NodeMcu? ???? ????? DIY
6 likes4,274 views
? ????? ????? ???? ???? ???? ???? NodeMCU? ?????. ? ????? ?? NodeMCU? ???? ????, NodeMCU? ?? ??? ????, ??? NodeMCU? ??? ? ? ?? ??? ???? ??? ??? ? ?? ?? ?? ???? ????.
1 of 28
Downloaded 55 times


























Recommended
Matter, open source connectivity standard for smart home and io t 2021.07.0...



Matter, open source connectivity standard for smart home and io t 2021.07.0...Hakyong Kim
?
In this material, I explained the major features of the Matter standard, not open to publit yet. Since the contents were collected from several companies presentation, it might differ from the Matter specification in detail.
? ??? 2021? ?? ?? ??? ???? ? ????? IoT ?? ??? ??(Matter)? ?? ?? ?? ? ??? ??? ??? ?? ??? ?????. ?? ?? ??? ???? ?? ????? ???? ????, ???? ??, TI ? Matter ????? ??? ?? ? ?? ??? ???? ??? ?? ? ??? ????, ?? ??? ???? ????? ?? ? ??? ?? ??????. Cloud, Fog & Edge Computing



Cloud, Fog & Edge ComputingEUBrasilCloudFORUM .
?
Congresso Sociedade Brasileira de Computa??o CSBC2016 Porto Alegre (Brazil)
Workshop on Cloud Networks & Cloudscape Brazil
Sergio Takeo Kofuji, Assistant Professor at the University of S?o Paulo, Coordinator to FI WARE LAB in University of S?o Paulo, Brazil
The European Commission, in a recent communication (April 19th), has identified 5G and Internet of Things (IoT) amongst the ICT standardisation priorities for the Digital Single Market (DSM). This session will discuss the emergence of the mobile edge computing paradigm to reduce the latency for processing near the source large quantities of data and the need of the emerging 5G technology to satisfy the requirements of different verticals. Mobile Edge Clouds have the potential to provide an enormous amount of resources, but it raises several research challenges related to the resilience, security, data portability and usage due to the presence of multiple trusted domains, as well as energy consumption of battery powered devices. Large and centralized clouds have been deployed and have shown how this paradigm can greatly improve performance and flexibility while reducing costs. However, there are many issues requiring solutions that are user and context aware, dynamic, and with the capability to handle heterogeneous demands and systems. This is a challenge triggered by the Internet of Things (IoT) scenario, which strongly requires cloud-based solutions that can be dynamically located and managed, on demand and with self-organization capabilities to serve the purposes of different verticals. Sensors on android



Sensors on androidChinmay V S
?
This document discusses sensors on Android devices. It covers an introduction to common sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes, how sensors are used in Android applications, tips for developing sensor applications, and porting new sensors to Android. The presentation is divided into multiple parts covering the Android sensor framework, sensor hardware, developing and debugging sensor applications, and future directions for sensors on Android.Misc: Introduction to ATSSS - Access Traffic Steering, Switching and Splitting



Misc: Introduction to ATSSS - Access Traffic Steering, Switching and Splitting3G4G
?
ATSSS (Access Traffic Steering, Switching and Splitting) is a new 5G functionality that allows traffic to be steered across multiple concurrent access networks, such as 3GPP, trusted non-3GPP, and untrusted non-3GPP, at a finer granularity than a single PDU session. It introduces the concept of multi-access PDU sessions. ATSSS is controlled by the 5G core network's PCF and can utilize higher layer MPTCP or lower layer steering methods to optimize traffic routing. Initial ATSSS deployments are expected to begin in 2021/2022 as 5G core networks and multi-access integration are implemented.Accelerating 5G enterprise networks with edge computing and latency assurance



Accelerating 5G enterprise networks with edge computing and latency assuranceADVA
?
Jim Zou shared insights into edge compute and latency assurance for enterprise networks at OFC, covering security and time-sensitive services.MILLIMETER WAVE FOR 5G CELLULAR



MILLIMETER WAVE FOR 5G CELLULARSudeeshvs01
?
Millimeter wave technology uses frequencies between 25GHz and 300GHz for 5G cellular networks. This allows for higher bandwidth and multi-Gbps data rates compared to existing wireless technologies. Millimeter waves enable highly directional beamforming through small antennas and narrow beams. This reduces interference while improving security. However, millimeter waves experience greater path loss and attenuation than lower frequencies, requiring line-of-sight propagation or reflective surfaces for connectivity. Further research is working to address limitations and realize the full potential of millimeter wave spectrum for 5G and beyond.Gi fi seminar Report



Gi fi seminar ReportShivam Joshi
?
Gi-Fi is a new wireless technology that offers faster data transfer rates than Wi-Fi and WiMax. It uses 60GHz frequency and can transfer data at rates up to 5 gigabits per second, which is 10 times faster than current wireless technologies. Gi-Fi uses an integrated transceiver chip developed in Australia that operates at low power. It allows quick transfer of large files like videos within seconds over short ranges. Gi-Fi is expected to become the dominant wireless technology for applications like wireless home networks and high-speed transfer between devices.Holographic seminar documentation



Holographic seminar documentationGeorgekutty Francis
?
This document discusses holographic memory and its potential applications. It provides background on holography and how holograms can be used for data storage. Holographic memory has the potential for ultra-high density data storage at terabyte capacities. It allows for three-dimensional page-based data access and retrieval at high speeds. Potential applications include high-performance data mining and petaflop computing due to holographic memory's ability to provide massive, fast storage.Og003 dbs3900hardwarestructureissue2.0



Og003 dbs3900hardwarestructureissue2.0?inh C?ng Thi?n Taydo University
?
The document describes the hardware structure of the Huawei DBS3900 distributed base station solution. The DBS3900 consists of an indoor baseband unit (BBU3900) and outdoor remote radio units (RRU3004). The BBU3900 performs centralized management and provides interfaces to the RRU3004 via CPRI. It can support up to 36 transceiver modules across multiple RRU3004 units.2014 ???? ???? ?? ?? 



