Modem
Download as PPTX, PDF11 likes20,668 views
Modems are devices that modulate analog carrier signals to encode digital data for transmission and demodulate carrier signals to decode received data. They are used for data conversion. Modems can be classified based on their range (short haul, voice grade, wide band), the type of line used (dialup, leased), and their operation mode (half duplex, full duplex, simplex). Common types include internal and external modems. Modems work by modulating digital signals onto analog carriers for transmission and demodulating the signals back to digital on the receiving end. Modem speeds have increased significantly over time from 300 bps in the 1960s to 56 kbps in 1998 and up to 8 mbps with technologies like ADS
1 of 12
Downloaded 1,069 times








Recommended
Presentation on modem



Presentation on modemDnyanesh Patil
Ěý
A modem is a device that modulates analog signals to transmit digital data and demodulates received analog signals to reconstruct the original digital data. It has a transmitter that converts digital to analog, a receiver that converts analog to digital, and a control unit that handles functions like auto-dialing. Modems use various modulation techniques like amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, and phase modulation. They are classified by operation mode, synchronization method, transmission medium, and modulation technique. Newer technologies like DSL provide higher speeds over telephone lines than traditional modems.Overview of Modem 



Overview of Modem Kishan Patel
Ěý
This document provides an overview of modems, including:
- Their history dating back to the 1950s for air defense communication needs.
- Their function of modulating digital data to analog signals for transmission and demodulating analog signals back to digital data.
- The main types based on connection, transmission mode, and speed of data transmission.
- The basic modulation techniques used including ASK, FSK, and PSK.Networking devices



Networking devicesfrestoadi
Ěý
This document discusses several common networking devices and their functions. It describes hubs, switches, bridges, routers, gateways, CSU/DSUs, NICs, ISDN adapters, modems, and firewalls. Hubs broadcast traffic to all ports, wasting bandwidth, while switches only forward frames to their destination port. Bridges operate at the data link layer and routers at the network layer. Gateways perform protocol translation. NICs connect devices to the network. Modems convert digital to analog signals for transmission over phone lines. Firewalls control network access for security.Cellular Telephone Systems



Cellular Telephone SystemsShantanu Krishna
Ěý
Today's cellular telephone systems operate by dividing geographic areas into cells served by base stations. Each cell is assigned certain radio frequencies that are reused in non-neighboring cells to increase coverage and capacity. When a mobile user moves between cells, the call is handed off from one base station to another through a mobile switching center to avoid disconnection. Modern cellular networks use digital technologies like CDMA, TDMA and FDMA to provide voice, text, and data services to users through cellular infrastructure.Modems



ModemsBits
Ěý
Modem is a network device that enables a computer to transfer data from telephone lines to computers and computers to telephone lines.
The word modem is derived from modulator and demodulator.
Modem performs modulation and demodulation.
Cdma ppt for ECE



Cdma ppt for ECEajitece
Ěý
CDMA is a digital cellular technology that allows multiple users to access a single radio channel simultaneously through the use of unique code assignments. The document discusses CDMA network architecture, which includes mobile stations, base stations, base station controllers, mobile switching centers, home and visitor location registers, and authentication centers. It also compares CDMA to earlier multiple access technologies like TDMA and FDMA, noting advantages of CDMA like increased capacity and soft handoffs between cells using the same frequency.Networking devices



Networking devicesTayyab Hussain
Ěý
Networking devices are components that connect electronic devices and allow them to share resources over a network. Common networking devices include network interface cards, hubs, switches, bridges, routers, and modems. A switch connects network segments and can perform error checking before forwarding data packets between devices on a local area network. A router connects two or more networks and reads address information in packets to determine the best path to forward packets between networks. Routers work at the network layer and contain routing tables to define the addresses of connected networks.8255 PPI



8255 PPIdeval patel
Ěý
The document discusses interfacing concepts and the Intel 8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface chip. It provides information on:
- Memory mapped I/O and I/O mapped I/O interfacing techniques.
- The 8255 PPI chip which has 3 8-bit I/O ports (Ports A, B, and C) that can be configured as input or output ports. It operates in I/O mode or Bit Set/Reset mode.
- Control word formats for configuring the ports in different modes like Mode 0, 1, and 2 for I/O mode and Bit Set/Reset mode.
- Example programs to initialize the 8255 ports using control words for differentSwitching techniques



Switching techniquesGupta6Bindu
Ěý
Circuit switching directly connects the sender and receiver through a dedicated physical path. Message switching transmits entire messages from node to node without establishing a dedicated path. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that can take different routes to the destination and are reassembled, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth but introducing complexity.I2C Protocol



I2C ProtocolSudhanshu Janwadkar
Ěý
This presentation discusses the details of the I2C protocol and interfacing of EEPROM with 8051 based on I2C protocol. It also discusses the other applications of I2C protocolBluetooth şÝşÝߣs



Bluetooth şÝşÝߣsAniruddha Gupta
Ěý
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the industrial, scientific and medical radio bands. It was created in 1994 by Ericsson to replace cables connecting devices like mobile phones, laptops, printers, and other electronic devices. Bluetooth allows for wireless connections between various devices to share information and transmit data wirelessly over short distances of around 10 meters. It uses a radio technology called frequency-hopping spread spectrum to handle interference and improve communication quality.Modem | A Quick Preview



