New china
- 3. YOU WILL KNOW ABOUT CHINA‟S  Basic information  GDP in Education  Literacy rate  Compulsory education  Grades of education  Examination system analysis  Administrative structure  Teacher education  Admission test
- 4. INTRODUCTION  name: People's Republic of China ,  Region: East Asia.  It is the world's most populous country.  Population: 1.37 billion  capital city: Beijing.  Area: 9,600,000 sq km.  Language: Chinese
- 5.  main religion and beliefs include atheist, Confucianism, Buddhism, Islam(ov er 22 million)  Its currency is known as Yuan.  It is consisted on 23 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 municipalities and 2 special administrative regions.  It came into existence on October 1, 1949.
- 6. STUDENT ENROLLED  There were over 103 million students enrolled in primary schools in 2008.  while the total enrollment for students in junior secondary schools (including vocational schools) totaled over 55 million.  The number of students enrolled in general academic senior secondary schools were 16 million in 2002, and by 2008, that total increased to just over 24 million.
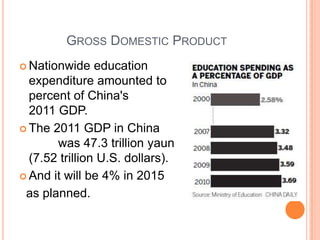
- 7. GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT  Nationwide education expenditure amounted to percent of China's 2011 GDP.  The 2011 GDP in China was 47.3 trillion yaun (7.52 trillion U.S. dollars).  And it will be 4% in 2015 as planned. 3.93
- 8. PAKISTAN VS CHINA Where China‟s GDP is 3.93%. Pakistan‟s GDP is just 2% of the total expenditures.  China‟s budget was 324.86 billion.  and Pakistan‟s budget was 2.463 Trillion PKR (26.7 Billion USD).
- 9. LITERACY RATE  China‟s literacy rate is 94.2%.  Male literacy rate is 96.7%  female literacy rate is 91.5%.  Criteria is that individual of age 15 can read and write.  Youth literacy rate is the percentage of people ages 15-24 that can read, write and understand a simple statement on their everyday life.
- 10. COMPARISON:  As compared to China Pakistan‟s Literacy rate is not so acceptable. Because  Male literacy rate in china is 96.7%, Pakistan‟s just 69%.  Female literacy rate in China is 91.5% and in Pakistan it is 45%.  And the total literate rate of China is 94.2% and in Pakistan it is 57%.
- 11. COMPULSORY EDUCATION  The Law on Nine-Year Compulsory Education. it took effect on July 1, 1986, established requirements and deadlines for attaining universal education tailored to local conditions and guaranteed school-age children the right to receive at least nine years of education (six-year primary education and three years secondary education).
- 12. COMPULSORY EDUCATION Education is free and compulsory for 9 years in China, split between Primary and Junior middle school at the age of 6-15. many children start their schooling at a nursery school (called Kindergarten in China) as early as 2 years old.  2-6: Kindergarten 6-12: Primary school (compulsory) 12-15: Junior middle school (compulsory) 15-18: Senior high school (middle school) or Vocational school 18-22: University or college 
- 13. COMPARISON: 9 year compulsory education vs  no compulsory education
- 14. AGE DISTRIBUTION  age 3-5 Pre-school or play group, kindergarten etc  6-10 Primary education till 1 grade to five  11-14 Elementary education till 6 grade to 8th grade  15-16 Secondary education grade 9th & 10th  17-18 Higher secondary or intermediate grade 11th & 12  8-22 Higher education
- 15. GRADES OF EDUCATION Education in China is divided into four categories  basic education  secondary vocational-technical education  regular higher education  adult education.
- 16. Basic education:  Kindergarten  Primary Primary schooling usually lasts six years.  secondary Junior secondary Senior secondary with each usually lasting three years.
- 17. SECONDARY VOCATIONAL-TECHNICAL EDUCATION:  Secondary vocational training provide short-term vocational programs of finance and economics, physical education, and arts.  Technical training provide medium-level skilled workers, farmers, as well as managerial and technical personnel.  Both have 3 or 4 years programs
- 18. Regular Higher Education:  Higher education is provided by institutions of various types including general universities, technical universities, specialized institutions and teacher-training colleges.  Regular higher Education provide graduate courses like the bachelor's degree, and postgraduate programs like the master's degree, and the doctorate degree.
- 19. Adult Education:  Adult education provide non-formal programs including literacy education and vocational and technical training. Like staff , correspondence, workers for primary school and secondary school and universities.  The agencies responsible for China's adult education include various ministries or commissions under the State Council, educational departments of provinces, business or industrial departments at different levels, such as machinery electronics, light industry, coalmining, metallurgy, railways, communication, agricult ure and forestry..
- 20. Examination System Analysis Semester system is used in the examination system. Basic education:  Primary:  The academic year is divided into two semesters, each consisting of 19 weeks, with a total of 38 weeks of instruction for the year.