2014 ???? ???? ?? ?? Soomin(Simon) Shim
?
???? ???? ??? ?? ?? ? ?? ?? ??
1. ??? ?? ???(Momentum)? ???
2. ???? ????? ??? ????
3. ?? ?? ? ?? ??? ?? ??? ??
4. Mass Market: B2B ??? ???? ???? ??
5. Long Tail: ????, ???? ???? ?? ??
6. ??? ? ??
WIVI Technology



WIVI TechnologyAkhil Kumar Pappula
?
This document describes WIVI (Wireless Identification and Virtual Imaging) technology. WIVI uses WiFi signals to detect and track moving objects like humans behind walls. It was invented at MIT and works by transmitting WiFi signals that reflect off objects and analyzing the reflections to identify movement. WIVI consists of WiFi transmitters and receivers and can determine the number of humans in a room, their locations, and even simple gestures behind walls. However, its resolution is lower than cameras and thicker walls limit its range. Potential applications include security, emergency response, and smart home assistance.Indoor positioning system



Indoor positioning systemPRADEEP Cheekatla
?
An indoor positioning system (IPS) uses wireless technologies like Wi-Fi to locate objects or people inside buildings, as GPS does not work well indoors. IPS relies on nearby nodes with known positions rather than satellites. Wi-Fi fingerprinting involves collecting and storing Wi-Fi signal strengths to develop location fingerprints. IPS has many potential uses including indoor navigation, location-based services, security, and analytics. Researchers are working to increase IPS accuracy by supplementing Wi-Fi with other sensor data.screen less display



screen less displaySukanya Mukherjee
?
The document discusses different types of screenless displays including visual images, retinal displays, and synaptic interfaces. Visual images use holograms, projections on windows, and heads-up displays to reflect light without a screen. Retinal displays project light directly onto the retina, allowing for larger images and prevention of snooping. Synaptic interfaces send images straight to the brain via an implanted electrode, bypassing the eyes, as seen in characters like Geordi La Forge in Star Trek. Examples given are Google Glass and the Oculus Rift virtual reality headset.Smartphone Hardware Architecture



Smartphone Hardware ArchitectureYong Heui Cho
?
This document provides information on smartphone hardware architecture. It discusses key components such as the application and connectivity processor chips, memory, wireless capabilities, batteries, and sensors. Specific smartphones are also summarized, including the Apple iPhone 5S which uses the A7 64-bit processor and Touch ID fingerprint sensor, and the Samsung Galaxy S4 which employs the Exynos 5 Octa chip with ARM's big.LITTLE architecture. Diagrams depict the internal layout and connectivity of components in these devices.Open v ran



Open v ranRajasa Pramudya Wardhana
?
The document discusses the open virtualized RAN (vRAN) ecosystem. It provides an overview of the ecosystem and its goals of accelerating adoption of open vRAN solutions. It describes traditional and evolving RAN architectures including centralized and virtualized RAN. It demonstrates early multi-vendor pre-5G and 5G SA proof of concept solutions using the open vRAN architecture. The demos show how the architecture enables new services through network slicing and edge computing. Finally, it discusses how the open vRAN ecosystem is accelerating the transition to software-defined mobile networks.Wi-Vi Technology - Seminar Presentation



Wi-Vi Technology - Seminar PresentationAlanShijo
?
Wireless vision is a device which operates wirelessly and captures the moving objects behind the wall. WiFi or Wireless Fidelity signals are information carriers between a transmitter and a receiver. Through Wireless Vision, WiFi can be extended to our senses thereby allowing visualizing moving objects through closed doors and walls. These signals are helpful in identifying the people number and their locations while they are in a closed room. It can also help in identifying gestures behind the wall and also it combines gestures to communicate the messages to the wireless receiver without carrying any transmitting device.Near field communication new



Near field communication newSanu Varghese
?
Near-Field Communication (NFC) allows contactless data exchange between devices within close proximity. NFC operates at 13.56 MHz and has a maximum range of about 4 cm. It can be used for applications such as contactless payment, ticketing, and data sharing when two NFC devices are tapped together. NFC has three operating modes - reader/writer mode where an NFC device can read from and write to tags, card emulation mode where a phone acts like a card, and peer-to-peer mode for data transfer between two NFC phones. NFC integration with mobile devices has potential for new opportunities but has limitations such as short range and low data transfer rates.Architecture of 5G



Architecture of 5GUdara Sandaruwan
?
The 5G architecture uses an entirely IP-based model to integrate various radio access technologies and provide quality service through cognitive radio technology. It converges different networks on a 5G MasterCore that can efficiently operate in parallel modes to control all networks and enable new combined services globally through an innovative World Combination Service Mode.RF Front-End Module Comparison 2021 ©C Vol. 2 ©C Focus on 5G Chipset



RF Front-End Module Comparison 2021 ©C Vol. 2 ©C Focus on 5G Chipsetsystem_plus
?
Technical and cost overview of the evolution of radio frequency front-end module technologies integrated in 5G mmWave and Sub-6 GHz Phones.
More : https://www.systemplus.fr/reverse-costing-reports/rf-front-end-module-comparison-2021-vol-2-focus-on-5g-chipset/Temperature measurement using nodemcu esp8266



Temperature measurement using nodemcu esp8266DheerendraKumar43
?
In this project, we will create a standalone web server using a NodeMCU ESP8266 that displays the?Temperature and Humidity with a DHT11 sensor using the Arduino ?IDE.
Actually, the webserver we will build can be easily accessed with any device that features a browser on your local network. NodeMCU ESP8266 Monitoring DHT11/DHT22 Temperature and Humidity with Local Web Server.
Gi-Fi ppt



Gi-Fi pptTushar Choudhary
?
GI-FI (Gigabit Fidelity) or Giga bit wireless refers to wireless communication at a data rate of more than one billion bits (gigabits) per second. GI-FI offers some advantages over WI-FI, a similar wireless technology. In that it offers faster information rate in GBPS, less power consumption and low cost for short range transmission as compare to current technology. GI-FI consists of a chip which has facility to deliver short-range multi gigabit data transfer in a local environment and compared to other technologies in the market it is ten times faster. GI-FI has the data transfer speed up to 5 GBPS within a short-range of 10 metres. It operates in 60 GHZ frequency band. GI-FI is developed on an integrated wireless transceiver chip. It has both transmitter and receiver, integrated on a single chip which is fabricated using the CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) process and it also consists of a small antenna. GI-FI allows transferring large videos, audio files, data files etc. within few seconds.ZIGBEE TECHNOLOGY ppt



ZIGBEE TECHNOLOGY pptOECLIB Odisha Electronics Control Library
?
The document discusses Zigbee technology, including its history, device types, how it works, uses and future. Zigbee is a wireless technology standard designed for control and sensor networks. It was created by the Zigbee Alliance based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for low-power wireless networks. Zigbee networks consist of coordinator, router and end devices and can operate using star, tree or mesh topologies to connect small, low-power digital radios. Common applications of Zigbee include home automation, lighting and appliance control.Introduction to Internet of Things Hardware