Modem | A Quick PreviewSyed Shujat Ali
Ěý
It is one of my semester project presentation along with my group members, of subject Data Communication, which covers a brief intro about all the vital things related to the modems.Introduction to 3G technology



Introduction to 3G technologyShweta Ghate
Ěý
This document provides an overview of 3G technology, including its history, features, advantages, applications, requirements, and comparisons to earlier 2G and 2.5G technologies. 3G allows for higher data transmission rates, advanced multimedia access, and global roaming. It has enabled new applications like mobile TV, video calling, and location-based services. The document also discusses 3G adoption worldwide and in India, as well as future developments like 4G networks.Digital switching system ppt



Digital switching system pptGopalakrishnaM4
Ěý
A digital switch is a device that handles digital signals generated at or passed through a telephone company central office and forwards them across the company's backbone network. ... A centrex is a digital switch at the central office that manages to switch for the private company from the central office.Transmission modes (simplex, duplex & half duplex)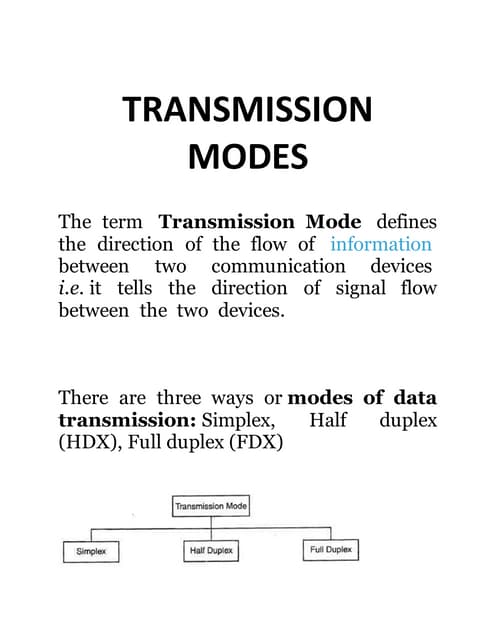



Transmission modes (simplex, duplex & half duplex)Rahul Kumar
Ěý
There are three transmission modes: simplex which allows transmission in one direction, half duplex which allows transmission in two directions but only one direction at a time, and full duplex which allows simultaneous two-way transmission. Simplex examples include television broadcasting and loudspeaker systems, half duplex includes walkie talkies, and full duplex includes telephone networks where two people can speak and listen simultaneously. Transmission modes define the direction of signal flow between communicating devices.Radio propagation



Radio propagationNguyen Minh Thu
Ěý
This document discusses radio propagation and propagation models. It begins with an introduction to radio and propagation mechanisms like free space propagation, refraction, diffraction, and scattering. It then discusses the objective of developing propagation models to predict signal strength at a receiver. The document outlines that propagation models are specialized based on scale, environment, and application. It covers large-scale path loss models and small-scale fading models. It discusses specific propagation mechanisms and models like free space, log-distance path loss, ground reflection, hilly terrain, indoor models, and statistical fading models.WCDMA



WCDMAHarshal Tiwari
Ěý
The document is a seminar report on Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) technology. It discusses the basics of WCDMA, including that it uses code division multiple access to separate users and spread signals over a wide 5MHz bandwidth. It also covers WCDMA specifications, generation, spreading principles, power control, handovers, and advantages such as service flexibility and spectrum efficiency.Modem presentation



Modem presentationMuhammad Bilal
Ěý
The document discusses modems and their functions. It begins with listing group members and an index of topics to be covered. It then defines a modem as a device that modulates and demodulates signals to transmit digital data over analog channels. Modems are classified by transmission speed and examples are given. The document outlines the history of modems and defines types including external, internal, standard, intelligent, short-haul, and wireless. It describes the purpose of modems in converting digital to analog signals for transmission and discusses modem functions like error correction and data compression. Security and references are mentioned at the end.NETWORK INTERFACE CARD™



NETWORK INTERFACE CARD™UzumakiMugiwara
Ěý
A network interface card (NIC) is a circuit board installed in computers to connect them to a network. It prepares data to be sent over network cables, controls data flow between the computer and cables, and receives incoming data to translate it for the computer's CPU. The NIC converts parallel computer data to serial signals to transmit over cables using an onboard or external transceiver. It supports different connector types depending on the network type, such as coaxial, AUI cable, RJ-45, or integrated wireless.Data communications



Data communicationsAshwini
Ěý
Data communication : entails electronically exchanging data or information. It is the movement of computer information from one point to another by means of electrical or optical transmission system. This system often is called data communication networks.Ěý
GSM Technology



GSM TechnologyAvanitrambadiya
Ěý
What is GSM?
The Global System for Mobile communications is a digital cellular communications system. It was developed in order to create a common European mobile telephone standard but it has been rapidly accepted worldwide.
Formerly it was “Groupe Spéciale Mobile” (founded in 1982)
now: Global System for Mobile Communication.
Services:
Tele-services
Bearer or Data Services
Supplementary services
Applications:
Mobile telephony
GSM-R
Telemetry System
- Fleet management
- Automatic meter reading
- Toll Collection
- Remote control and fault reporting of DG sets
Value Added Services
Advantages:
Better Quality of speech
Data transmission is supported
New services offered due to ISDN compatibility
International Roaming possible
Large market
Crisper, cleaner quieter calls
disadvantages:
Dropped and missed calls
Less Efficiency
Security Issues
conclusion
The mobile telephony industry rapidly growing and that has become backbone for business success and efficiency and a part of modern lifestyles all over the world.
In this session I have tried to give and over view of the GSM system. I hope that I gave the general flavor of GSM and the philosophy behind its design.
The GSM is standard that insures interoperability without stifling competition and innovation among the suppliers to the benefit of the public both in terms of cost and service quality.
Bandwidth Presentation



