Neurogenic bladder
Download as PPTX, PDF113 likes5,790 views
This document discusses neurogenic bladder, which occurs when there is a lesion or injury affecting the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nerves that disrupt normal micturition. It begins by describing normal bladder function controlled by the brain, pons, and sacral spinal cord through the autonomic and somatic peripheral nervous systems. Pathophysiology of neurogenic bladder can result from brain lesions, spinal cord lesions from acute injury or sacral cord injury, or peripheral nerve lesions. The document outlines types of neurogenic bladder and diagnostic procedures and treatments, which include medications and surgical management.
1 of 34
Downloaded 422 times



























Recommended
Bladder involvement in spine disorders



Bladder involvement in spine disordersJayant Sharma
Ěý
The document discusses bladder function and various types of neurogenic bladder disorders. It covers:
- Normal bladder function and neural control of the bladder
- Different types of neurogenic bladder disorders that can result from brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nerve lesions
- Evaluation and treatment of different disorders, including catheterization options like indwelling, suprapubic, and intermittent cathetersMeralgia Paresthetica 



Meralgia Paresthetica Ade Wijaya
Ěý
Meralgia Paresthetica (MP) is a condition caused by impingement of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, causing numbness and pain along the front of the thigh. It is often caused by entrapment of the nerve under the inguinal ligament. Diagnosis involves history, physical exam including the pelvic compression test, and may include imaging or nerve blocks. Treatment options include removing any underlying causes, medications, physical therapy, injections, or surgery.Neurogenic bladder



Neurogenic bladderDr Junish Singh Bagga
Ěý
This document discusses neurogenic bladder, which occurs due to neurological dysfunction or insult to the nervous system. It describes the anatomy and functions of the normal bladder, as well as the different types of neurogenic bladder based on the level of neurological insult (e.g. suprapontine, pontine, spinal). Treatment options are discussed, including behavioral therapies, medications, injections, surgeries and procedures like clean intermittent catheterization and sacral anterior root stimulation. The goals of bladder management and treatment considerations for different types of neurogenic bladder are also summarized.Spinal dysraphism and its management



Spinal dysraphism and its managementMukhtar Khan
Ěý
a comprehensive presentation on the subject of spinal dysraphism and spina bifida and its neurosurgical management as well as the management of its various other typesNeurogenic bladder



Neurogenic bladderYouttam Laudari
Ěý
This document discusses neurogenic bladder and its management. It begins by outlining the physiology of normal bladder control and describes various types of neurogenic bladder dysfunction that can occur depending on the level of spinal cord or brain injury, including detrusor hyperreflexia, detrusor sphincter dyssynergia, and detrusor areflexia. Diagnostic investigations and treatments are then discussed, including medications, catheterization, neuromodulation, and surgeries. The goal of treatment is to balance bladder emptying and continence for each type of neurogenic bladder dysfunction.Tuberculosis of hip



Tuberculosis of hipHardik Pawar
Ěý
Tuberculosis of the hip is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. It typically affects people aged 20-30 years old. The infection spreads hematogenously from a primary focus and causes destruction of bone and joints over several years. Clinical features include limping, decreased range of motion, and deformities in advanced cases. Imaging shows osteopenia, joint space narrowing, and bone erosion. Treatment involves chemotherapy for at least 6-9 months along with local measures like joint aspiration and traction. Surgery may be needed for debridement, arthrodesis, or arthroplasty in advanced cases.Posterior Spine Fixation



Posterior Spine FixationGhazwan Bayaty
Ěý
The document discusses posterior spine fixation using pedicle screw instrumentation. It provides details on the anatomy of the posterior spine elements and pedicles. Pedicle screw fixation provides a rigid construct that can increase fusion rates and reduce pain. Precise screw placement is important to avoid neurological or vascular injury. Proper preoperative planning and technique are essential to achieve a stable construct and reduce complications. Lateral mass screws



Lateral mass screwsProf. Dr. Mohamed Mohi Eldin
Ěý
Lateral mass screw fixation is a widely used technique for cervical spine fixation that has been used for over 25 years. It is indicated for trauma, tumors, deformities, and degenerative conditions. Important factors for determining the surgical approach include the spinal alignment, rigidity of deformity, number of levels involved, presence of subluxation, patient's medical status, and presence of axial neck pain. Lateral mass screws are directed laterally from the lateral mass to avoid injury to the spinal nerve, vertebral artery, and dorsal ramus. Studies show high fusion success and stability with lateral mass screws and relatively low complication rates.Peripheral Nerve Repair