Introduction to Internet of Things HardwareDaniel Eichhorn
?
This presentation introduces to the world of hardware everyone can use to get stated with Internet of Things (IoT) such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi and ESP8266.5G Network Slicing



5G Network SlicingSridhar Bhaskaran
?
Network slicing in 5G allows a single UE to connect to multiple network slices simultaneously. Each slice is identified by a Specific Network Slice Selection Assistance Information (S-NSSAI). The 5G core uses the S-NSSAI to select the appropriate functions like the Session Management Function (SMF) for each slice. This enables isolation of services and network functions on a per-slice basis. The Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) is common across all slices, but the SMF and User Plane Function (UPF) can differ per slice. This facilitates customized network slices for different use cases and isolation of traffic and functions.Introduction to 6G, prepare now training



Introduction to 6G, prepare now trainingTonex
?
Tonex offers a one-day training course on 6G technology to help organizations gain an advantage over competitors. While 6G is 10 years away, planning and preparation take 10 years. The course provides an overview of the 6G vision, expected capabilities like speeds over 1 TB/s, and technologies to achieve its goals. It explains how 6G will build on 5G and the benefits of understanding 6G now to influence its development.Mobile jammer



Mobile jammerAvay Minni
?
The document discusses mobile phone jammers, including what they are, how they work, different types, and applications. Mobile jammers transmit signals that block the communication between mobile phones and cell towers, rendering phones unusable. The document outlines five main jamming techniques (A through E), provides a sample block diagram, and discusses potential future applications while noting legal restrictions.Fire detection system using arduino 



Fire detection system using arduino UT-028
?
Here you will find details about how you can make a fire detection system by using arduino and flame sensor. We have also added the budget you need to make this project.Integrating Wireless Sensor Network into Cloud Services for Real-time Data Co...



Integrating Wireless Sensor Network into Cloud Services for Real-time Data Co...Mokpo National University
?
This document summarizes a presentation given by Rajeev Piyare on integrating wireless sensor networks with cloud services for real-time data collection. Piyare proposed an architecture with three layers - a sensor layer to collect data, a coordinator layer to manage data, and a supervision layer in the cloud to store data and provide interfaces. He demonstrated collecting temperature and voltage readings and accessing the data through RESTful web services. The system alerts users when sensor values exceed thresholds, with average notification times of 11 seconds. Experiments showed the impact of packet size and sleep cycles on battery lifetime for battery-powered sensors. The presentation concluded the architecture provides a flexible way to integrate sensor networks with cloud computing.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Og003 dbs3900hardwarestructureissue2.0



Og003 dbs3900hardwarestructureissue2.0?inh C?ng Thi?n Taydo University
?
The document describes the hardware structure of the Huawei DBS3900 distributed base station solution. The DBS3900 consists of an indoor baseband unit (BBU3900) and outdoor remote radio units (RRU3004). The BBU3900 performs centralized management and provides interfaces to the RRU3004 via CPRI. It can support up to 36 transceiver modules across multiple RRU3004 units.2014 ???? ???? ?? ?? 



2014 ???? ???? ?? ?? Soomin(Simon) Shim
?
???? ???? ??? ?? ?? ? ?? ?? ??
1. ??? ?? ???(Momentum)? ???
2. ???? ????? ??? ????
3. ?? ?? ? ?? ??? ?? ??? ??
4. Mass Market: B2B ??? ???? ???? ??
5. Long Tail: ????, ???? ???? ?? ??
6. ??? ? ??
WIVI Technology



WIVI TechnologyAkhil Kumar Pappula
?
This document describes WIVI (Wireless Identification and Virtual Imaging) technology. WIVI uses WiFi signals to detect and track moving objects like humans behind walls. It was invented at MIT and works by transmitting WiFi signals that reflect off objects and analyzing the reflections to identify movement. WIVI consists of WiFi transmitters and receivers and can determine the number of humans in a room, their locations, and even simple gestures behind walls. However, its resolution is lower than cameras and thicker walls limit its range. Potential applications include security, emergency response, and smart home assistance.Indoor positioning system



Indoor positioning systemPRADEEP Cheekatla
?
An indoor positioning system (IPS) uses wireless technologies like Wi-Fi to locate objects or people inside buildings, as GPS does not work well indoors. IPS relies on nearby nodes with known positions rather than satellites. Wi-Fi fingerprinting involves collecting and storing Wi-Fi signal strengths to develop location fingerprints. IPS has many potential uses including indoor navigation, location-based services, security, and analytics. Researchers are working to increase IPS accuracy by supplementing Wi-Fi with other sensor data.screen less display



screen less displaySukanya Mukherjee
?
The document discusses different types of screenless displays including visual images, retinal displays, and synaptic interfaces. Visual images use holograms, projections on windows, and heads-up displays to reflect light without a screen. Retinal displays project light directly onto the retina, allowing for larger images and prevention of snooping. Synaptic interfaces send images straight to the brain via an implanted electrode, bypassing the eyes, as seen in characters like Geordi La Forge in Star Trek. Examples given are Google Glass and the Oculus Rift virtual reality headset.Smartphone Hardware Architecture



Smartphone Hardware ArchitectureYong Heui Cho
?
This document provides information on smartphone hardware architecture. It discusses key components such as the application and connectivity processor chips, memory, wireless capabilities, batteries, and sensors. Specific smartphones are also summarized, including the Apple iPhone 5S which uses the A7 64-bit processor and Touch ID fingerprint sensor, and the Samsung Galaxy S4 which employs the Exynos 5 Octa chip with ARM's big.LITTLE architecture. Diagrams depict the internal layout and connectivity of components in these devices.Open v ran



Open v ranRajasa Pramudya Wardhana
?
The document discusses the open virtualized RAN (vRAN) ecosystem. It provides an overview of the ecosystem and its goals of accelerating adoption of open vRAN solutions. It describes traditional and evolving RAN architectures including centralized and virtualized RAN. It demonstrates early multi-vendor pre-5G and 5G SA proof of concept solutions using the open vRAN architecture. The demos show how the architecture enables new services through network slicing and edge computing. Finally, it discusses how the open vRAN ecosystem is accelerating the transition to software-defined mobile networks.Wi-Vi Technology - Seminar Presentation



