Milano 2012 Cusinato & Colesso
- 1. CIRF – Università di Padova ECONOMIC HARDSHIP & FAMILY RELATIONAL RESOURCES MARIO CUSINATO & WALTER COLESSO 5th Congress of the ESFR 29 September-2 October 2010 Famiglie 2000 Milano - Italy
- 2. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions Literature review on Economic Hardship and Family Relational Resources shows that Economic pressure in previous economic recessions was associated to: - negative impact on spouse’s marital quality (happiness/satisfaction) and marital instability (thoughts or action related to divorce), (Conger, Elder, Lorenz et al, 1990) in US Midwest counties; - hostile marital interactions (Leinonen, Solantaus, & Punamäki, 2003) in Finland; - marital conflict and disruption in skillful parenting (Conger, Elder, Lorenz et al, 1992) in US Midwest countries; - less parenting efficacy (Scaramella, Preston, Callahan, & Mirabile, 2008) in New Orleans area; - increased punitive parenting (Leinonen, Solantaus, & Punamäki, 2003) in Finland.
- 3. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions A preliminary study (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) with North-East Italian couples, presented at the 20th Anniversary Conference IAFP - International Academy of Family Psychology “Families in changing world: Challenges, risks, and resilience” Callaways Gardens. Pine Mountain, Georgia USA 13 -16 May 2010 ... showed: 1. The results for the Italian sample are congruent with Conger & Elder (1994) and Leinonen, Solantaus, & Punamäki (2002) research findings on American and Finnish people. 2. The current economic recession seems to have a negative impact on relational resources in North-East Italian families. 3. Results suggest that Economic Pressure acts directly on social networks and consequently on family relations. 4. Preliminary study can’t explain the effects on relational resources of families included in social network.
- 4. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions Aim A further collection of data has been run in order to: 1. Verify preliminary findings (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) on relations between economic hardships and family internal and external relational resources in the North-East of Italy. 2. Evaluate the impact of social volunteering on families relational resources.
- 5. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions Participants N = 356 participants = 178 couples Origin: North-East of Italy: Veneto region Status: married (or cohabiting) 100%, with or without children. n1 = 250 ( =125 couples) with no social network. Age1: M = 40.5; SD = 8.0; range = 20 ÷ 60 Sex1: 50% males, 50% females. n2 = 106 ( = 53 couples) with a social network*. Age2: M = 39.8; SD = 5.3; range = 28 ÷ 53 Sex2 : 50% males, 50% females. *Volunteers attending social skills enhancement training.
- 6. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions Measures and their reliability Economic Indexes (Leinonen, Solantaus, & Punamäki, 2002) Economic Hardship Scale in this study α = .63 Economic Pressures scale in this study α = .71 Family Relation Resources measures Relational Closeness Style Scales (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) Abusive-Apatethic AA in this study α = .72 Reactive-Repetitive, RR in this study α = .67 Conductive-Creative, CC in this study α = .78 Family Satisfaction Scale (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) in this study α = .83 External Family Relational Resources measures UCLA Loneliness Scale by Russel, Peplau, & Cutrona (1980) revised, composed of three subscales: Social Relations scale in this study α = .82 Network Intimacy scale in this study α = .87 Social Seclusion scale in this study α = .67 “decrescita felice” – “happy decrease” Scale in this study α = .70 (positive and ethical attitude toward adversities)
- 7. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions Analyses 1) T – Test Analysis was performed to evaluate differences between non volunteers and volunteers families. 1) Pearson Correlations to assess relations among Economic Indexes and Relational Resources for the two groups. 3) Structural Equation Modeling (Causal Model for Observed Variables) were used to select the best confirmative fit for the two groups.
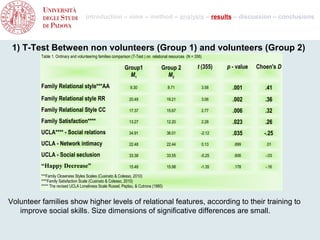
- 8. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions 1) T-Test Between non volunteers (Group 1) and volunteers (Group 2) Table 1. Ordinary and volunteering families comparison (T-Test ) on relational resources (N = 356) Group1 Group 2 t (355) p - value Choen's D M1 M2 Family Relational style***AA 9.30 8.71 3.58 .001 .41 Family Relational style RR 20.49 19.21 3.06 .002 .36 Family Relational Style CC 17.37 15.67 2.77 .006 .32 Family Satisfaction**** 13.27 12.20 2.28 .023 .26 UCLA**** - Social relations 34.91 36.01 -2.12 .035 -.25 UCLA - Network intimacy 22.48 22.44 0.13 .899 .01 UCLA - Social seclusion 33.38 33.55 -0.25 .806 -.03 “Happy Decrease” 15.48 15.98 -1.35 .178 -.16 ***Family Closeness Styles Scales (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) ****Family Satisfaction Scale (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) The revised UCLA Loneliness Scale Russel, Peplau, & Cutrona (1980) Volunteer families show higher levels of relational features, according to their training to improve social skills. Size dimensions of significative differences are small.