Bandwidth PresentationGrace=] Penda
Ěý
This is my mini project on bandwidth. Its the best i could do and if theres any enquires on my powerpoint slide show, please let me know lol :)
thankyou.Internet protocols Report şÝşÝߣs



Internet protocols Report şÝşÝߣsBassam Kanber
Ěý
The document discusses Internet protocols and their history. It describes how Internet protocols were first developed in the 1970s by DARPA to facilitate communication between research institutions. This led to the development of TCP/IP, which later became the foundation for the Internet and World Wide Web. The document then provides details on various Internet protocols like IP, TCP, UDP, and application-layer protocols. It describes features of each protocol and how they enable communication over the Internet.Tdm and fdm



Tdm and fdmshyamaliamale
Ěý
Outline:-
TDM and FDM
Basics of TDM and FDM.
Block Diagram of TDM and FDM.
Working of TDM and FDM.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Applications
Presentation on different modes of data communication



Presentation on different modes of data communicationTafadzwa Gonera
Ěý
This document discusses different modes of data communication, including wired and wireless technologies. It describes protocol models like OSI and TCP/IP that define network layers. Wired technologies covered include coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, and twisted pair cable. Wireless technologies discussed are Bluetooth, WiMAX, infrared, and Wi-Fi. The document provides definitions, diagrams, advantages and disadvantages of each technology discussed.Optical networks



Optical networkskritika91jawa
Ěý
Optical fiber communications networks use various topologies and protocols. A local area network interconnects users within a building, while metro and access networks connect between buildings and to homes. The physical layer refers to the transmission medium, while higher layers establish links and route data packets. Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) standards define optical carrier (OC) rates and frame formats to interconnect transmission equipment. Networks can be configured in ring or mesh topologies with self-healing capabilities. Passive optical networks (PON) use passive splitters and no electronic regeneration between transmitters and receivers.Transmission modes



Transmission modesManaswi Sharma
Ěý
This document discusses different modes of data transmission including parallel transmission, serial transmission, asynchronous transmission, and synchronous transmission. Parallel transmission transmits all bits simultaneously but requires multiple wires, while serial transmission transmits bits one after the other on a single wire. Asynchronous transmission uses start and stop bits but does not require synchronization, while synchronous transmission transmits data in a continuous stream under a common clock and provides higher speeds without start/stop bits.PULSE CODE MODULATION (PCM)



PULSE CODE MODULATION (PCM)vishnudharan11
Ěý
It is a digital representation of an analog signal that takes samples of the amplitude of the analog signal at regular intervals. The sampled analog data is changed to, and then represented by, binary data.Ims Sdp Lte Market



Ims Sdp Lte MarketMarie-Paule Odini
Ěý
1. The document discusses the evolution of mobile networks from 2G to 4G technologies like LTE, and the increasing capabilities and speeds they provide. It also describes the growth of the mobile industry in terms of users, traffic, and revenue.
2. A key concept discussed is IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem), which enables the convergence of voice, data, and multimedia services over an IP-based network, and allows interworking between mobile and fixed networks.
3. Trial deployments of early 4G networks like LTE are mentioned, though performance has been lower than expected, with peak speeds of 12Mbps downlink and 5Mbps uplink achieved. Further improvements are anticipated as the technologiesFiber Optic Modems and Its Working



Fiber Optic Modems and Its WorkingVERSITRONINC
Ěý
Fiber optic modems (FOM) are nowadays being used in several applications such as data communication network systems, inter-network communication systems, etc. Since these fiber optic modems are gaining popularity, it is important to have information about before using it blindly.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Switching techniques



Switching techniquesGupta6Bindu
Ěý
Circuit switching directly connects the sender and receiver through a dedicated physical path. Message switching transmits entire messages from node to node without establishing a dedicated path. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that can take different routes to the destination and are reassembled, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth but introducing complexity.I2C Protocol



I2C ProtocolSudhanshu Janwadkar
Ěý
This presentation discusses the details of the I2C protocol and interfacing of EEPROM with 8051 based on I2C protocol. It also discusses the other applications of I2C protocolBluetooth şÝşÝߣs



Bluetooth şÝşÝߣsAniruddha Gupta
Ěý
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the industrial, scientific and medical radio bands. It was created in 1994 by Ericsson to replace cables connecting devices like mobile phones, laptops, printers, and other electronic devices. Bluetooth allows for wireless connections between various devices to share information and transmit data wirelessly over short distances of around 10 meters. It uses a radio technology called frequency-hopping spread spectrum to handle interference and improve communication quality.Modem | A Quick Preview



Modem | A Quick PreviewSyed Shujat Ali
Ěý
It is one of my semester project presentation along with my group members, of subject Data Communication, which covers a brief intro about all the vital things related to the modems.Introduction to 3G technology