Wi-Vi Technology - Seminar PresentationAlanShijo
?
Wireless vision is a device which operates wirelessly and captures the moving objects behind the wall. WiFi or Wireless Fidelity signals are information carriers between a transmitter and a receiver. Through Wireless Vision, WiFi can be extended to our senses thereby allowing visualizing moving objects through closed doors and walls. These signals are helpful in identifying the people number and their locations while they are in a closed room. It can also help in identifying gestures behind the wall and also it combines gestures to communicate the messages to the wireless receiver without carrying any transmitting device.Near field communication new



Near field communication newSanu Varghese
?
Near-Field Communication (NFC) allows contactless data exchange between devices within close proximity. NFC operates at 13.56 MHz and has a maximum range of about 4 cm. It can be used for applications such as contactless payment, ticketing, and data sharing when two NFC devices are tapped together. NFC has three operating modes - reader/writer mode where an NFC device can read from and write to tags, card emulation mode where a phone acts like a card, and peer-to-peer mode for data transfer between two NFC phones. NFC integration with mobile devices has potential for new opportunities but has limitations such as short range and low data transfer rates.Architecture of 5G



Architecture of 5GUdara Sandaruwan
?
The 5G architecture uses an entirely IP-based model to integrate various radio access technologies and provide quality service through cognitive radio technology. It converges different networks on a 5G MasterCore that can efficiently operate in parallel modes to control all networks and enable new combined services globally through an innovative World Combination Service Mode.RF Front-End Module Comparison 2021 ©C Vol. 2 ©C Focus on 5G Chipset



RF Front-End Module Comparison 2021 ©C Vol. 2 ©C Focus on 5G Chipsetsystem_plus
?
Technical and cost overview of the evolution of radio frequency front-end module technologies integrated in 5G mmWave and Sub-6 GHz Phones.
More : https://www.systemplus.fr/reverse-costing-reports/rf-front-end-module-comparison-2021-vol-2-focus-on-5g-chipset/Temperature measurement using nodemcu esp8266



Temperature measurement using nodemcu esp8266DheerendraKumar43
?
In this project, we will create a standalone web server using a NodeMCU ESP8266 that displays the?Temperature and Humidity with a DHT11 sensor using the Arduino ?IDE.
Actually, the webserver we will build can be easily accessed with any device that features a browser on your local network. NodeMCU ESP8266 Monitoring DHT11/DHT22 Temperature and Humidity with Local Web Server.
Gi-Fi ppt



Gi-Fi pptTushar Choudhary
?
GI-FI (Gigabit Fidelity) or Giga bit wireless refers to wireless communication at a data rate of more than one billion bits (gigabits) per second. GI-FI offers some advantages over WI-FI, a similar wireless technology. In that it offers faster information rate in GBPS, less power consumption and low cost for short range transmission as compare to current technology. GI-FI consists of a chip which has facility to deliver short-range multi gigabit data transfer in a local environment and compared to other technologies in the market it is ten times faster. GI-FI has the data transfer speed up to 5 GBPS within a short-range of 10 metres. It operates in 60 GHZ frequency band. GI-FI is developed on an integrated wireless transceiver chip. It has both transmitter and receiver, integrated on a single chip which is fabricated using the CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) process and it also consists of a small antenna. GI-FI allows transferring large videos, audio files, data files etc. within few seconds.ZIGBEE TECHNOLOGY ppt



ZIGBEE TECHNOLOGY pptOECLIB Odisha Electronics Control Library
?
The document discusses Zigbee technology, including its history, device types, how it works, uses and future. Zigbee is a wireless technology standard designed for control and sensor networks. It was created by the Zigbee Alliance based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for low-power wireless networks. Zigbee networks consist of coordinator, router and end devices and can operate using star, tree or mesh topologies to connect small, low-power digital radios. Common applications of Zigbee include home automation, lighting and appliance control.Introduction to Internet of Things Hardware



Introduction to Internet of Things HardwareDaniel Eichhorn
?
This presentation introduces to the world of hardware everyone can use to get stated with Internet of Things (IoT) such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi and ESP8266.5G Network Slicing



5G Network SlicingSridhar Bhaskaran
?
Network slicing in 5G allows a single UE to connect to multiple network slices simultaneously. Each slice is identified by a Specific Network Slice Selection Assistance Information (S-NSSAI). The 5G core uses the S-NSSAI to select the appropriate functions like the Session Management Function (SMF) for each slice. This enables isolation of services and network functions on a per-slice basis. The Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) is common across all slices, but the SMF and User Plane Function (UPF) can differ per slice. This facilitates customized network slices for different use cases and isolation of traffic and functions.Introduction to 6G, prepare now training



Introduction to 6G, prepare now trainingTonex
?
Tonex offers a one-day training course on 6G technology to help organizations gain an advantage over competitors. While 6G is 10 years away, planning and preparation take 10 years. The course provides an overview of the 6G vision, expected capabilities like speeds over 1 TB/s, and technologies to achieve its goals. It explains how 6G will build on 5G and the benefits of understanding 6G now to influence its development.Mobile jammer



Mobile jammerAvay Minni
?
The document discusses mobile phone jammers, including what they are, how they work, different types, and applications. Mobile jammers transmit signals that block the communication between mobile phones and cell towers, rendering phones unusable. The document outlines five main jamming techniques (A through E), provides a sample block diagram, and discusses potential future applications while noting legal restrictions.Fire detection system using arduino 



Fire detection system using arduino UT-028
?
Here you will find details about how you can make a fire detection system by using arduino and flame sensor. We have also added the budget you need to make this project.Integrating Wireless Sensor Network into Cloud Services for Real-time Data Co...



Integrating Wireless Sensor Network into Cloud Services for Real-time Data Co...Mokpo National University
?
This document summarizes a presentation given by Rajeev Piyare on integrating wireless sensor networks with cloud services for real-time data collection. Piyare proposed an architecture with three layers - a sensor layer to collect data, a coordinator layer to manage data, and a supervision layer in the cloud to store data and provide interfaces. He demonstrated collecting temperature and voltage readings and accessing the data through RESTful web services. The system alerts users when sensor values exceed thresholds, with average notification times of 11 seconds. Experiments showed the impact of packet size and sleep cycles on battery lifetime for battery-powered sensors. The presentation concluded the architecture provides a flexible way to integrate sensor networks with cloud computing.Integrating Wireless Sensor Network into Cloud Services for Real-time Data Co...