Peripheral Nerve Repairwashingtonortho
Ěý
This document discusses peripheral nerve repair. It indicates that direct repair or nerve grafting after nerve transection offers the only chance for functional recovery. Quick reconnection of the nerve within 18 months leads to better results. Isolated nerve lacerations should be repaired within 1-2 weeks. Classification systems like Seddon describe the severity of nerve injuries. Diagnosis involves tests like Tinel's sign and EMG. Repair involves freshening the nerve ends and suturing them together tension-free. Nerve grafts or tubes can bridge gaps when direct repair is not possible.Foot drop



Foot dropSupraja Avula
Ěý
Foot drop is the inability to lift the front part of the foot. It can be caused by injuries or conditions that damage the common peroneal nerve. Symptoms include difficulty lifting the foot and dragging the toes. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include bracing, nerve stimulation, tendon transfers, or joint fusions. The goal is to improve mobility and gait.Physeal injuries



Physeal injuriesAsi-oqua Bassey
Ěý
A broad overview of injuries to the physis. It would be of particular interest/use to trainee Orthopaedic surgeons.Cubitus varus deformity



Cubitus varus deformityramachandra reddy
Ěý
Cubitus varus, or gunstock deformity, is caused by malunion of supracondylar fractures and results in the forearm being deviated inward at the elbow with loss of the carrying angle. It is a triplanar deformity involving varus, hyperextension, and internal rotation. Treatment options include observation for young children, hemiepiphysiodesis to alter growth, and corrective osteotomy. The lateral closing wedge osteotomy is commonly used to safely correct the varus deformity through removal of a lateral wedge. Other techniques include medial opening wedge, oblique, dome, and step-cut osteotomies. Postoperative management focuses on immobilizing the arm in extensionCauda Equina Syndrome 



Cauda Equina Syndrome Ade Wijaya
Ěý
Cauda Equina Syndrome is a condition involving the bundle of nerves originating from the lower end of the spinal cord. It can result from central disc herniations, spinal tumors, trauma, or other causes. Patients may experience LMN signs, saddle anesthesia, gait ataxia, and sexual/bladder/bowel dysfunction. MRI is used for diagnosis. Treatment requires immediate neurosurgical consultation and decompression, as delays can lead to permanent deficits.Spinal dysraphism



Spinal dysraphismairwave12
Ěý
This document discusses spinal dysraphism, which refers to congenital anomalies resulting from failed fusion of the dorsal spinal elements. It describes different types including spina bifida occulta, meningocele, myelomeningocele, myelocystocele, and lipomeningocele. Meningocele involves a mass composed of CSF, meninges, and skin, but no neural elements. Myelomeningocele contains neural tissue and is usually associated with neurological deficits. Myelocystocele and lipomeningocele involve fatty tissue herniating through spinal defects. Radiological imaging plays an important role in diagnosis, with ultrasound, CT, MRI, and myelography discussed.Madelung deformity



Madelung deformityDr. Anurag Mittal
Ěý
Madelung deformity is an abnormality of the palmar ulnar part of the distal radial physis in which progressive ulnar and volar tilt develops at the distal radial articular surface, with dorsal subluxation of the distal ulna.Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis



Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosisvinod naneria
Ěý
This document discusses diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), also known as Forestier's disease. It most commonly affects the elderly, especially between the ages of 60-70. Key features include bone proliferation at sites of tendon and ligament insertion, especially along the spine. Pathology involves calcification and ossification of spinal ligaments. Extra spinal features can include enthesopathy of bones like the iliac crest and greater trochanters. DISH is characterized by flowing ossification along at least four contiguous vertebrae that preserves disc spaces and can result in ankylosis.Distal radius fractures



Distal radius fracturesAsi-oqua Bassey
Ěý
Distal radius fractures are the most common fractures seen in orthopaedic trauma. They typically occur due to falls in older populations and can be classified based on the degree of articular involvement and instability. Treatment depends on fracture pattern but generally involves closed reduction and casting for non-displaced fractures, while more displaced or unstable fractures may require operative fixation to restore anatomy and maximize function. Rehabilitation focuses on early range of motion exercises and recovery of grip strength.sudecks osteodystrophy



sudecks osteodystrophyBipulBorthakur
Ěý
This document discusses Sudeck's osteodystrophy, also known as complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). It defines CRPS as a chronic progressive disease characterized by disproportionate regional pain and abnormalities in sensory, motor, and autonomic nervous system function. It describes three stages of CRPS based on dystrophic and atrophic changes. Treatment involves prevention, non-operative approaches like physical therapy, nerve stimulation, nerve blockade, and in some cases surgical sympathectomy. The goal is to reduce pain and limit progression of the chronic condition.Urinary bladder