Introduction to 3G technologyShweta Ghate
Ěý
This document provides an overview of 3G technology, including its history, features, advantages, applications, requirements, and comparisons to earlier 2G and 2.5G technologies. 3G allows for higher data transmission rates, advanced multimedia access, and global roaming. It has enabled new applications like mobile TV, video calling, and location-based services. The document also discusses 3G adoption worldwide and in India, as well as future developments like 4G networks.Digital switching system ppt



Digital switching system pptGopalakrishnaM4
Ěý
A digital switch is a device that handles digital signals generated at or passed through a telephone company central office and forwards them across the company's backbone network. ... A centrex is a digital switch at the central office that manages to switch for the private company from the central office.Transmission modes (simplex, duplex & half duplex)



Transmission modes (simplex, duplex & half duplex)Rahul Kumar
Ěý
There are three transmission modes: simplex which allows transmission in one direction, half duplex which allows transmission in two directions but only one direction at a time, and full duplex which allows simultaneous two-way transmission. Simplex examples include television broadcasting and loudspeaker systems, half duplex includes walkie talkies, and full duplex includes telephone networks where two people can speak and listen simultaneously. Transmission modes define the direction of signal flow between communicating devices.Radio propagation



Radio propagationNguyen Minh Thu
Ěý
This document discusses radio propagation and propagation models. It begins with an introduction to radio and propagation mechanisms like free space propagation, refraction, diffraction, and scattering. It then discusses the objective of developing propagation models to predict signal strength at a receiver. The document outlines that propagation models are specialized based on scale, environment, and application. It covers large-scale path loss models and small-scale fading models. It discusses specific propagation mechanisms and models like free space, log-distance path loss, ground reflection, hilly terrain, indoor models, and statistical fading models.WCDMA



WCDMAHarshal Tiwari
Ěý
The document is a seminar report on Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) technology. It discusses the basics of WCDMA, including that it uses code division multiple access to separate users and spread signals over a wide 5MHz bandwidth. It also covers WCDMA specifications, generation, spreading principles, power control, handovers, and advantages such as service flexibility and spectrum efficiency.Modem presentation



Modem presentationMuhammad Bilal
Ěý
The document discusses modems and their functions. It begins with listing group members and an index of topics to be covered. It then defines a modem as a device that modulates and demodulates signals to transmit digital data over analog channels. Modems are classified by transmission speed and examples are given. The document outlines the history of modems and defines types including external, internal, standard, intelligent, short-haul, and wireless. It describes the purpose of modems in converting digital to analog signals for transmission and discusses modem functions like error correction and data compression. Security and references are mentioned at the end.NETWORK INTERFACE CARD™



NETWORK INTERFACE CARD™UzumakiMugiwara
Ěý
A network interface card (NIC) is a circuit board installed in computers to connect them to a network. It prepares data to be sent over network cables, controls data flow between the computer and cables, and receives incoming data to translate it for the computer's CPU. The NIC converts parallel computer data to serial signals to transmit over cables using an onboard or external transceiver. It supports different connector types depending on the network type, such as coaxial, AUI cable, RJ-45, or integrated wireless.Data communications



Data communicationsAshwini
Ěý
Data communication : entails electronically exchanging data or information. It is the movement of computer information from one point to another by means of electrical or optical transmission system. This system often is called data communication networks.Ěý
GSM Technology



GSM TechnologyAvanitrambadiya
Ěý
What is GSM?
The Global System for Mobile communications is a digital cellular communications system. It was developed in order to create a common European mobile telephone standard but it has been rapidly accepted worldwide.
Formerly it was “Groupe Spéciale Mobile” (founded in 1982)
now: Global System for Mobile Communication.
Services:
Tele-services
Bearer or Data Services
Supplementary services
Applications:
Mobile telephony
GSM-R
Telemetry System
- Fleet management
- Automatic meter reading
- Toll Collection
- Remote control and fault reporting of DG sets
Value Added Services
Advantages:
Better Quality of speech
Data transmission is supported
New services offered due to ISDN compatibility
International Roaming possible
Large market
Crisper, cleaner quieter calls
disadvantages:
Dropped and missed calls
Less Efficiency
Security Issues
conclusion
The mobile telephony industry rapidly growing and that has become backbone for business success and efficiency and a part of modern lifestyles all over the world.
In this session I have tried to give and over view of the GSM system. I hope that I gave the general flavor of GSM and the philosophy behind its design.
The GSM is standard that insures interoperability without stifling competition and innovation among the suppliers to the benefit of the public both in terms of cost and service quality.
Bandwidth Presentation



Bandwidth PresentationGrace=] Penda
Ěý
This is my mini project on bandwidth. Its the best i could do and if theres any enquires on my powerpoint slide show, please let me know lol :)
thankyou.Internet protocols Report şÝşÝߣs



Internet protocols Report şÝşÝߣsBassam Kanber
Ěý
The document discusses Internet protocols and their history. It describes how Internet protocols were first developed in the 1970s by DARPA to facilitate communication between research institutions. This led to the development of TCP/IP, which later became the foundation for the Internet and World Wide Web. The document then provides details on various Internet protocols like IP, TCP, UDP, and application-layer protocols. It describes features of each protocol and how they enable communication over the Internet.Tdm and fdm