Integrating Wireless Sensor Network into Cloud Services for Real-time Data Co...Mokpo National University
?
Similar to NodeMcu? ???? ????? DIY (20)
???? ???- June 2013. Industrial Communication Network MAGAZINE



???? ???- June 2013. Industrial Communication Network MAGAZINESeungMo Oh
?
?? ???? ??? ???? POWERLINK.
?? ???? ? ?? ??? ???? ???? ???? ?? ???? ?? ???? ??? ????. ?? ?? ???? ??? ??? ???? ?? ??? ??? ??. ?????? ???? ?? ???? ??? ??? ??. ??? ?? ?? ??? ?? ???, ??? ?? ???, ??, ??, ??? ? ???? ?? ? ? ??. ?? ??? ?? ?? ?? ??? ???? ?? ? ???? ????? ???? ????? ???? ??? ??? ???? ???? ??. ?? ??? ?? ?? ??? ??? ?? ??? ????? ?? ??? ?? ??? ???? ??.
??? ??, ?? ? ??? ??? ???? ?? ????? ?? ??? ?? ? ??? ?? ?? ??? ???? ?? ????. ??? ?? ??? ???? ??? ???? ???? ??? ????. ???? ??? ??? ??, ???? ??? ? ?? ????? ??? ?? POWERLINK? ?? ?? ??? ?? ???? ?? ???? ???.
??? ?? ?? ???? ?? ??? ???? ???? ???? ??? ???? ????? ??, ?? ? ??? ??? ??? ? ?? ???? ???? ??. ???, ?? ??? ??? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ? ?? ??. ??? ??? ??, ???? ?? ? ? ??? ??? ??.Eyecatcher artwall ?????



Eyecatcher artwall ?????Goodmorning Information Technology Co., Ltd.
?
??? ????? ????? STB? ???? ?? ???? ????MCU(nanheekim)



MCU(nanheekim)Nanhee Kim
?
@Powersupply(YeungnamUniv.) @NanheeKim @nh9k
??? ??? ???? ?????!
Please, feel free to contact me, if you have any questions!
github: https://github.com/nh9k
email: kimnanhee97@gmail.com????&???SCM(MONTHLY AIDC+SMART SCM) 2013? 11??



????&???SCM(MONTHLY AIDC+SMART SCM) 2013? 11??????
?
????&???SCM(MONTHLY AIDC+SMART SCM) 2013? 11??
COVER STORY
RFID/IoT World Congress 2013
RFID/IoT ??? ??? ?? ???? ?? Ī«RFID/IoT World Congress 2013Ī»
EDITORĪ»s NOTE
Ī░?? ??? ??, ???? ???? ????Ī▒
EXPERT COLUMN
??? NFC ?? ??? 2
FOCUS RFID
??????? RFID ??? ??? ??
????? ?? ?? ??, ??? RFID
FOCUS AIDC
Ī░2012? ??? AIDC ??, 112? 6,400? ??Ī▒
FOCUS NFC
????? NFC ?? ??????? ?? ??
ST, Ī«RFID/IoT ?? ???? 2013Ī»?? ?? NFC ??? ???
FOCUS ????
?? ?? ???? ???
???? ?? ?? ???? ?? ? ?? ?????
FOCUS POLICY
??, Ī«???? ??? ????Ī» ??
Seminar & Conference
Ī░?? ??? HID Global? ???Ī▒
POWER INTERVIEW
???? ??? ????
Ī░??? ?? ???? ?? RFID ?? ??? ??? ?? ? ?? ?Ī▒
SPECIAL REPORT
Ī░RFID? ?? ? ??? ?? ?? ???? ??? ???? ?????Ī▒
INTERVIEW
???, Ī░UHF ? HF ?? ???? ?? ??Ī▒
PACKAGING ISSUE
5?? ??? ??? ? ?????
PACKAGING TREND
??? ?? ?? ??? ??
CASE STUDY
In-Sight ????? ??? ?? ?? ??? ???
TECHNICAL REPORT
RFID? ??? ?? ?? ? ???? ????? (3)
NEWS INSIGHT ???/??/??
NEWS INSIGHT RFID
NEWS INSIGHT NFC
NEWS INSIGHT ??/??
HOT ISSUE
RFID, ?????(Environmental Sustainability)? ????.
?? ????/??/??/?? ?? ???? ???20150912 IoT ????? ?? windows 10 iot core ??



20150912 IoT ????? ?? windows 10 iot core ???? ?
?
MDS?? ???? ??? MVP?? Windows 10 IoT Core? ?? ?? ???. ????&???SCM(MONTHLY AIDC+SMART SCM) 2013? 12??



????&???SCM(MONTHLY AIDC+SMART SCM) 2013? 12??????
?
????&???SCM(MONTHLY AIDC+SMART SCM) 2014? 1??
COVER STORY
?? ??? ????, Ī░??ĪżICT ??? ????Ī▒ ? ?? ?????
EDITORĪ»s NOTE
RFID/USN? ?? ??? ????? ?? ????
EXPERT COLUMN
??? NFC ??? ???
FOCUS RFID
?? RFID ??? Ī░??? ?? ? ?? ?? ?? ???Ī▒
???, ??? RFID/NFC ??? ?? ?? ?? ????? ??
FOCUS AIDC
Ī░??? ???, ???? ??? ?? ??? ??? ??? ?? ???? ?????Ī▒
FOCUS ID ?? ???
HID Global, FARGO DTC ??? ????? ??? ?? ??
FOCUS ??/??
??? ??? ???? Ī░?? ??? ?????Ī▒
FOCUS ?????(IoT)
?? 95%, RFIDĪż?? ? IoT ?? ?? ??
?????? ?? ?? ?? Ī«?????? ??? ??Ī»
POWER INTERVIEW
???? ??? ????
Ī░RFID? NFC ??? ?? ????? ????Ī▒
SPECIAL REPORT
RFID? ???? ??? ?????
SCM REPORT
???? ??? ??? ?? ?? ??
SMART SCM
TMS ??? 8?? ???
VERTICAL REPORT
RFID? ??? ?? ??? ?? ?
CASE STUDY
?? ??? ??? ???, ?????? ?? ??? ??
Ī░???? ????? ??? ?? 3? ??? ?? ????Ī▒
TECHNICAL REPORT
??? ????? ?????(IoT) ???? ??
RFID? ??? ?? ?? ? ???? ????? (4)
NEWS INSIGHT ???/??/??
NEWS INSIGHT RFID
NEWS INSIGHT NFC
106 ?? ????/??/??/?? ?? ???? ???
HOT ISSUE
????? ???, ??? ????? ?? ?????Maker ??? ??