- 21. Secondary:  The academic year is divided into two semesters for junior middle school and senior middle school consists of 39 or 40 weeks of instruction, with one week in reserve. Vocational and Technical education:  Semester system is used and each year has two semester. It includes 39or 40 weeks. Adult education:  Semester system is used and each year have 2 semester. It includes 39 or 40 weeks.
- 22. HIGHER EDUCATION: Semester system is used in colleges and universities.  Three semester system dividing the academic year. 1. Fall term (September to December) 2. Winter term (January to April) 3. summer term (May to August) 
- 23. IN PAKISTAN  At school level there are usually 3 terms or semester in a year.  Then at college it becomes annual system.  Further at university level it is divided into both. Semester system in some courses and annual examination at others.
- 24. Administrative structure      Ministry of education Education commission bureau of higher education of provinces Education commission at city level Education commission at county level Education commission at township level
- 25. Ministry of education:  Universities are under the ministry of education Education commission of bureau of higher education of provinces:  higher education  Primary and secondary education  Vocational education  Adult education
- 26. Education commission at city level:  Key primary and secondary schools  Secondary vocational schools  Adult schools Education commission at county level:  Primary and secondary schools  Rural vocational schools Education commission at township level:  Preschools  Primary and secondary schools  Rural vocational schools
- 27. PAKISTAN‟S ADMIN STRUCTURE: Education at higher level is conducted by HEC(higher education commission).  Then secondary and higher secondary education is conducted by BISE( board of intermediate and secondary education).  The middle and primary education is conducted by PEC(Pakistan education commission). 
- 28. Teacher education There are two main categories of teachers in China.  state-paid teachers  community-paid teachers The system of teacher education comprises two distinct subsystems:  Pre-service  In-service
- 29. Teacher Education There are two main categories of teachers in China.  The first category is state-paid teachers who are regarded as state employees and earn a regular monthly salary comparable to other civil servants or workers in state-owned enterprises.  The second category is the community-paid teachers who are paid by the local community. Their monthly income depends on the economic conditions of the local community.
- 30. Pre-service:  Pre-service education is housed in monotechnic colleges or specialized teacher education institutions. This is a four-year bachelor's degree. In-service:  The in-service teacher education is organized at city, country and township colleges or schools. This is a two- to three-year diploma program.
- 31.  After 9 year compulsory education there was a huge lack of trained teachers. It was needed that institutions should be made for producing teachers. Till 1990 1000 teacher training institutes were made and by the passage of time those gradually increased.
- 32. INDUCTION  induction programs are irregularly conducted in china as when novice teacher go for job, a group is made of novice teacher and experienced teacher. Then there practical teaching begins. Time period also vary at different places. Some times it is one or two year and several short periods, such as a half year, or several periods of ten days, or some workdays in the semester.
- 33. TEACHER EDUCATION IN PAKISTAN: in service and pre service teacher education is organized in Pakistan but there is no conditional requirement needed for induction for getting a job.  Many special institutions are working for this sake. 
- 34. ADMISSION PROCEDURE  At Initial stages procedure of admission is simple as completion of previous class is necessary.  but at higher level some special tests are taken.  Important one is GOA KOA or high test. It is organized in July for getting admission in university. It is equal to SAT.
- 35. GAO KAO    The gao kao (pronounced gow kow) roughly translated means “the high test”. The gaokao is China„s, ultracompetitive university entrance exam. Its the nine-hour test is offered just once a year and is the sole determinant for admission to virtually all Chinese colleges and universities. Taken at the end of high school, the gaokao is given over a three day period across the country. It emphasizes math and science but also measure knowledge of written Chinese, English and Marxist thought. about 9.15 million students who took the gaokao in 2012. Only 60% make it into university on the basis of their gao kao score
- 36. PREPARATION FOR THE HIGH TEST
- 37. EXAMINATION HALL
- 38. ADMISSION PROCEDURE IN PAKISTAN  There are some special entry tests in Pakistan for students.  School admission test  Engineering or medical college admission test  MCAT OR ECAT  GAT  NAT
- 39. CHINA‟S CURRICULUM it carries various educational philosophies like of Dewey, Montessori, skinner, Thorndike, Bruner and especially Vigotsky and piaget etc.  If we think about it we suppose that china have a effective curriculum in his education. And the progress report supports it also.  it has gain a special name in technology.  but a complaint from students has also appeared that china‟s tough education and examination system enhanced cramming. 
- 40. THE CHINA China‟s education is as refined as the country it self. Its at 11th number on world ranking.  It has not only helped its own students to study but it invites foreign students too.  around the 300,000 foreigner students study at China.  And approx 340,000 Chinese study abroad too.  China the world‟s sixth-largest study abroad destination.  America has signed an agreement to send its 100000 students to study in China. 
- 41. If you have any Question, please ask.
- 42. 