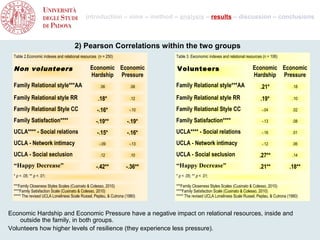
- 9. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions 2) Pearson Correlations within the two groups Table 2.Economic indexes and relational resources (n = 250) Table 3. Eeconomic indexes and relational resources (n = 106) Non volunteers Economic Economic Volunteers Economic Economic Hardship Pressure Hardship Pressure Family Relational style***AA .06 .06 Family Relational style***AA .21* .18 Family Relational style RR .18* .12 Family Relational style RR .19* .10 Family Relational Style CC -.16* -.10 Family Relational Style CC -.04 .02 Family Satisfaction**** -.19** -.19* Family Satisfaction**** -.13 .08 UCLA**** - Social relations -.15* -.16* UCLA**** - Social relations -.16 .01 UCLA - Network intimacy -.09 -.13 UCLA - Network intimacy -.12 .06 UCLA - Social seclusion .12 .10 UCLA - Social seclusion .27** .14 “Happy Decrease” -.42** -.36** “Happy Decrease” .21** .18** * p < .05; ** p < .01; * p < .05; ** p < .01; ***Family Closeness Styles Scales (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) ***Family Closeness Styles Scales (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) ****Family Satisfaction Scale (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) ****Family Satisfaction Scale (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) The revised UCLA Loneliness Scale Russel, Peplau, & Cutrona (1980) The revised UCLA Loneliness Scale Russel, Peplau, & Cutrona (1980) Economic Hardship and Economic Pressure have a negative impact on relational resources, inside and outside the family, in both groups. Volunteers how higher levels of resilience (they experience less pressure).
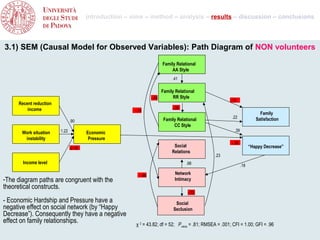
- 10. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions 3.1) SEM (Causal Model for Observed Variables): Path Diagram of NON volunteers Family Relational AA Style .41 Family Relational -.49 RR Style -.12 Recent reduction income -.36 -.14 Family .22 Satisfaction .90 Family Relational CC Style 1.22 .39 Work situation Economic instability Pressure -.35 Social “Happy Decrease” -2.19 Relations .23 Income level .98 .18 -.66 Network -The diagram paths are congruent with the Intimacy theoretical constructs. -.70 - Economic Hardship and Pressure have a Social negative effect on social network (by “Happy Seclusion Decrease”). Consequently they have a negative effect on family relationships. χ 2 = 43.82; df = 52; Pvalue = .81; RMSEA = .001; CFI = 1.00; GFI = .96
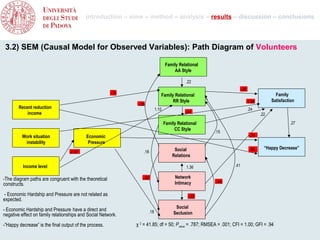
- 11. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions 3.2) SEM (Causal Model for Observed Variables): Path Diagram of Volunteers Family Relational AA Style .22 -.20 -.14 Family Family Relational RR Style -1.66 Satisfaction -.26 Recent reduction 1.10 .24 income -.44 .22 Family Relational .27 CC Style .15 Work situation Economic -.25 instability Pressure Social -.86 “Happy Decrease” -2.42 .18 Relations Income level 1.36 .41 -The diagram paths are congruent with the theoretical -.40 Network Intimacy -.44 constructs. - Economic Hardship and Pressure are not related as -.25 expected. Social - Economic Hardship and Pressure have a direct and .18 negative effect on family relationships and Social Network. Seclusion -”Happy decrease” is the final output of the process. χ 2 = 41.85; df = 50; Pvalue = .787; RMSEA = .001; CFI = 1.00; GFI = .94
- 12. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions Findings 1. The preliminary study research’s results (Cusinato & Colesso, 2010) are confirmed. 2. The current economic recession seems to have a negative impact on relational resources in North-East Italian families. 3. Results suggest that Economic Pressure acts directly on social networks and consequently on family relations. 4. Volunteering families show higher levels of relational features, as result of their training. However they show also negative effects of the current economic crisis on family relationships and social network.
- 13. introduction – aims – method – analysis – results – discussion – conclusions Suggestions for practical implications Relational competence in social network relationships can reduce the negative effects of economic hardship on family relations. Limits The participants were not purposely selected as a representative sample of North-East Italian families. Future Investigations - Economic hardship and gender roles (in progress) - The effect of number of children on the processes considered.
- 14. CIRF – Università di Padova Thank you for your attention mario.cusinato@unipd.it walter.colesso@unipd.it