Tdm and fdmshyamaliamale
Ěý
Outline:-
TDM and FDM
Basics of TDM and FDM.
Block Diagram of TDM and FDM.
Working of TDM and FDM.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Applications
Presentation on different modes of data communication



Presentation on different modes of data communicationTafadzwa Gonera
Ěý
This document discusses different modes of data communication, including wired and wireless technologies. It describes protocol models like OSI and TCP/IP that define network layers. Wired technologies covered include coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, and twisted pair cable. Wireless technologies discussed are Bluetooth, WiMAX, infrared, and Wi-Fi. The document provides definitions, diagrams, advantages and disadvantages of each technology discussed.Optical networks



Optical networkskritika91jawa
Ěý
Optical fiber communications networks use various topologies and protocols. A local area network interconnects users within a building, while metro and access networks connect between buildings and to homes. The physical layer refers to the transmission medium, while higher layers establish links and route data packets. Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) standards define optical carrier (OC) rates and frame formats to interconnect transmission equipment. Networks can be configured in ring or mesh topologies with self-healing capabilities. Passive optical networks (PON) use passive splitters and no electronic regeneration between transmitters and receivers.Transmission modes



Transmission modesManaswi Sharma
Ěý
This document discusses different modes of data transmission including parallel transmission, serial transmission, asynchronous transmission, and synchronous transmission. Parallel transmission transmits all bits simultaneously but requires multiple wires, while serial transmission transmits bits one after the other on a single wire. Asynchronous transmission uses start and stop bits but does not require synchronization, while synchronous transmission transmits data in a continuous stream under a common clock and provides higher speeds without start/stop bits.PULSE CODE MODULATION (PCM)



PULSE CODE MODULATION (PCM)vishnudharan11
Ěý
It is a digital representation of an analog signal that takes samples of the amplitude of the analog signal at regular intervals. The sampled analog data is changed to, and then represented by, binary data.Similar to Modem (20)
Ims Sdp Lte Market



Ims Sdp Lte MarketMarie-Paule Odini
Ěý
1. The document discusses the evolution of mobile networks from 2G to 4G technologies like LTE, and the increasing capabilities and speeds they provide. It also describes the growth of the mobile industry in terms of users, traffic, and revenue.
2. A key concept discussed is IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem), which enables the convergence of voice, data, and multimedia services over an IP-based network, and allows interworking between mobile and fixed networks.
3. Trial deployments of early 4G networks like LTE are mentioned, though performance has been lower than expected, with peak speeds of 12Mbps downlink and 5Mbps uplink achieved. Further improvements are anticipated as the technologiesFiber Optic Modems and Its Working



Fiber Optic Modems and Its WorkingVERSITRONINC
Ěý
Fiber optic modems (FOM) are nowadays being used in several applications such as data communication network systems, inter-network communication systems, etc. Since these fiber optic modems are gaining popularity, it is important to have information about before using it blindly.router and a Modem.pdf



router and a Modem.pdfinoviseo
Ěý
A modem converts digital signals from a computer to analog signals for transmission over telephone lines or cable, and vice versa. A router creates a local area network (LAN) and allows multiple devices to connect to the internet simultaneously and communicate with each other on the LAN. While a modem connects to the internet, a router connects to both the modem and devices on the LAN. Most homes require both a modem and a router, though some internet service providers offer combo devices that integrate both.Modem technology



Modem technologyDhruv Patel
Ěý
Short for modulator-demodulator. A modem is a device or program that enables a computer to transmit data over, for example, telephone or cable lines. Computer information is stored digitally, whereas information transmitted over telephone lines is transmitted in the form of analog waves. A modem convertsbetween these two forms.Communication over modem by anam younas



Communication over modem by anam younasAnamYounas1
Ěý
This document discusses computer modems and their use in network communication. It explains that a modem converts digital data to analog signals for transmission over phone lines and vice versa. It describes different types of modems, their requirements, and how they connect computers via telephone lines to provide internet access and transfer of data and information over distance.Modulation demodulation assignment



Modulation demodulation assignmentSBEntertainments
Ěý
The document discusses modems and their functions. It begins by defining a modem as a device that modulates and demodulates signals to allow computers to communicate over telephone lines. It then describes the main components of a modem:
1. Modulation: The process of varying a carrier signal to encode digital data for transmission.
2. Demodulation: The process of extracting the original digital data from the received modulated carrier signal.
3. Analog to digital and digital to analog conversion: Processes that allow analog signals to be transmitted over phone lines by converting between analog and digital formats.
The document goes on to discuss different types of modulation, demodulation, and conversion techniques in more detail.I-Mode in mobile communication.