Urinary bladderNeurologyKota
Ěý
This document summarizes the anatomy and physiology of the urinary bladder and urinary sphincters. It describes the neural pathways that control bladder filling and emptying from the cortical and subcortical areas down to the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. It then discusses various types of neurogenic bladder disorders that can result from lesions or injuries in different parts of the neural pathways.Baker's cyst



Baker's cystSiwaporn Khureerung
Ěý
A Baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled bulge behind the knee caused by an escape of synovial fluid from the knee joint. It is most common in children aged 4-7 and adults aged 35-70. A primary cyst develops spontaneously while a secondary cyst is usually caused by an underlying knee problem like arthritis. Symptoms may include swelling, pain, and tightness behind the knee. Ultrasound and MRI scans can confirm the diagnosis. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying knee issue through rest, ice, compression, elevation, physiotherapy, injections, or occasionally surgery.Cervical radiculopathy.pptx



Cervical radiculopathy.pptxGopalSedain
Ěý
Cervical radiculopathy is pain caused by compression or irritation of cervical nerve roots. It commonly affects the C7 and C6 nerve roots and symptoms include pain and sensory or motor changes in the upper extremities. While most cases resolve within 3 months with conservative treatment like NSAIDs, oral steroids, or gabapentin, surgery may be considered for worsening symptoms. Minimally invasive posterior cervical foraminotomy has been shown to effectively treat radiculopathy with low complication rates and reduced need for further surgery compared to other options like anterior cervical discectomy and fusion.Dr.S.Senthil Sailesh-functional cast bracing,PTBcast,sarmiento principle



Dr.S.Senthil Sailesh-functional cast bracing,PTBcast,sarmiento principleSenthil sailesh
Ěý
The document discusses functional casting and bracing techniques used to treat fractures while allowing restricted movement. It describes the principles of functional casting which include maintaining stability and reduction while promoting blood flow and muscle contraction to encourage healing. Specific casts for treating fractures of the humerus, tibia, femur and hip are outlined, including the Sarmiento cast and hip spica cast. The timing, positioning and complications of different casts are summarized. Functional casting aims to continue function during fracture healing to accelerate rehabilitation.Full Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy 



Full Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Reza Aminnejad
Ěý
Full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy is an innovative, minimally invasive alternative to microdiscectomy for patients with symptomatic lumbar disc herniations. IELD and TELD offer two complementary surgical corridors to spinal pathology and allow for treatment of the vast majority of lumbar disc herniations. There is level one evidence suggesting that full-endoscopic spine surgery results in similar functional outcomes compared with microsurgical technique, and has a favorable rate of perioperative complications.Dupuytrens Contracture



Dupuytrens ContractureApoorv Jain
Ěý
Apply gentle pressure proximally
Surgeon: Check distal pulses and capillary refill
If no improvement:
ď‚ž Consider temporary arteriotomy or venous shunt
ď‚ž Delay closure and observe
ď‚ž Flap or graft may be neededMalunited Distal End Radius Fractures



Malunited Distal End Radius FracturesDr. Nitish Khosla
Ěý
VERY IMPORTANT TOPIC AS PER PRACTICAL AND ACEDEMIC POINT OF VIEW. ALL THE ASPECTS OF THE TOPIC ARE COVERED IN THESE SLIDES... ENJOYSpondylolisthesis 



Spondylolisthesis Mahak Jain
Ěý
Dr. Mahak Jain presented on spondylolisthesis. Key points include:
1) Spondylolisthesis is the forward translation of one vertebra on another, commonly caused by defects in the pars interarticularis known as spondylolysis.
2) It is classified based on etiology, with dysplastic, isthmic, degenerative, traumatic, and pathological types.
3) Treatment depends on factors like grade, symptoms, and etiology, ranging from conservative care to surgical options like decompression, fusion, and instrumentation.
4) Studies show surgery with fusion has better outcomes for pain and function than nonsurgical treatment or decompression alone for degenerativeCervical Disc Replacement



