OSCILLATIONS.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes106 views
This document discusses oscillations, including different types of motion like simple harmonic motion. It covers topics such as periodic motion, terminologies, linear and angular simple harmonic motion, energies in SHM, examples of SHM like a spring and pendulum, and equations of motion. It also discusses free oscillations, damped oscillations, and forced oscillations, specifically resonance. Forces, displacements, velocities, and accelerations of SHM are examined. Combinations of springs and their effective spring constants are analyzed.
1 of 90
Download to read offline























Recommended
Waves and oscillation undergraduates .pptx



Waves and oscillation undergraduates .pptxrajnishkumar361716
Ėý
1. The lecture goals were to describe oscillations and simple harmonic motion, analyze them using energy concepts, and apply SHM to different physical situations like pendulums and driving forces.
2. The document then covered topics like equilibrium, restoring forces, characteristics of periodic motion, and the mathematics of simple harmonic oscillators.
3. It concluded by discussing mechanical waves, including transverse and longitudinal waves, wave speed, interference, and standing waves on a string.Pre chapter 7 and 8



Pre chapter 7 and 8Muhammad Imtiaz
Ėý
The document discusses oscillatory and vibratory motion, describing it as motion where an object moves back and forth about a mean position in a periodic fashion. It defines simple harmonic motion as oscillatory motion produced by a restoring force proportional to displacement. Key concepts discussed include restoring force, amplitude, frequency, period, displacement, velocity, acceleration, phase, energy conservation, and free vs forced oscillations. It also covers waves, types of waves, progressive waves, superposition, interference, beats, and stationary waves.Oscillations



OscillationsJulieber Bersabe
Ėý
This document discusses oscillations and wave motion. It begins by introducing mechanical vibrations and simple harmonic motion. It then covers damped and driven oscillations, as well as different oscillating systems like springs, pendulums, and driven oscillations. The document goes on to discuss traveling waves, the wave equation, periodic waves on strings and in electromagnetic fields. It also covers waves in three dimensions, reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference of waves. Key concepts covered include amplitude, frequency, period, angular frequency, energy of oscillating systems, and resonance.Simple Harmonic Motion



Simple Harmonic MotionChris Staines
Ėý
This document discusses simple harmonic motion (SHM) and related concepts like angular velocity, restoring forces, displacement, velocity, acceleration, energy, resonance, and damping. It provides equations for angular velocity, SHM acceleration, displacement, velocity, energy, and the simple pendulum. Examples are given and questions provided for practice calculations involving these equations and concepts.Simple-harmonic-motion.ppt



Simple-harmonic-motion.pptYashHirveGautam
Ėý
This document provides an overview of simple harmonic motion (SHM). It begins with learning outcomes related to defining SHM, analyzing energy in SHM, effects of damping and forced vibrations, and solving problems involving SHM. It then discusses challenges students face in understanding SHM and provides a brief history of SHM. The document gives examples to build intuition about SHM and derives equations to describe displacement, velocity, and acceleration in SHM. It also discusses related topics like damping, forced vibrations, resonance, and energy in SHM. Finally, it provides examples of SHM systems and problems for students to practice.An Overview of Simple harmonic motion ppt.pptx



An Overview of Simple harmonic motion ppt.pptxphysicsEMG
Ėý
This document discusses simple harmonic motion (SHM). SHM occurs when the restoring force on an object is directly proportional to the object's displacement from equilibrium. A mass on an ideal spring follows Hooke's law, where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement. This results in SHM, where the displacement as a function of time is described by a cosine function. The velocity is the time derivative of displacement, and the acceleration is the time derivative of velocity. Therefore, the graphs of displacement, velocity, and acceleration for SHM are cosine, sine, and cosine functions, respectively, with the same frequency of oscillation.Module-1-2.pptx



Module-1-2.pptxRAMAKRISHNASEN1
Ėý
The document discusses Newton's applications and special theory of relativity. It covers topics like periodic motion, oscillation, restoring force, damping force, simple harmonic oscillations, examples of SHO like simple pendulum and loaded vertical spring. It also discusses damped harmonic oscillations including underdamped, overdamped and critically damped cases. Small oscillations in a bound system and molecular vibrations are also summarized.Shm



Shmnlahoud
Ėý
The document discusses oscillations and simple harmonic motion. It defines periodic motion, oscillatory motion, and harmonic motion. Harmonic motion can be described using sine and cosine functions. Examples of oscillations include a swinging pendulum and vibrating springs. The period and frequency of oscillations are defined. For simple harmonic motion, the displacement is directly proportional to the displacement from equilibrium and opposite in sign. The velocity and acceleration functions for SHM are derived. For a mass-spring system, the restoring force is proportional to the displacement. The total mechanical energy of a simple harmonic oscillator remains constant over time as the kinetic and potential energy alternately increase and decrease during oscillation.Topic 2 damped oscillation



Topic 2 damped oscillationGabriel O'Brien
Ėý
The document discusses damped oscillations, where some energy is lost through a resistive process. There are three cases of damped oscillations: heavy damping results in non-oscillatory behavior and returns to equilibrium slowly; critical damping balances damping and stiffness for the fastest return to equilibrium; light damping results in oscillatory damped simple harmonic motion where the amplitude decays over time. Methods to describe damping include the logarithmic decrement, relaxation time, and quality factor Q.Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Introduction to Mechanical Vibration lec4



Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Introduction to Mechanical Vibration lec4manojkumarg1990
Ėý
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
Periodic Motion.ppt



Periodic Motion.pptKimberlyAnnePagdanga1
Ėý
1) The document discusses periodic motion and simple harmonic motion. It provides equations and graphs describing the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of objects undergoing SHM.
2) Damped oscillations are discussed where a damping force like friction causes the amplitude of the oscillations to decrease over time as the mechanical energy is dissipated.
3) The relationship between SHM and circular motion is explained where the x-component of uniform circular motion traces out a simple harmonic pattern.Periodic Motion KKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKK.ppt



Periodic Motion KKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKK.pptkimerlyannepagdangan
Ėý
1) The document discusses periodic motion and simple harmonic motion, providing examples of oscillatory motion in springs and pendulums.
2) Simple harmonic motion is characterized by displacement, velocity, and acceleration functions that are sinusoidal and 90 degrees out of phase. The total mechanical energy of an oscillator is constant.
3) Examples are given of damped oscillations where friction causes the amplitude to decrease over time according to an exponential function.Chapter13_1-3_FA05.ppt



Chapter13_1-3_FA05.pptKimberlyAnnePagdanga1
Ėý
Periodic motion repeats on a regular time basis and includes examples like the rising and setting of the sun, the changing of seasons, tides, bird songs, and the rotation of a bicycle wheel. The motion period is the time to return to the same point, while the frequency is the inverse of the period. Harmonic motion is oscillatory motion where the applied force depends on position and reverses direction, as seen in pendulums and spring-mass systems. Clocks use harmonic motion in their pendulums or vibrating quartz crystals to keep time.unit-4 wave optics new_unit 5 physic.pdf



unit-4 wave optics new_unit 5 physic.pdfs88220632
Ėý
Ghhhhbvvb gdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxcc namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram gdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccSimple Harmonic & Circular Motion



