rathod
╠²
This document discusses different types of maintenance for assets including aircraft. It defines maintenance as work carried out to preserve assets and enable continued use over their design life. The main types of maintenance discussed are: breakdown, preventive (periodic and predictive), and corrective. Periodic maintenance involves regular inspection and servicing, while predictive uses condition monitoring. Aircraft maintenance checks ranging from light A/B checks every 500-800 hours to comprehensive D checks every 5 years are also outlined. Nondestructive testing methods like liquid penetrant and eddy current are used during aircraft maintenance inspections.Maintenance Management



Maintenance ManagementBisina Keshara
╠²
The document discusses the importance and objectives of maintenance management. Modern maintenance aims to keep equipment running at high capacity and producing quality products at the lowest possible cost. It also aims to minimize unplanned downtime and maximize availability. Preventive maintenance is important as it can reduce breakdowns, repairs and costs while increasing availability and efficiency. Condition-based maintenance allows failures to be detected early and repairs to be planned in advance. The goals of maintenance are to maintain availability at the lowest cost while ensuring safety.





Similar to Metastability (20)
Intro



IntroMohamed Rayan
╠²
Is an introduction for digital design crash course using Verilog,
Those slides are just quick refreshment for most important parts in logic circuits, Brief history about the field and steps we follow to get a chip.20 Real-World Use Cases to help pick a better MySQL Replication scheme (2012)



20 Real-World Use Cases to help pick a better MySQL Replication scheme (2012)Darpan Dinker
╠²
MySQL Replication: Pros and Cons
Achieve Higher Performance, Uptime, Reliability and Simplicity
for Real-World Use Cases.
Synchronous, semi-synchronous, asynchronous replication with parallel Slave appliers.
High availability.ECI OpenFlow 2.0 the Future of SDN 



ECI OpenFlow 2.0 the Future of SDN ECI ŌĆō THE ELASTIC NETWORKŌäó
╠²
- The document proposes adding stateful capabilities to OpenFlow 2.0 in order to better support use cases that require stateful processing like APS and load balancing.
- It suggests including a stateful flow table, programmable state machines, and the ability to generate and process frames within OpenFlow switches.
- To ensure interoperability, it recommends adopting a bytecode approach where any programming language could be used to define state machines which are then compiled to a common bytecode format and run on switches from different vendors.Lec sequential



Lec sequentialUmAir AsgHar
╠²
Sequential circuits have memory which allows the output to depend on the current and previous inputs. A basic memory element called a latch can be created using feedback in a combinational circuit. Two latches connected in a specific way create a flip-flop which changes state only on the rising or falling edge of a clock signal. For sequential circuits to operate reliably, there must be constraints on the timing of inputs including setup time and hold time relative to the clock edge.High performance network programming on the jvm oscon 2012 



High performance network programming on the jvm oscon 2012 Erik Onnen
╠²
This document summarizes a talk on high performance network programming on the JVM. The talk discusses choosing between synchronous and asynchronous I/O, with examples of when each approach is best. It also covers how to optimize synchronous I/O on the JVM to maximize throughput. The document provides benchmarks comparing the performance of a simple synchronous memcache client versus an asynchronous one.wd1-01-jaseel-madhusudan-pres-user



wd1-01-jaseel-madhusudan-pres-userjaseel_abdulla
╠²
This document presents a novel approach to emulate power islands in FPGA platforms to enable earlier validation of low power features. It proposes corrupting logic in power-gated domains by connecting power gating enables to asynchronous set/clear signals on flip-flops. This approach more realistically mimics silicon behavior during power-off and can find issues like incorrect power sequencing bugs. The methodology was implemented using a custom EDF library and randomization to corrupt a parameterized percentage of logic. Challenges around FPGA architecture and optimization were addressed. Results showed the approach introduced minimal overhead while enabling important power management validation earlier in the design flow.ZERO WIRE LOAD MODEL.pptx



ZERO WIRE LOAD MODEL.pptxVishalYadav29718
╠²
Here are the key points about setup time, hold time, and insertion delay in VLSI physical design:
- Setup time is the minimum time before the clock edge that the data needs to be stable in order for it to be correctly captured by the flip-flop.
- Hold time is the minimum time after the clock edge that the data needs to remain stable. It provides a "window" after the clock edge for the data to remain valid.
- Insertion delay is the time it takes for the clock signal to propagate from the clock source to a flip-flop input pin through the clock tree.
- During clock tree synthesis, the tool aims to balance the insertion delays across the clock tree to minimizeCLOCKLESS CHIP BY Saurabh singh



