One year -old infants follow others' voice direction
- 1. One- Year- Old infants Follow OthersĪ» Voice Direction Rossano, F., Carpenter, M., & Tomsaello, M. (2012). Journal of Psychological Science, 23(11), 1298-1302. 1
- 2. ? Joint attention: ©C the shared focus of two individuals on an object 2
- 3. ©C foundational for childrenĪ»s earliest intersubjective social interactions ? intentional communication ? linguistic communication 3
- 4. ? Follow the direction of othersĪ» gaze to external targets: ©C human infants ©C many nonhuman primates. 4
- 5. ? No research investigating infantsĪ» (or adultsĪ») ability to follow the direction of someoneĪ»s voice to an external entity. 5
- 6. ? This study investigating: ©C ability of 1-year-old infants to follow the direction of an adultĪ»s voice to an external target ©C when they could not see the adult 6
- 7. Study 1 ? Investigated whether infants could determine where an unseen adult was looking just by hearing her voice. 7
- 8. Method ? Participants: Age N Mean Range 16 months 32 16:0 months 15:15 ~ 16:15 ©C 12 excluded ? fussy ( n= 7) ? distracted by parents ( n= 1) ? did not move (n= 4) 8
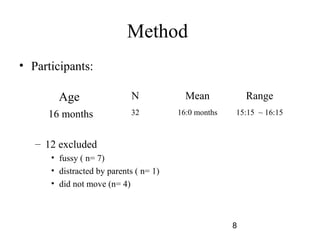
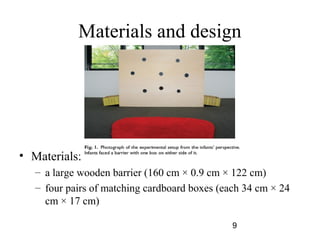
- 9. Materials and design ? Materials: ©C a large wooden barrier (160 cm Ī┴ 0.9 cm Ī┴ 122 cm) ©C four pairs of matching cardboard boxes (each 34 cm Ī┴ 24 cm Ī┴ 17 cm) 9
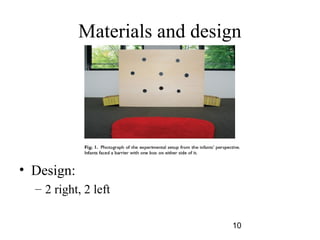
- 10. Materials and design ? Design: ©C 2 right, 2 left 10
- 11. Procedure an experimenter positioned herself behind a tall barrier opened two boxes on the floor at either side of it(one of the boxes contained a toy) behind the barrier verbally expressed excitement while looking (with her head turned) toward one of the two boxes whether infants subsequently went to that box to get the toy 11
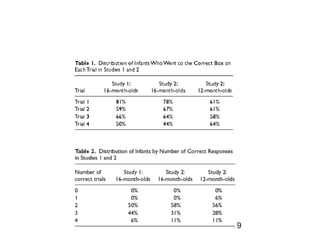
- 12. Results and discussion ? 1st trial: ©C 81%, above chance (sign test, p < .001, g = .32) ? Four trial: ©C still significantly better than chance ©C mean number of correct trials = 2.56, SD = 0.62; Wilcoxon signed-rank exact test: T+ = 136, N = 161, p < .001; r = .68 12
- 13. Results and discussion ? 16-month-olds: ©C follow another personĪ»s voice direction ©C can use it to infer what that person is attending to (even if he or she cannot be seen) ? Another explanation: ©C mouth was not at the center of the barrier ©C Ī░come hereĪ▒ 13
- 14. Study 2 ? Study 2 pitted the source-of-sound explanation against the voice-direction explanation. 14
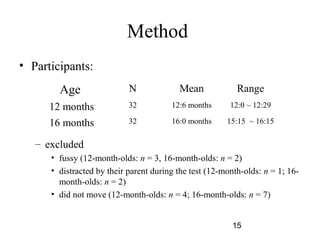
- 15. Method ? Participants: Age N Mean Range 12 months 32 12:6 months 12:0 ~ 12:29 16 months 32 16:0 months 15:15 ~ 16:15 ©C excluded ? fussy (12-month-olds: n = 3, 16-month-olds: n = 2) ? distracted by their parent during the test (12-month-olds: n = 1; 16- month-olds: n = 2) ? did not move (12-month-olds: n = 4; 16-month-olds: n = 7) 15
- 16. Procedure ? Same as study 1 except: ©C the experimenter positioned herself on the side opposite the correct box 16
- 17. Results and discussion ? 16 m: ©C 1st trial: ? 78%, above chance, (sign test, p < .01, g = .28) ©C Four trial: ? better than chance ? mean number of correct trials = 2.53, SD = 0.70; Wilcoxon signed-rank exact test: T + = 120, N = 15, p < .001; r = .60 17
- 18. Results and discussion ? 12 m: ©C 1st trial: ? 61%, at chance, (sign test, p = .24, g = .11) ©C Four trial: ? better than chance ? mean number of correct trials = 2.44, SD = 0.77; Wilcoxon signed-rank exact test: T + = 123, N = 16, p < .01; r = .50 18
- 19. 19
- 20. Study 3 ? Primate: chimpanzees ? Subjects : 16 chimpanzees(7 m, 9 f) 20
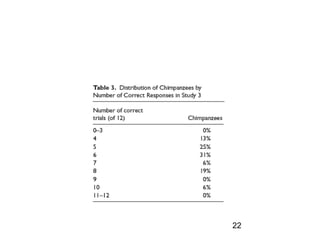
- 21. Results ? 1st trial: ©C 7/16 at chance, (sign test, p = .80) ? 12 trials: ©C at chance ©C mean number of correct trials = 6.19, SD = 1.64; Wilcoxon signed-rank exact test: T+ = 38, N = 11, p = .65; r = .11 21
- 22. 22
- 23. General discussion ? When the experimenter was out of sight behind the barrier and talked excitedly about the toy. 23
- 24. General discussion ? They were able to determine which box the toy was in, even on their very first trial. 24
- 25. General discussion ? Study 2 : ©C not just approaching the source of the sound and chancing upon the toy ©C rather, they were following the experimenterĪ»s voice direction to the toy ? 12-month-olds: ©C less robust but it too was above chance level overall 25
- 26. General discussion ? 1-year-old infants: ©C can discern the directionality of a voice without seeing the speaker ©C appear to be able to use voice direction to infer the speakerĪ»s focus of (visual) attention 26
- 27. Joint Attention 27
- 28. 28