Simple Harmonic & Circular MotionPaula Mills
Ėý
1. This document discusses key concepts related to oscillations and waves including: simple harmonic motion (SHM), parameters that describe SHM like amplitude, period, frequency, phase, and the relationships between displacement, velocity, and acceleration in SHM.
2. Examples of SHM include a mass on a spring and a simple pendulum. The frequency and period of oscillations can be determined from the properties of the object and spring/pendulum.
3. Forced oscillations and resonance are explored where a driving force can excite the natural frequency of an object, causing large oscillations. This can be useful or destructive depending on the situation.harmonic-1.ppt



harmonic-1.pptLeoSimporios1
Ėý
Simple harmonic motion (SHM) describes the oscillatory motion of objects like springs, pendulums, and waves. The document discusses key aspects of SHM including:
- Defining SHM and providing examples like pendulums and waves.
- Relating SHM to circular motion using an auxiliary circle with angular velocity.
- Deriving equations for displacement, velocity, and acceleration of objects in SHM.
- Exploring concepts like damping, forced vibrations, and resonance through experiments with springs, pendulums, and other oscillating objects.Introduction to oscillations and simple harmonic motion



Introduction to oscillations and simple harmonic motionMichael Marty
Ėý
Physics presentation about Simple Harmonic Motion of Hooke's Law springs and pendulums with derivation of formulas and connections to Uniform Circular Motion.
References include links to illustrative youtube clips and other powerpoints that contributed to this peresentation.springs&waves.ppt



springs&waves.pptvadona7098
Ėý
1. Hooke's law describes the elastic properties of springs and relates the spring force (Fs) to the displacement (x) of an object from its equilibrium position by Fs = -kx, where k is the spring constant.
2. When an object attached to a spring is displaced from its equilibrium position, the restoring force (Fs) pushes the object back toward equilibrium in simple harmonic motion.
3. The motion of a spring-mass system provides an example of simple harmonic motion, where the displacement (x) varies with time (t) as x = Acos(Ït), with A as the amplitude and Ï as the angular frequency.Vibrations 



Vibrations EngrHabibullah3
Ėý
"The World of Vibration: Exploring Understanding, Effects, and Control"
Welcome to our website dedicated to the intriguing realm of vibration. Vibration is a fundamental and omnipresent force that shapes our world. From the tiniest particles to the grandest structures, it influences everything around us. In this online resource, we'll delve into the essence of vibration, understanding its core principles, exploring its diverse manifestations, and discovering how it impacts our lives.
Whether you're a student, researcher, engineer, or simply curious about the vibrations that surround us, you've come to the right place. Join us on this informative journey as we unlock the secrets of vibration, its causes, effects, and innovative techniques for control and mitigation. Together, we'll gain a deeper appreciation for this dynamic force that shapes our world. Welcome to the world of vibration.Engineering Physics 



Engineering Physics Karthik Rajendran
Ėý
1. Oscillations and waves can be free, damped, or forced. Free oscillations follow the differential equation of motion for simple harmonic motion.
2. Springs can be connected in series or parallel configurations. Springs in series have an equivalent spring constant that is the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual spring constants. Springs in parallel have an equivalent spring constant equal to the sum of the individual spring constants.
3. Complex notation can represent oscillations using a complex number with real and imaginary parts or using polar coordinates with magnitude and phase angle, providing an alternative representation of simple harmonic motion.Final m1 march 2019



Final m1 march 2019drdivakaras
Ėý
This document provides an overview of Module 1: Oscillations and Waves. It covers the following topics:
1. Free oscillations, including the definition and characteristics of simple harmonic motion, the differential equation of motion, mechanical oscillations using a mass-spring system, and complex notation.
2. Damped and forced oscillations, including the theory of damped oscillations involving overdamping, critical damping, and underdamping. It also discusses forced oscillations and resonance.
3. Shock waves, including definitions of Mach number, properties and laws governing shock waves, and applications involving shock tube experiments.
4. The document concludes with references on oscillations, vibrations, and waves from various textbooks and journalsSmall amplitude oscillations



Small amplitude oscillationsharshsharma5537
Ėý
This document summarizes classical dynamics and small amplitude oscillations. It discusses oscillatory motion near equilibrium positions and developing the theory using Lagrange's equations. Normal modes of coupled oscillating systems are explored, where the normal coordinates represent eigenvectors that oscillate at characteristic frequencies. The principles of superposition and matrix representations are used to analyze examples like two coupled pendulums and a system of two masses connected by three springs.Mechanical waves.pptx



Mechanical waves.pptxOsamaYousuf7
Ėý
1. Mechanical waves are disturbances that propagate through a medium, causing the particles of the medium to vibrate about their equilibrium positions without transporting matter.
2. Transverse waves have displacements perpendicular to the direction of propagation, while longitudinal waves have displacements parallel to propagation.
3. Periodic waves have particles undergoing simple harmonic motion, allowing their behavior to be described mathematically using wave functions involving variables like amplitude, wavelength, frequency, wave number, and phase.
4. The wave equation relates the second derivatives of a wave's displacement with respect to time and position, showing that disturbances can propagate as waves with a characteristic speed.Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) lecture 



Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) lecture Shriyesh Gautam
Ėý
Periodic motion repeats after a fixed duration, like oscillations where a particle moves back and forth around a fixed mean position. Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is a type of periodic motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to displacement in the opposite direction. SHM includes linear and angular motions. The motion of a spring follows SHM, with displacement measured from equilibrium, amplitude as maximum displacement, and period as the time for one cycle. Any system with a restoring force proportional to negative displacement exhibits SHM, following the equation of motion that the solution has a sinusoidal form. SHM also relates to uniform circular motion, where the x-component motion is SHM. Energy in SHM systems includes potential, kinetic, andSteady axisymetric-torsional-flows



Steady axisymetric-torsional-flowssaira alvi
Ėý
swirling torsional flows explained information about these flows.Different cases of flow between rotating vertical coaxial cylinders.HARMONIC OSCILLATOR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (SANDEEP).pptx



HARMONIC OSCILLATOR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (SANDEEP).pptxSandeepKSahu
Ėý
HARMONIC OSCILLATOR AND ITS SOLUTIONS
APPLICATIONS OF HARMONIC OSCILLATOR
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
ONE DIMENTIONAL HARMONIC MOTION
THREE DIMENTIONAL HARMONIC MOTION
QUANTUM MECHANICS PHYSICAL SCIENCE
MASTER OF SCIENCE
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
SCIENCE PRESENTATION
TYPES OF MOTIONEngineering Physics (18 PHY112/22) notes



Engineering Physics (18 PHY112/22) notesDrDileepCS
Ėý
This document provides an overview of key concepts in engineering physics related to oscillations and waves. It defines terms like displacement, amplitude, frequency, period, equilibrium position, and angular frequency. It describes simple harmonic motion and derives the differential equation of motion. It also covers topics like restoring force, force constant, free and forced vibrations, damping, and quality factor. The document is intended as course material for an engineering physics module taught by Dr. Dileep C.S. in the department of physics.Science project class 10 Covid-19 Tuberculosis



Science project class 10 Covid-19 TuberculosisVEENAKSHI PATHAK
Ėý
Coronaviruses are a large family of
Viruses that are common
Throughout the world and can cause
Respiratory illness in people and
Animals.
(February 25th, 2025) Real-Time Insights into Cardiothoracic Research with In...