CLOCKLESS CHIP BY Saurabh singhSaurabh Singh
╠²
This document discusses clockless or asynchronous chips. It notes that synchronous chips require a global clock signal which wastes power and limits performance. Clockless chips use handshake signals instead of a clock to coordinate data exchange between components, allowing different parts to work at individual speeds. This reduces power consumption and heat generation compared to synchronous chips. While clockless chips offer advantages, challenges remain in interfacing them with existing synchronous devices and a lack of expertise and tools in asynchronous design.Manja ppt



Manja pptDruva Gowda
╠²
The document summarizes research on designing high-speed, low-power domino logic circuits. It first introduces domino logic and its advantages over static CMOS logic in terms of performance. It then describes the conventional design method for domino logic circuits before proposing an optimized method. Simulation results show the proposed method achieves lower power consumption compared to CMOS implementations for full adder circuits. The document concludes that domino logic circuits offer improved speed and power performance making them well-suited for high-performance, low-power applications.Intro to IO-Link



Intro to IO-LinkNeil Farrow, P.E.
╠²
IEC 61131-9 is an international standard for IO-Link, a digital communication protocol for sensors and actuators. IO-Link allows bi-directional communication between a sensor and PLC, enabling features like sensor diagnostics, configuration, and process data beyond just on/off signals. IO-Link uses the same M12, M8, and M5 connectors as traditional sensors, providing compatibility while adding digital capabilities. The IO-Link standard provides for interoperability between sensors, masters, and PLCs from any manufacturer.MySQL Replication: Pros and Cons



MySQL Replication: Pros and ConsRachel Li
╠²
The document discusses different types of MySQL replication including asynchronous, semi-synchronous, and synchronous. It provides pros and cons of each type and describes how they handle transaction ordering, parallelism, flow control, and consistency. The key points are that asynchronous replication has potential for data loss and stale reads, semi-synchronous reduces but does not eliminate data loss risk, while SchoonerSQL's synchronous replication guarantees no data loss and failover without stalled transactions.Vsync track c



Vsync track cAlona Gradman
╠²
This document discusses synchronization issues that can arise in designs with multiple clock domains and presents techniques for reliably handling clock domain crossings. It describes how metastability can occur during data transfers between clock domains and impact reliability. Advanced synchronization techniques using synchronization IP blocks and EDA tools are recommended to automatically handle clock domain crossings in a correct-by-design manner and verify the design is sign off-ready. Synchronization is a critical part of most modern chip designs that must be carefully analyzed and validated.Vlsi interview questions1



Vlsi interview questions1SUKESH Prathap
╠²
The document contains interview questions and answers related to CMOS design. Some key topics covered include:
1. Latch-up and how it can permanently damage a device due to excessive current flow.
2. NAND gates are preferred over NOR gates in fabrication due to higher electron mobility and lower gate leakage in NAND structures.
3. Noise margin is the minimum amount of noise that can be allowed on the input without affecting the output.Ch 1 overview



Ch 1 overviewEr Ankita Kapoor
╠²
Combinational logic circuits use Boolean algebra to calculate outputs solely based on the present inputs. They do not have memory and are used to build circuits like adders and decoders. Sequential logic circuits can store past inputs in memory elements like flip-flops to determine outputs. Most computer circuits mix combinational and sequential logic. Metastability refers to unstable states that can occur when synchronizing signals across clock domains and can lead to unpredictable behavior if not resolved. Techniques like adding flip-flops are used to synchronize signals and eliminate metastability.Digital Electronics ŌĆō Unit V.pdf



Digital Electronics ŌĆō Unit V.pdfKannan Kanagaraj
╠²
Introduction to Logic families ŌĆō RTL, TTL, ECL and CMOS
Basic memory structure ŌĆō ROM : ROM, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM -
RAM : Static and dynamic RAM
Programmable Logic Devices ŌĆō Programmable Logic Array (PLA),
Programmable Array Logic (PAL) ŌĆō Implementation of
combinational logic circuits using PLA, PAL
FPGA - Basic Architecture.Project Report



Project ReportRushil Goyal
╠²
This document describes a project to control the speed of a robot using pulse width modulation (PWM). Rushil Goyal and Siddharth Agarwal developed a robot that can be controlled wirelessly to move forward, backward, left, and right at different speeds set by transmitting a PWM signal over UART. They used an Atmega16 microcontroller, L293D motor drivers, switches, LEDs, and a LCD display. The program code for controlling the robot with PWM is included. The document also provides background information on robots, including classifications, components like manipulators and control systems, and applications of sensors, actuators, and artificial intelligence in robotics.Understanding and Specifying Outdoor LFD with Samsung