Maker ??? ????? FunFun Yoo
?
Maker ? Embedded Engineer ?? ??? ?? ???? Maker ??? ?? ????? ?? ??? ??? ??? ???? ??? ???? ??? ???? ??? ?? ???? ???? ?? ???? ??More from Hakyong Kim (20)
???? ?? ?? ??(Matter) ?? ?? ????



???? ?? ?? ??(Matter) ?? ?? ????Hakyong Kim
?
??? ???? ?? ??? ??? ?? ?? ??? ?? ???? ????. ????, ??, ???, ???, ????? ??? ???? ?? ????. ?? ??? ????? ?? ???? ???? ? ??, ??? "?? ???"?? ????? ??? ?? ?? ? ??? ???? ? ????. https://youtu.be/gNn6DSSULKc
??? ???? ???? ?? ??? ??? ????



??? ???? ???? ?? ??? ??? ????Hakyong Kim
?
?? ??? ???? ???? ???(Leaders)? ? ? <??? - ? ??? ???? ??? ????>? ???????. ?????? ??? ???? ???? ??? ? ??? ????. ???? ??? ???? ?????, ??? ??? pdf ??? ?????. pdf ??? ?? ??? ???? ???? ??? ??? ??? ??? ?????.Ces 2021 review - All Digital Paradigm in the On-tact Era - 2021.02



Ces 2021 review - All Digital Paradigm in the On-tact Era - 2021.02Hakyong Kim
?
? ??? CES 2021? ?? ?? ??? ??? ??? All Digital ????? ?? ??? ???? ????. CES 2021 ?? ? 40?? ?? ?? ??? ?? ??? ???, ??? ??? ?? ??? ???? ?? ???, ?? ??? ???? ????? ?? ???? ??? ??? ??? ??????.
?? ??? CES ? CES 2021? ?? ? ??? CTA? ??? 6?? ???, ??? ????? LG??? ??? ?????? ??? ??????.
???? ?? ?? ??? iotstlabs@gmail.com ?? Digibizinsight@gmail.com?? ??????.
?????.
CES 2021?? ??? Digital Healthcare ???



CES 2021?? ??? Digital Healthcare ???Hakyong Kim
?
CES 2021?? ??? ??? ???? ???? ?? ??? ?????. ????? CES 2021? ?? ???? Sustainabe? Better? ???? ?? ???? ?? ???? ??? ???? ???? ???? ?? ???? ?? ??????. ?????? ??? ???? ??? ???? ???? ????? ????.
Digital Healthcare Trends
1. Remote care & Servitization
2. Personalized Care and Service
3. Mental care and Digital Therapeutics
4. Untact & Natural User Interface
5. Disinfection and Counter-COVID-19
6. Care Robots?? ???? ??? ?? ? ???? ??? ???



?? ???? ??? ?? ? ???? ??? ???Hakyong Kim
?
2020? 8? 10? ??? ??????????? ??? ??? ?????. ?? 77??? ??? 64??? ??? ?? ?? ?????. ??? ????? ???? ???? ?? ??, ?? ???? ????? ??, ??? ???? ??? ????? ?? ??, ?????? ???? ??? ?? ???, ??? ???? ??? ?? ???? ?? ????. ??? ??? ??? ??????? ????? ??????? ?? ?? ??? ??? ????? ????????. ??? ???????? ??? ?? ?? - Understanding of digital transformation and examples...



??? ???????? ??? ?? ?? - Understanding of digital transformation and examples...Hakyong Kim
?
? ????? ??? ???????(DX)? ?? ??? ?? ???? ???? DX? ?? ? ?? ??? ????. ??, ??? ??? ?? ??? ???? ???? ?? ??? ?? ???? ????. ????? ??? ???????? ??? ??? ?? ???? ??? ????? ???? ?? ???? ??? ????. (? ??? 3~4?? ?? ???? ?? ??? 1?? 30? ???? ??? ?? ????.)
4??? ?? ??????. ?? ??? ??? ???? ?? ????? ???? ???? ?? <??? ???????? ??? ?? ?? ??>? ??? ???.
https://youtu.be/4dmRcrvJ8lE???, ?2? ???



???, ?2? ???Hakyong Kim
?
?? ???? ??? ? ???? ?? ??? ?? ? ??? ?? ??? ??? ?????. ??? ??? ????? ? ? ???, ???? ????? ??? ????? ???? ??? ???? ???? ???? ?? ? ???? ???? ?????? ?? ?????. ??? ?? ?? ??? ??? ????? ?????.?????? ???? ????



?????? ???? ????Hakyong Kim
?
???????? ??? ??? ????. ??? ?????? ???? ???? ?????? ?? ???? ? ? ?? ??? ??? CPS? ??? ??? ??? ??? ?????? ???? ???? ?? ??? ??? ? ??? ??? ?????. IoT? 4? ????? ??? ???? ? ??? ???? - 2019.07.25



IoT? 4? ????? ??? ???? ? ??? ???? - 2019.07.25Hakyong Kim
?
IoT? 4? ????? ??? ???? ? ??? ??????? ??? ????? ????????? ????? ????. IoT ? 4? ????? ?? ????? ??? ?? ?? IoT? ????? ?? Digital Twin? CPS? ???? ???? ?? ???? ?? ?? 4? ??????? ??????.
??? 4? ???? ??? ???? ??? ?? 4-5? ???? ???? ??? ??? ?? ??????. ?? ??? ??? ??, ????? ? ?? ??, ??? ??? ??(Smart Divide) ?? ?? ??? ???????. ??? ?? ??? ??????? ??



??? ?? ??? ??????? ??Hakyong Kim
?
???????? ???? '??? ??' 5?? ????
'???/?????? ??? ???? ??'? <??? ?? ??? ??????? ??>??? ???? ??? ?? ?????.
5G ??? ?? (5G technology and services) - 2019.05.11



5G ??? ?? (5G technology and services) - 2019.05.11Hakyong Kim
?
? ??? ? ???? ??? ??? ??? ?????? ???? ????. 5G ??? ???? ??? ??? ???? ????, 5G ???? ?? ??? ??, ???, ??? ??? ?? ?? ?? ??? ?? ?????. ??, ??? ???? ???? ?? 5G ?????? ?? ???? ????. ?? ???? ???? ???? ??? ???, ??? ?????? ????? ??? ? ??? ??? ?????. ???, ?????? 5G ??? ?? ??? ???? ????.??? ??? ??



