Microsoft Project Presentation For Beginners
- 1. Microsoft Project Presentation By Corey Johnson 10/11/00
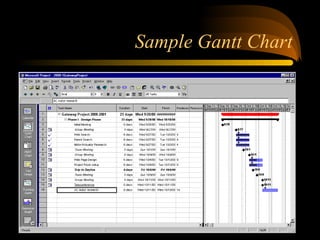
- 2. What is a Gantt Chart? ? A Gantt Chart is a visual tool to help Plan, Manage, and Track a project or projects.
- 4. Planning a Project ? Define Goals ? Develop Tasks ? Establish Timeframes ? Resource Availability? ? Organize
- 5. Managing and Tracking a Project ? Track Progress ®C Are the tasks being completed on time? ®C Is one task holding up the whole project? ? Manage Finances ®C Is the project going to stay within the budget?
- 6. Using MS Project ? Define the Project ? Build the Plan ®C Set a start date ®C Enter tasks/durations ®C Assign resources ®C Link tasks ®C Fine tune the plan
- 7. Using MS Project (cont°Ød) ? Track and Manage ®C Set a baseline ®C Enter actuals ®C Adjust plan ? Close Project
- 8. Defining the Project ? The objective of the project should be defined by the person/group that is going to manage the project. ? Tasks, start times, and deadlines should be clearly established.
- 9. Setting a Start Date ? When opening a new Microsoft Project file, the user is automatically prompted for a start date. Setting an accurate start date will make future entries more convenient.
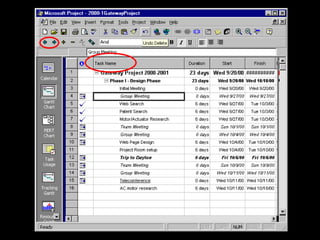
- 10. Entering Tasks and Durations ? Tasks are entered in the °∞Task Name°± column ? Subtasks are created by indenting a task. ? Durations may be entered in number of working days or start and finish dates may be used
- 12. Standard Markers ? Normal Task ®C designates ordinary task duration ? Summary Bar ®C designates the duration of a group of sub-tasks
- 13. Special Markers ? Milestones ®C A reference point marking a major event in a project and used to monitor the project's progress ®C To create a milestone, Enter °∞0°± in the duration field
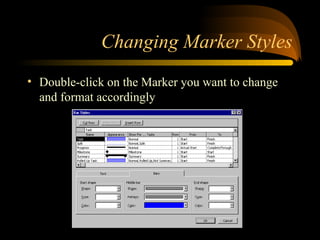
- 14. Changing Marker Styles ? Double-click on the Marker you want to change and format accordingly
- 15. Assigning Resources ? A resource can be a single person, a piece of equipment, or it can represent a group, such as Plumbers ? Information on resources include Availability, Costs, and Working Time ? Resources are very important in accurate scheduling
- 16. Assigning Resources ? To Assign a Resource: ®C Select the task to which you want to assign the resource ®C Click the Assign Resources button on the toolbar
- 17. Assigning Resources ? If resources are not already set up, double click on the name box
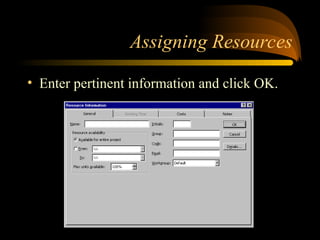
- 18. Assigning Resources ? Enter pertinent information and click OK.
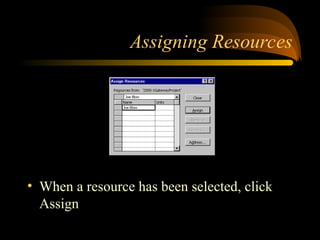
- 19. Assigning Resources ? When a resource has been selected, click Assign
- 20. Linking Tasks ? Some tasks require that another task be completed before it can begin. These tasks must be linked. ? Tasks and subtasks are linked by assigning Predecessors.