Understanding and Specifying Outdoor LFD with SamsungrAVe [PUBS]
╠²
The document discusses LCD technology and specifications for outdoor LCD displays. It explains how LCDs work using liquid crystals and polarization of light. It also covers important specifications for outdoor displays such as brightness, temperature and humidity ranges, duty cycle, and IP ratings. Samsung's outdoor LCD display lines - OMD-W, OMD-K, OME, and OH series - are introduced as products designed for outdoor use with features like high brightness, wide operating temperature ranges, and water/dust resistance.training report on embedded system and AVR



training report on embedded system and AVRUrvashi Khandelwal
╠²
containing basics of embedded system , embedded c , basic electronic components, microcontroller,avr, programs and hardware interfacingMetastability
- 1. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 1 Metastability 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
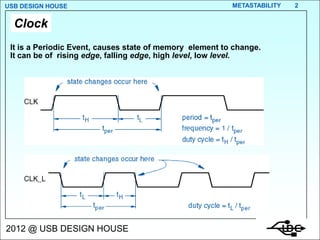
- 2. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 2 Clock It is a Periodic Event, causes state of memory element to change. It can be of rising edge, falling edge, high level, low level. 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
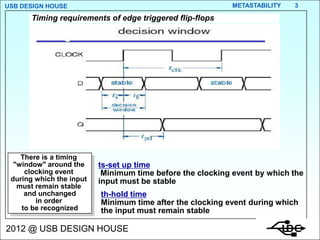
- 3. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 3 Timing requirements of edge triggered flip-flops There is a timing "window" around the ts-set up time clocking event Minimum time before the clocking event by which the during which the input input must be stable must remain stable and unchanged th-hold time in order Minimum time after the clocking event during which to be recognized the input must remain stable 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
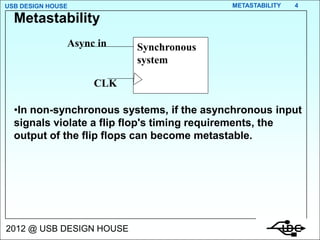
- 4. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 4 Metastability Async in Synchronous system CLK ŌĆóIn non-synchronous systems, if the asynchronous input signals violate a flip flop's timing requirements, the output of the flip flops can become metastable. 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
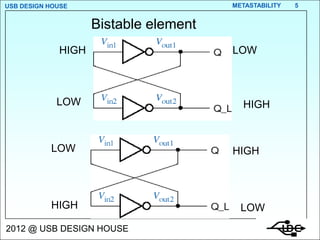
- 5. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 5 Bistable element HIGH LOW LOW HIGH LOW HIGH HIGH LOW 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
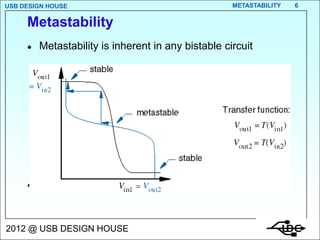
- 6. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 6 Metastability ’ü¼ Metastability is inherent in any bistable circuit ’ü¼ Two stable points, one metastable point 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
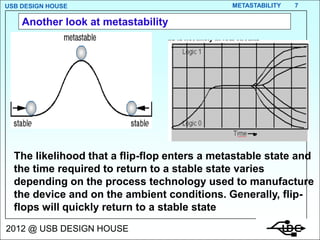
- 7. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 7 Another look at metastability The likelihood that a flip-flop enters a metastable state and the time required to return to a stable state varies depending on the process technology used to manufacture the device and on the ambient conditions. Generally, flip- flops will quickly return to a stable state 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
- 8. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 8 Avoiding Metastability How? ŌĆóInputs must be synchronized with the system clock before being applied to a synchronous system. 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
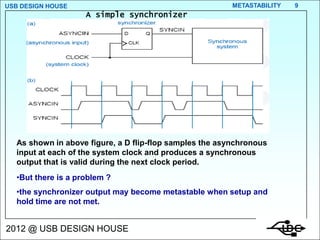
- 9. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 9 A simple synchronizer As shown in above figure, a D flip-flop samples the asynchronous input at each of the system clock and produces a synchronous output that is valid during the next clock period. ŌĆóBut there is a problem ? ŌĆóthe synchronizer output may become metastable when setup and hold time are not met. 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