??? ??? ??Hakyong Kim
?
????????? 4? ?? ??? ?? ???? ?? ??? ? ?? ?? ??? ?????. ??? ?? ?? ?????? ???? ?? ???? ??? ???? ?? ?? ???? ???? ??? ????. ???? ??? ???? ??? ??? ?? ?????? ?????, ?? ?? ???? ???? ?? ?? ??? ???? ??? ??? ???? ?? ???? ???? ?? ???? ? ???? ?????. ???? ??? 5G ???? ????



???? ??? 5G ???? ????Hakyong Kim
?
??? ?? 2019? 4? ??? ?? ???? ?? ????. 5G ??, ??? ?? ??? ????? ???? ???? ???? ???? 5G ???? ??? ? ??? ?? ??? ????. IoT ??? ???? ???? ? ???? ?? ???? ????



IoT ??? ???? ???? ? ???? ?? ???? ????Hakyong Kim
?
??? ??????? ??? <????? ?? ??? ?? ????? ????> ????? <IoT ??? ???? ???? ? ???? ?? ???? ?? ??>?? ??? ??? ????.
????? ?????? ?? ??? ???? ?? ???? ???? ??? ??? ?? ?? ??????. ???, ???? ????? ????? ?? ??? ??????.
???? ??+??? ?? ???? ??



???? ??+??? ?? ???? ??Hakyong Kim
?
???? ???? ??? ? ??? ???? ??? ?????. 25?? ????? ???? ??? ?? ?????. ????? ??? ????? ????? ?? ???? ??? ??? ?? ???? ??, ?????? ??? ?? ??? ??? ???? ??? ????. ?????? ??? ?? ??? ????? ?? ?? ??? ???? ??? ???, ??? ??? ????(context) ??? ????? ???? ????, ??? ????? ??? ??? ???? ???. ??? ??? ???? ???(monetizing)?? ?? ???? ??? ????? ???? ???? ????? ??????. ????? ??? ?? ?? ?? ???



????? ??? ?? ?? ?? ???Hakyong Kim
?
? ????? ???? ???? ?????. ???? ???? ???? ????? ?? ? ?? ??, ?? ? ?? ??, ??? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?????? ??? ??? ?? ?? ????. ???? ????? ???? ????? ????? ????. ?????. ?????, ????? ??? ??



?????, ????? ??? ??Hakyong Kim
?
SK??? ?? 11??? ?? ????. CPS(Cyber-Physical System)? ??? ?? 4? ???? ??? ??? ???? ?? ??? ?? ????? ????? ???? ????? ??? ???? ???? ????. ??, ??? ???? ????? ???? ?? ???? ??? ???? ????? ??? ??? ???? ??? ? ??? ?? ??????. ????? IoT ??? ?? ???? ??? ???? ???? ??



????? IoT ??? ?? ???? ??? ???? ???? ??Hakyong Kim
?
?? 10? 25? ?? ?? ?? ????? ??? ??, ??, ?? ??? ??????? ?? ????? ??? ?????. ?????? 4? ????? ??? ???? ??? ??? ??? ???? ??? ???? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??????.
Io t based business paradigm shift in beauty & health care industry - 2018.10.25??? ?? : ???? ??? 1? ?? ??? ????



??? ?? : ???? ??? 1? ?? ??? ????Hakyong Kim
?
? ????? ?? ???? 1? ??? ???? ???? ?? ??? ???? ????. ?? 60???? ?? ????, ?? ?? ?? ?? ??? ??? ??? ??? ?????. ????? ?? : ?67? ??????? (??)