- 21. Linking Tasks ? Predecessor ®C A task that must start or finish before another task can start or finish ? Successor ®C A task that cannot start or finish until another task starts or finishes ®C A task becomes a successor when a row number is entered in the predecessor column
- 22. Linking Tasks
- 23. Fine Tune the Plan ? When all resources have been assigned and appropriate tasks are linked, the original Gantt chart will be complete ? Check to make sure tasks have been linked correctly and task durations are correct ? The project is now ready to begin
- 24. Set a Baseline ? A baseline compares your original plan for the project with the actual course of the project. ? You can see which tasks started earlier or later than planned, exceeded their original budget, took longer than planned, and so on.
- 25. Set a Baseline ? Create a baseline after you've polished it and just before you actually start work on the project ? To track costs, be sure to enter cost information before you create the baseline ? Updates can easily be made to the baseline if information is missing
- 26. Set a Baseline ? The Baseline plan includes: ®C Tasks (start and finish dates, duration, work, cost, splits, timephased work, and timephased cost) ®C Resources (work, cost, timephased work, and timephased cost) ®C Assignments (start and finish dates, work, cost, timephased work, and timephased cost)
- 27. Set a Baseline ? To set a baseline: ®C Point to Tracking on the Tools menu ®C Click Save Baseline
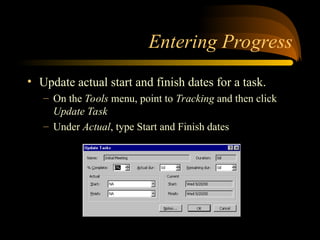
- 28. Entering Progress ? Update actual start and finish dates for a task. ®C On the Tools menu, point to Tracking and then click Update Task ®C Under Actual, type Start and Finish dates
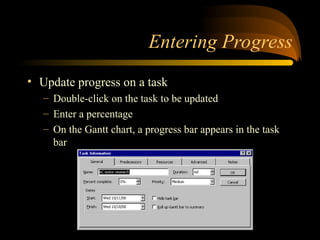
- 29. Entering Progress ? Update progress on a task ®C Double-click on the task to be updated ®C Enter a percentage ®C On the Gantt chart, a progress bar appears in the task bar
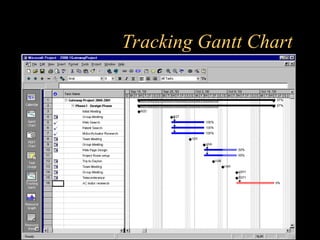
- 30. Tracking Gantt Chart ? Tracks the progress of the project ? Shows what tasks are overdue and what has been completed on time ? Click on the Tracking Gantt icon to view
- 32. Tracking Progress ? Determining if tasks are starting and finishing according to plan: ®C In the Tracking Gantt, point to Table (View menu) and click Variance ®C Drag the Divider bar to the right to view variance. ®C Variance is shown in Days
- 33. Tracking Progress ? Determine if tasks cost more or less than budgeted ®C In the Tracking Gantt, point to Table (View menu) and click Cost ®C Drag the Divider bar to the right to view Total Cost and Baseline fields
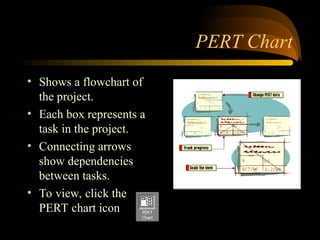
- 34. PERT Chart ? Shows a flowchart of the project. ? Each box represents a task in the project. ? Connecting arrows show dependencies between tasks. ? To view, click the PERT chart icon
- 35. Calendar View ? Keeps tabs on when tasks occur. ? Quickly see how long tasks take, when they start and finish, and how they occur in relation to other tasks. ? To view, click the Calendar icon
- 36. Task Usage View ? Work with task and resource information side by side. ? Easily create useful reports about when a resource is scheduled to work on a task. ? To view, click the Task Usage icon
- 37. Resource Graph View ? See whether resources are overallocated, what capacity they're working at, and how much they cost in a timescale graph ? To view, click the Resource Graph icon
- 38. More Views ? Resource Sheet View ®C Easy way to review, add, edit data about resources ? Resource Usage View ®C Work with resource and task information side by side
- 39. The Project is Now Complete !! ? MS Project is a very powerful tool if it is used correctly ? This program can save a lot of time for engineers who are interested in time, cost, etc. ? Automatically keeps your project organized.
- 40. Thank you !! Please feel free to ask any questions