Cervical Disc Replacementfathi neana
Ěý
Spine Arthroplasty or Artificial Disc Replacement is a new term which is used more and more in international scientific meetings and publications starts to dominate the scenery. The last three decades have been the most revolutionary in the history of spine treatment. The 80’s were dominated by the development of modern implants for internal segmental fixation such as pedicle screw systems and others. In the 90’s „Mini-open“ as well as „closed“ endoscopic techniques replaced the majority of conventional surgical approaches . Progress in biological and biochemical research seems to open new perspectives in fusion technology. We must not forget that bony fusion of a functional spinal unit is non physiological and it is associated with a variety of proven and (yet) unproven undesired effects and sequelae. At the beginning of this century, the progress in implant technology open a new dimension for spinal reconstructive non-fusion surgery. A variety of new implants are used today for: nucleus pulposus, total disc replacement, dynamic posterior reconstruction systems, posterior shock absorbers and injectable intradiscal materials. Cervical Disc Replacement is a Motion preserving surgery, Treat painful / pathologic process while restoring/maintaining motion, Decreased stress in adjacent levels, May prevent problems of adjacent segment disease, secondary surgery, pseudoarthrosis.
Comparing arthroplasty (ACDR) vs fusion (ACDF) most of the studies are in favour of (ACDR) because of, Higher neurologic success, Earlier return to work, Degrees of maintained motion, Adjacent Segment Degeneration 5 yrs, Statistically significant better scores (NDI, Arm pain, VAS, and SF-36 scores), lower revision rate (Reoperation rate for ACDF – 11.3% vs 2.9% ACDR)
Treatment of tb spine



Treatment of tb spineramachandra reddy
Ěý
This document discusses the history and treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. It can be summarized in 3 sentences:
The treatment of tuberculosis of the spine has evolved from purely conservative approaches like immobilization to include chemotherapy and surgical interventions like decompression and fusion. Current guidelines recommend initial treatment with anti-tubercular drugs and surgery only for cases with neurological deficits or failure to improve. Ongoing monitoring is important to detect treatment failure or drug resistance requiring modified treatment plans.PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...



PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...ABHAY INSTITUTION
Ěý
Personality theory is a collection of ideas that explain how a person's personality develops and how it affects their behavior. It also seeks to understand how people react to situations, and how their personality impacts their relationships.
Key aspects of personality theory
Personality traits: The characteristics that make up a person's personality.
Personality development: How a person's personality develops over time.
Personality disorders: How personality theories can be used to study personality disorders.
Personality and environment: How a person's personality is influenced by their environment. More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Peripheral Nerve Repair



Peripheral Nerve Repairwashingtonortho
Ěý
This document discusses peripheral nerve repair. It indicates that direct repair or nerve grafting after nerve transection offers the only chance for functional recovery. Quick reconnection of the nerve within 18 months leads to better results. Isolated nerve lacerations should be repaired within 1-2 weeks. Classification systems like Seddon describe the severity of nerve injuries. Diagnosis involves tests like Tinel's sign and EMG. Repair involves freshening the nerve ends and suturing them together tension-free. Nerve grafts or tubes can bridge gaps when direct repair is not possible.Foot drop



Foot dropSupraja Avula
Ěý
Foot drop is the inability to lift the front part of the foot. It can be caused by injuries or conditions that damage the common peroneal nerve. Symptoms include difficulty lifting the foot and dragging the toes. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include bracing, nerve stimulation, tendon transfers, or joint fusions. The goal is to improve mobility and gait.Physeal injuries



Physeal injuriesAsi-oqua Bassey
Ěý
A broad overview of injuries to the physis. It would be of particular interest/use to trainee Orthopaedic surgeons.Cubitus varus deformity



Cubitus varus deformityramachandra reddy
Ěý
Cubitus varus, or gunstock deformity, is caused by malunion of supracondylar fractures and results in the forearm being deviated inward at the elbow with loss of the carrying angle. It is a triplanar deformity involving varus, hyperextension, and internal rotation. Treatment options include observation for young children, hemiepiphysiodesis to alter growth, and corrective osteotomy. The lateral closing wedge osteotomy is commonly used to safely correct the varus deformity through removal of a lateral wedge. Other techniques include medial opening wedge, oblique, dome, and step-cut osteotomies. Postoperative management focuses on immobilizing the arm in extensionCauda Equina Syndrome 



Cauda Equina Syndrome Ade Wijaya
Ěý
Cauda Equina Syndrome is a condition involving the bundle of nerves originating from the lower end of the spinal cord. It can result from central disc herniations, spinal tumors, trauma, or other causes. Patients may experience LMN signs, saddle anesthesia, gait ataxia, and sexual/bladder/bowel dysfunction. MRI is used for diagnosis. Treatment requires immediate neurosurgical consultation and decompression, as delays can lead to permanent deficits.Spinal dysraphism