????? ?? : ?67? ??????? (??)Hakyong Kim
?
??? ????, ????, ????? ???? ?????? ??? ?????? ? ????, ??? ???? ??? ??? ???? ???, ?? ??? ??? ??? ??? ?? ???? ?? ??? ??????. ?? ?? ??? ???? ???? ??? ?? ??? ??????. ??? ??? ??? ??? ?? ? ????, ???? ???? ???? ?? ?? ???? ?? 4? ???? ??? ?? ? ????? ??? ??? ??? ???? ?? ??? ??????? ^^NodeMcu? ???? ????? DIY
- 2. Speaker : ??? ??/????/??/????? ? ¼F) ?????? IoT?????? ?? ? ¼F) IoT????? ?? ???? ? Ū░) ????? ????????? ?? ? Ū░) LG???? M2M???? ?? ? Ū░) ??SDS ??????? ?? 4????? ??? ???? ?? ???? ??? ????
- 3. ?? ????? ?? ??
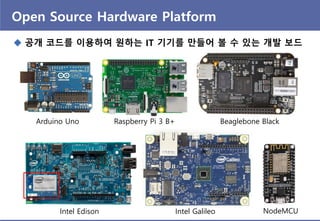
- 4. Open Source Hardware Platform ? ?? ??? ???? ??? IT ??? ??? ? ? ?? ?? ?? Arduino Uno Raspberry Pi 3 B+ Beaglebone Black Intel Edison Intel Galileo NodeMCU
- 5. ????(Arduino) ? ATmel? 8-bit ???? ???? ??? ??? ??????? ? ???? IDE? ???? ???? ???? ??? ?? ???? ??? ??? ????? ??? ?? ?? ?? ? ???? ???? ???? ?? ??? ????? ? Arduino Mega ? Arduino UNO R3 ? Arduino Nano 3 ? Arduino Mini ? Arduino Gemma
- 6. ???? ???? ???? Ball and Plate PID Control Rubik Cube Solver Gesture Controlled Robotic Arm Spider Quadruped Robot
- 7. ????? ?? ? ????? ?? ?? ?? ?? ??? ???? ?? ? Digital I/O pins : 14? (D0~D13) ? Analog I/O pins : 6? (A0~A5) ? ?? ??? 5V?? ? ??? ?? ??/?? ?? ? ??? ??? ??? ???? ?? ? Smart Device? ?? ? ???, Smart Connected Device ??? ??? ? ????? ??????? ???
- 8. ?????? ????? ???? ?? ???? ?? ???? ?? (ESP8266) NodeMCU ? 2?? ?? ???? ?? ????? ?? ? Wi-Fi Shield ?? ?? ?? ?? ? ?? ?? ? ?? ??? ??? ???? ?? ?? ? ??(Ė▀ār) ? ESP8266??? ??? ???? ?? ??
- 9. WeMos D1/D1R2 ? Arduino Uno + ESP8266-12E ? ???? ??? ??? ?? ???? ?? ? 1?? ??? ??? ?? ? ?? ?? : 3.3V ? Digital I/O pins : 11? ? Analog I/O pins : 1? ? Clock Speed : 80MHz/160MHz
- 10. Raspberry Pi 3 B+ ? ?? ?? ?? ????? ???? ??? ?? ?? ? ???? BCM2837(1.2GHz) ? BCM2837B0(1.4GHz Quad Core) ?? ? ???? : 2.4GHz ? 5GHz ?? ?? ? ???? : 4.2 ? BLE ?? ? USB 2.0 : ?? 300Mbps? ??? ?? ? ???? ??? ? PoE ??
- 11. ESP8266 ? ?? ???? ?? ESPressif Systems?? ??? ???? ?? (2013? 12? 30? ??) ? TCP/IP Full Stack? Micro-Controller? ?? ? 2014? 8?, AI-Thinker?? ????? ESP-01??? ?? ?? ? ESP8266? ?? ?? ? Tensilica Xtensa? L106 32-bit microprocessor core ? 802.11 b/g/n ?? (2.4GHz ??) ? WEP, WPA/WPA2 ?? ?? ?? ? 16?? GPIO, 1?? ???? ?? (10-bit ADC) ? ?????? TX/RX ?? ?? ??? ?? ? SPI, I2C, I2S, UART ? ??? ????? ?? ? ESP8266 SDK, Arduino IDE, Lua, ESPRUINO, MicroPhython, Sming ? ??? ?? ?? ??
- 12. NodeMCU or ESP8266-12E ? ESP8266? ?? ESP-12E NodeMCU
- 13. NodeMCU or ESP8266-12E ? ESP8266-12E? ? ?? ? 11?? GPIO ?? ???? 22?? ???
- 14. NodeMCU ESP-12E ? NodeMCU? ?? ?? ? Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11b/g/n) ?? ©C 11b ???? ?? 19.5dBm (89mW) ?? ?? ©C Power down leakage current of < 10?A ? Wi-Fi Direct (P2P) ? Soft-AP ?? ? Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack ? 32-bit RISC CPU 80MHz (OC 160MHz) ? 64KB instruction RAM, 96KB data RAM, 4BM flash memory ? 13 GPIO pins ©C Not 5v tolerant ? SPI, I2C ? 1 10-bit AD (1 analog pin) ? ?? ?? ?? : -40Īµ~125Īµ ? Can be programmed with Lua, Arduino IDE, C/C++, Python, Basic, JavaScript
- 15. NodeMCU ? An open-source firmware and development kit that helps you to prototype your IOT product within a few Lua script lines ? Lua ???? ???? ???? ?? ?? ? Arduino IDE ???? Sketch ?? ? IoT ??? ?????? ??? ? ? ?? ??? ? ?? ?? ???? ??? (?? ??) 5-pin micro USB USB to UART bridge (CH340 or CP210X) 3.3V (800mA) regulator ESP8266 (ESP-12) Wi-Fi Module (Espressif Systems) Tensilica Xtensa LX106 core 2.4GHz Antenna Vin : 5V
- 16. NodeMCU or ESP8266-12E ? NodeMCU? ?? NodeMCU 1.0NodeMCU 0.9 (Lolin) NodeMCU 0.9 NodeMCU 1.0 ? ESP8266-12 ? CH340 ? ESP8266-12E ? CH340 or CP2102
- 17. NodeMCU ESP-12E Pinouts and GPIO Numbers GPIO ???? ???? ?
- 18. ESP-32S? ?? ?? ? Xtensa? single-/dual-core 32-bit LX6 microprocessor ?? ? Wi-Fi ?? ??? Bluetooth? ??? ?? ESP-8266 ESP-32S Microprocessor Xtensa LX106 (32-bit) Xtensa LX6 (dual-core 32-bit) Memory 128KB 448KB ROM, 520KB SRAM, 16KB SRAM in RTC Storage 4MB Flash RAM 4MB Flash RAM GPIO 13 GPIOs 34 programmable GPIOs Analog support 1 10-bit AD Converter 2 12-bit SAR ADC Clock Speed 80MHz (160MHz) 80/160/240MHz Communications 802.11 b/g/n (2.4GHz) 802.11 b/g/n/e/i 802.11 n (2.4GHz), up to 150Mbps WPA/WPA2/WPA2-Enterprise/WPS Bluetooth v4.2 BR/EDR & BLE Price (AliExpress) 3$ ?? 6$ ??
- 19. ESP8266 ?? ?? ? ESP8266? ?? ??? ??? ??? ??? ?? ? ?? ? ? Weather Station, Wi-Fi Analyzer, AI Speaker controlled devices, ĪŁ
- 20. NodeMCU? ??? ?? ? ??? ? ??? ?? ?? ? ??? ???? ?? ??? ?? ? OLED? ??? ??? ?? ? ?????? ??? ??? ?? ? ????? ??? ??? ??
- 21. NodeMCU? ??? ?? ? ??? ? ?? ?? ??
- 22. NodeMCU? ??? ?? ? ??? ? ???? ?? ??
- 23. NodeMCU? ??? ?? ? ??? ? ??? ?? ThingSpeak (IoT Platform)
- 24. NodeMCU? ??? ?? ? ??? ? ??? ??
- 25. NodeMCU? ??? ?? ? ??? ? ??? ???
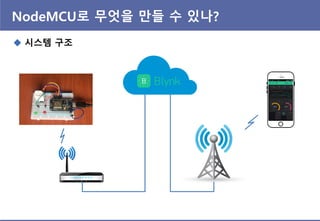
- 26. NodeMCU? ??? ?? ? ??? ? ??? ?? & ?? ???
- 27. ???? ?? ?? ? ???? ?? ?? ? ???? ??
- 28. For more information, please visit ? IoT Strategy Labs Homepage http://weshare.kr ? ????? ?? : http://cafe.naver.com/iotioe ? ??? ??? : http://blog.naver.com/honest72 ? https://www.facebook.com/hakyong.kim.12139 or contact me ? phone : 010-4711-1434 ? e-mail : iotstlabs@gmail.com


![[???? ????] ? ??](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/random-171210000428-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Td 2015]??????? windows 10 io t core ??? ?? ??(???)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/td2015windows10iotcore-151104052603-lva1-app6891-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)