(February 25th, 2025) Real-Time Insights into Cardiothoracic Research with In...Scintica Instrumentation
Ėý
s a major gap - these methods can't fully capture how cells behave in a living, breathing system.
That's where Intravital Microscopy (IVM) comes in. This powerful imaging technology allows researchers to see cellular activity in real-time, with incredible clarity and precision.
But imaging the heart and lungs presents a unique challenge. These organs are constantly in motion, making real-time visualization tricky. Thankfully, groundbreaking advances - like vacuum-based stabilization and motion compensation algorithms - are making high-resolution imaging of these moving structures a reality.
What You'll Gain from This Webinar:
- New Scientific Insights â See how IVM is transforming our understanding of immune cell movement in the lungs, cellular changes in heart disease, and more.
- Advanced Imaging Solutions â Discover the latest stabilization techniques that make it possible to capture clear, detailed images of beating hearts and expanding lungs.
- Real-World Applications â Learn how these innovations are driving major breakthroughs in cardiovascular and pulmonary research, with direct implications for disease treatment and drug development.
- Live Expert Discussion â Connect with experts and get answers to your biggest questions about in vivo imaging.
This is your chance to explore how cutting-edge imaging is revolutionizing cardiothoracic research - shedding light on disease mechanisms, immune responses, and new therapeutic possibilities.
- Register now and stay ahead of the curve in in vivo imaging!More Related Content
Similar to OSCILLATIONS.pptx (20)
Topic 2 damped oscillation



Topic 2 damped oscillationGabriel O'Brien
Ėý
The document discusses damped oscillations, where some energy is lost through a resistive process. There are three cases of damped oscillations: heavy damping results in non-oscillatory behavior and returns to equilibrium slowly; critical damping balances damping and stiffness for the fastest return to equilibrium; light damping results in oscillatory damped simple harmonic motion where the amplitude decays over time. Methods to describe damping include the logarithmic decrement, relaxation time, and quality factor Q.Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Introduction to Mechanical Vibration lec4



Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Introduction to Mechanical Vibration lec4manojkumarg1990
Ėý
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
Periodic Motion.ppt



Periodic Motion.pptKimberlyAnnePagdanga1
Ėý
1) The document discusses periodic motion and simple harmonic motion. It provides equations and graphs describing the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of objects undergoing SHM.
2) Damped oscillations are discussed where a damping force like friction causes the amplitude of the oscillations to decrease over time as the mechanical energy is dissipated.
3) The relationship between SHM and circular motion is explained where the x-component of uniform circular motion traces out a simple harmonic pattern.Periodic Motion KKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKK.ppt



Periodic Motion KKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKK.pptkimerlyannepagdangan
Ėý
1) The document discusses periodic motion and simple harmonic motion, providing examples of oscillatory motion in springs and pendulums.
2) Simple harmonic motion is characterized by displacement, velocity, and acceleration functions that are sinusoidal and 90 degrees out of phase. The total mechanical energy of an oscillator is constant.
3) Examples are given of damped oscillations where friction causes the amplitude to decrease over time according to an exponential function.Chapter13_1-3_FA05.ppt



Chapter13_1-3_FA05.pptKimberlyAnnePagdanga1
Ėý
Periodic motion repeats on a regular time basis and includes examples like the rising and setting of the sun, the changing of seasons, tides, bird songs, and the rotation of a bicycle wheel. The motion period is the time to return to the same point, while the frequency is the inverse of the period. Harmonic motion is oscillatory motion where the applied force depends on position and reverses direction, as seen in pendulums and spring-mass systems. Clocks use harmonic motion in their pendulums or vibrating quartz crystals to keep time.unit-4 wave optics new_unit 5 physic.pdf



unit-4 wave optics new_unit 5 physic.pdfs88220632
Ėý
Ghhhhbvvb gdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxcc namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram namskaram gdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccgdxxcggvxxxzzZxvhjnnnbcffddxxccSimple Harmonic & Circular Motion



Simple Harmonic & Circular MotionPaula Mills
Ėý
1. This document discusses key concepts related to oscillations and waves including: simple harmonic motion (SHM), parameters that describe SHM like amplitude, period, frequency, phase, and the relationships between displacement, velocity, and acceleration in SHM.
2. Examples of SHM include a mass on a spring and a simple pendulum. The frequency and period of oscillations can be determined from the properties of the object and spring/pendulum.
3. Forced oscillations and resonance are explored where a driving force can excite the natural frequency of an object, causing large oscillations. This can be useful or destructive depending on the situation.harmonic-1.ppt



harmonic-1.pptLeoSimporios1
Ėý
Simple harmonic motion (SHM) describes the oscillatory motion of objects like springs, pendulums, and waves. The document discusses key aspects of SHM including:
- Defining SHM and providing examples like pendulums and waves.
- Relating SHM to circular motion using an auxiliary circle with angular velocity.
- Deriving equations for displacement, velocity, and acceleration of objects in SHM.
- Exploring concepts like damping, forced vibrations, and resonance through experiments with springs, pendulums, and other oscillating objects.Introduction to oscillations and simple harmonic motion



Introduction to oscillations and simple harmonic motionMichael Marty
Ėý
Physics presentation about Simple Harmonic Motion of Hooke's Law springs and pendulums with derivation of formulas and connections to Uniform Circular Motion.
References include links to illustrative youtube clips and other powerpoints that contributed to this peresentation.springs&waves.ppt



springs&waves.pptvadona7098
Ėý
1. Hooke's law describes the elastic properties of springs and relates the spring force (Fs) to the displacement (x) of an object from its equilibrium position by Fs = -kx, where k is the spring constant.
2. When an object attached to a spring is displaced from its equilibrium position, the restoring force (Fs) pushes the object back toward equilibrium in simple harmonic motion.
3. The motion of a spring-mass system provides an example of simple harmonic motion, where the displacement (x) varies with time (t) as x = Acos(Ït), with A as the amplitude and Ï as the angular frequency.Vibrations 



Vibrations EngrHabibullah3
Ėý
"The World of Vibration: Exploring Understanding, Effects, and Control"
Welcome to our website dedicated to the intriguing realm of vibration. Vibration is a fundamental and omnipresent force that shapes our world. From the tiniest particles to the grandest structures, it influences everything around us. In this online resource, we'll delve into the essence of vibration, understanding its core principles, exploring its diverse manifestations, and discovering how it impacts our lives.
Whether you're a student, researcher, engineer, or simply curious about the vibrations that surround us, you've come to the right place. Join us on this informative journey as we unlock the secrets of vibration, its causes, effects, and innovative techniques for control and mitigation. Together, we'll gain a deeper appreciation for this dynamic force that shapes our world. Welcome to the world of vibration.Engineering Physics 



Engineering Physics Karthik Rajendran
Ėý
1. Oscillations and waves can be free, damped, or forced. Free oscillations follow the differential equation of motion for simple harmonic motion.
2. Springs can be connected in series or parallel configurations. Springs in series have an equivalent spring constant that is the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual spring constants. Springs in parallel have an equivalent spring constant equal to the sum of the individual spring constants.
3. Complex notation can represent oscillations using a complex number with real and imaginary parts or using polar coordinates with magnitude and phase angle, providing an alternative representation of simple harmonic motion.Final m1 march 2019



Final m1 march 2019drdivakaras
Ėý
This document provides an overview of Module 1: Oscillations and Waves. It covers the following topics:
1. Free oscillations, including the definition and characteristics of simple harmonic motion, the differential equation of motion, mechanical oscillations using a mass-spring system, and complex notation.
2. Damped and forced oscillations, including the theory of damped oscillations involving overdamping, critical damping, and underdamping. It also discusses forced oscillations and resonance.
3. Shock waves, including definitions of Mach number, properties and laws governing shock waves, and applications involving shock tube experiments.
4. The document concludes with references on oscillations, vibrations, and waves from various textbooks and journalsSmall amplitude oscillations



Small amplitude oscillationsharshsharma5537
Ėý
This document summarizes classical dynamics and small amplitude oscillations. It discusses oscillatory motion near equilibrium positions and developing the theory using Lagrange's equations. Normal modes of coupled oscillating systems are explored, where the normal coordinates represent eigenvectors that oscillate at characteristic frequencies. The principles of superposition and matrix representations are used to analyze examples like two coupled pendulums and a system of two masses connected by three springs.Mechanical waves.pptx