Spinal dysraphismairwave12
Ěý
This document discusses spinal dysraphism, which refers to congenital anomalies resulting from failed fusion of the dorsal spinal elements. It describes different types including spina bifida occulta, meningocele, myelomeningocele, myelocystocele, and lipomeningocele. Meningocele involves a mass composed of CSF, meninges, and skin, but no neural elements. Myelomeningocele contains neural tissue and is usually associated with neurological deficits. Myelocystocele and lipomeningocele involve fatty tissue herniating through spinal defects. Radiological imaging plays an important role in diagnosis, with ultrasound, CT, MRI, and myelography discussed.Madelung deformity



Madelung deformityDr. Anurag Mittal
Ěý
Madelung deformity is an abnormality of the palmar ulnar part of the distal radial physis in which progressive ulnar and volar tilt develops at the distal radial articular surface, with dorsal subluxation of the distal ulna.Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis



Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosisvinod naneria
Ěý
This document discusses diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), also known as Forestier's disease. It most commonly affects the elderly, especially between the ages of 60-70. Key features include bone proliferation at sites of tendon and ligament insertion, especially along the spine. Pathology involves calcification and ossification of spinal ligaments. Extra spinal features can include enthesopathy of bones like the iliac crest and greater trochanters. DISH is characterized by flowing ossification along at least four contiguous vertebrae that preserves disc spaces and can result in ankylosis.Distal radius fractures



Distal radius fracturesAsi-oqua Bassey
Ěý
Distal radius fractures are the most common fractures seen in orthopaedic trauma. They typically occur due to falls in older populations and can be classified based on the degree of articular involvement and instability. Treatment depends on fracture pattern but generally involves closed reduction and casting for non-displaced fractures, while more displaced or unstable fractures may require operative fixation to restore anatomy and maximize function. Rehabilitation focuses on early range of motion exercises and recovery of grip strength.sudecks osteodystrophy



sudecks osteodystrophyBipulBorthakur
Ěý
This document discusses Sudeck's osteodystrophy, also known as complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). It defines CRPS as a chronic progressive disease characterized by disproportionate regional pain and abnormalities in sensory, motor, and autonomic nervous system function. It describes three stages of CRPS based on dystrophic and atrophic changes. Treatment involves prevention, non-operative approaches like physical therapy, nerve stimulation, nerve blockade, and in some cases surgical sympathectomy. The goal is to reduce pain and limit progression of the chronic condition.Urinary bladder



Urinary bladderNeurologyKota
Ěý
This document summarizes the anatomy and physiology of the urinary bladder and urinary sphincters. It describes the neural pathways that control bladder filling and emptying from the cortical and subcortical areas down to the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. It then discusses various types of neurogenic bladder disorders that can result from lesions or injuries in different parts of the neural pathways.Baker's cyst



Baker's cystSiwaporn Khureerung
Ěý
A Baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled bulge behind the knee caused by an escape of synovial fluid from the knee joint. It is most common in children aged 4-7 and adults aged 35-70. A primary cyst develops spontaneously while a secondary cyst is usually caused by an underlying knee problem like arthritis. Symptoms may include swelling, pain, and tightness behind the knee. Ultrasound and MRI scans can confirm the diagnosis. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying knee issue through rest, ice, compression, elevation, physiotherapy, injections, or occasionally surgery.Cervical radiculopathy.pptx



Cervical radiculopathy.pptxGopalSedain
Ěý
Cervical radiculopathy is pain caused by compression or irritation of cervical nerve roots. It commonly affects the C7 and C6 nerve roots and symptoms include pain and sensory or motor changes in the upper extremities. While most cases resolve within 3 months with conservative treatment like NSAIDs, oral steroids, or gabapentin, surgery may be considered for worsening symptoms. Minimally invasive posterior cervical foraminotomy has been shown to effectively treat radiculopathy with low complication rates and reduced need for further surgery compared to other options like anterior cervical discectomy and fusion.Dr.S.Senthil Sailesh-functional cast bracing,PTBcast,sarmiento principle



Dr.S.Senthil Sailesh-functional cast bracing,PTBcast,sarmiento principleSenthil sailesh
Ěý
The document discusses functional casting and bracing techniques used to treat fractures while allowing restricted movement. It describes the principles of functional casting which include maintaining stability and reduction while promoting blood flow and muscle contraction to encourage healing. Specific casts for treating fractures of the humerus, tibia, femur and hip are outlined, including the Sarmiento cast and hip spica cast. The timing, positioning and complications of different casts are summarized. Functional casting aims to continue function during fracture healing to accelerate rehabilitation.Full Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy 