I-Mode in mobile communication.hari krishnan.n
Ěý
i-mode in mobile communication and Sync-ml topic.
a detailed description of i-mode and its features.I - Mode Technology



I - Mode Technologyvasanthimuniasamy
Ěý
i-mode is a wireless service developed by NTT DoCoMo that provides email, internet access, and other multimedia services to mobile phones. It uses cHTML, a subset of HTML, to display webpages on small screens. i-mode was launched in 1999 and became very popular in Japan with over 45 million subscribers due to its convenient features. It uses a packet-switched network and protocols based on TCP/IP to deliver an "always on" internet experience to users on-the-go.New Technology Lecture L17 The Mobile Revolution



New Technology Lecture L17 The Mobile RevolutionÓlafur Andri Ragnarsson
Ěý
The ideas for cellular phones were developed in the 1940s. However, it was not until the microprocessor becomes available that practical commercial solutions are possible.
Today there are more than 4 billion mobile phone subscriptions in the world. In the last few years the increase has been most dramatic in developing countries. Telecoms operators have tried to capitalise on this by offering new services that will generate new revenues for them. Mobile Applications are increasing revenues for the operators while voices revenues are getting less and less. But what are mobile applications?
In this lecture we look mobile.
Report on modem



Report on modemAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document provides an overview of modems, including their history, classification, types, and modulation techniques. It discusses how modems originated to allow teletype machines to connect over phone lines instead of leased lines. It classifies modems based on range, data rate, line type, operation mode, and synchronization. It also describes the differences between internal and external modems and how modulation techniques like AM, QAM, FM, CPM, and PM work to transmit digital data over analog phone lines.Bluetooth technology



Bluetooth technologyRohit Roy
Ěý
This document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology. It discusses that Bluetooth was invented in 1994 by Ericsson to unify telecommunications and computing industries. It then defines Bluetooth as an open standard for short-range wireless connectivity between various devices. The document explains how Bluetooth works using small radio frequency chips to transmit information wirelessly. It also describes Bluetooth's topology of forming temporary ad-hoc networks between one master device and up to seven slave devices. Finally, it outlines some advantages like wireless connectivity and disadvantages like short range of Bluetooth technology.I mode



I modeShashwat Shriparv
Ěý
i-mode is a popular wireless service in Japan that provides multimedia messaging capabilities. It uses a packet-switched network and cHTML, a subset of HTML, to deliver content and services to mobile phones. Key features of i-mode include email, transactions, information, entertainment and internet browsing. It was very successful in Japan due to its convenient offerings and continues adding new services. While similar to WAP, a competing standard, i-mode includes images and color while utilizing packet switching rather than circuit switching.Modbus



ModbusManoj89p
Ěý
The document discusses the Modbus TCP/IP client network. It begins by providing background on the Modbus protocol, TCP/IP, and how Modbus TCP/IP combines the two. It then describes the key components of a Modbus TCP/IP client network including the client, servers, and how requests and responses are handled. It also discusses using an ARM BeagleBone Black as the client processor in the network.Introduction to modem



Introduction to modemRiyan Mansoori
Ěý
Modems enable computers to connect over telephone lines using modulation and demodulation techniques. Early modems in the 1950s operated at speeds up to 300 bps and were used to connect remote terminals to mainframe computers. Through the 1980s and 1990s, modem speeds increased to 14.4 kbps and 56 kbps, allowing individuals to connect to remote systems and the emerging Internet to download software and participate in online discussions. Modern alternatives to analog modems include cable modems, DSL, and fiber optic connections, providing speeds of over 1 Mbps. Cable and DSL use existing coaxial cable and telephone lines respectively but provide higher speeds than traditional modems.Presentation



Presentationamrendra001
Ěý
- Modems allow computers to transmit digital data over analog telephone lines by modulating and demodulating digital signals. They convert digital signals to audio tones that can be transmitted and received by telephone networks.
- There are three main types of modems: external modems connected via cable, internal modems installed inside computers, and PC Card modems that fit into slots on portable computers.
- When connecting, one modem modulates digital data into audio tones to send over phone lines, while the receiving modem demodulates the tones back into digital data for the receiving computer. Checksums ensure accurate data transmission.Beyond 3G: Bringing Networks, Terminals and the Web Together



Beyond 3G: Bringing Networks, Terminals and the Web TogetherMobileMonday Norway
Ěý
Martin Sauter gave a presentation on future mobile services and the possibilities for network operators. He discussed 5 key trends: [1] the evolution of wireless networks to higher speeds with technologies like LTE; [2] advances in fixed line networks; [3] the reintegration of fixed and wireless networks as operators understand users want both; [4] the role of femtocells in utilizing fixed line assets; and [5] cloud computing. He argued these trends enable connected home services utilizing both wireless and fixed networks, representing an opportunity for operators versus internet companies dominating cloud services.Bluetooth 



Bluetooth Sajan Sahu
Ěý
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard that allows various digital devices to connect and exchange information over short distances without cables. It uses short-wavelength radio transmissions in the industrial, scientific and medical radio bands to facilitate connections between devices like mobile phones, headphones, laptops and printers. Key benefits of Bluetooth include its global acceptance, ability to connect a wide range of devices easily, secure connections, and low power consumption. It works by creating personal area networks between devices within about 30 feet of each other. bluetooth technology



bluetooth technologydeepak kumar
Ěý
This document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology. It discusses what Bluetooth is, its history and development by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group. The key technical features of Bluetooth like its operating spectrum, data rates, encryption standards and classifications are explained. The document also outlines the Bluetooth protocol stack including the baseband, link manager and middleware layers. Common Bluetooth profiles and potential applications are reviewed. Finally, the security measures used by Bluetooth and its advantages compared to alternatives like infrared are summarized.Modem