Mechanical waves.pptxOsamaYousuf7
Ėý
1. Mechanical waves are disturbances that propagate through a medium, causing the particles of the medium to vibrate about their equilibrium positions without transporting matter.
2. Transverse waves have displacements perpendicular to the direction of propagation, while longitudinal waves have displacements parallel to propagation.
3. Periodic waves have particles undergoing simple harmonic motion, allowing their behavior to be described mathematically using wave functions involving variables like amplitude, wavelength, frequency, wave number, and phase.
4. The wave equation relates the second derivatives of a wave's displacement with respect to time and position, showing that disturbances can propagate as waves with a characteristic speed.Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) lecture 



Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) lecture Shriyesh Gautam
Ėý
Periodic motion repeats after a fixed duration, like oscillations where a particle moves back and forth around a fixed mean position. Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is a type of periodic motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to displacement in the opposite direction. SHM includes linear and angular motions. The motion of a spring follows SHM, with displacement measured from equilibrium, amplitude as maximum displacement, and period as the time for one cycle. Any system with a restoring force proportional to negative displacement exhibits SHM, following the equation of motion that the solution has a sinusoidal form. SHM also relates to uniform circular motion, where the x-component motion is SHM. Energy in SHM systems includes potential, kinetic, andSteady axisymetric-torsional-flows



Steady axisymetric-torsional-flowssaira alvi
Ėý
swirling torsional flows explained information about these flows.Different cases of flow between rotating vertical coaxial cylinders.HARMONIC OSCILLATOR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (SANDEEP).pptx



HARMONIC OSCILLATOR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (SANDEEP).pptxSandeepKSahu
Ėý
HARMONIC OSCILLATOR AND ITS SOLUTIONS
APPLICATIONS OF HARMONIC OSCILLATOR
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
ONE DIMENTIONAL HARMONIC MOTION
THREE DIMENTIONAL HARMONIC MOTION
QUANTUM MECHANICS PHYSICAL SCIENCE
MASTER OF SCIENCE
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
SCIENCE PRESENTATION
TYPES OF MOTIONEngineering Physics (18 PHY112/22) notes



Engineering Physics (18 PHY112/22) notesDrDileepCS
Ėý
This document provides an overview of key concepts in engineering physics related to oscillations and waves. It defines terms like displacement, amplitude, frequency, period, equilibrium position, and angular frequency. It describes simple harmonic motion and derives the differential equation of motion. It also covers topics like restoring force, force constant, free and forced vibrations, damping, and quality factor. The document is intended as course material for an engineering physics module taught by Dr. Dileep C.S. in the department of physics.Recently uploaded (20)
Science project class 10 Covid-19 Tuberculosis



Science project class 10 Covid-19 TuberculosisVEENAKSHI PATHAK
Ėý
Coronaviruses are a large family of
Viruses that are common
Throughout the world and can cause
Respiratory illness in people and
Animals.
(February 25th, 2025) Real-Time Insights into Cardiothoracic Research with In...



(February 25th, 2025) Real-Time Insights into Cardiothoracic Research with In...Scintica Instrumentation
Ėý
s a major gap - these methods can't fully capture how cells behave in a living, breathing system.
That's where Intravital Microscopy (IVM) comes in. This powerful imaging technology allows researchers to see cellular activity in real-time, with incredible clarity and precision.
But imaging the heart and lungs presents a unique challenge. These organs are constantly in motion, making real-time visualization tricky. Thankfully, groundbreaking advances - like vacuum-based stabilization and motion compensation algorithms - are making high-resolution imaging of these moving structures a reality.
What You'll Gain from This Webinar:
- New Scientific Insights â See how IVM is transforming our understanding of immune cell movement in the lungs, cellular changes in heart disease, and more.
- Advanced Imaging Solutions â Discover the latest stabilization techniques that make it possible to capture clear, detailed images of beating hearts and expanding lungs.
- Real-World Applications â Learn how these innovations are driving major breakthroughs in cardiovascular and pulmonary research, with direct implications for disease treatment and drug development.
- Live Expert Discussion â Connect with experts and get answers to your biggest questions about in vivo imaging.
This is your chance to explore how cutting-edge imaging is revolutionizing cardiothoracic research - shedding light on disease mechanisms, immune responses, and new therapeutic possibilities.
- Register now and stay ahead of the curve in in vivo imaging!(Journal Club) - DNA replication and repair kinetics of Alu, LINEâ1 and satel...



(Journal Club) - DNA replication and repair kinetics of Alu, LINEâ1 and satel...David Podorefsky, PhD
Ėý
Journal Club (5/20/19)
DNA replication and repair kinetics of Alu, LINEâ1 and satellite III genomic repetitive elementsInvestigational New drug application process



Investigational New drug application processonepalyer4
Ėý
This file basically contains information related to IND application process in order to get approval for clinical trials.Variation and Natural Selection | IGCSE Biology



Variation and Natural Selection | IGCSE BiologyBlessing Ndazie
Ėý
This extensive slide deck provides a detailed exploration of variation and natural selection for IGCSE Biology. It covers key concepts such as genetic and environmental variation, types of variation (continuous and discontinuous), mutation, evolution, and the principles of natural selection. The presentation also explains Darwinâs theory of evolution, adaptation, survival of the fittest, selective breeding, antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and speciation. With illustrative diagrams, real-life examples, and exam-style questions, this resource is ideal for IGCSE students, teachers, and independent learners preparing for exams.Direct Gene Transfer Techniques for Developing Transgenic Plants



Direct Gene Transfer Techniques for Developing Transgenic PlantsKuldeep Gauliya
Ėý
This presentation will explain all the methods adopted for developing transgenic plant using direct gene transfer technique.The Solar Systemâs passage through the Radcliffe wave during the middle Miocene



The Solar Systemâs passage through the Radcliffe wave during the middle MioceneSÃĐrgio Sacani
Ėý
As the Solar System orbits the Milky Way, it encounters various Galactic environments, including dense regions of the
interstellar medium (ISM). These encounters can compress the heliosphere, exposing parts of the Solar System to the ISM, while also
increasing the influx of interstellar dust into the Solar System and Earthâs atmosphere. The discovery of new Galactic structures, such
as the Radcliffe wave, raises the question of whether the Sun has encountered any of them.
Aims. The present study investigates the potential passage of the Solar System through the Radcliffe wave gas structure over the past
30 million years (Myr).
Methods. We used a sample of 56 high-quality, young (âĪ30 Myr) open clusters associated with a region of interest of the Radcliffe
wave to trace its motion back and investigate a potential crossing with the Solar Systemâs past orbit.
Results. We find that the Solar Systemâs trajectory intersected the Radcliffe wave in the Orion region. We have constrained the timing
of this event to between 18.2 and 11.5 Myr ago, with the closest approach occurring between 14.8 and 12.4 Myr ago. Notably, this
period coincides with the Middle Miocene climate transition on Earth, providing an interdisciplinary link with paleoclimatology. The
potential impact of the crossing of the Radcliffe wave on the climate on Earth is estimated. This crossing could also lead to anomalies
in radionuclide abundances, which is an important research topic in the field of geology and nuclear astrophysics.PROTEIN DEGRADATION via ubiquitous pathaway



PROTEIN DEGRADATION via ubiquitous pathawayKaviya Priya A
Ėý
Protein degradation via ubiquitous pathway In general science, a ubiquitous pathway refers to a biochemical or metabolic pathway that is:
1. *Widely present*: Found in many different organisms, tissues, or cells.
2. *Conserved*: Remains relatively unchanged across different species or contexts.
Examples of ubiquitous pathways include:
1. *Glycolysis*: The process of breaking down glucose for energy, found in nearly all living organisms.
2. *Citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle)*: A key metabolic pathway involved in energy production, present in many cells.
3. *Pentose phosphate pathway*: A metabolic pathway involved in energy production and antioxidant defenses, found in many organisms.
These pathways are essential for life and have been conserved across evolution, highlighting their importance for cellular function and survival.
Cell Structure & Function | Cambridge IGCSE Biology



Cell Structure & Function | Cambridge IGCSE BiologyBlessing Ndazie
Ėý
This IGCSE Biology presentation provides a detailed look at cell structure and function, covering the differences between animal and plant cells, the roles of organelles (nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, etc.), specialized cells, and levels of organization. Learn about diffusion, osmosis, and active transport in cells, with clear diagrams and explanations to support exam preparation. A must-have resource for Cambridge IGCSE students!animal cell plant cell power point presentation



animal cell plant cell power point presentationJosephinePaguio2
Ėý
A power point presentation about plant and animal cell(Journal Club) - Transgenic mice for in vivo epigenome editing with CRISPR-ba...