Full Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Reza Aminnejad
Ěý
Full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy is an innovative, minimally invasive alternative to microdiscectomy for patients with symptomatic lumbar disc herniations. IELD and TELD offer two complementary surgical corridors to spinal pathology and allow for treatment of the vast majority of lumbar disc herniations. There is level one evidence suggesting that full-endoscopic spine surgery results in similar functional outcomes compared with microsurgical technique, and has a favorable rate of perioperative complications.Dupuytrens Contracture



Dupuytrens ContractureApoorv Jain
Ěý
Apply gentle pressure proximally
Surgeon: Check distal pulses and capillary refill
If no improvement:
ď‚ž Consider temporary arteriotomy or venous shunt
ď‚ž Delay closure and observe
ď‚ž Flap or graft may be neededMalunited Distal End Radius Fractures



Malunited Distal End Radius FracturesDr. Nitish Khosla
Ěý
VERY IMPORTANT TOPIC AS PER PRACTICAL AND ACEDEMIC POINT OF VIEW. ALL THE ASPECTS OF THE TOPIC ARE COVERED IN THESE SLIDES... ENJOYSpondylolisthesis 



Spondylolisthesis Mahak Jain
Ěý
Dr. Mahak Jain presented on spondylolisthesis. Key points include:
1) Spondylolisthesis is the forward translation of one vertebra on another, commonly caused by defects in the pars interarticularis known as spondylolysis.
2) It is classified based on etiology, with dysplastic, isthmic, degenerative, traumatic, and pathological types.
3) Treatment depends on factors like grade, symptoms, and etiology, ranging from conservative care to surgical options like decompression, fusion, and instrumentation.
4) Studies show surgery with fusion has better outcomes for pain and function than nonsurgical treatment or decompression alone for degenerativeCervical Disc Replacement



Cervical Disc Replacementfathi neana
Ěý
Spine Arthroplasty or Artificial Disc Replacement is a new term which is used more and more in international scientific meetings and publications starts to dominate the scenery. The last three decades have been the most revolutionary in the history of spine treatment. The 80’s were dominated by the development of modern implants for internal segmental fixation such as pedicle screw systems and others. In the 90’s „Mini-open“ as well as „closed“ endoscopic techniques replaced the majority of conventional surgical approaches . Progress in biological and biochemical research seems to open new perspectives in fusion technology. We must not forget that bony fusion of a functional spinal unit is non physiological and it is associated with a variety of proven and (yet) unproven undesired effects and sequelae. At the beginning of this century, the progress in implant technology open a new dimension for spinal reconstructive non-fusion surgery. A variety of new implants are used today for: nucleus pulposus, total disc replacement, dynamic posterior reconstruction systems, posterior shock absorbers and injectable intradiscal materials. Cervical Disc Replacement is a Motion preserving surgery, Treat painful / pathologic process while restoring/maintaining motion, Decreased stress in adjacent levels, May prevent problems of adjacent segment disease, secondary surgery, pseudoarthrosis.
Comparing arthroplasty (ACDR) vs fusion (ACDF) most of the studies are in favour of (ACDR) because of, Higher neurologic success, Earlier return to work, Degrees of maintained motion, Adjacent Segment Degeneration 5 yrs, Statistically significant better scores (NDI, Arm pain, VAS, and SF-36 scores), lower revision rate (Reoperation rate for ACDF – 11.3% vs 2.9% ACDR)
Treatment of tb spine



Treatment of tb spineramachandra reddy
Ěý
This document discusses the history and treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. It can be summarized in 3 sentences:
The treatment of tuberculosis of the spine has evolved from purely conservative approaches like immobilization to include chemotherapy and surgical interventions like decompression and fusion. Current guidelines recommend initial treatment with anti-tubercular drugs and surgery only for cases with neurological deficits or failure to improve. Ongoing monitoring is important to detect treatment failure or drug resistance requiring modified treatment plans.Recently uploaded (20)
PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...



PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT & DEFENSE MECHANISMS.pptxPersonality and environment:...ABHAY INSTITUTION
Ěý
Personality theory is a collection of ideas that explain how a person's personality develops and how it affects their behavior. It also seeks to understand how people react to situations, and how their personality impacts their relationships.
Key aspects of personality theory
Personality traits: The characteristics that make up a person's personality.
Personality development: How a person's personality develops over time.
Personality disorders: How personality theories can be used to study personality disorders.
Personality and environment: How a person's personality is influenced by their environment. Public health 101 x health disinformation.pptx



Public health 101 x health disinformation.pptxTina Purnat
Ěý
Public health approaches to health disinformation E Book Daniya Sanal.pdf#healthy books.com



