Pharmacology .. Anit-migraine Drugs
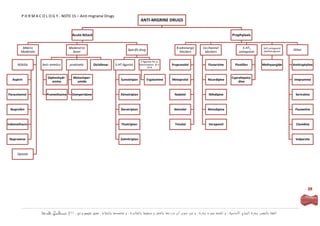
- 1. P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 15 – Anit-migraine Drugs ANTI-MIGRINE DRUGS Acute Attack Prophylaxis Mild to Moderat to β adrenergic Ca channel 5-HT2 5HT2 antagonist Specific drug /partial agonist Other Moderate Sever blockers blockers antagonist P Agonest for α- NSAIDs Anti- emetics prokinetic Diclofenac 5-HT Agonist Adrenceptors & 5- Propranolol Flunarizine Pizotifen Methysergide Amitryptyline HT R Diphenhydr- Metocloper- Cyprohepata- Aspirin Sumatripan Ergotamine Metoprolol Nicardipine Imipramine amine amide dine Paracetamol Promethazine Domperidone Almotriptan Nadolol Nifedipine Sertraline Ibuprofen Naratriptan Atenolol Nimodipine Fluoxetine Indomethacin Pizatriptan Timolol Verapamil Clonidine Naproxene Zolmitriptan Valporate Opioids 39 ‫| نسألكم الدعاء‬
- 2. P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 15 – Anit-migraine Drugs  Acute attack of Migraine DRUG PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION USES SIDE EFFECT Aspirin  Given orally.  Analgesic.  acute migraine attack. Mild to Moderate Paracetamol  they must be given early to be absorbed before NSAIDs Ibuprofen there is vomiting. attack Indomethacin Naproxene Opioids  Given parentrally (I.V. or I.M.).  Refractory cases of acute attack of Efficient use of analgesic & migraine(rarly) antiemetic is sufficient for the Diphenhydramine  Prevent vomiting. Anti- emetics majority of ACUTE ATTACKS Moderat to Sever Promethazine attack Metocloperamide  Given by I.V. injection.  They promote gastric emptying,  With very severe prokinetic  So, enhances absorption of vomiting. Domperidone  Given as rectal suppositories for vomiting can analgesics. be tried Diclofenac Sumatripan  Given by oral route or S.C. injection.  stimulate 5-HT1 R on pre-  acute severe migraine  Malaise ,fatigue.  Fast absorbtion. synaptic endings of V cn. attack(1st line).  Sedation.  Bioavailabilty by s.c. route is 96%  inhibit releasing of  Dizziness, vertigo, nausea & vomiting.  Dose not cross BBB. vasodilators .  NOT used with  feeling of chest pressure, tightness & pain. 5-HT Agonist  Plasma t1/2 is 2 hours.  selectively stimulates  IHD.  CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA & myocardial infarction. 5HT1B/1D R in cranial BV,  unstable angina.  due to coronary artery spasm.  constrict them.  previous MI Almotriptan  they are congeners of Sumatriptan.  Less side effects. Specific drug for acute attake + effects on CNS Naratriptan  improved pharmacokinetic  Reduce cardiac side effects. Pizatriptan  better Bioavailability.  better and longer duration. Zolmitriptan Ergotamine Ergotamine tartrate  stimulate 5-HT1 R on pre-synaptic  Migrine (high specific).  Paresthesiae in hands & feet.  Given by o Entral route (oral, sublingual, rectal). endings of V cn.  Peripheral ischaemia. P Agonest for α-Adrenceptors & 5-HT R o Parentral route (inhaler).  inhibit releasing of  Peripheral GANGRENE with overdose.  rectal route is preferred ???. vasodilators .  Precipitate angina pectoris.  caffeine facilitates absorption of ergot alkaloid.  Fetal damage.  It metabolized in the liver.  t ½ is 2 hrs  NOT used with disease  DOSE. of: o Tablet (1mg + Caffeine 100mg).  Coronary BV. o 1-2 tab. at onset ,then 1 tab/ 30min.  Peripheral BV. o NO > 6 mg/attack & NO >10 mg/wk. 40  For severe attack, it ginen may be IM/IV injct.  Dihydroergotamine o For intractable migraine. o Given by IV inj.(0.5-1mg) ‫| نسألكم الدعاء‬
- 3. P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 15 – Anit-migraine Drugs  Prophylaxis drugs for Migrine. DRUG PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION USES SIDE EFFECT Propranolol • PROPRANOLOL– (effect ,  the d-isomer part of structure lacks β  They are effective and widely used.  Fatigue. also prevent migraine ). blocking action;  Broncho-constriction. β adrenergic blockers  Alter the permeability of the membrane. Metoprolol Nadolol Atenolol Timolol  Block Ca channel.  Ca channel blockers Flunarizine effective in the preventive treatment Nicardipine of Migraine Nifedipine Nimodipine Verapamil Pizotifen  antagonize5-HT2 receptors.  They are RARELY used  Weight gain. antagonist  Atropine like action.  Anti-cholinergic side effects. 5-HT2 Cyprohepatadine  Antagonize 5-HT2 R & H 1 R.  Sedation.  Block Ca channels  weight gain. Methysergide  effective in about 60% patients.  It is 5HT2 antagonist /partial agonist  Serious Toxicities like; 5HT2 antagonist /partial agonist o RETROPERITONEAL  obstruction to the Ureters. o Subendocardial, Pericardial or Pleural fibrosis.  Nausea, vomiting & diarrhoea. Amitryptyline  effective for the PROPHYLAXIS of Imipramine migraine in some patients. Other Sertraline Fluoxetine Clonidine Valporate 41 ‫| نسألكم الدعاء‬