(Journal Club) - Transgenic mice for in vivo epigenome editing with CRISPR-ba...David Podorefsky, PhD
Ėý
Journal Club (9/21/21)
Transgenic mice for in vivo epigenome editing with CRISPR-based systemsDigestive System - Digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.ppt



Digestive System - Digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.pptJamakala Obaiah
Ėý
Useful to studentsB-FPGM: Lightweight Face Detection via Bayesian-Optimized Soft FPGM Pruning



B-FPGM: Lightweight Face Detection via Bayesian-Optimized Soft FPGM PruningVasileiosMezaris
Ėý
Presentation of our paper, "B-FPGM: Lightweight Face Detection via Bayesian-Optimized Soft FPGM Pruning", by N. Kaparinos and V. Mezaris. Presented at the RWS Workshop of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV 2025), Tucson, AZ, USA, Feb. 2025. Preprint and software available at http://arxiv.org/abs/2501.16917 https://github.com/IDT-ITI/B-FPGMWORKING AND APPLICATION OF LC-MS/MS 2025



WORKING AND APPLICATION OF LC-MS/MS 2025PSG College of Technology
Ėý
LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry) is a powerful analytical tool for comparing innovator and biosimilar drugs. It ensures precise characterization, detecting structural variations, impurities, and post-translational modifications, ensuring biosimilar quality, efficacy, and regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical development.Sujay Rao Mandavilli public profile March 2025 - (2)



Sujay Rao Mandavilli public profile March 2025 - (2)Sujay Rao Mandavilli
Ėý
Sujay Rao Mandavilli public profile March 2025 - (2)(Journal Club) Focused ultrasound excites neurons via mechanosensitive calciu...



(Journal Club) Focused ultrasound excites neurons via mechanosensitive calciu...David Podorefsky, PhD
Ėý
Journal Club (2/11/21)
Focused ultrasound excites neurons via mechanosensitive calcium accumulation and ion channel amplificationElectrical Quantities and Circuits | IGCSE Physics



Electrical Quantities and Circuits | IGCSE PhysicsBlessing Ndazie
Ėý
This extensive slide deck provides a detailed exploration of electrical quantities and circuits for IGCSE Physics. It covers key electrical quantities, including charge, current, voltage (potential difference), resistance, power, energy, electromotive force (EMF), and internal resistance. The presentation also explains series and parallel circuits, with in-depth discussions on Ohmâs Law, Kirchhoffâs Laws, electrical components, circuit calculations, and practical applications. Packed with illustrative diagrams, worked examples, and exam-style questions, this resource is ideal for IGCSE students, teachers, and independent learners preparing for exams.(Journal Club) - Integration of multiple lineage measurements from the same c...



(Journal Club) - Integration of multiple lineage measurements from the same c...David Podorefsky, PhD
Ėý
Journal Club (3/18/22)
Integration of multiple lineage measurements from the same cell reconstructs parallel tumor evolutionThe Sense Organs: Structure and Function of the Eye and Skin | IGCSE Biology



The Sense Organs: Structure and Function of the Eye and Skin | IGCSE BiologyBlessing Ndazie
Ėý
This detailed presentation covers the structure and function of the sense organs, focusing on the eye and skin as part of the Cambridge IGCSE Biology syllabus. Learn about the anatomy of the eye, how vision works, adaptations for focusing, and common eye defects. Explore the role of the skin in temperature regulation, protection, and sensory reception. Perfect for students preparing for exams!(February 25th, 2025) Real-Time Insights into Cardiothoracic Research with In...



(February 25th, 2025) Real-Time Insights into Cardiothoracic Research with In...Scintica Instrumentation
Ėý
(Journal Club) - DNA replication and repair kinetics of Alu, LINEâ1 and satel...



(Journal Club) - DNA replication and repair kinetics of Alu, LINEâ1 and satel...David Podorefsky, PhD
Ėý
(Journal Club) - Transgenic mice for in vivo epigenome editing with CRISPR-ba...



(Journal Club) - Transgenic mice for in vivo epigenome editing with CRISPR-ba...David Podorefsky, PhD
Ėý
(Journal Club) Focused ultrasound excites neurons via mechanosensitive calciu...



(Journal Club) Focused ultrasound excites neurons via mechanosensitive calciu...David Podorefsky, PhD
Ėý
(Journal Club) - Integration of multiple lineage measurements from the same c...