E Book Daniya Sanal.pdf#healthy books.comDaniyaSanal
Ěý
good health for good life good heart for safe and secure life..the good quality of life will makes good and #haelthy vibes...Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples & Clinical Significance



Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples & Clinical SignificanceSumeetSharma591398
Ěý
This presentation explains the crucial role of enzyme induction and inhibition in drug metabolism. It covers:
✔️ Mechanisms of enzyme regulation in the liver
✔️ Examples of enzyme inducers (Rifampin, Carbamazepine) and inhibitors (Ketoconazole, Grapefruit juice)
✔️ Clinical significance of drug interactions affecting efficacy and toxicity
✔️ Factors like genetics, age, diet, and disease influencing enzyme activity
Ideal for pharmacy, pharmacology, and medical students, this presentation helps in understanding drug metabolism and dosage adjustments for safe medication use.Digestive Powerhouses: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas for Nursing Students



Digestive Powerhouses: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas for Nursing StudentsViresh Mahajani
Ěý
This educational PowerPoint presentation is designed to equip GNM students with a solid understanding of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. It explores the anatomical structures, physiological processes, and clinical significance of these vital organs. Key topics include:
Liver functions: detoxification, metabolism, and bile synthesis.
Gallbladder: bile storage and release.
Pancreas: exocrine and endocrine functions, including digestive enzyme and hormone production. This presentation is ideal for GNM students seeking a clear and concise review of these important digestive system components."Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples, and Clinical Significance



Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples, and Clinical SignificanceSumeetSharma591398
Ěý
This presentation explains the concepts of enzyme induction and enzyme inhibition in drug metabolism. It covers the mechanisms, examples, clinical significance, and factors affecting enzyme activity, with a focus on CYP450 enzymes. Learn how these processes impact drug interactions, efficacy, and toxicity. Essential for pharmacy, pharmacology, and medical students.Dr. Jaymee Shell’s Perspective on COVID-19



Dr. Jaymee Shell’s Perspective on COVID-19Jaymee Shell
Ěý
Dr. Jaymee Shell views the COVID-19 pandemic as both a crisis that exposed weaknesses and an opportunity to build stronger systems. She emphasizes that the pandemic revealed critical healthcare inequities while demonstrating the power of collaboration and adaptability.
Shell highlights that organizations with gender-diverse executive teams are 25% more likely to experience above-average profitability, positioning diversity as a business necessity rather than just a moral imperative. She notes that the pandemic disproportionately affected women of color, with one in three women considering leaving or downshifting their careers.
To combat inequality, Shell recommends implementing flexible work policies, establishing clear metrics for diversity in leadership, creating structured virtual collaboration spaces, and developing comprehensive wellness programs. For healthcare providers specifically, she advocates for multilingual communication systems, mobile health units, telehealth services with alternatives for those lacking internet access, and cultural competency training.
Shell emphasizes the importance of mental health support through culturally appropriate resources, employee assistance programs, and regular check-ins. She calls for diverse leadership teams that reflect the communities they serve and community-centered care models that address social determinants of health.
In her words: "The COVID-19 pandemic didn't create healthcare inequalities – it illuminated them." She urges building systems that reach every community and provide dignified care to all.Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptx



Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptxKafrELShiekh University
Ěý
Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ěý
Co-Chairs and Presenters, Gerald Appel, MD, and Dana V. Rizk, MD, discuss kidney disease in this CME activity titled “Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Pathway Therapies.” For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/48UHvVM. CME credit will be available until February 25, 2026.Rabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptx



Rabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptxWahid Husein
Ěý
A decade of rabies control programmes in Bali with support from FAO ECTAD Indonesia with Mass Dog Vaccination, Integrated Bite Case Management, Dog Population Management, and Risk Communication as the backbone of the programmesSyncope in dentistry.pptx



Syncope in dentistry.pptxDr Kingshika Joylin
Ěý
This presentation provides an overview of syncope, a common medical emergency in dental practice. Created during my internship, this presentation aims to educate dental students on the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and management of syncope with a focus on dental specific considerations.
Understanding Trauma: Causes, Effects, and Healing Strategies



Understanding Trauma: Causes, Effects, and Healing StrategiesBecoming Institute
Ěý
Trauma affects millions of people worldwide, shaping their emotional, psychological, and even physical well-being. This presentation delves into the root causes of trauma, its profound effects on mental health, and practical strategies for healing. Whether you are seeking to understand your own experiences or support others on their journey, this guide offers insights into coping mechanisms, therapy approaches, and self-care techniques. Explore how trauma impacts the brain, body, and relationships, and discover pathways to resilience and recovery.
Perfect for mental health advocates, therapists, educators, and anyone looking to foster emotional well-being. Watch now and take the first step toward healing!Research Problems - Nursing Research....