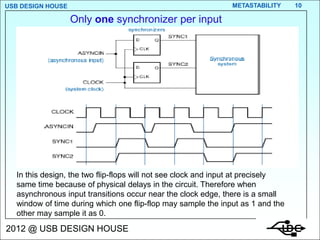
- 10. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 10 Only one synchronizer per input In this design, the two flip-flops will not see clock and input at precisely same time because of physical delays in the circuit. Therefore when asynchronous input transitions occur near the clock edge, there is a small window of time during which one flip-flop may sample the input as 1 and the other may sample it as 0. 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
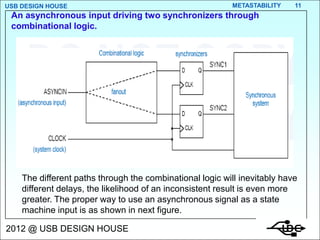
- 11. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 11 An asynchronous input driving two synchronizers through combinational logic. The different paths through the combinational logic will inevitably have different delays, the likelihood of an inconsistent result is even more greater. The proper way to use an asynchronous signal as a state machine input is as shown in next figure. 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
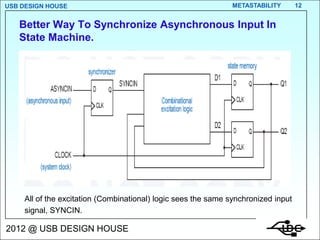
- 12. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 12 Better Way To Synchronize Asynchronous Input In State Machine. All of the excitation (Combinational) logic sees the same synchronized input signal, SYNCIN. 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
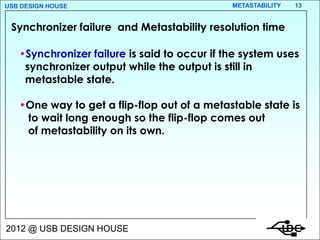
- 13. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 13 Synchronizer failure and Metastability resolution time ŌĆóSynchronizer failure is said to occur if the system uses synchronizer output while the output is still in metastable state. ŌĆóOne way to get a flip-flop out of a metastable state is to wait long enough so the flip-flop comes out of metastability on its own. 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
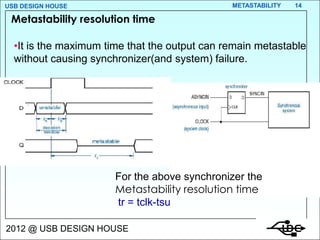
- 14. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 14 Metastability resolution time ŌĆóIt is the maximum time that the output can remain metastable without causing synchronizer(and system) failure. For the above synchronizer the Metastability resolution time tr = tclk-tsu 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
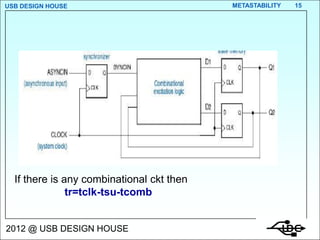
- 15. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 15 If there is any combinational ckt then tr=tclk-tsu-tcomb 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
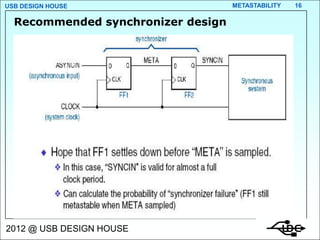
- 16. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 16 Recommended synchronizer design 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
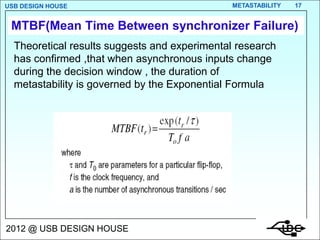
- 17. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 17 MTBF(Mean Time Between synchronizer Failure) Theoretical results suggests and experimental research has confirmed ,that when asynchronous inputs change during the decision window , the duration of metastability is governed by the Exponential Formula 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
- 18. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 18 Example ŌĆóFor a typical 74LS74 flipflop,for which To=0.4 ns an T(twoe)=1.5ns. ŌĆóTsu=20 ns; and the clock period is 100ns (10 MHz); ŌĆótr(resolution time)=tclk-tsu=100-20=80 ns; ŌĆóIf the synchronizer input changes 100,000 times per second,the ŌĆó MTBF(80 ns)=exp(80/1.5)/0.4.(10)7 .(10)5 =3.6. 1011 seconds = about 100 centuries between failures. ŌĆóWith clk period of 62.5 ns MTBF=3.1 s !!!!!!!!!! 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE
- 19. USB DESIGN HOUSE METASTABILITY 19 THANK YOU 2012 @ USB DESIGN HOUSE