(Journal Club) - Integration of multiple lineage measurements from the same c...David Podorefsky, PhD
Ėý
OSCILLATIONS.pptx
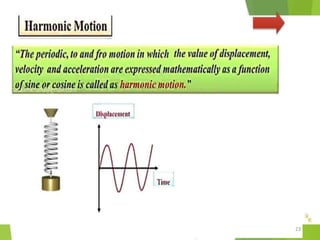
- 1. OSCILLATIONS
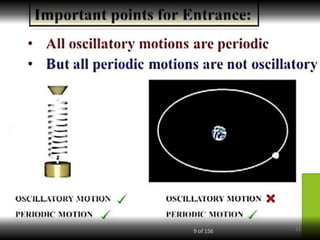
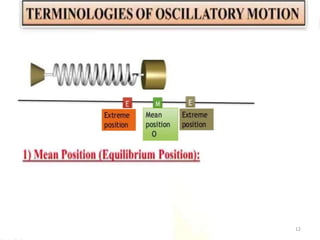
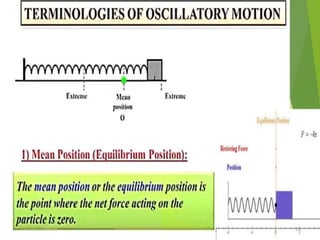
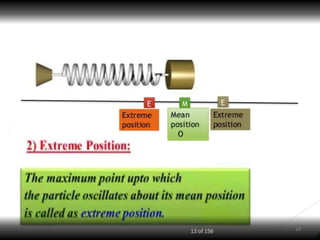
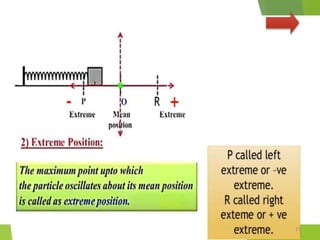
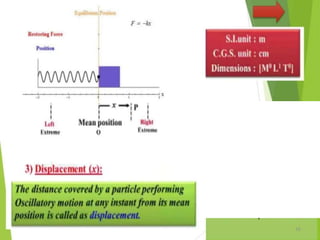
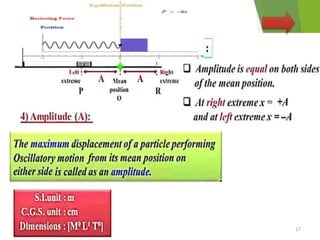
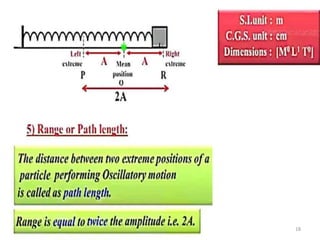
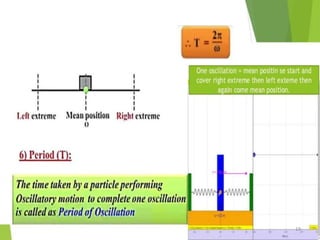
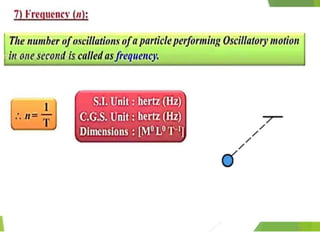
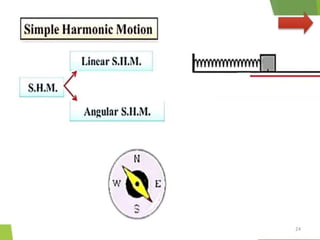
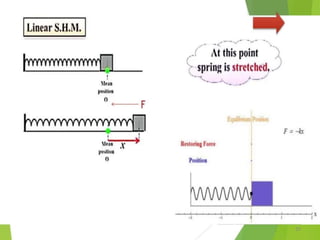
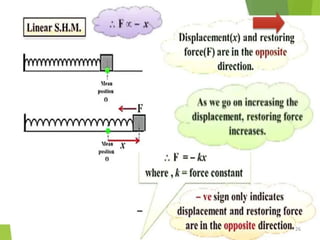
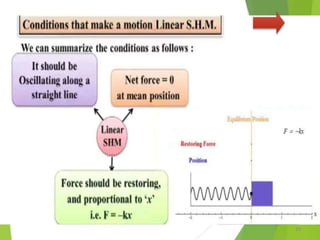
- 2. Overview - Types of motion - Periodic motion - Terminologies in Oscillations - Simple Harmonic Motion - Linear SHM â Oscillations due to a spring - Combination of springs - Angular SHM - Energies in SHM- Kinetic, Potential - Examples of SHM â Oscillations due to spring, Simple pendulum, Oscillation of liquid in a U-tube - Free Oscillation - Damped Oscillation - Forced Oscillation â Resonance 2
- 4. 4
- 5. 5
- 6. 6
- 7. 7
- 8. 8
- 9. 9
- 10. 10
- 11. 11
- 12. 12
- 13. 13
- 14. 14
- 15. 15
- 16. 16
- 17. 17
- 18. 18
- 19. 19
- 20. 20
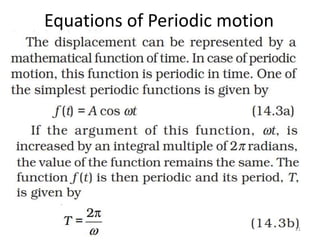
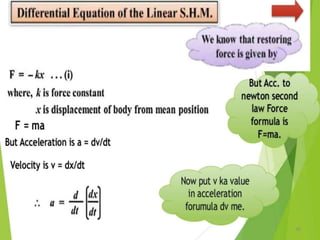
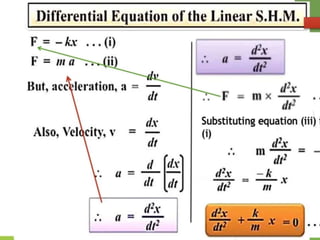
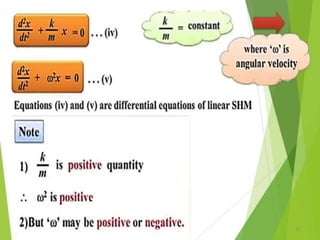
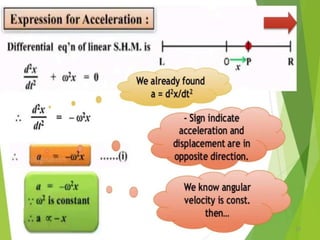
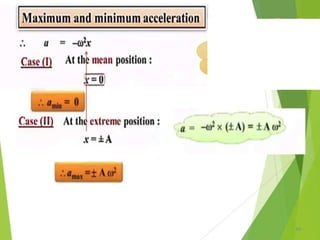
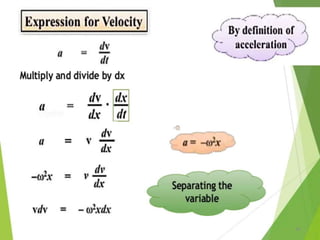
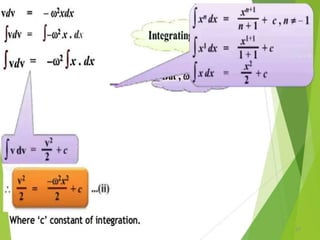
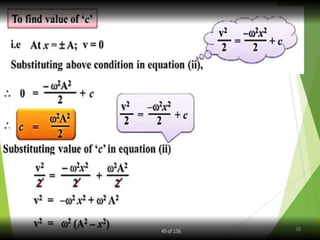
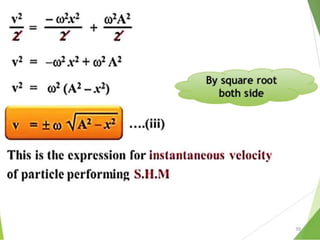
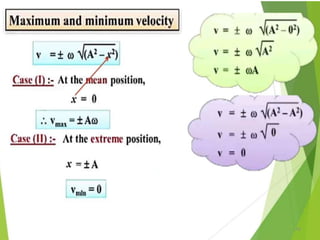
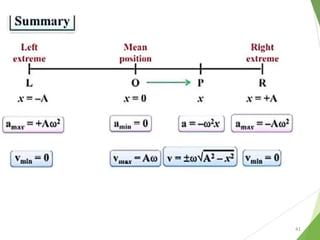
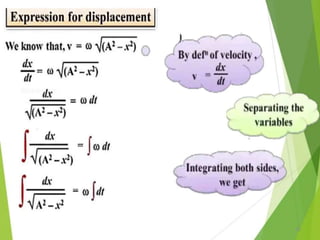
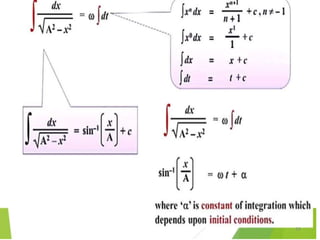
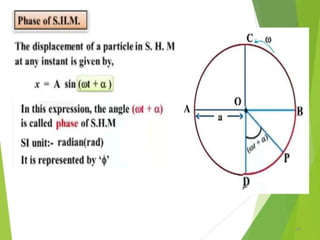
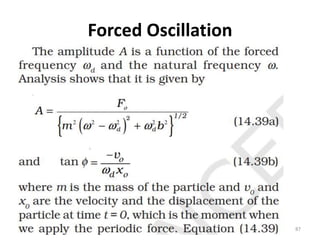
- 21. Equations of Periodic motion 21
- 23. 23
- 24. 24
- 25. 25
- 26. 26
- 27. 27
- 28. 28
- 29. 29
- 30. 30
- 31. 31
- 32. 32
- 33. 33
- 34. 34
- 35. 35
- 36. 36
- 37. 37
- 38. 38
- 39. 39
- 40. 40
- 41. 41
- 42. 42
- 43. 43
- 44. 44
- 45. 45
- 46. 46
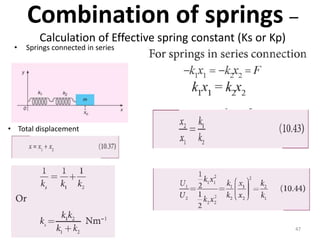
- 47. Combination of springs â Calculation of Effective spring constant (Ks or Kp) 47 âĒ Springs connected in series âĒ Total displacement
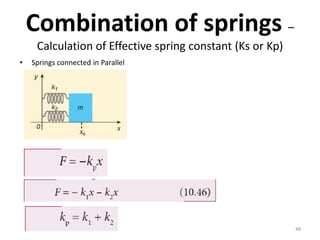
- 48. Combination of springs â Calculation of Effective spring constant (Ks or Kp) 48 âĒ Springs connected in Parallel
- 49. 49
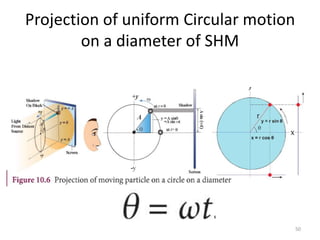
- 50. Projection of uniform Circular motion on a diameter of SHM 50
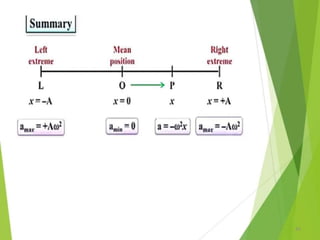
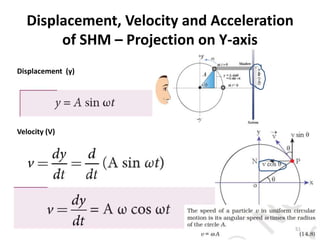
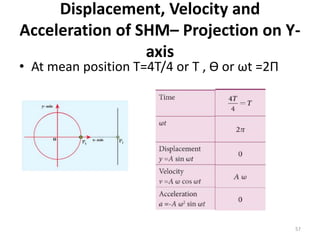
- 51. Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration of SHM â Projection on Y-axis Displacement (y) Velocity (V) 51
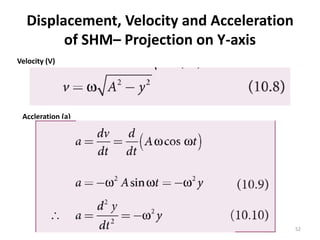
- 52. Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration of SHMâ Projection on Y-axis Velocity (V) Accleration (a) 52
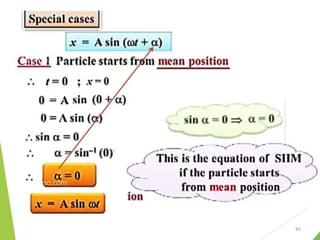
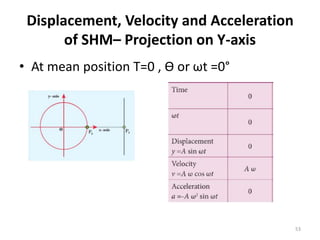
- 53. Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration of SHMâ Projection on Y-axis âĒ At mean position T=0 , Æ or Ït =0° 53
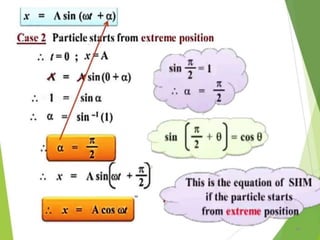
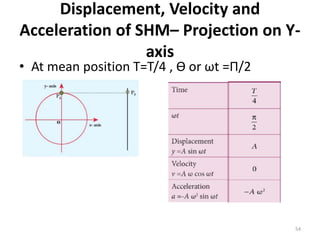
- 54. Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration of SHMâ Projection on Y- axis âĒ At mean position T=T/4 , Æ or Ït =Î /2 54
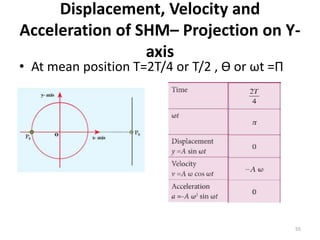