Research Problems - Nursing Research....Dr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
Ěý
Research Problems - Nursing ResearchIntroduction-to-the-PuroKalusugan-InitiativeCHD12.pptx



Introduction-to-the-PuroKalusugan-InitiativeCHD12.pptxhepopolomolok2023
Ěý
An introduction to the PuroKalusugan InitiativeDistribution of Drugs – Plasma Protein Binding and Blood-Brain Barrier



Distribution of Drugs – Plasma Protein Binding and Blood-Brain BarrierSumeetSharma591398
Ěý
This presentation provides a detailed overview of drug distribution, focusing on plasma protein binding and the blood-brain barrier (BBB). It explains the factors affecting drug distribution, the role of plasma proteins in drug binding, and how drugs penetrate the BBB. Key topics include the significance of protein-bound vs. free drug concentration, drug interactions, and strategies to enhance drug permeability across the BBB. Ideal for students, researchers, and healthcare professionals in pharmacology and drug development.IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINE



IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINERelianceNwosu
Ěý
This presentation emphasizes the role of immunodiagnostics and Immunotherapy. Powerpoint presentation about the influence of cultural and helath belief sys...



Powerpoint presentation about the influence of cultural and helath belief sys...JessakinNaron
Ěý
study about the influence of cultural and health belief system on health care practiceCOLD PCR application used in breast cancer research



COLD PCR application used in breast cancer researchSona Thesis Consultancy
Ěý
COLD-PCR is a modified version of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique used to selectively amplify and enrich rare or minority DNA sequences, such as mutations or genetic variations. Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples, and Clinical Significance



Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples, and Clinical SignificanceSumeetSharma591398
Ěý
Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ěý
Neurogenic bladder
- 1. NEUROGENIC BLADDER DR.TARUN KUMAR BADAM PG DNB ORTHO INSTITUTE OF ORTHOPEDIC RESEARCH AND ACCIDENT SURGERY (IORAS)
- 4. BRAIN
- 5. PONS
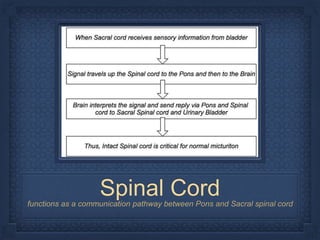
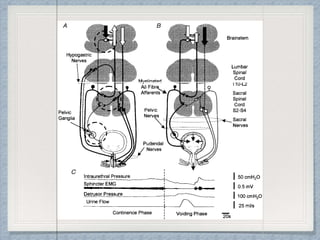
- 6. Spinal Cordfunctions as a communication pathway between Pons and Sacral spinal cord
- 10. SOMATIC PNS
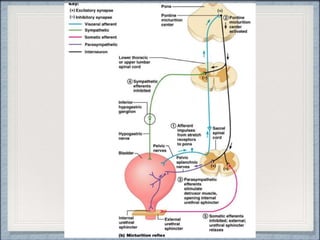
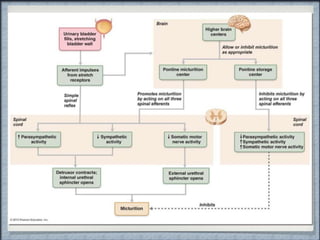
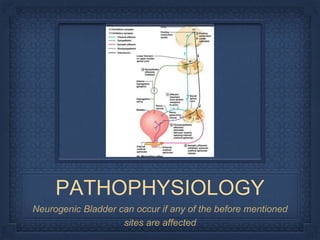
- 14. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Neurogenic Bladder can occur if any of the before mentioned sites are affected
- 15. BRAIN LESIONS
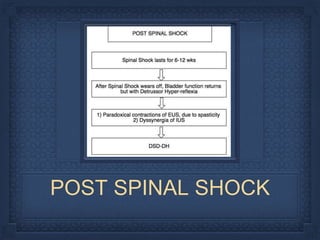
- 18. ACUTE SPINAL CORD INJURY
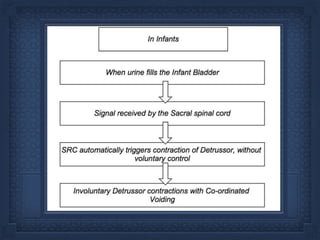
- 23. NEUROGENIC BLADDER malfunctioning of Bladder due to Neurologic dysfunction
- 24. TYPES
- 28. MANAGEMENT
- 29. MEDICATIONS
- 34. THANK YOU