Modemvenaychawda
Ěý
A modem is a device that allows computers to transmit data over telephone lines by converting digital signals to analog signals and vice versa. Modems can be external, connecting to computers through serial or USB ports, or internal, inserting directly into expansion slots inside computers. Modem standards have evolved from early speeds of 300 bps up to 56 kbps with V.90 and V.92 standards, and modem types include cable modems, DSL modems, ISDN modems, and wireless modems.Mobile communication cdr



Mobile communication cdrVivek Paripudi
Ěý
This document discusses mobile communication and call detail records (CDR). It begins by providing background on the increasing use of mobile phones and their advanced capabilities. It then explains the basics of mobile communication, including cellular networks, GSM standards, and full-duplex communication systems. The document delves into technical aspects like network components, addresses/identifiers used, and multiplexing. It defines CDRs and their importance for investigations by providing location data. CDR analysis is illustrated as a tool to trace criminals based on calls made near crime scenes.More from Amandeep Kaur (20)
Video/ Graphics cards



Video/ Graphics cardsAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to video/graphics cards. It discusses the components and functions of a graphics card, including different types, color depth, bit depth, and uses. Graphics cards are boards that plug into computers to provide display capabilities. They work with the display monitor using circuitry and different color combinations determined by red, green, and blue light intensities at each pixel. Common uses include gaming, animation, drafting, and other purposes requiring fast rendering and high resolutions. Advanced graphics cards can produce effects like texture mapping, lens flare, motion blur, and Fresnel effects.Menu vb



Menu vbAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
This document provides code examples for creating and handling popup menus in VB. It shows how to display a popup menu on right click, determine which menu item was selected, and toggle font styles like bold, italic, and underline when their corresponding menu items are clicked. Code is presented for handling the click events of bold, italic, and underline menu items to toggle the corresponding font properties and checked state of the menu items.Menu pop up menu mdi form and playing audio in vb



Menu pop up menu mdi form and playing audio in vbAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the contents to be covered in a presentation on using menus, popup menus, MDI forms and playing audio in Visual Basic. It will include three applications: a snake and ladder game using menus; a media player that plays audio; and connecting the two applications using MDI menus and popup menus. The snake and ladder game application will include picture boxes, labels, text boxes and buttons, along with coding for rolling dice, switch case statements and if/else functions. The media player will include text boxes and command buttons, and code to play media using the media player object. The final application demonstrates connecting the first two using an MDI form, popup menus and associated coding.Active x control



Active x controlAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document discusses how to create and run ActiveX controls in Visual Basic. It provides steps to create a simple calculator ActiveX control and system clock ActiveX control. The key steps include starting Visual Basic, clicking on the ActiveX control, giving the project a name, adding coding for functionality, adding the component to the toolbox, dragging it onto a form, setting the project properties, and executing the ActiveX control.Image contro, and format functions in vb



Image contro, and format functions in vbAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document discusses various aspects of using picture boxes and image controls in Visual Basic forms and applications. It covers how to add, load images into, format text in, handle events of, and animate picture boxes. It also compares picture boxes and image controls, describing how picture boxes allow more customization but image controls automatically resize images. Formatting functions for numbers, currency, percentages, and dates are also outlined.Data base connectivity and flex grid in vb



Data base connectivity and flex grid in vbAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document discusses database connectivity in Visual Basic 6 using ADO (Active Data Objects). It describes the Connection object that represents a connection to a data source, the Command object that specifies database operations, and the Recordset object that represents a set of records. It explains how to define these objects, connect to a database, execute commands to retrieve data, and manipulate the retrieved data in a Recordset.Toolbar, statusbar, coolbar in vb



Toolbar, statusbar, coolbar in vbAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document discusses different toolbar controls in Visual Basic - toolbars, status bars, and coolbars. It provides steps for adding each control to a form and customizing their appearance and functionality. For toolbars, this includes adding buttons, handling button clicks, adding separators and images. For status bars, it covers adding panels and displaying text. For coolbars, it outlines adding controls to the bands.Richtextbox



RichtextboxAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
This presentation covers four controls: the timer, combo box, rich text box, and slider. It discusses how each control works and provides code examples for using them. For the timer, it shows how to use it as a stopwatch. For the combo box, it demonstrates populating one and changing text color based on selection. The rich text box example adds formatting to text. And the slider examples set the range and handle value change events.Treeview listview



Treeview listviewAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document discusses different types of controls in Visual Basic including tree view, list view, chart control, and grid controls. It provides instructions on how to add each control to a form and set basic properties. Details are given on displaying data hierarchically in a tree view, displaying items in different views in a list view, creating different chart types, and using a flex grid control to display data in rows and columns.Progress bar



Progress barAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document discusses different types of graphical user interface components including image animation, progress bars, and tab strips. It provides details on how progress bars visualize the progress of long operations and how animated GIFs work by compressing multiple images together to create a mini movie-like effect. Steps are outlined for creating an image animation in a program by adding picture boxes, selecting images to add, making all pictures the same size, overlapping them, and toggling their visibility to simulate movement.Filehandling



FilehandlingAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document discusses file handling operations in Visual Basic. It defines a file as a collection of stored data and describes three types of files: sequential access, random access, and binary. It then explains various file handling operations like opening, closing, writing, reading and detecting the end of a file. It provides syntax for performing these operations and describes how to apply these concepts in a sample application for creating, appending to, reading from and writing to a file.Socket



SocketAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
A socket is an endpoint for communication between two programs over a network. It represents a connection between a client program and a server program. The server runs on a specific machine and port, listening for connection requests from clients. Clients know the server's hostname and port number to request a connection. If accepted, the server gets a new socket to communicate with that client while listening for new connections, and the client can use its socket to communicate with the server. Sockets are identified by their paired IP addresses and port numbers to allow multiple connections. The Java Socket class implements sockets to allow platform-independent network communication between Java programs.Ppt of socket



Ppt of socketAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
This document discusses socket programming concepts in Java including server-client communication using sockets, the InetAddress class and its methods like getLocalHost(), getByName(), and getAllByName(), and the Socket and ServerSocket classes. It provides code examples to demonstrate how to use these classes and methods to establish connections between a client and server and exchange data over the network.Introduction to computer graphics



Introduction to computer graphicsAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
Computer graphics refers to creating and manipulating pictures and drawings using a computer. There are two main types: passive graphics which have no interaction and active graphics which allow two-way communication and interaction between the user and hardware. Computer graphics has many applications including user interfaces, scientific visualization, animation, computer aided design, presentation graphics, image processing, and education/training.Introduction to computer graphics



Introduction to computer graphicsAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
Computer graphics refers to creating and manipulating pictures and drawings using a computer. There are two main types: passive graphics which have no interaction and active graphics which allow two-way communication and interaction between the user and hardware. Computer graphics has many applications including user interfaces, scientific visualization, animation, computer aided design, presentation graphics, image processing, and education/training.Introduction to computer graphics



Introduction to computer graphicsAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
Computer graphics refers to creating and manipulating pictures and drawings using a computer. There are two main types: passive graphics which have no interaction and active graphics which allow two-way communication and interaction between the user and hardware. Computer graphics has many applications including user interfaces, scientific visualization, animation, computer aided design, presentation graphics, image processing, and education/training.Internet working



Internet workingAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the internet including its history, components, positive and negative impacts, and future developments. It discusses how the internet began as a US government project and has since grown exponentially. Positive impacts highlighted include improved communication, access to vast information, entertainment options, and e-commerce capabilities. Potential negative impacts discussed are theft of personal information, spamming, virus threats, pornography, and internet addiction. The future of the internet is predicted to include increased cloud computing, improved interfaces, fewer viruses, enhanced online video/TV, and customized online experiences based on personal preferences. Various internet connection types such as dial-up, DSL, cable, wireless, ISDN, leased lines, and internet service providers are alsoReport on browser war



Report on browser warAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Safari and Opera are some of the most popular web browsers currently available. They each have different histories, features and market shares. This document provides an overview of the key details and differences between these major browsers.Report of internet connections



Report of internet connectionsAmandeep Kaur
Ěý
The document discusses various types of internet connections including dial-up, ISDN, DSL, cable, T-carrier, USB, satellite, 3G, 4G and provides details on their speeds and advantages. It compares these connections and discusses the future scope of internet technologies.Modem
- 1. Modems Presented ByPalwinderKaur8/19/2010How Modem Works!!1
- 2. ModemFormal Definition “AĚýmodemĚý(modulator-demodulator) is aĚýdeviceĚýthatĚýmodulatesĚýan analog carrierĚýsignalĚýto encodeĚýdigitalĚýinformation, and alsoĚýdemodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. So it is Data Conversion Equipment”.8/19/2010How Modem Works!!2
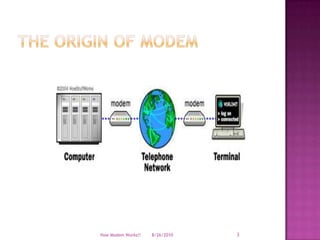
- 3. The Origin of Modem8/19/2010How Modem Works!!3
- 4. Classification of ModemsBased on RangeShort HaulVoice Grade Wide Band8/19/2010How Modem Works!!4
- 5. Continue…Based on Line TypeDialup Leased /Private8/19/2010How Modem Works!!5
- 6. ContinueBased on Operation ModeHalf DuplexFull DuplexSimplex8/19/2010How Modem Works!!6
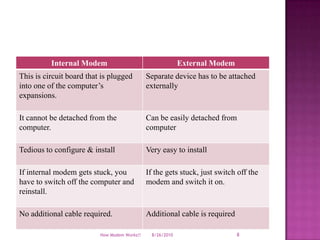
- 7. Types of ModemInternal ModemExternal Modem8/19/2010How Modem Works!!7
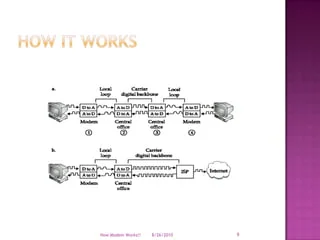
- 9. How it Works8/19/2010How Modem Works!!9
- 11. Speed Variations From 1960 to till now!!300 bps - 1960s through 1983 or so1200 bps - Gained popularity in 1984 and 19852400 bps9600 bps - First appeared in late 1990 and early 199119.2 kilobits per second (Kbps)33.6 Kbps56 Kbps - Became the standard in 1998ADSL, with theoretical maximum of up to 8 megabits per second (Mbps) - Gained popularity in 19998/19/2010How Modem Works!!11
- 12. Future Trends 8/19/2010How Modem Works!!12