- 55. Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration of SHMâ Projection on Y- axis âĒ At mean position T=2T/4 or T/2 , Æ or Ït =Î 55
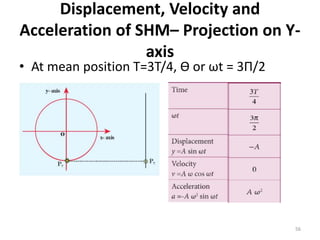
- 56. Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration of SHMâ Projection on Y- axis âĒ At mean position T=3T/4, Æ or Ït = 3Î /2 56
- 57. Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration of SHMâ Projection on Y- axis âĒ At mean position T=4T/4 or T , Æ or Ït =2Î 57
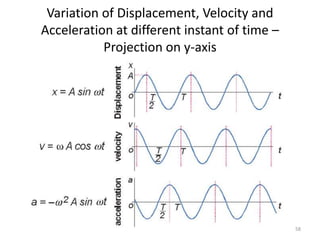
- 58. Variation of Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration at different instant of time â Projection on y-axis 58
- 59. 59
- 60. 60
- 61. 61
- 62. 62
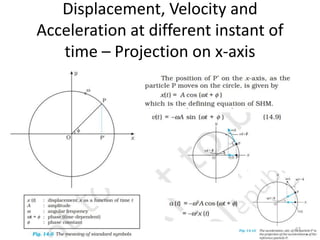
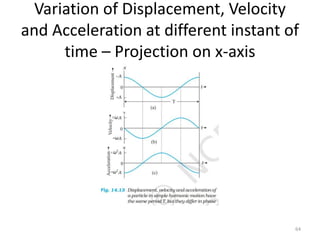
- 63. Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration at different instant of time â Projection on x-axis 63
- 64. Variation of Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration at different instant of time â Projection on x-axis 64
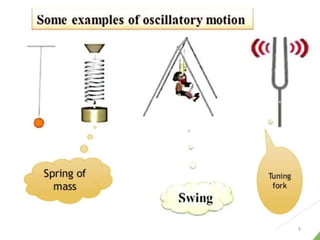
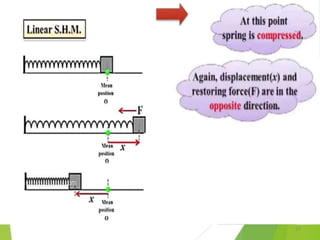
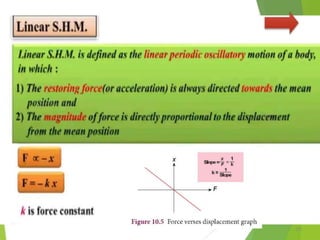
- 65. Other examples of Linear SHM âSimple harmonic Motion occurs when a particle or object moves back and forth within a stable equilibrium position under the influence of a restoring force proportional to its displacement.â Spring Mass system Pendulum Swing Shock absorber of a car Strings of a musical instrument Bungee Jumping 65
- 66. Angular SHM 66
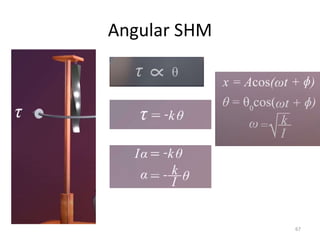
- 67. Angular SHM 67
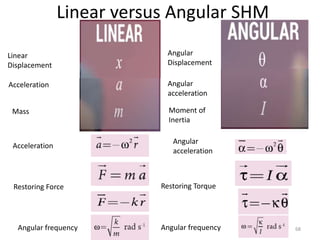
- 68. Linear versus Angular SHM Linear Displacement Acceleration Mass Moment of Inertia Angular acceleration Angular Displacement Acceleration Angular acceleration Restoring Force Restoring Torque Angular frequency Angular frequency 68
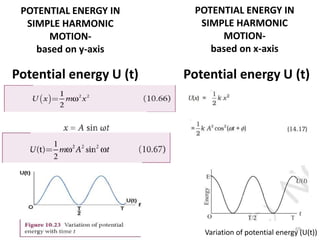
- 69. POTENTIAL ENERGY IN SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION- based on y-axis Potential energy U (t) POTENTIAL ENERGY IN SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION- based on x-axis Potential energy U (t) Variation of potential energy (U(t)) 69
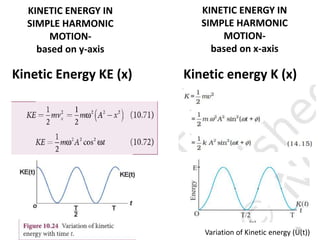
- 70. KINETIC ENERGY IN SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION- based on y-axis Kinetic Energy KE (x) KINETIC ENERGY IN SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION- based on x-axis Kinetic energy K (x) Variation of Kinetic energy (U(t)) 70
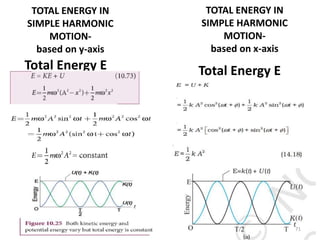
- 71. TOTAL ENERGY IN SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION- based on y-axis Total Energy E TOTAL ENERGY IN SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION- based on x-axis Total Energy E 71
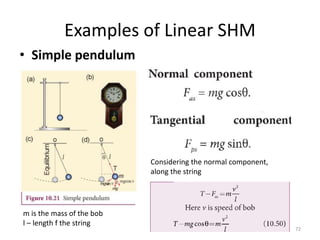
- 72. Examples of Linear SHM âĒ Simple pendulum Considering the normal component, along the string 72 m is the mass of the bob l â length f the string
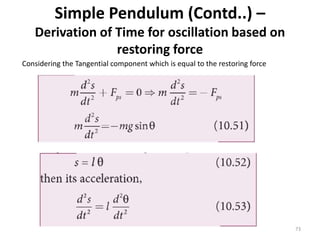
- 73. Simple Pendulum (Contd..) â Derivation of Time for oscillation based on restoring force 73 Considering the Tangential component which is equal to the restoring force
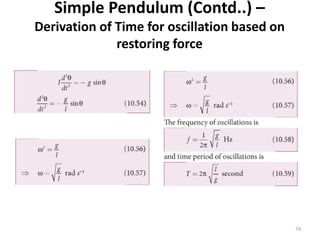
- 74. Simple Pendulum (Contd..) â Derivation of Time for oscillation based on restoring force 74
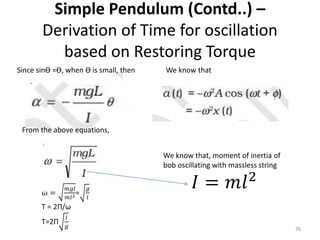
- 75. Simple Pendulum (Contd..) â Derivation of Time for oscillation based on restoring torque 75 Considering the tangential component , restoring torque is
- 76. Simple Pendulum (Contd..) â Derivation of Time for oscillation based on Restoring Torque 76 Since sinÆ =Æ, when Æ is small, then We know that From the above equations, We know that, moment of inertia of bob oscillating with massless string ðž = ðð2 Ï = ððð ðð2= ð ð T = 2Î /Ï T=2Î ð ð
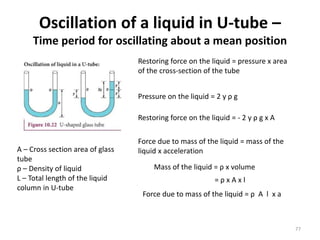
- 77. Oscillation of a liquid in U-tube â Time period for oscillating about a mean position 77 Restoring force on the liquid = pressure x area of the cross-section of the tube Pressure on the liquid = 2 y Ï g A â Cross section area of glass tube Ï â Density of liquid L â Total length of the liquid column in U-tube Restoring force on the liquid = - 2 y Ï g x A Force due to mass of the liquid = mass of the liquid x acceleration Mass of the liquid = Ï x volume = Ï x A x l Force due to mass of the liquid = Ï A l x a
- 78. Oscillation of a liquid in U-tube â Time period for oscillating about a mean position 78 Restoring force on the liquid = Force due to mass of the liquid -2 y Ï g x A = Ï A L a -2 y g = L a a = 2 y g / L a = (2g/L)*y We know that, Ï = 2ð ðŋ T = 2Î /Ï T=2Î ð 2ð
- 79. Free oscillations âĒ The free oscillation possesses constant amplitude and period without any external force to set the oscillation. âĒ Ideally, free oscillation does not undergo damping. But in all-natural systems damping is observed unless and until any constant external force is supplied to overcome damping. âĒ In such a system, the amplitude, frequency and energy all remain constant. 79
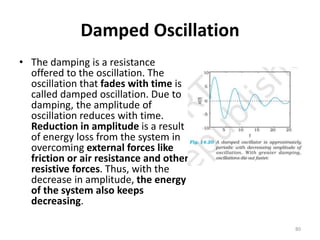
- 80. Damped Oscillation âĒ The damping is a resistance offered to the oscillation. The oscillation that fades with time is called damped oscillation. Due to damping, the amplitude of oscillation reduces with time. Reduction in amplitude is a result of energy loss from the system in overcoming external forces like friction or air resistance and other resistive forces. Thus, with the decrease in amplitude, the energy of the system also keeps decreasing. 80
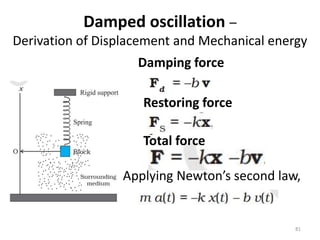
- 81. Damped oscillation â Derivation of Displacement and Mechanical energy 81 Damping force Restoring force Total force Applying Newtonâs second law,
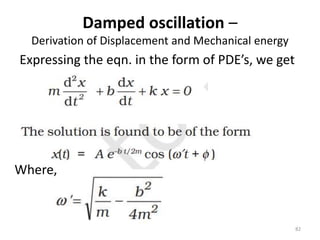
- 82. Damped oscillation â Derivation of Displacement and Mechanical energy 82 Expressing the eqn. in the form of PDEâs, we get Where,
- 83. Damped oscillation â Derivation of Displacement and Mechanical energy 83 Mechanical Energy of undamped oscillator E(t) = Â― KA2
- 84. Forced Oscillations âĒ When a body oscillates by being influenced by an external periodic force, it is called forced oscillation. Here, the amplitude of oscillation, experiences damping but remains constant due to the external energy supplied to the system. âĒ For example, when you push someone on a swing, you have to keep periodically pushing them so that the swing doesnât reduce. 84
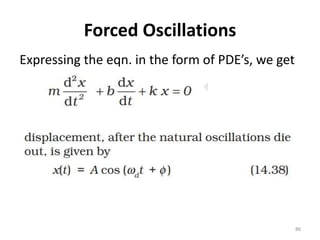
- 86. Forced Oscillations 86 Expressing the eqn. in the form of PDEâs, we get
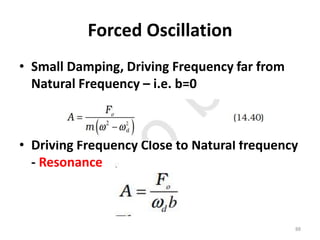
- 88. Forced Oscillation âĒ Small Damping, Driving Frequency far from Natural Frequency â i.e. b=0 âĒ Driving Frequency Close to Natural frequency - Resonance 88
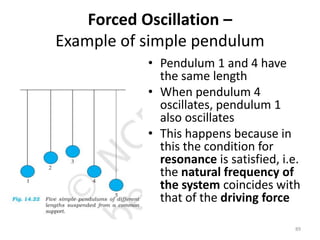
- 89. Forced Oscillation â Example of simple pendulum âĒ Pendulum 1 and 4 have the same length âĒ When pendulum 4 oscillates, pendulum 1 also oscillates âĒ This happens because in this the condition for resonance is satisfied, i.e. the natural frequency of the system coincides with that of the driving force 89
- 90. Thank you 90


